Music EOY - Baroque, Classical, Romantic, General Music Elements
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Stepwise/Scalic
movement of a melody upwards or downwards using the note of the scales in order

Leap
movement of a melody up or down with a jump from one note to another more distant
passing note
a note witch links the note before and after, usually on the weak beat of the bar
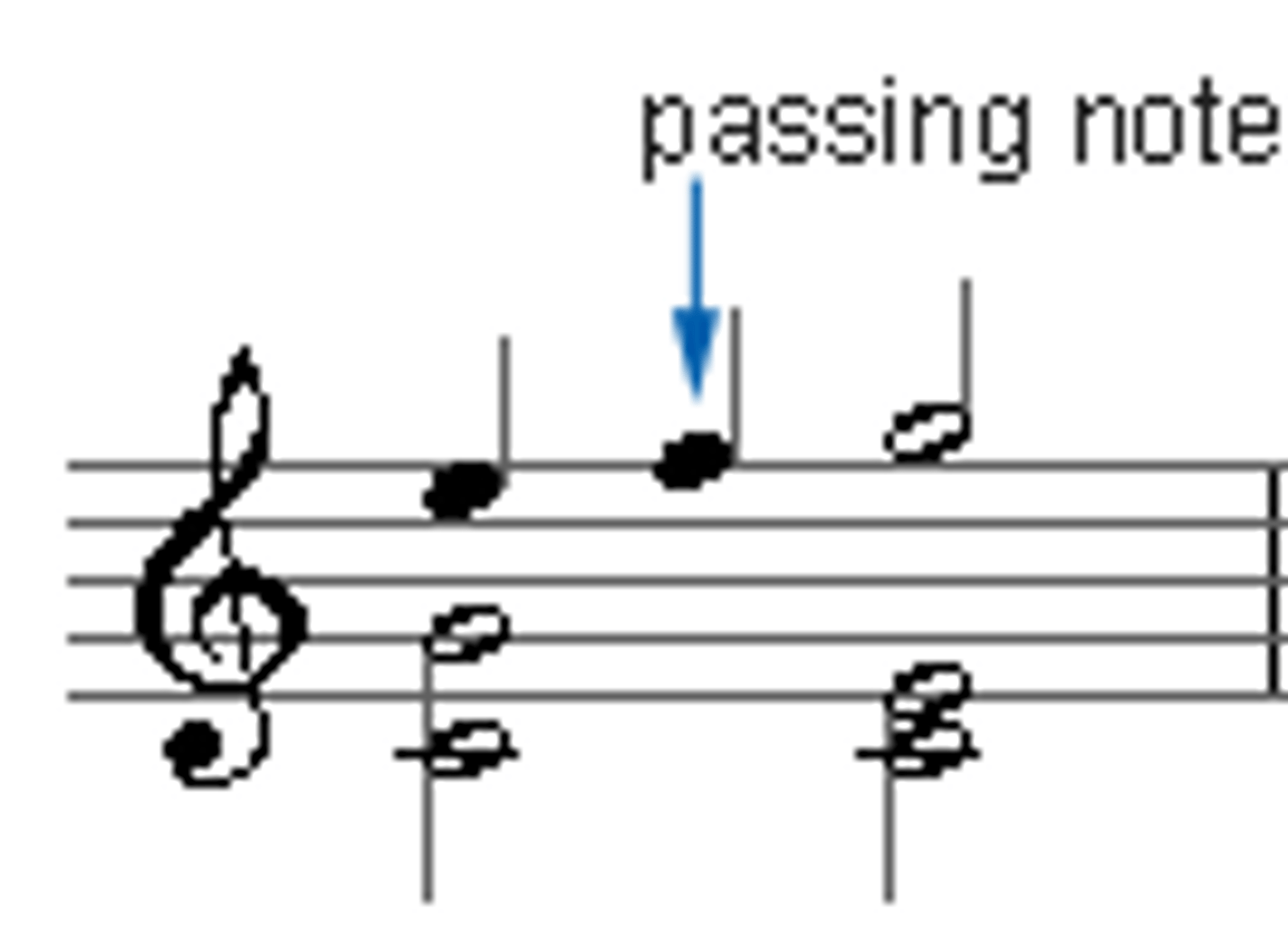

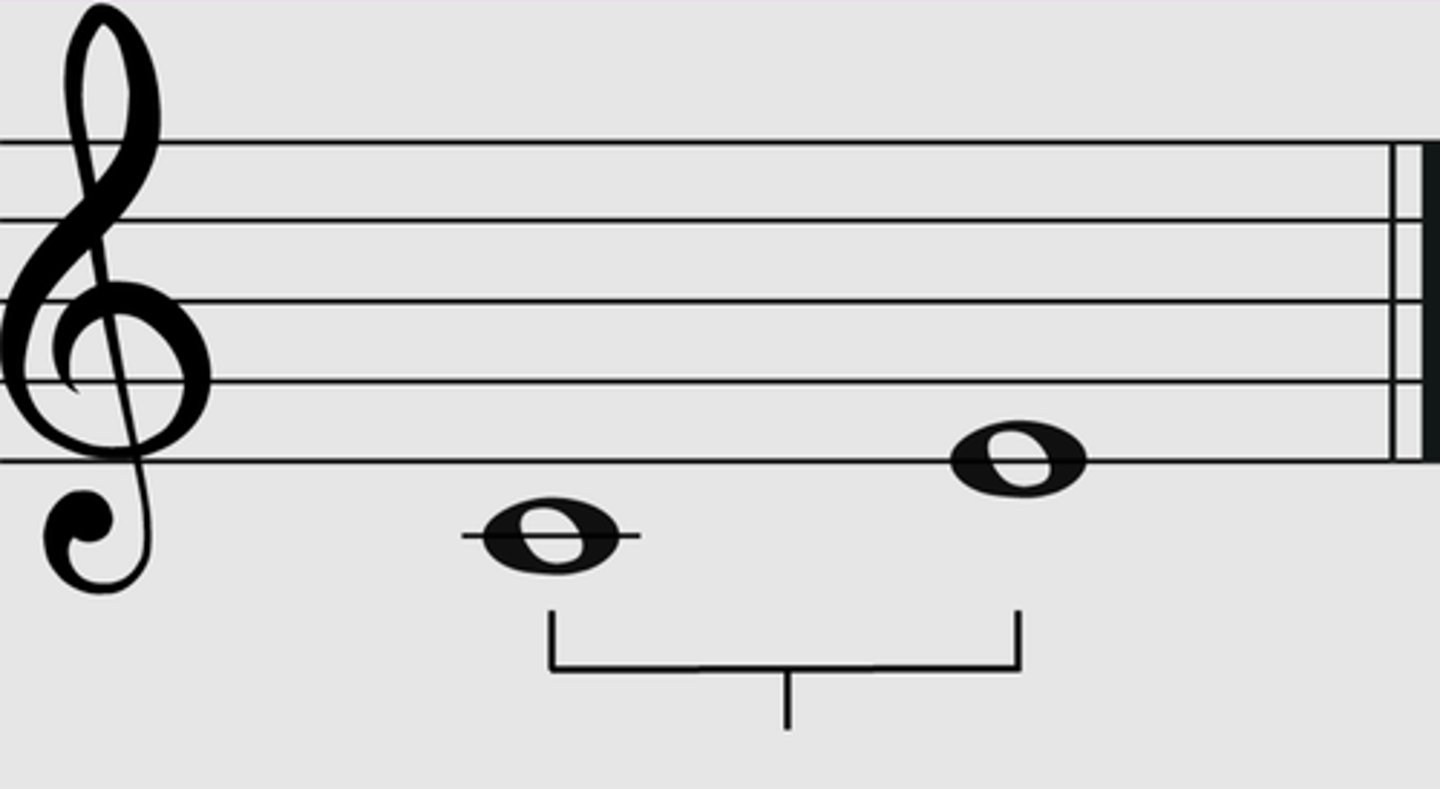
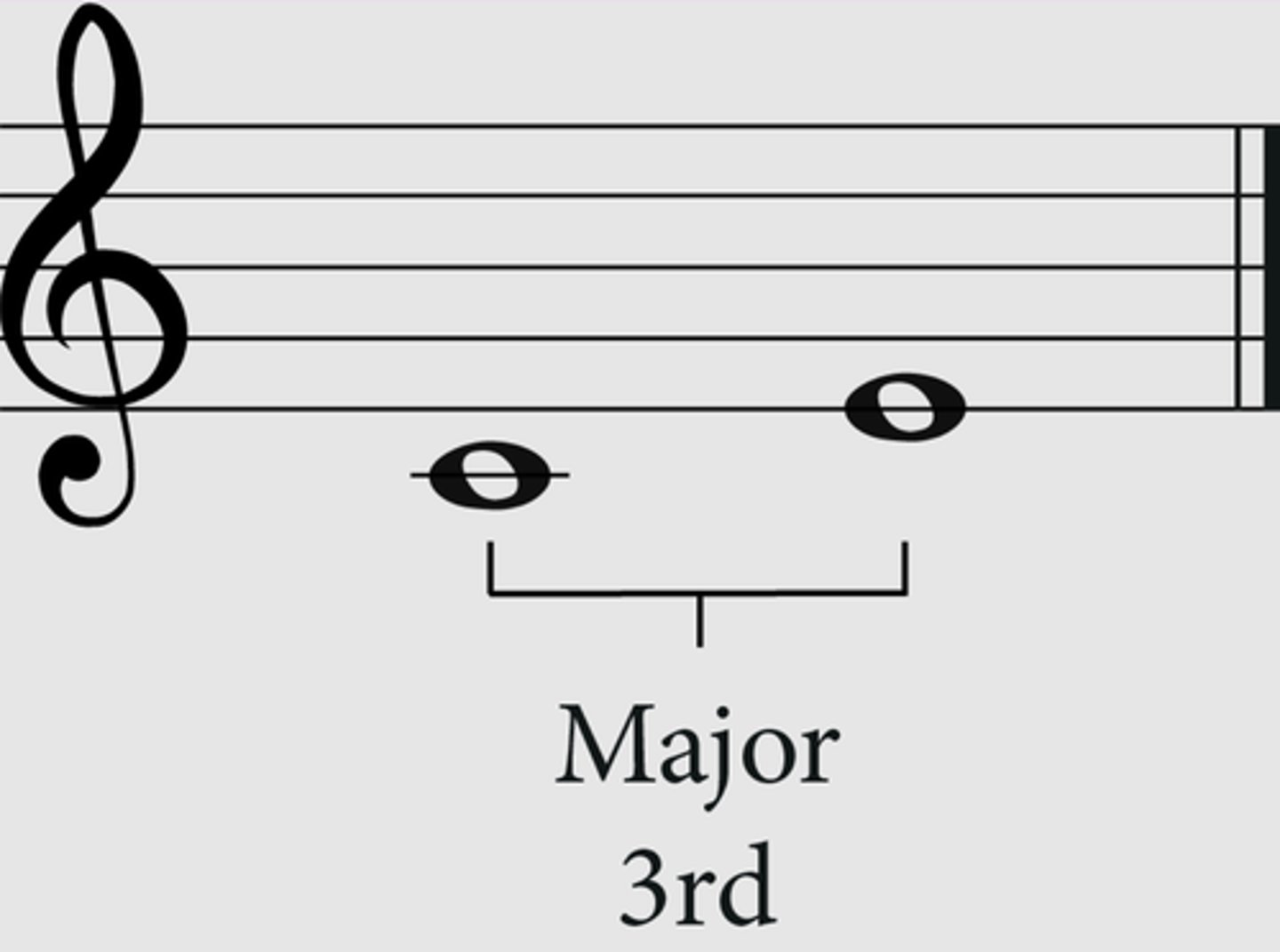
interval
the distance between two notes
Scale - Major
happy sounding scale
Scale - minor
Sad sounding scale - form of harmonic, natural, melodic

Scale - chromatic
a 13 note scale, where every step is a semitone

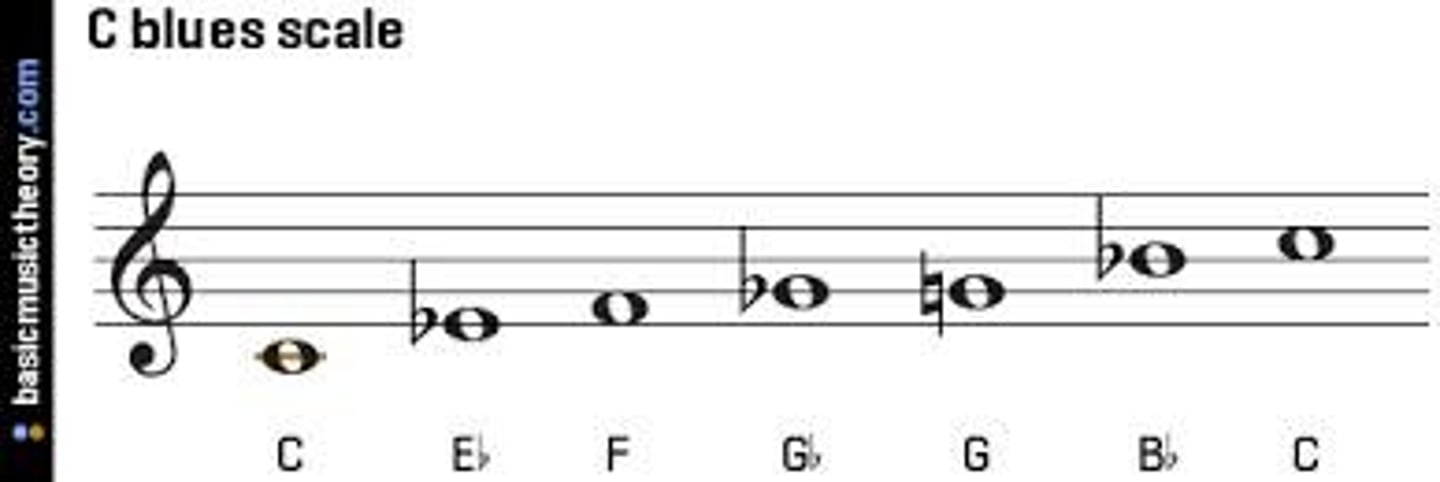
Scale - blues
major scale with a flattened third and seventh, which replaced the second and sixth note

Scale - Raga
an indian scale - sa , ri , ga , ma , pa , dha , ni
scale - slendro
the five note gamelan scale

scale - pelog
the seven note gamelan scale

Range
the notes that an instrument plays, highest - lowest
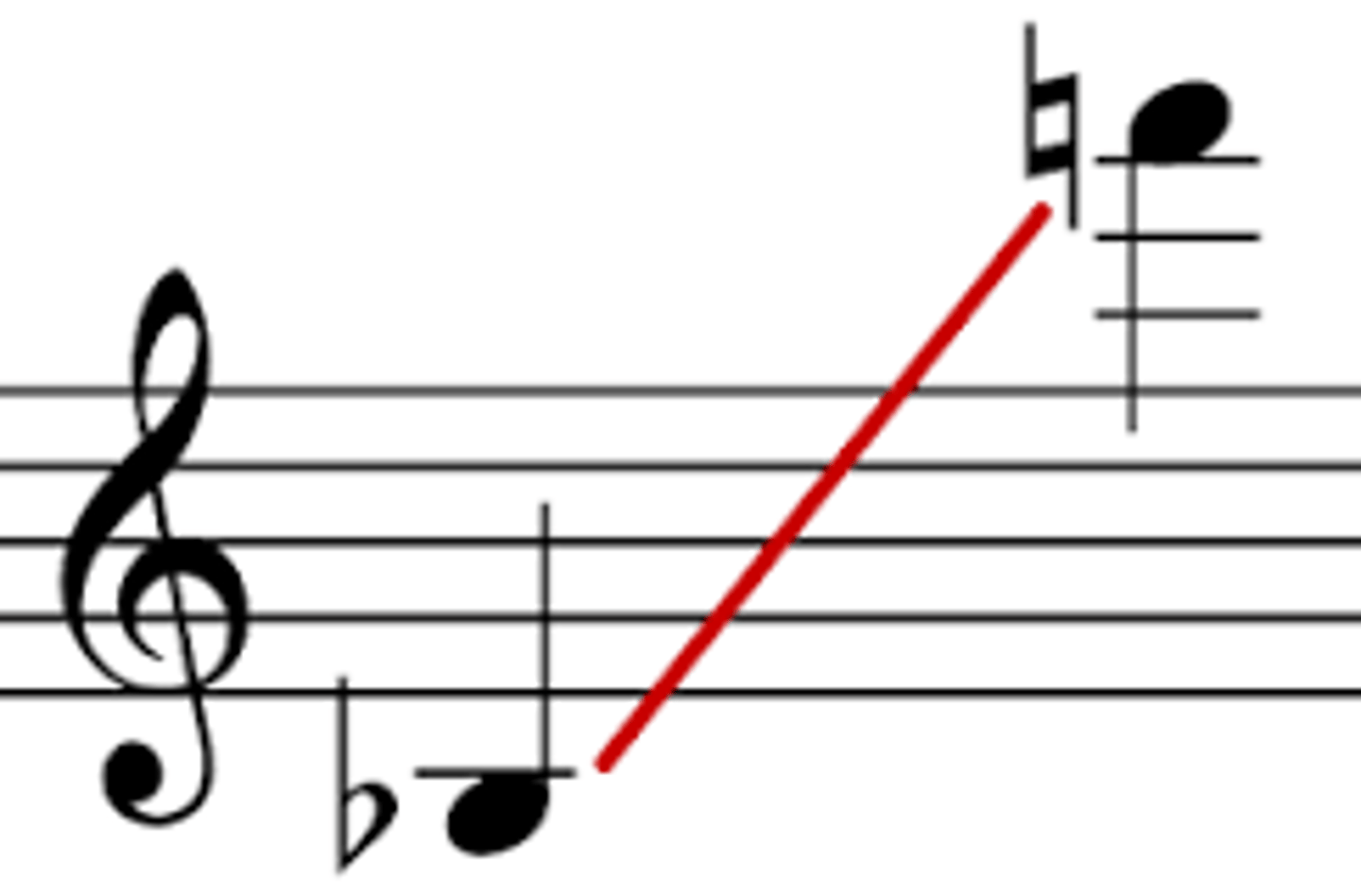

