Unit 7: Gravitation
5.0(1)Studied by 109 people
0%Unit 7: Gravitation Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/26
Last updated 4:54 AM on 4/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
Kepler’s First Law
Every planet moves in an elliptical orbit, with the Sun at one focus.
2
New cards
Kepler’s Second Law
As a planet moves in its orbit, a line drawn from the Sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals.
3
New cards
Kepler’s Third Law
If T is the period, the time required to make one revolution, and a is the length of the semimajor axis of a planet’s orbit, then the ratio T^2/a^3 is the same for all planets orbiting the same star.
4
New cards
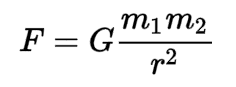
Newton's Law of Gravitation
States that every particle of matter in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
5
New cards
Gravitational Constant
a fundamental constant of nature and has a value of approximately 6.674 x 10^-11 N * m^2 / kg^2
6
New cards
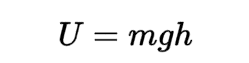
Gravitational potential energy
It is the energy possessed by an object due to its position in a gravitational field. It is defined as the work done in moving an object from infinity to a point in the gravitational field.
7
New cards
eccentricity
The deviation of an ellipse from a perfect circle is measured by a parameter called its \______.
8
New cards
barycenter
The focus is at the center of mass of the Sun-planet system, because when one body orbits another, both bodies orbit around their center of mass, a point called the _________.
9
New cards
barycenter
Actually, the focus is at the center of mass of the Sun-planet system, because when one body orbits another, both bodies orbit around their center of mass, a point called the \______.
10
New cards
Gravity
The force of attraction between two objects with mass.
11
New cards
Orbit
The path of an object as it revolves around another object in space.
12
New cards
Elliptical orbit
An orbit that is shaped like an ellipse, which is an elongated circle.
13
New cards
Orbital velocity
The speed at which an object must travel to maintain a stable orbit around another object.
14
New cards
Mass
The amount of matter in an object.
15
New cards
Distance
The amount of space between two objects.
16
New cards
Escape velocity
The minimum speed an object needs to escape the gravitational pull of a planet or other celestial body.
17
New cards
Period
The time it takes for an object to complete one orbit around another object.
18
New cards
Solar system
The collection of planets, moons, and other celestial objects that orbit around the Sun
19
New cards
Gravity
The force of attraction between two objects with mass.
20
New cards
Orbit
The path of an object as it revolves around another object in space.
21
New cards
Elliptical orbit
An orbit that is shaped like an ellipse, which is an elongated circle.
22
New cards
Orbital velocity
The speed at which an object must travel to maintain a stable orbit around another object.
23
New cards
Mass
The amount of matter in an object.
24
New cards
Distance
The amount of space between two objects.
25
New cards
Escape velocity
The minimum speed an object needs to escape the gravitational pull of a planet or other celestial body.
26
New cards
Period
The time it takes for an object to complete one orbit around another object.
27
New cards
Solar system
The collection of planets, moons, and other celestial objects that orbit around the Sun