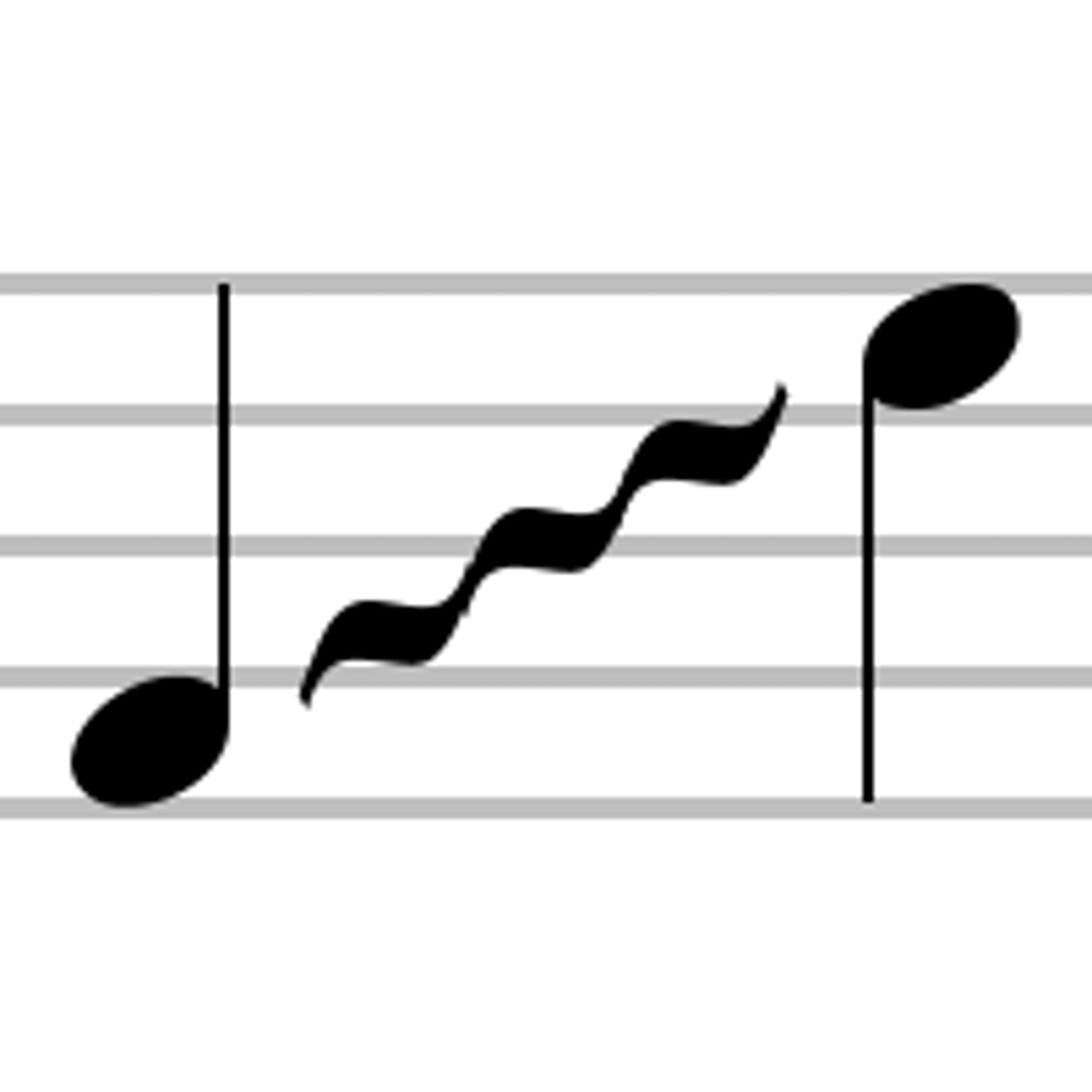
Glissando/slide/bend
a slide from one note to the next
Repetition
repeating music heard previously

sequence
where a melodic phrase is repeated at a different pitch

imitation (melodic)
the repetition of a melody in a different voice. can be played in a different pitch or changed a bit but the character remains.

ostinato (melodic)
phrase that constantly repeats usually at the same pitch

inversion (melodic)
melodic phrase turned horisontal / upside down

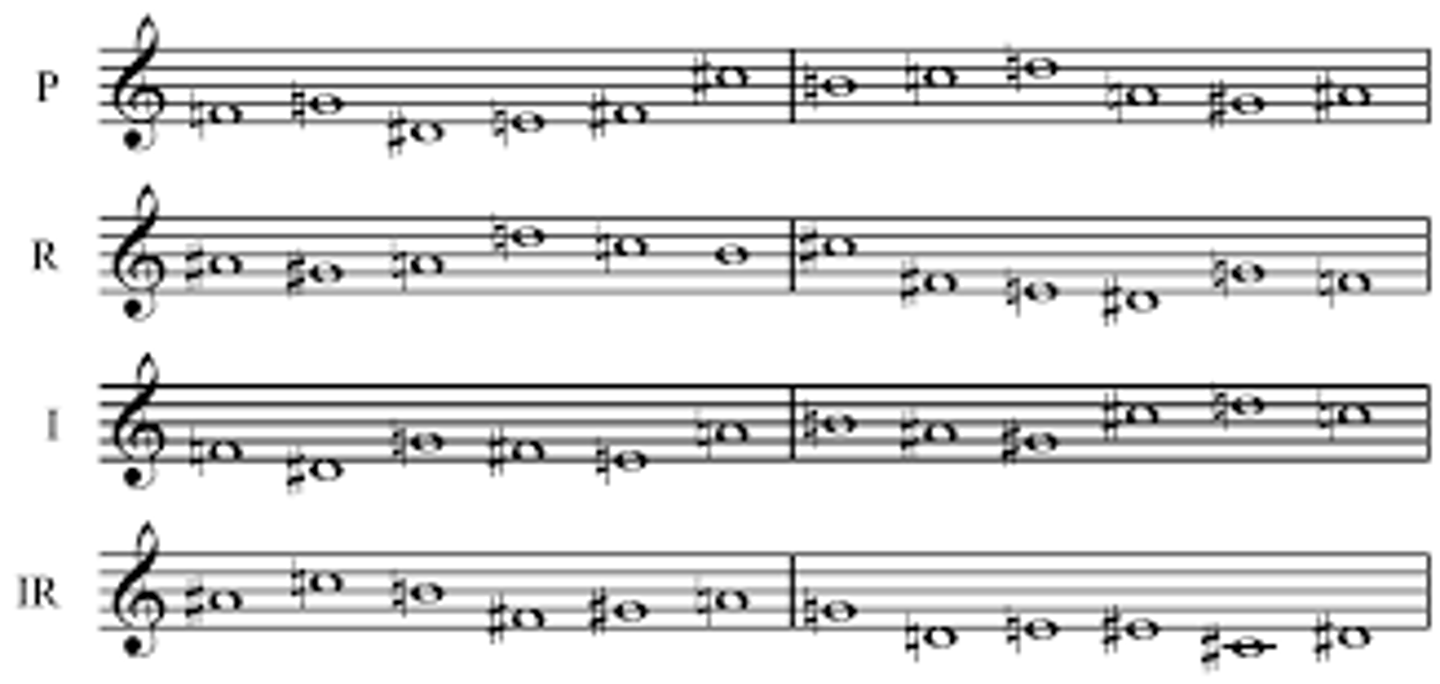
retrograde
phrase is played backwards to create contrast

riff
another word for ostinato but used in the context of popular music

improvisation
associated with jazz and Indian classical music. music built up on the spot during a performance.
call and response
a short melody (call) followed by an answering phrase (response)

Prego & Choro (salsa)
type of call and response used in salsa music

Walking bass
A bassline consisting of small steps or intervals up and down the scale

Fills (melodic)
short section of music between phrases

Stabs
short, accented notes, usually on an offbeat
Hook
Short, memorable bit of tune

Stave
The five lines on which music is written
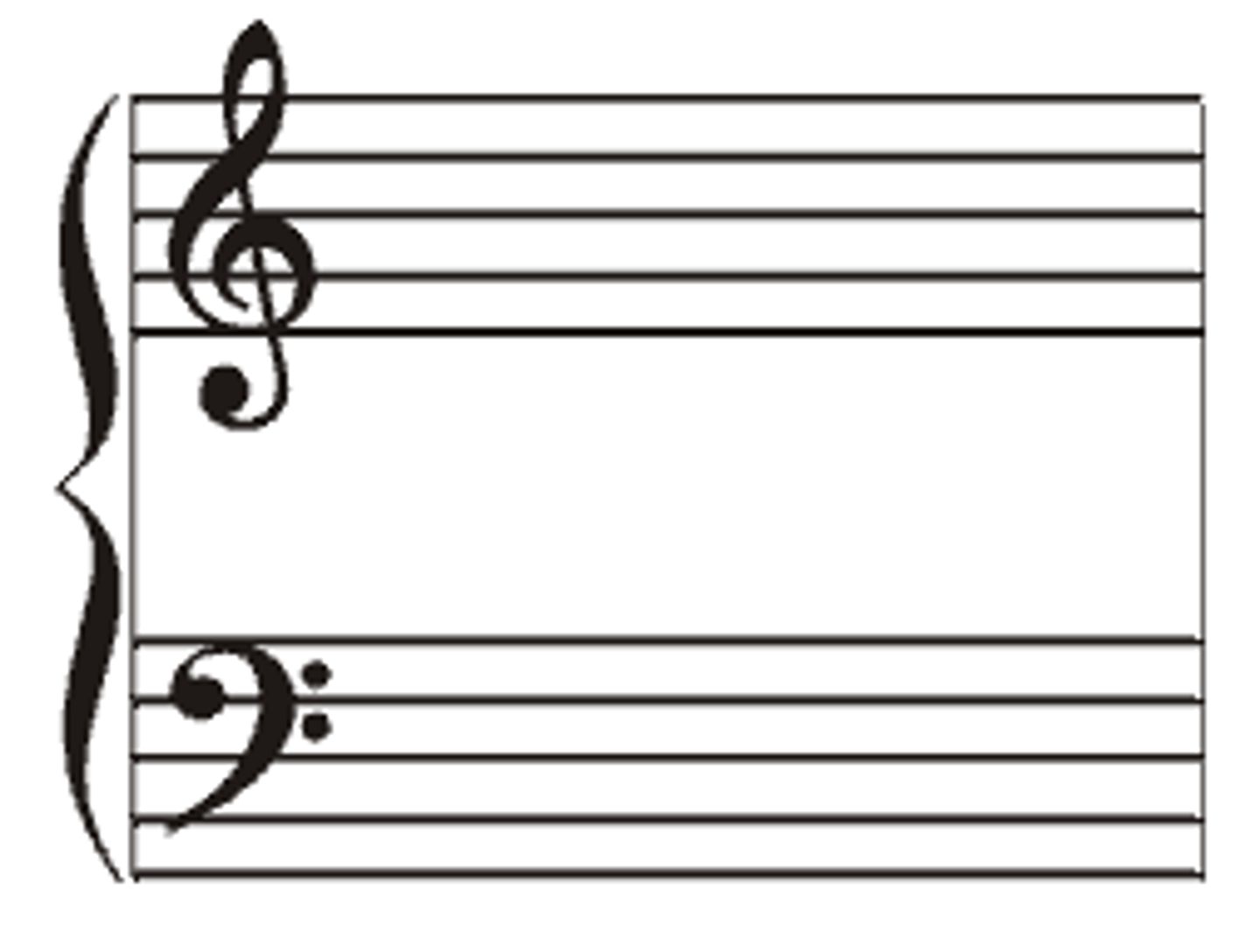
Score
Musical name for sheet music

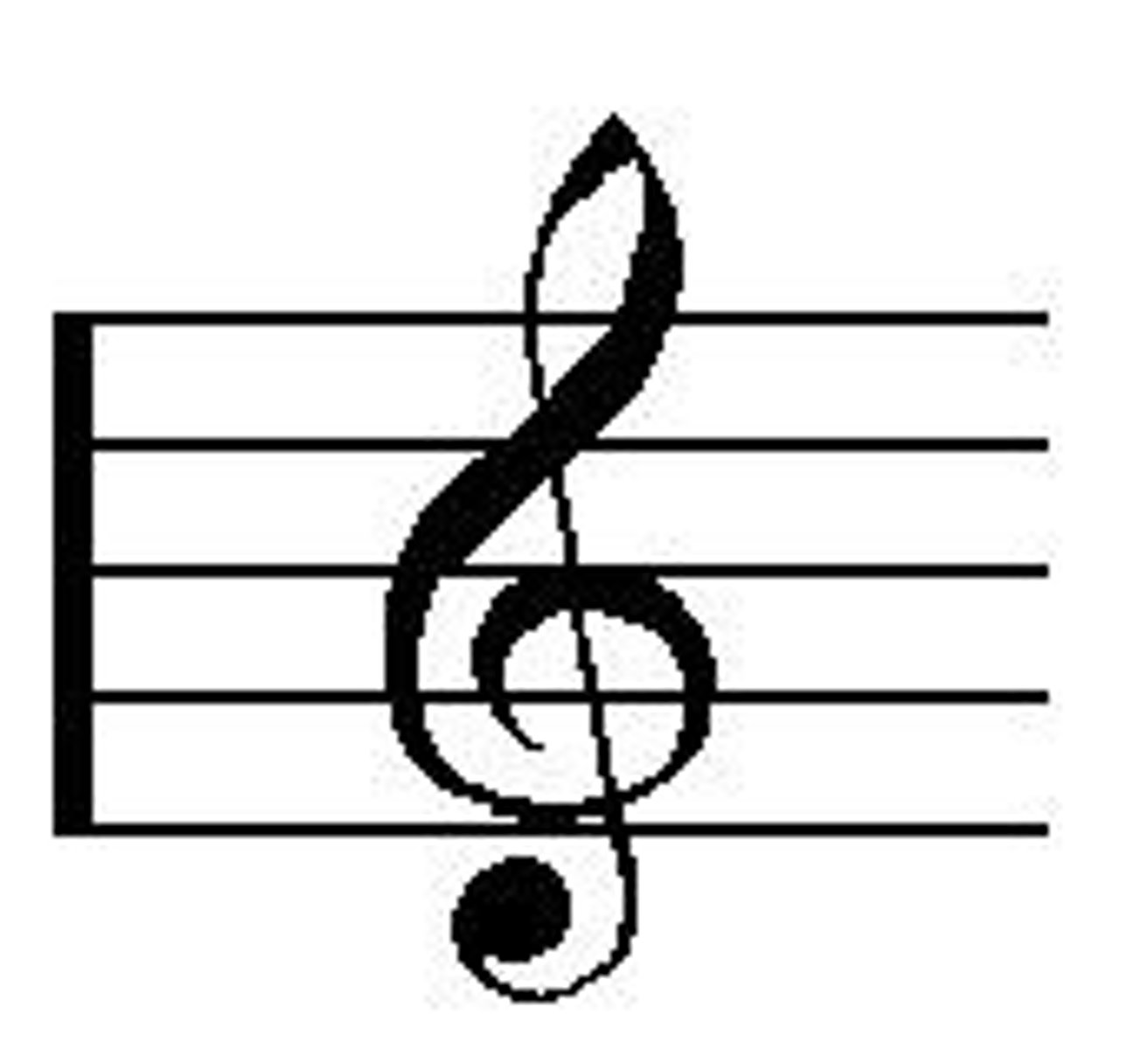
Treble clef
Used for the higher sounding pitches. Also known as the G clef.

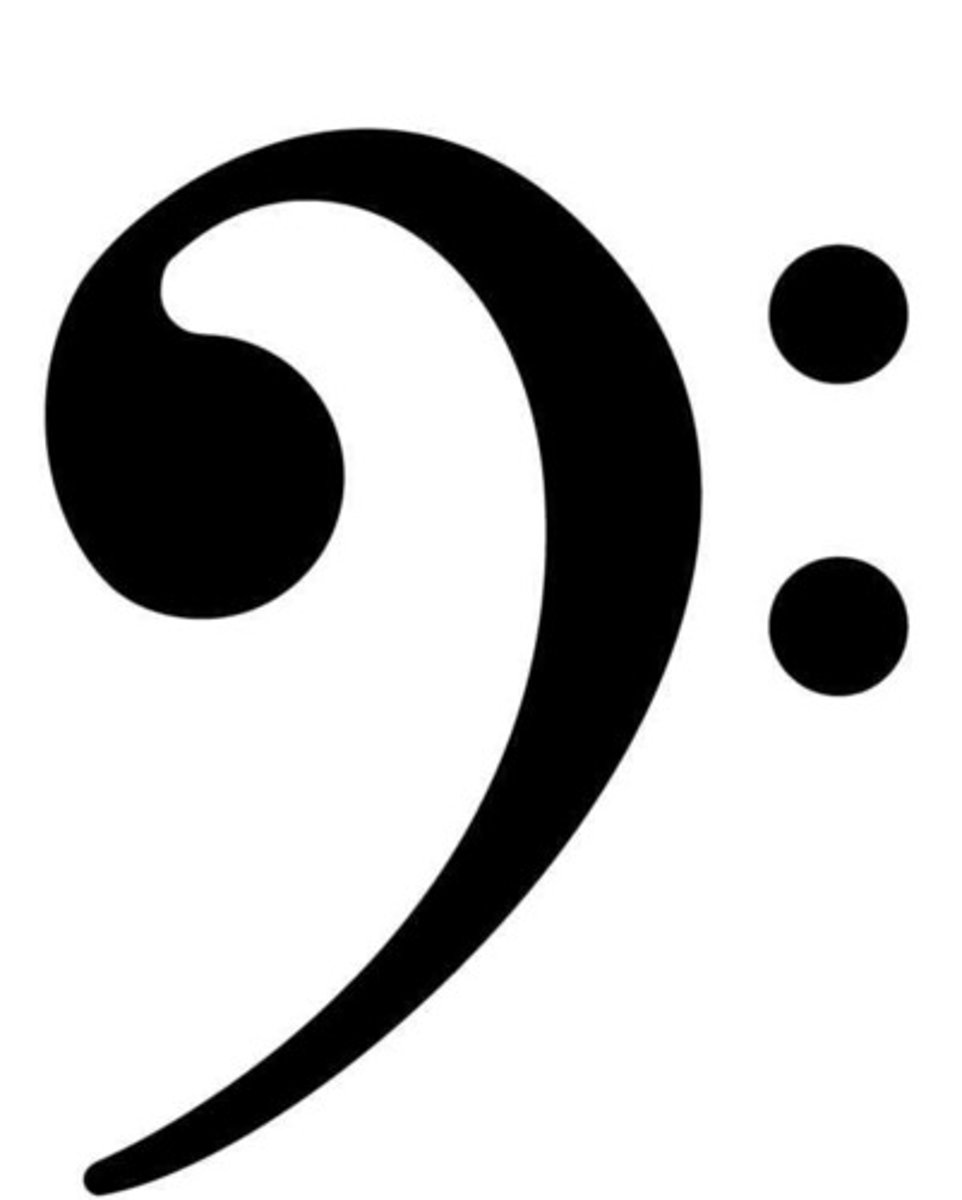
Bass cleff
used for lower pitched instruments. Blob goes on the line for F below middle C

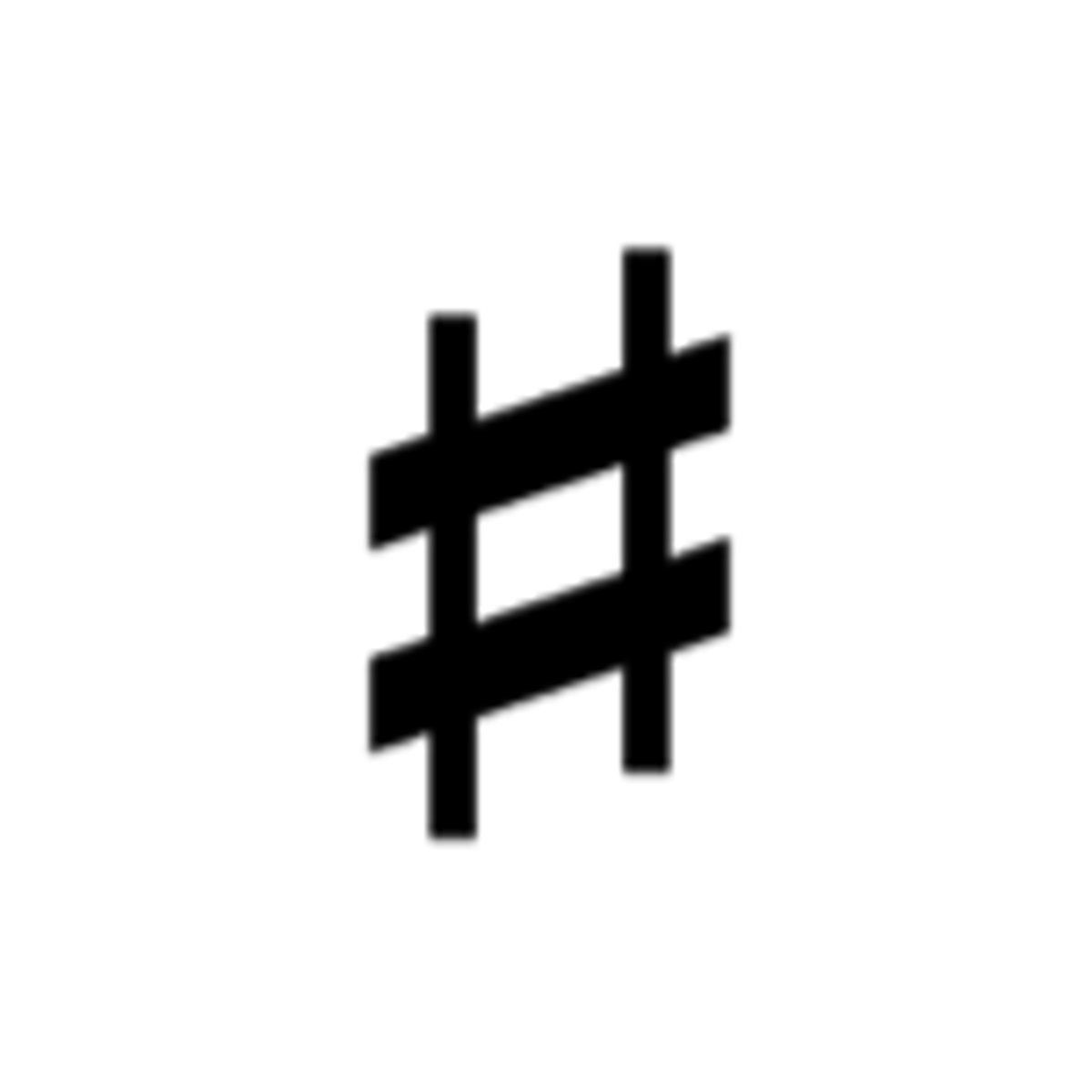
Sharp
Raises a note by a half step
Flat
lowers a note by a half step
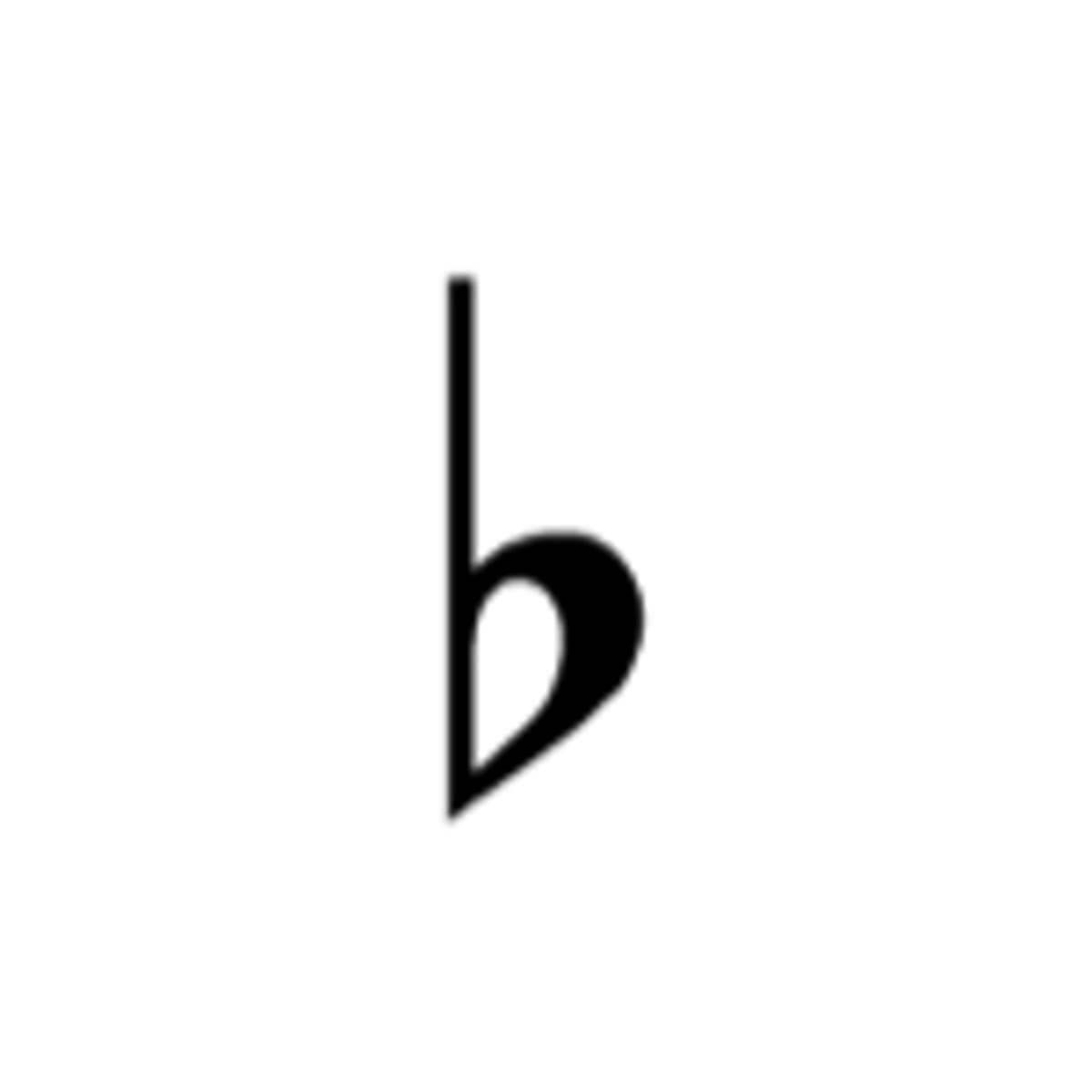
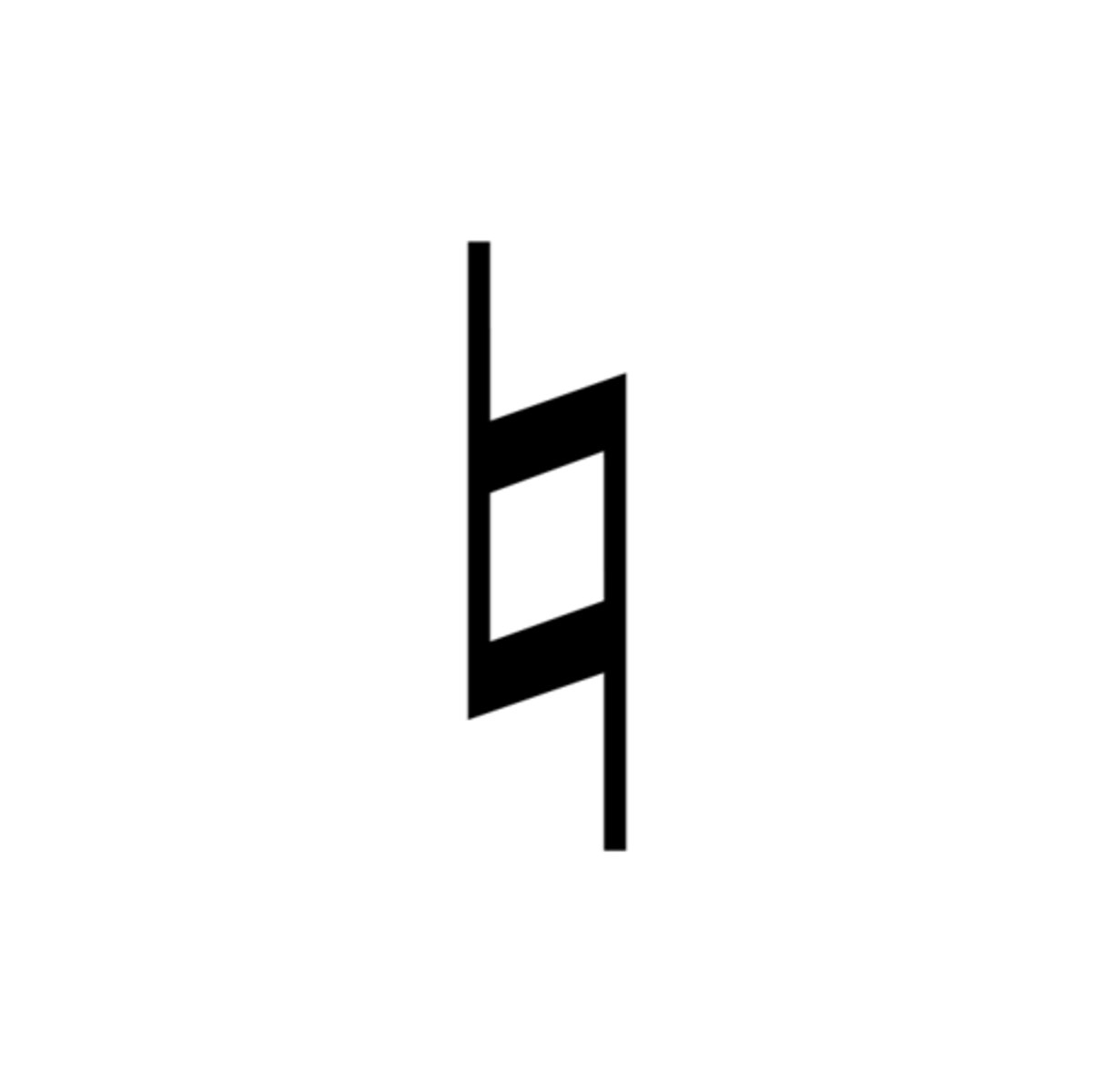
Natural
cancels a sharp or flat
Phrase marks
indicate the length of a phrase
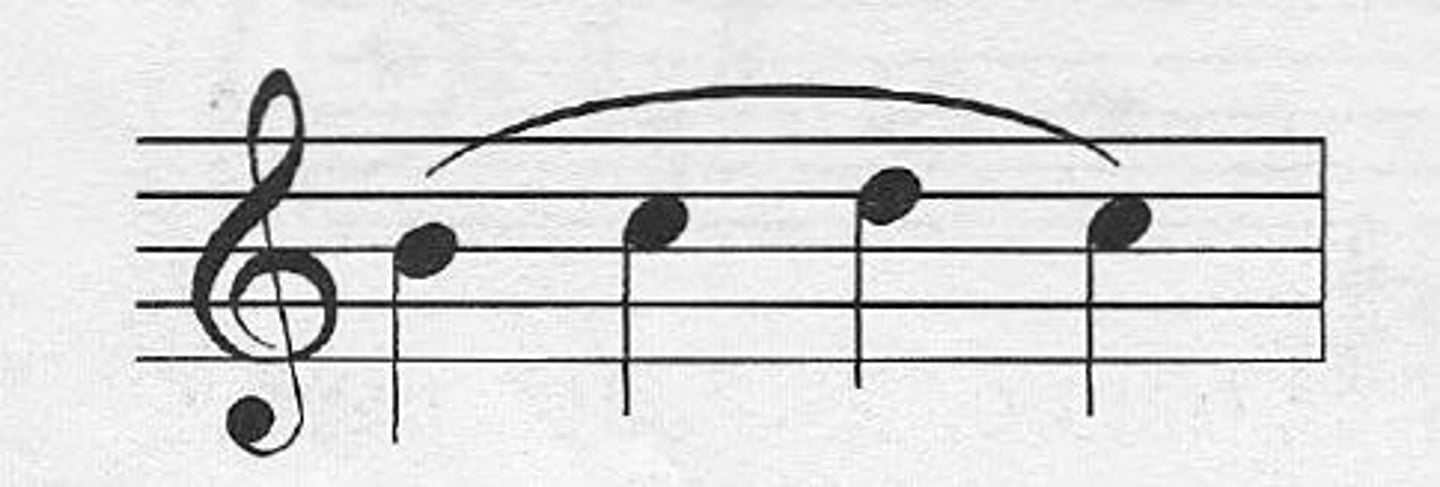
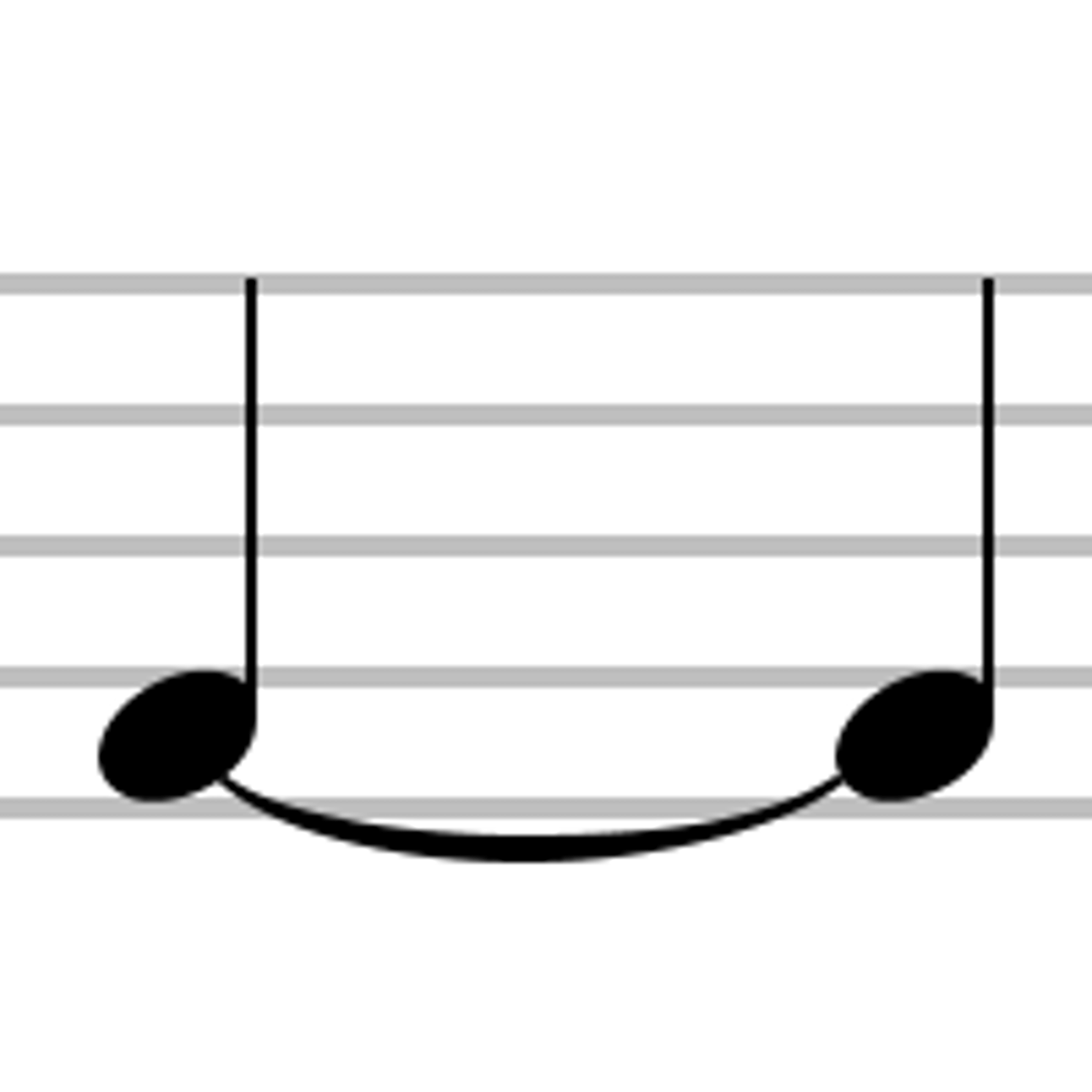
Tie
Curved line that joins 2 notes of the same pitch to sound like one note
Trill
Rapid alternation between the note indicated and the note directly above it

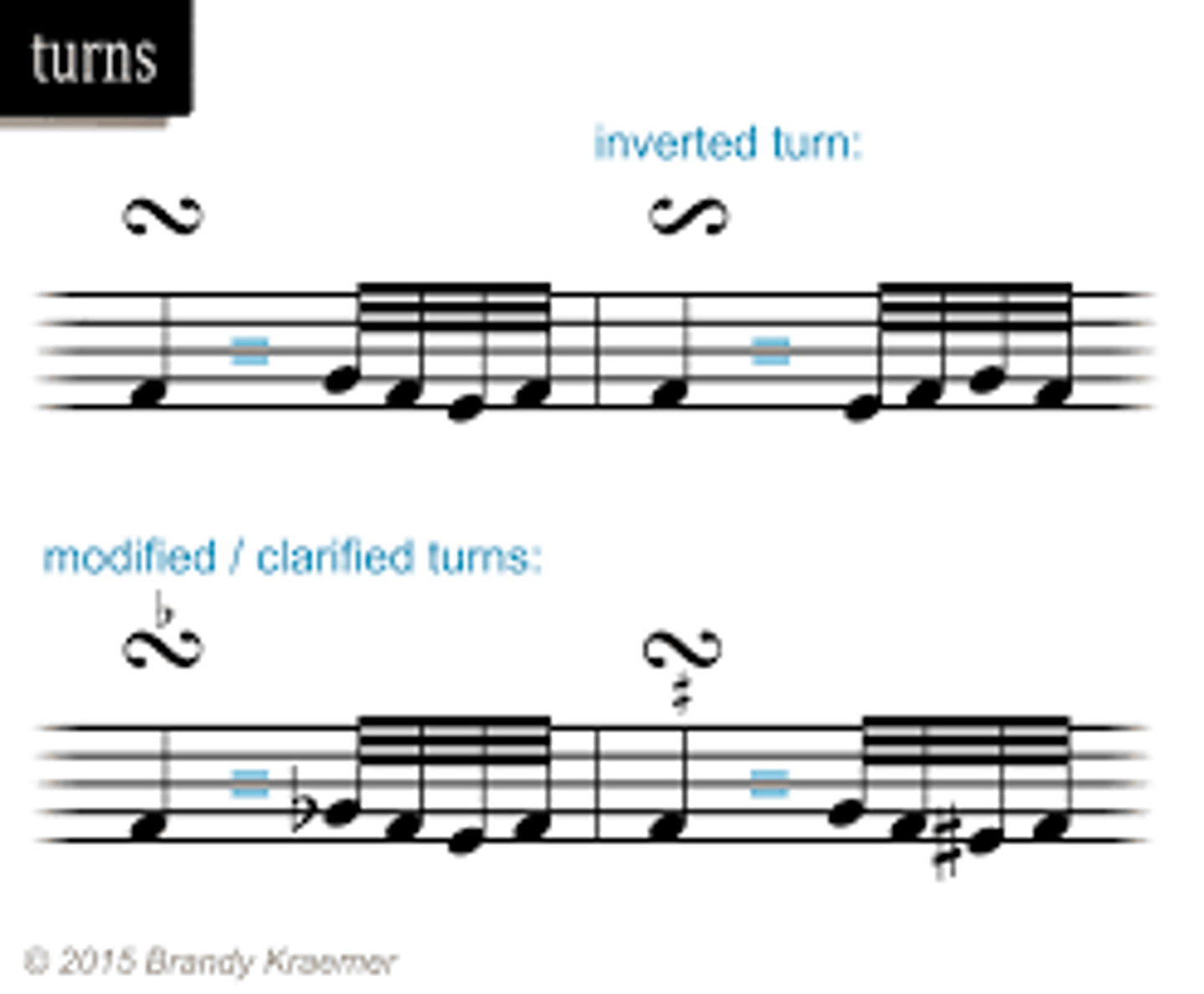
Turn
Playing of the note above the one on the score, the note itself, the note below the one on the score and the note itself again
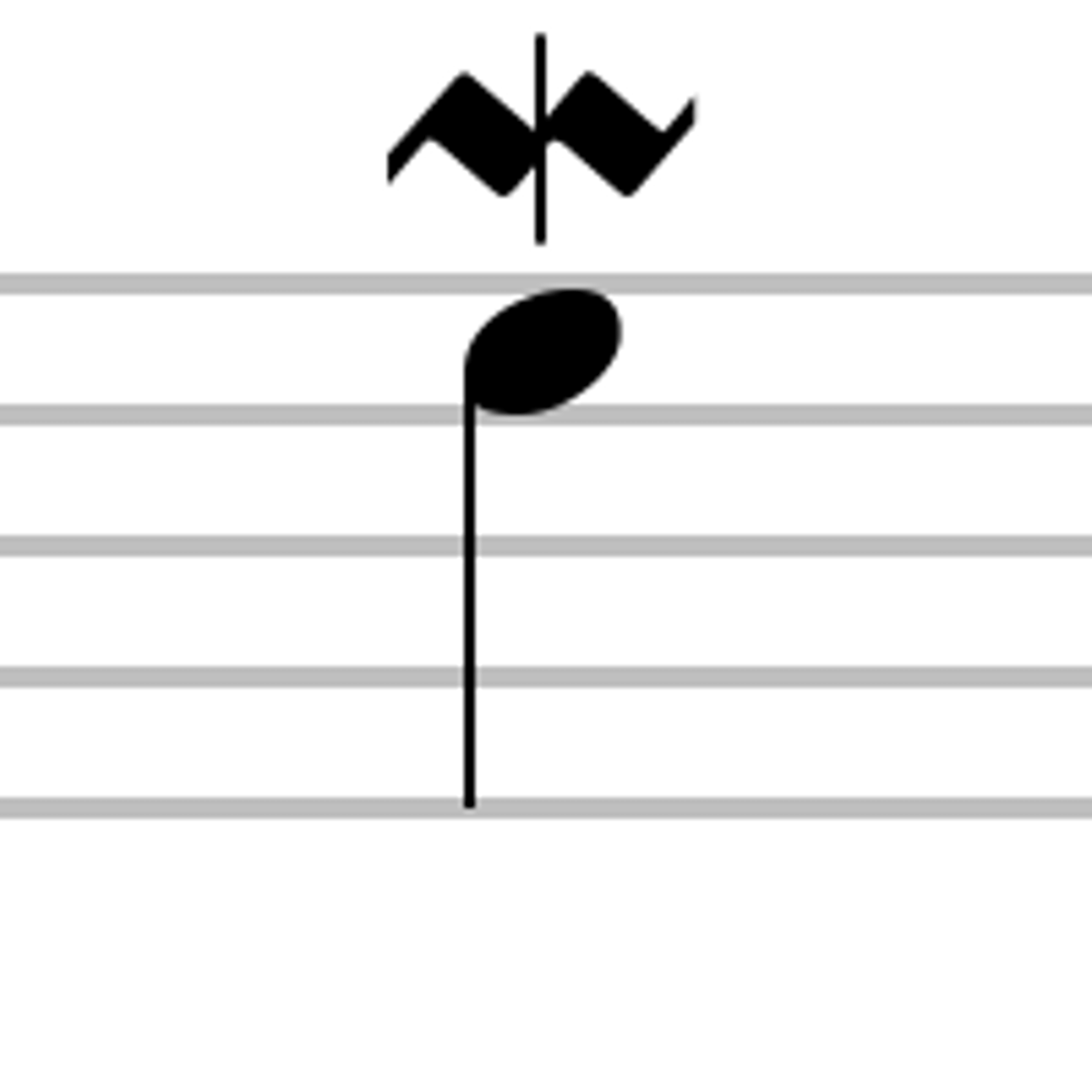
Mordent
A single rapid alternation with the note above (upper mordent) or the note below (lower mordent)
Acciaccatura
An ornament which sounds like a crushed note played very quickly on the beat or just before it.
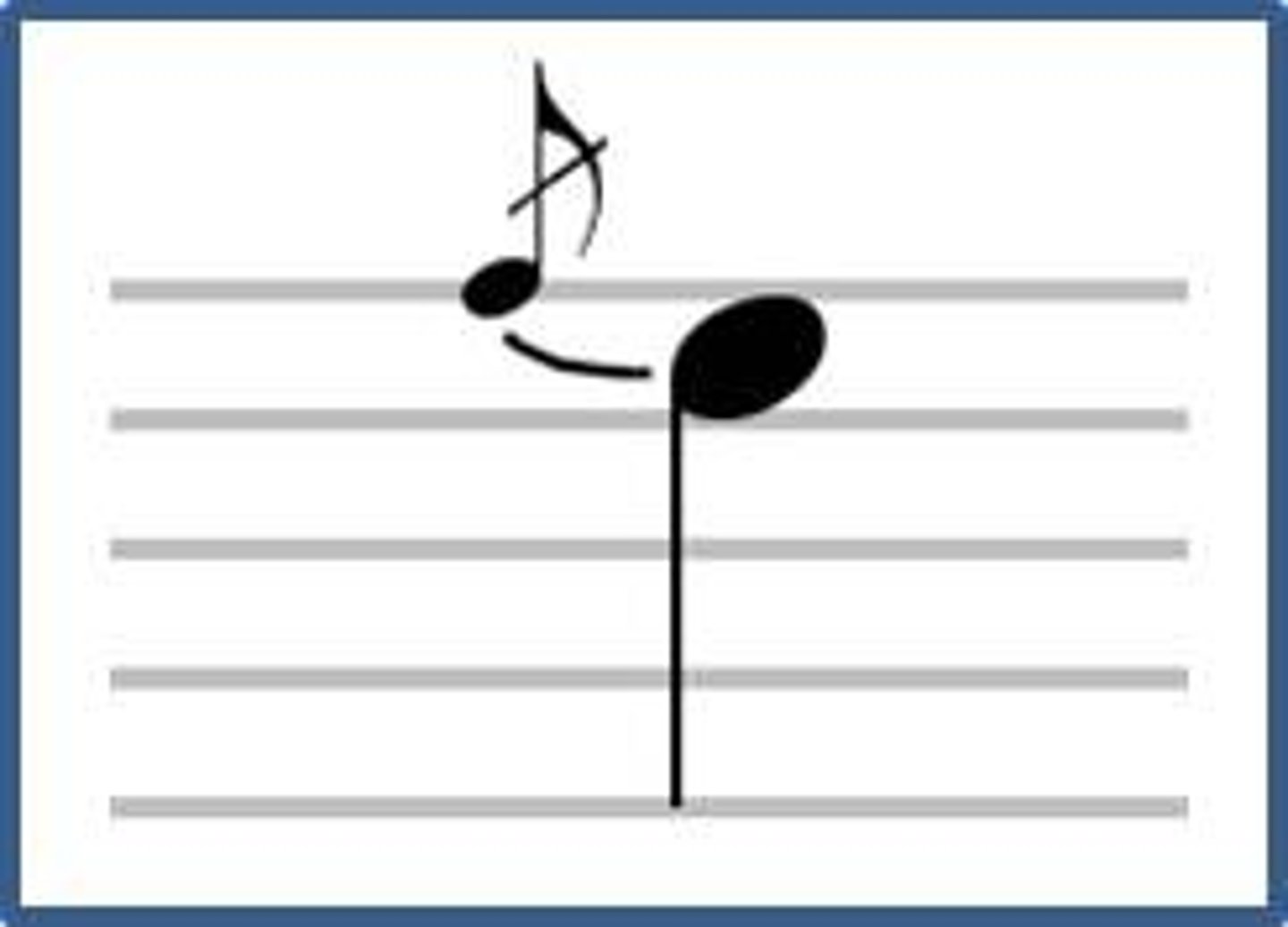

Appogiatura
a grace note performed before a note of the melody and falling on the beat
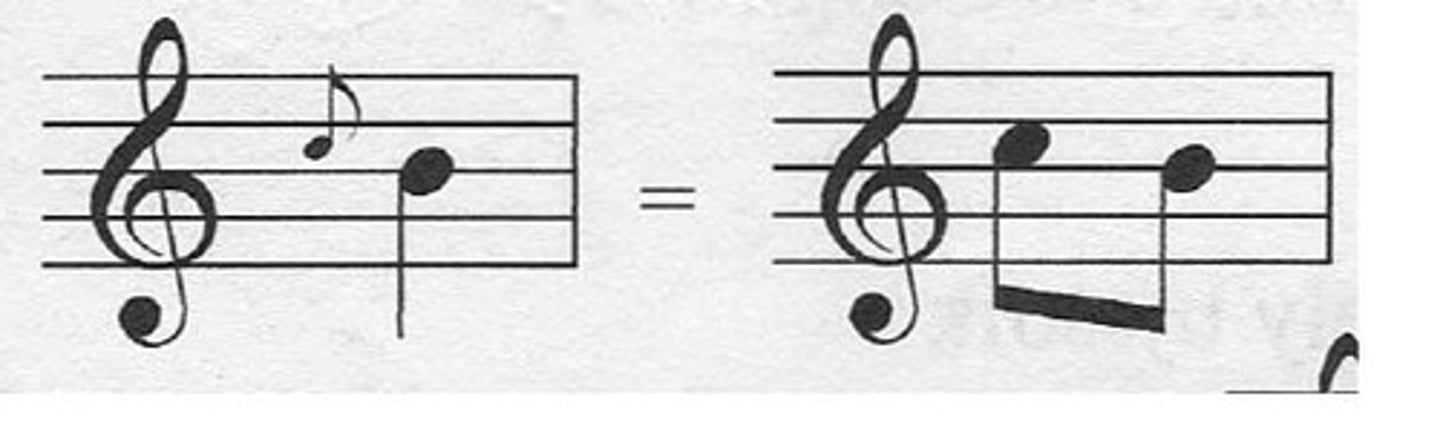

Anacrusis
an unstressed note or group of notes at the start of a phrase
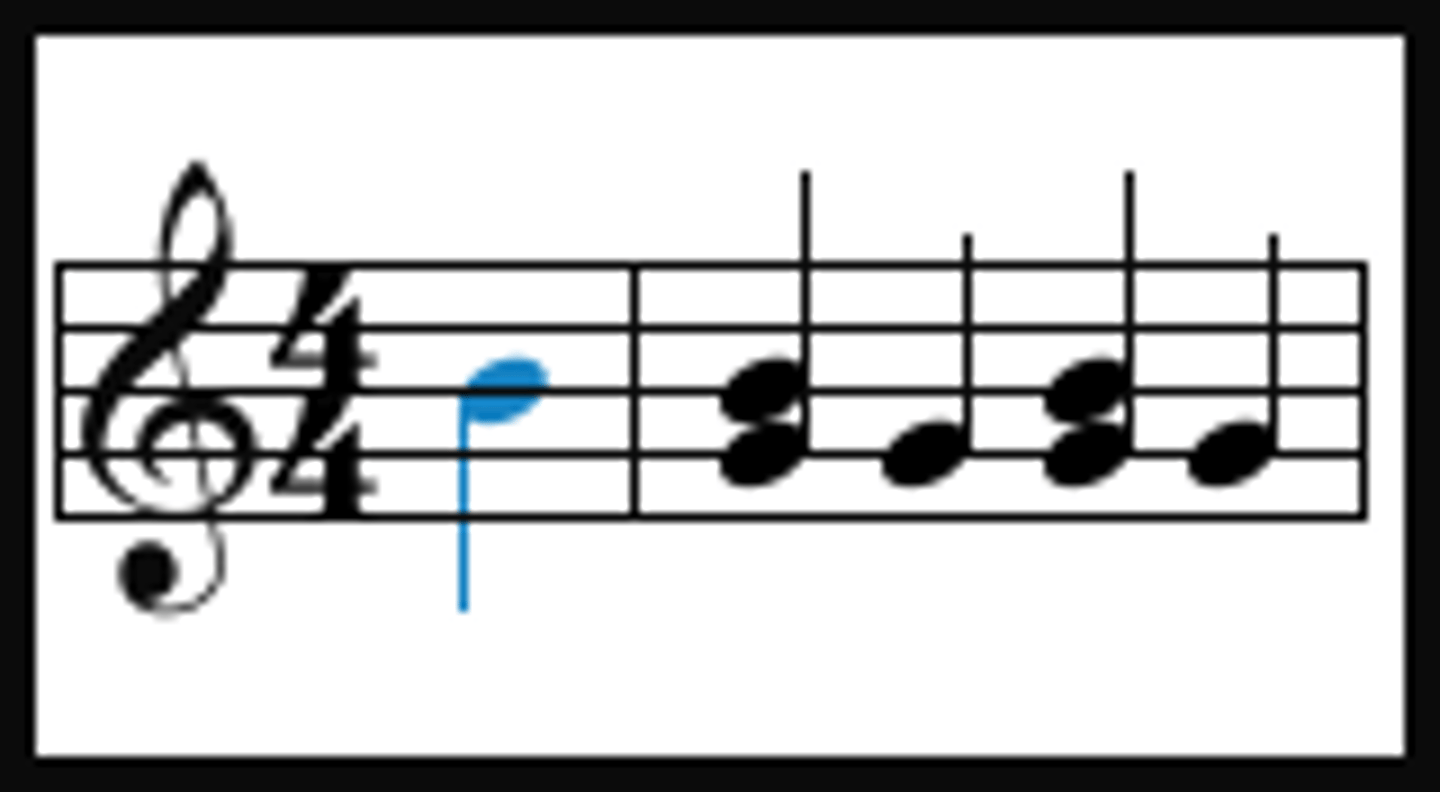

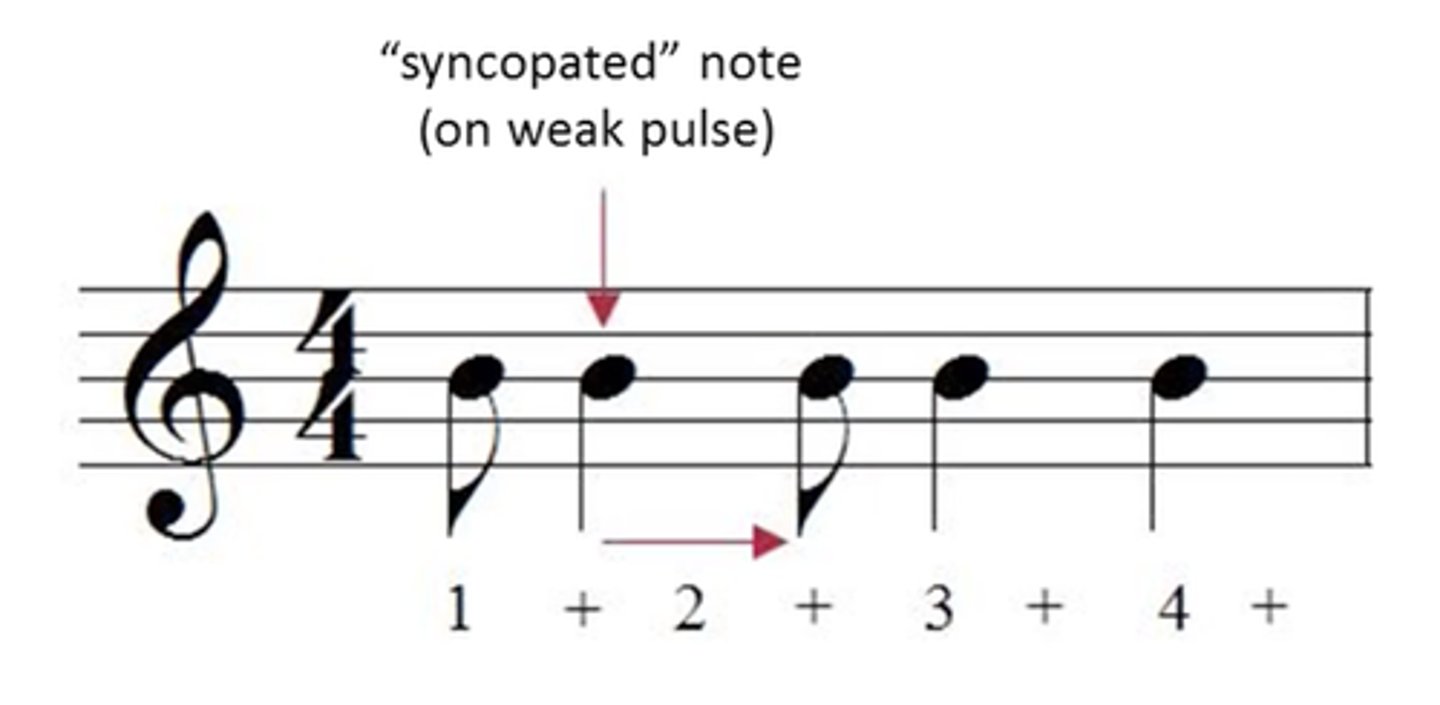
Syncopation
emphasising or accenting the weaker beats of the bar
Metre
the regular pattern of beats indicated by a time signature
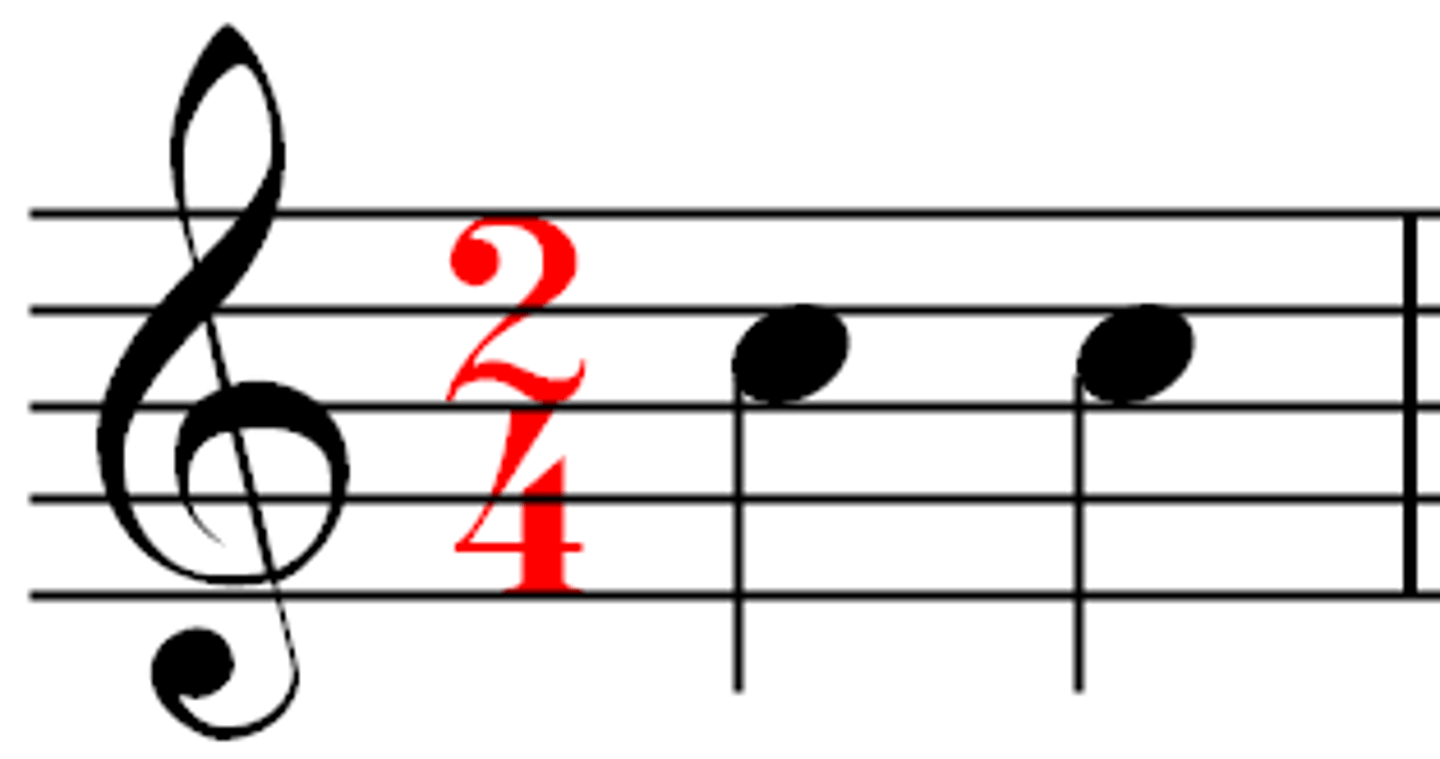
Pulse
the 'heartbeat' of the music. although the music may have rhythms made up of different note lengths, the pulse will be steady.
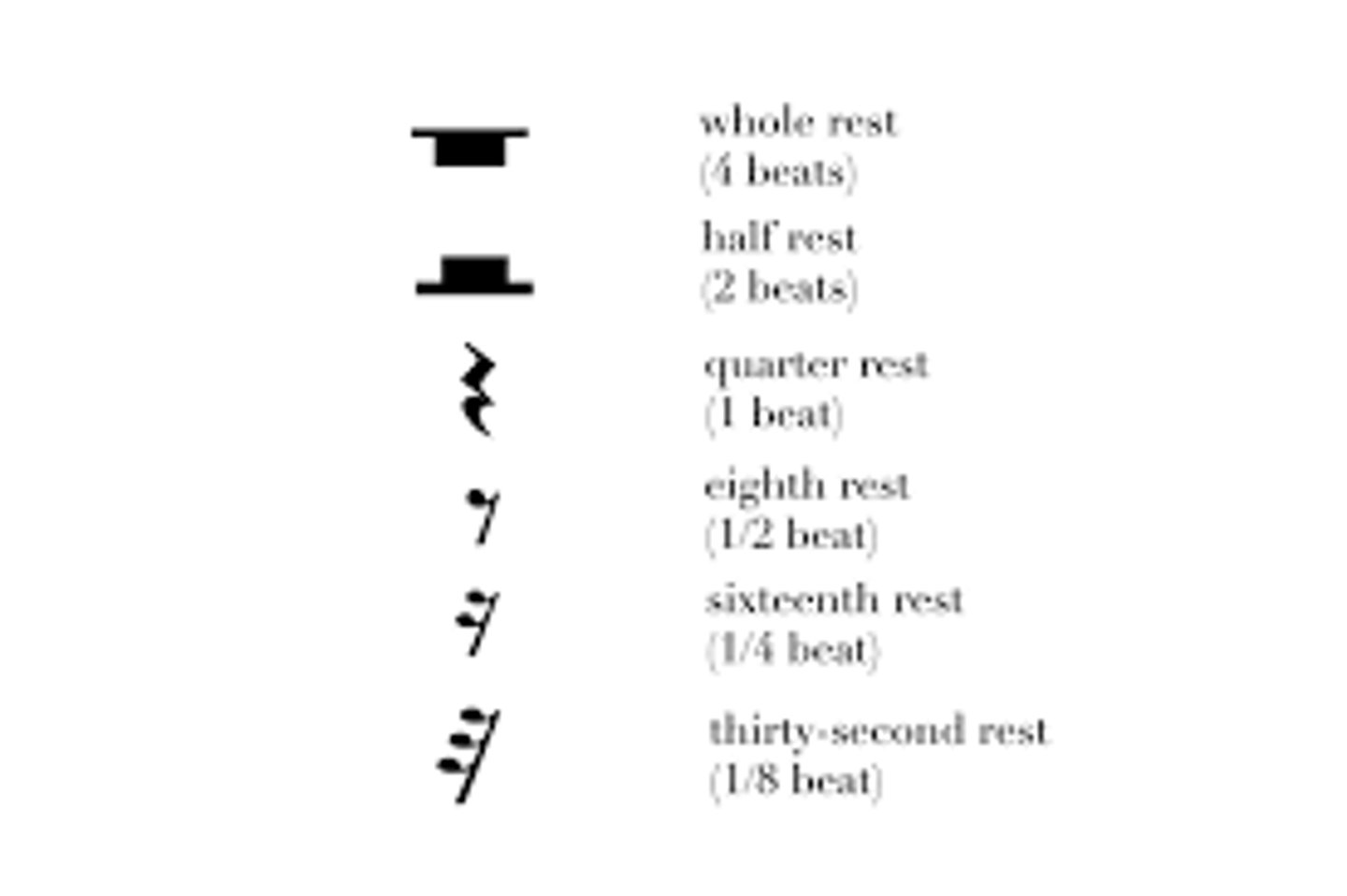
rest
an interval of silence indicated with a symbol
Pianissimo
very quiet

Piano
quiet
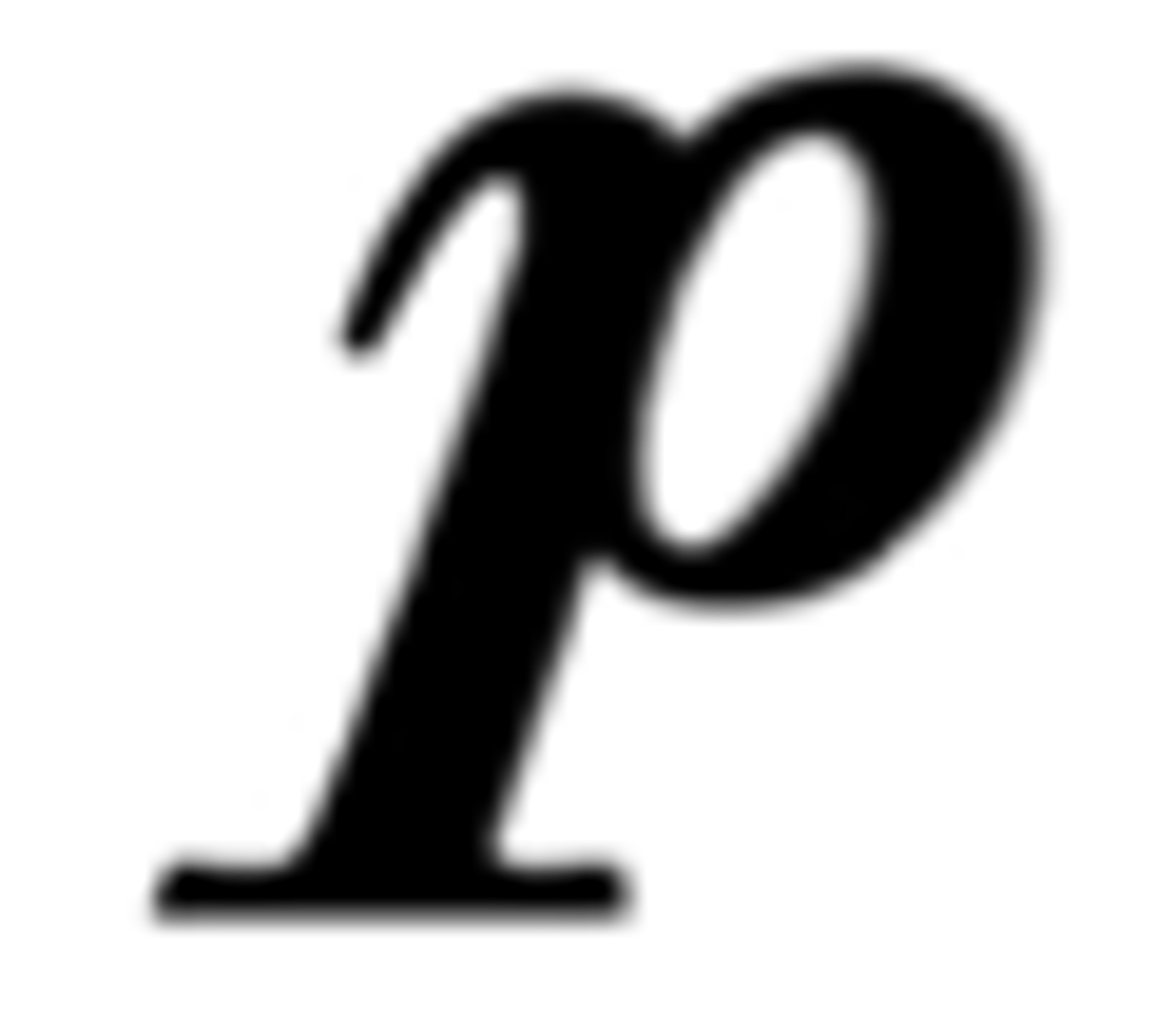
Mezzo piano
moderately quiet

Mezzo forte
moderately loud

Fortissimo
very loud

Crescendo
getting louder gradually
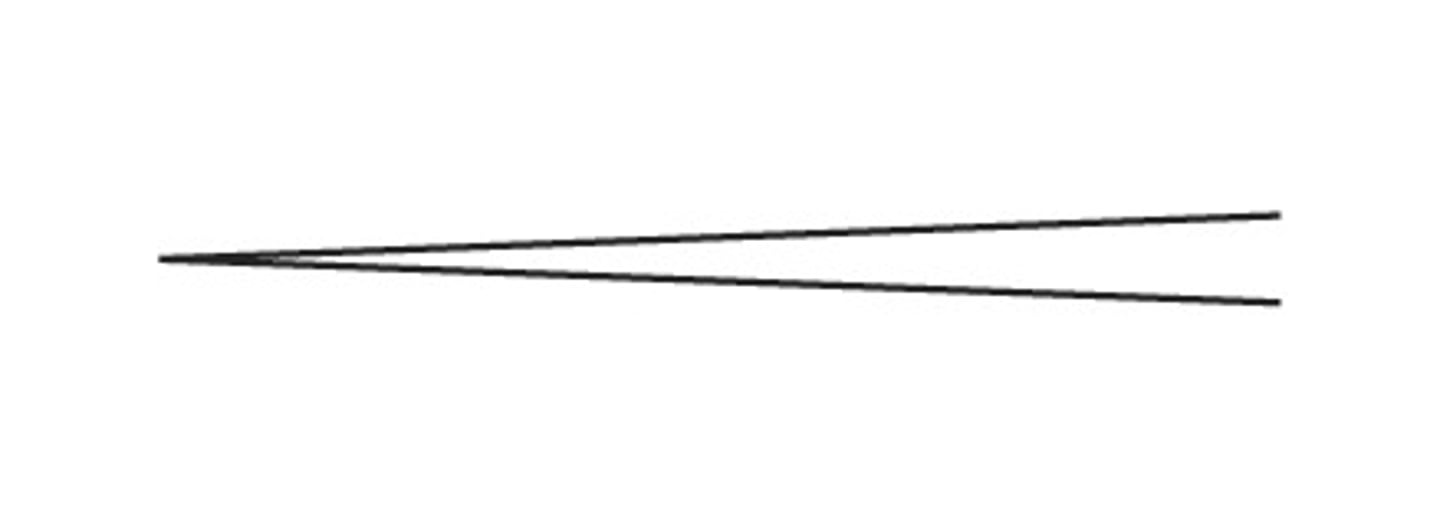
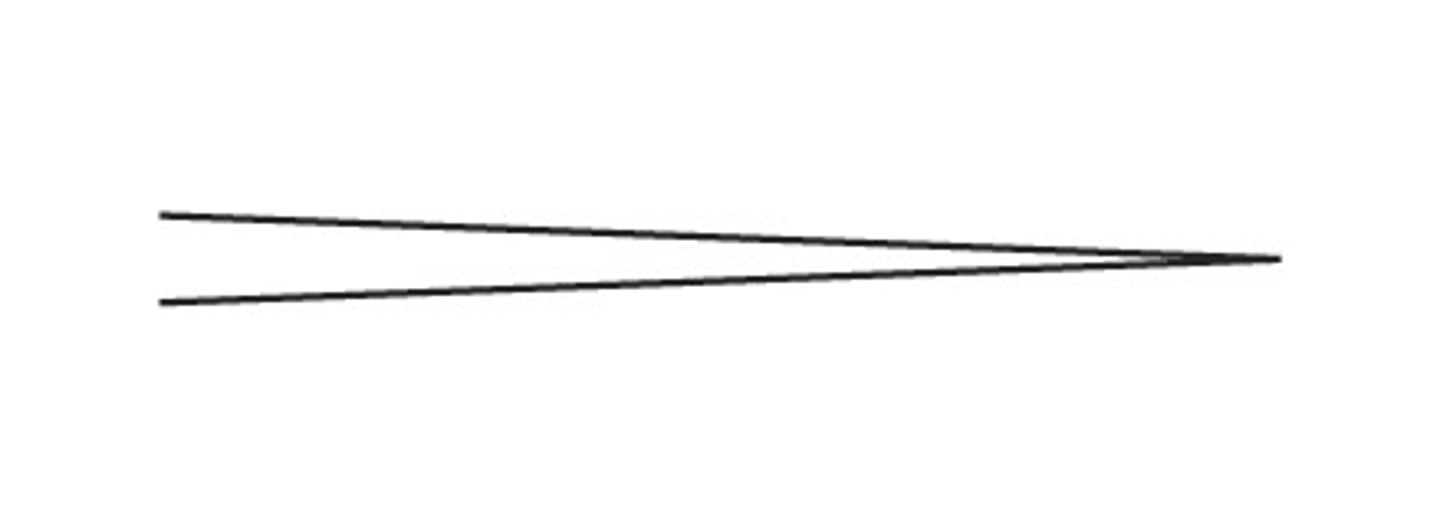
diminuendo
getting quieter gradually
monophonic
single melodic line ( without harmonies ) . a solo or instrument section such as violin 1s
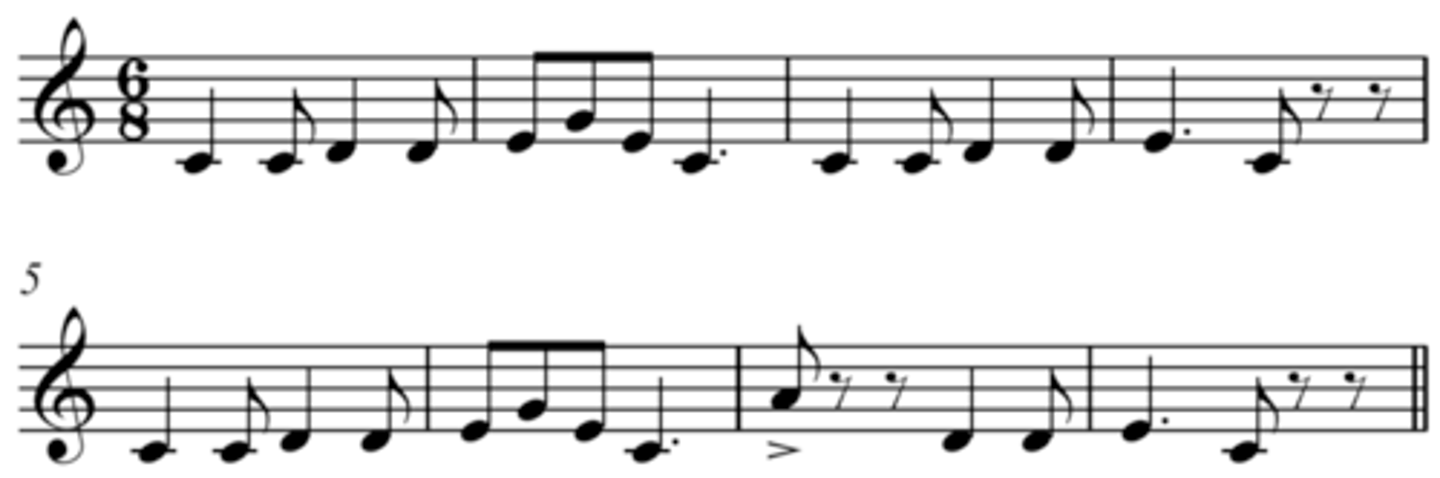

Homophonic / chordal
a CHORDAL texture where all the parts move together, but there is one line thats most important (e.g. a hymn tune)

Polyphonic / contrapuntal
The weaving together of two or more equally important melodic lines, which all fit together harmonically. the texture sounds 'busy'

Unison
all instruments or voices playing or singing notes at the same pitch

Parallel motion
were parts move in the same direction as one another

Contrary motion
where parts move in the opposite direction

Counter melody
a second melody played at the same time as the main tune

Descant
a harmonising tune sung at the same time as melody but at a higher pitch

melody and accompaniment
a form on homophony - when the main tune is supported by accompaniment

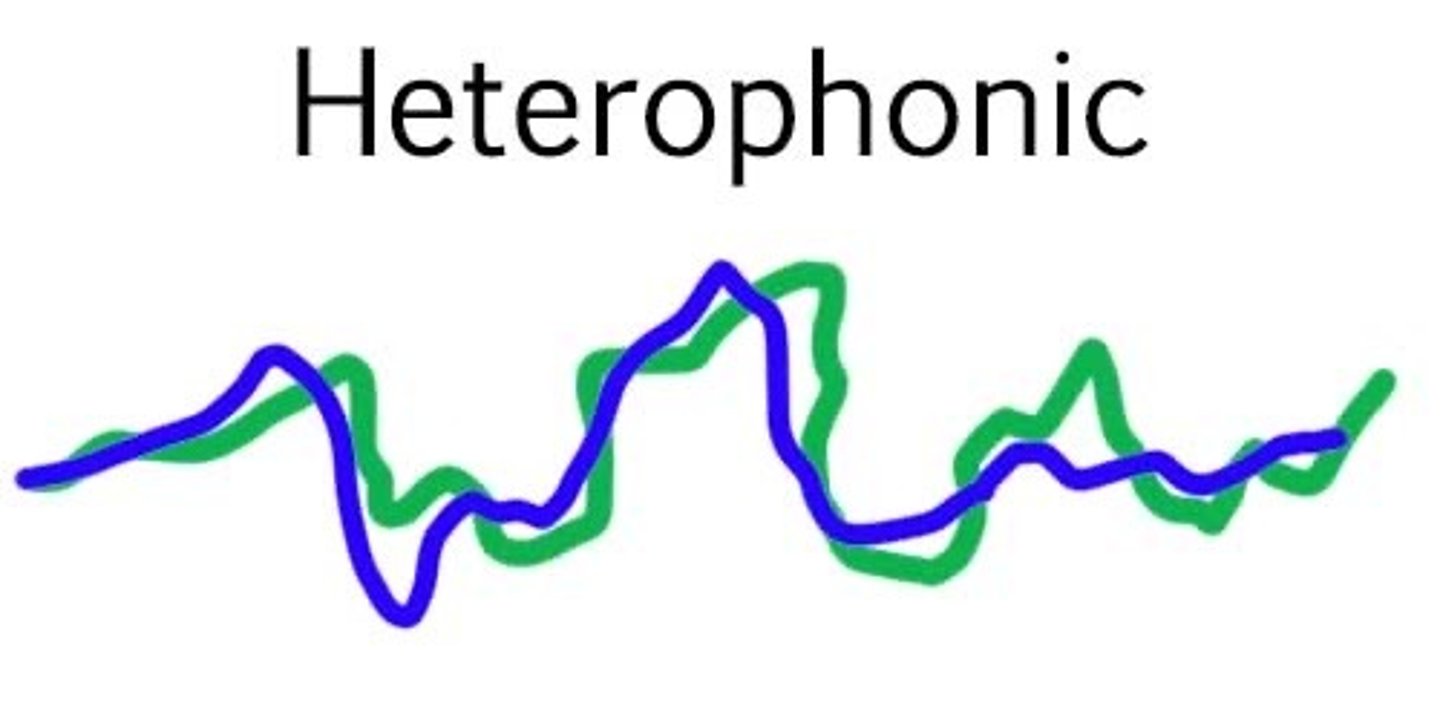
heterophony
music made up of lots of versions of the main tune

Diatonic
Harmony using just notes from the scale
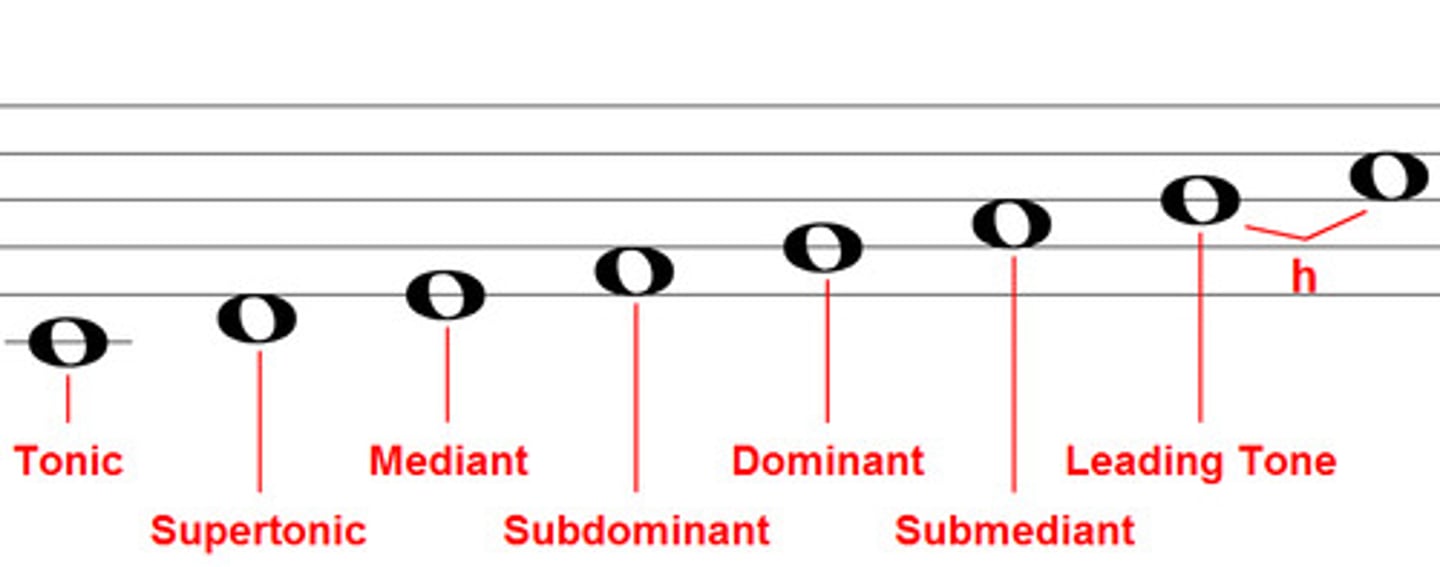
concordant
notes is the chord that all agree with each other
Dissonant
notes that disagree with each other and creating a clash
Atonal
music without any sense of key
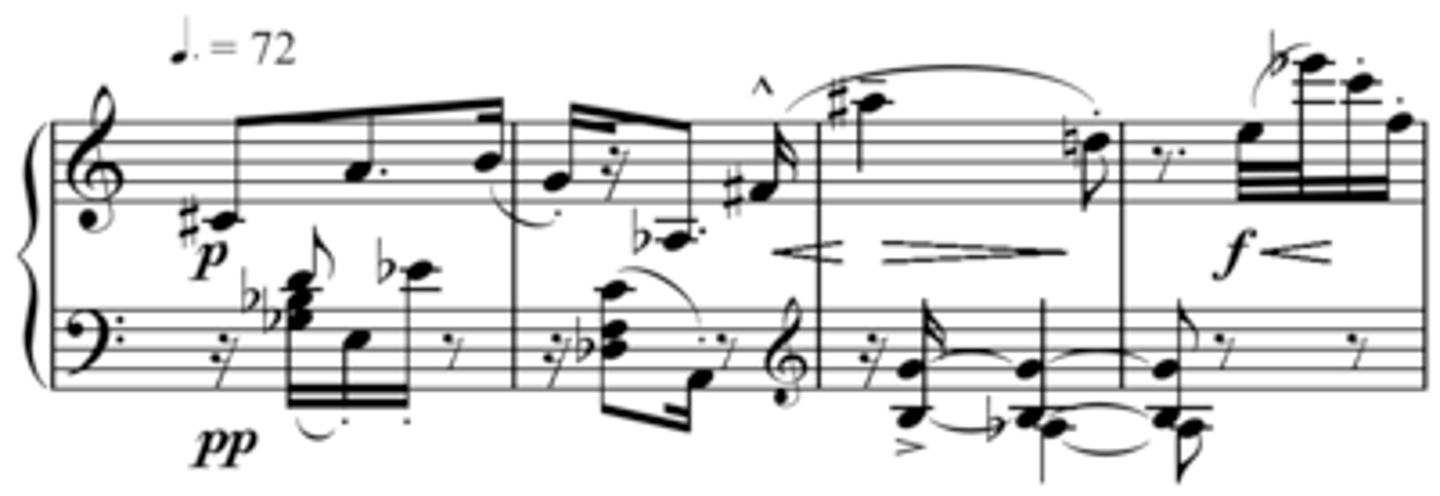

Seventh chord
a four note chord with an added 7th.
- major 7th: major triad with 7th note of scale added
- Dominant 7th: Major triad with a flattened 7th added
- Minor 7th: Minor triad with a flattened 7th
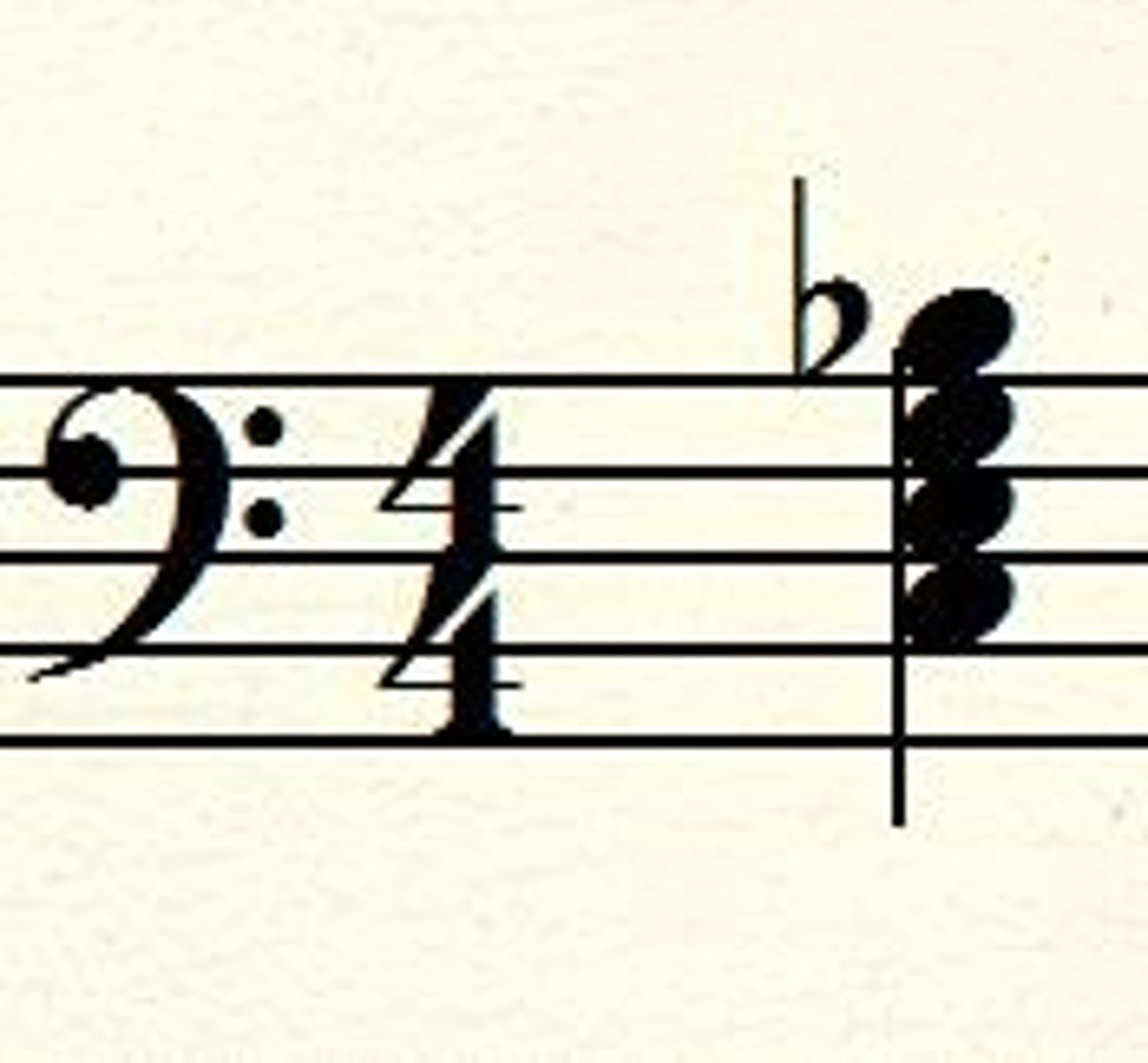
Tonic chord (I)
the home or root chord built on the root note of the key you are in
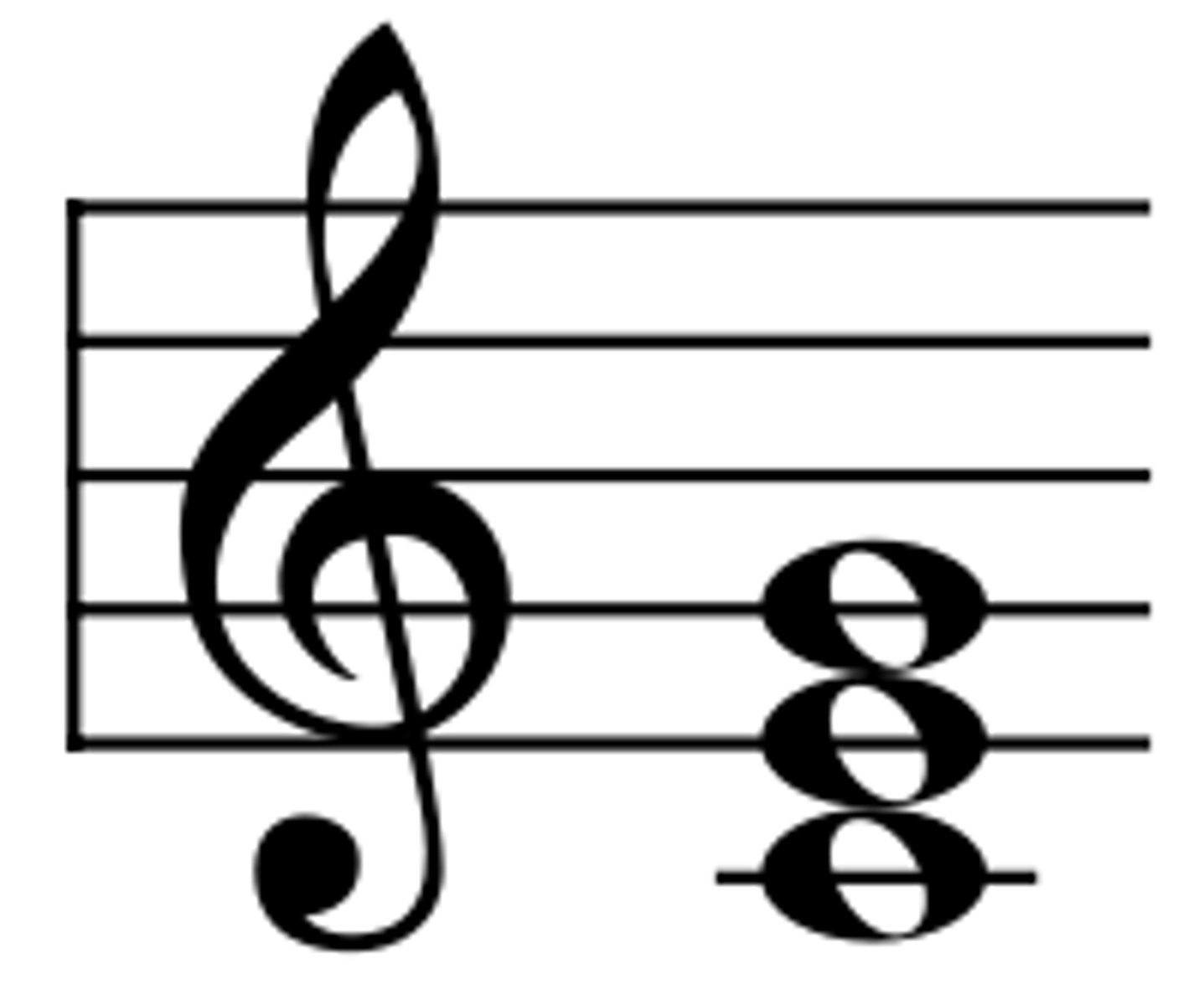

Sub-dominant chord (IV)
The chord built around the fourth note of the key you are in
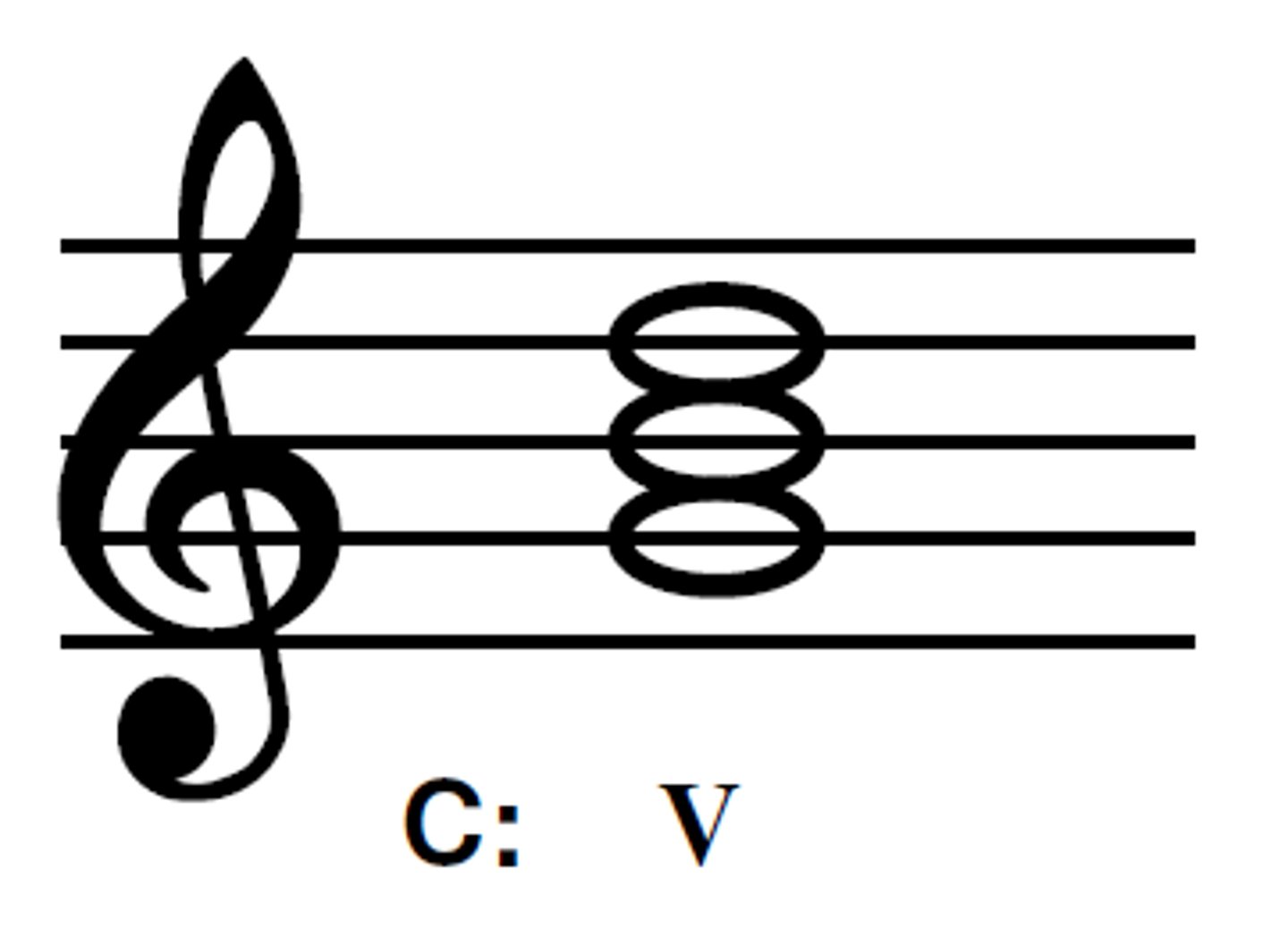
Dominant chord (V)
the chord built around the fifth note of the key you are in
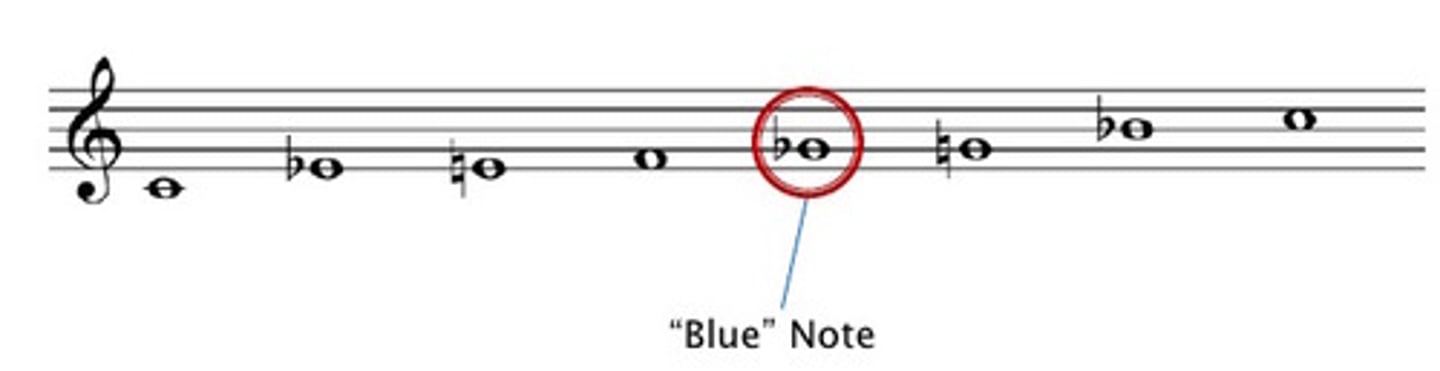
Blue note
A note that has been altered or flattened in blues music, most frequently the 3rd 5th of 7th degree of the scale
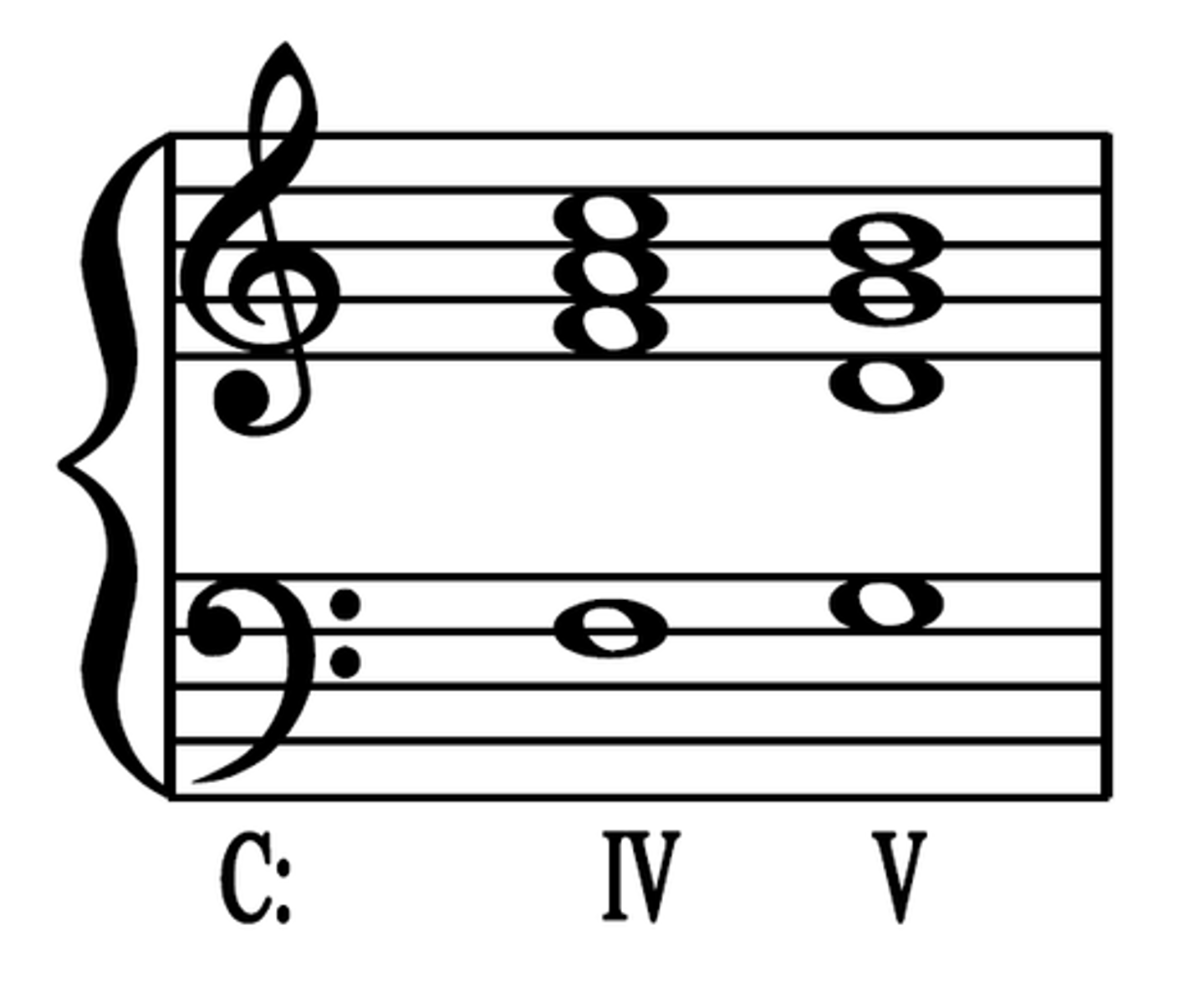
Perfect cadence
V - I (sounds finished)
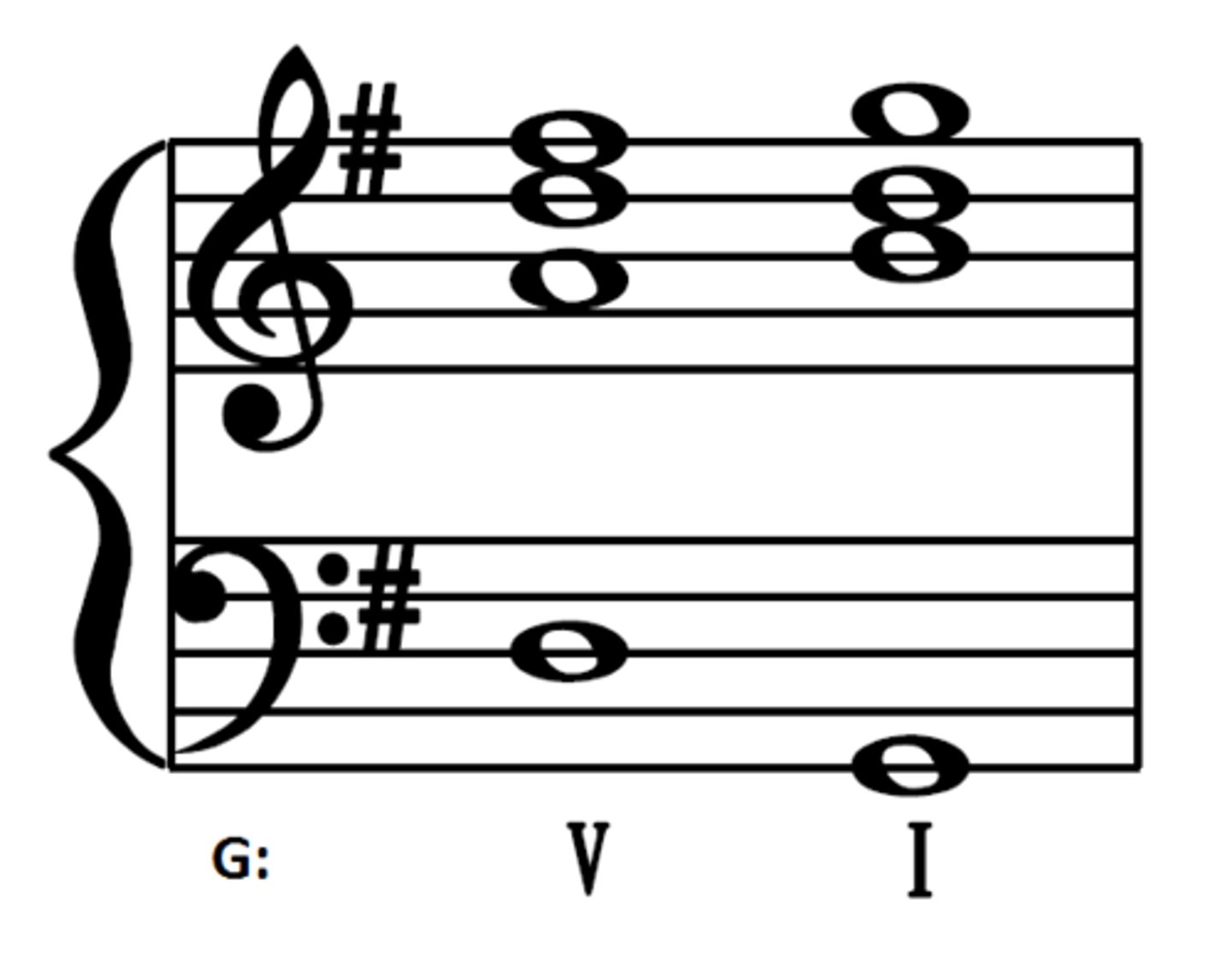
Imperfect cadence
Anything - V (sounds unfinished)
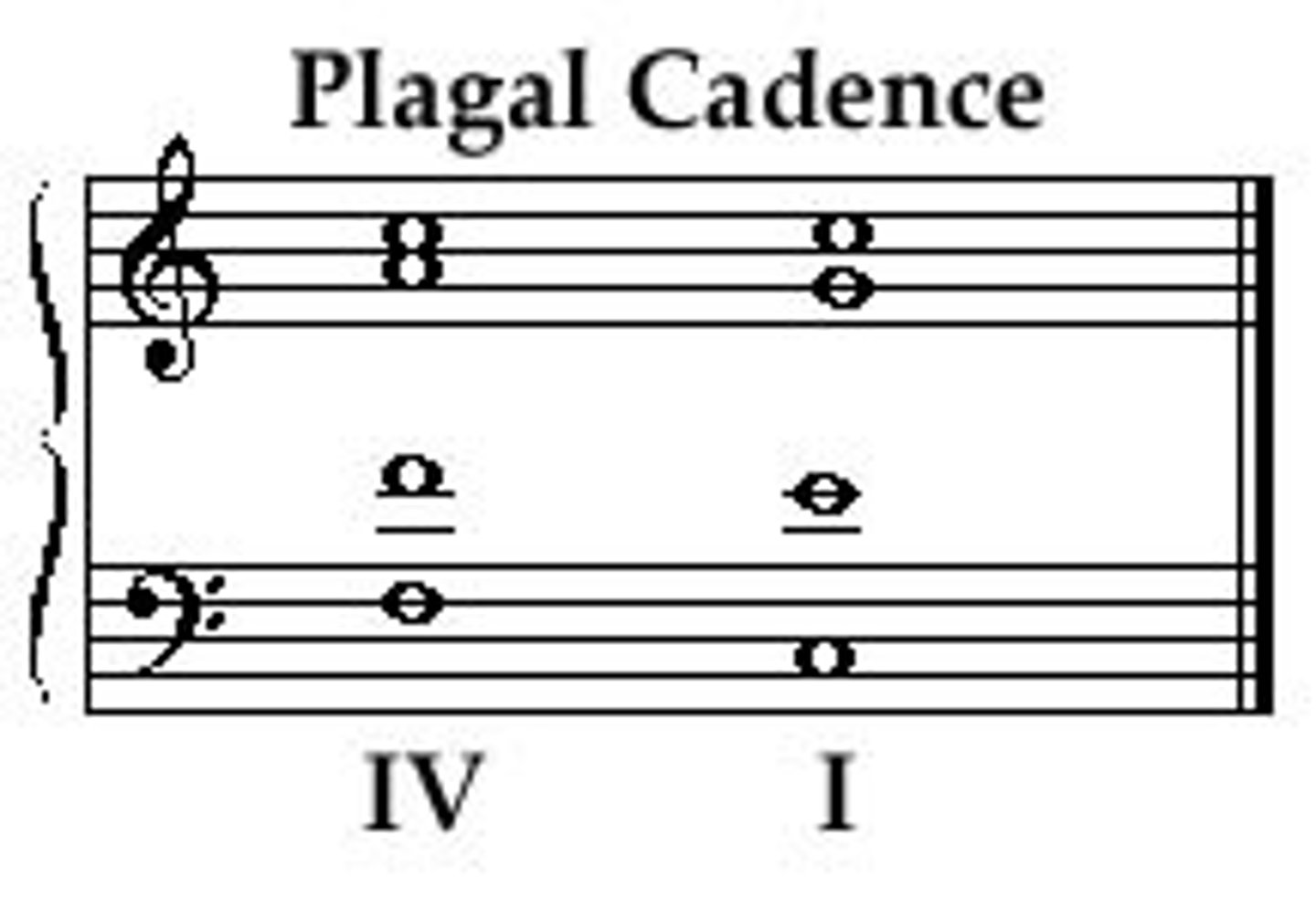
Plagal cadence
IV - I (sounds finished)
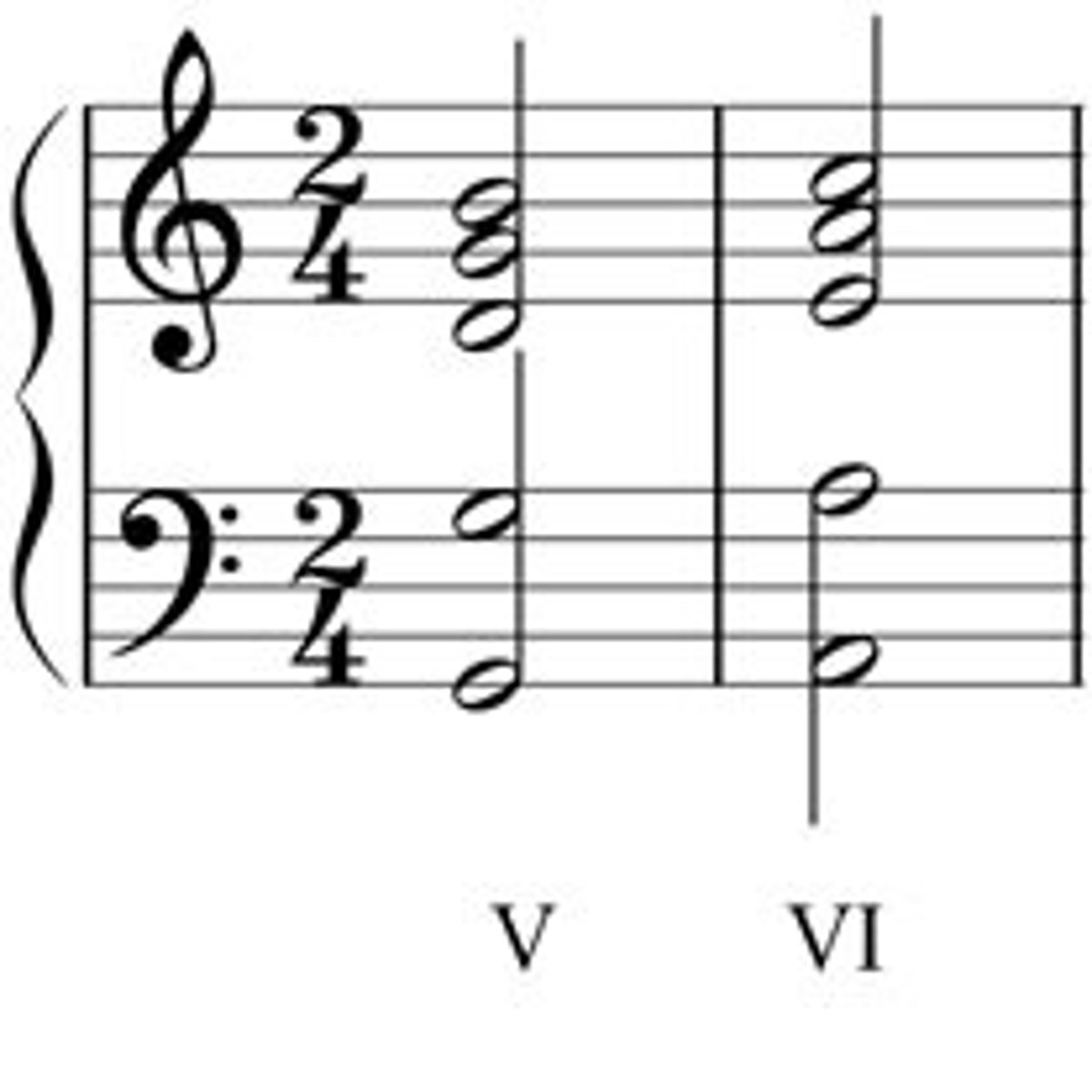
Interrupted cadence
V - VI (sounds surprising)
Arpeggio / broken chords
Playing the notes of a chord separately
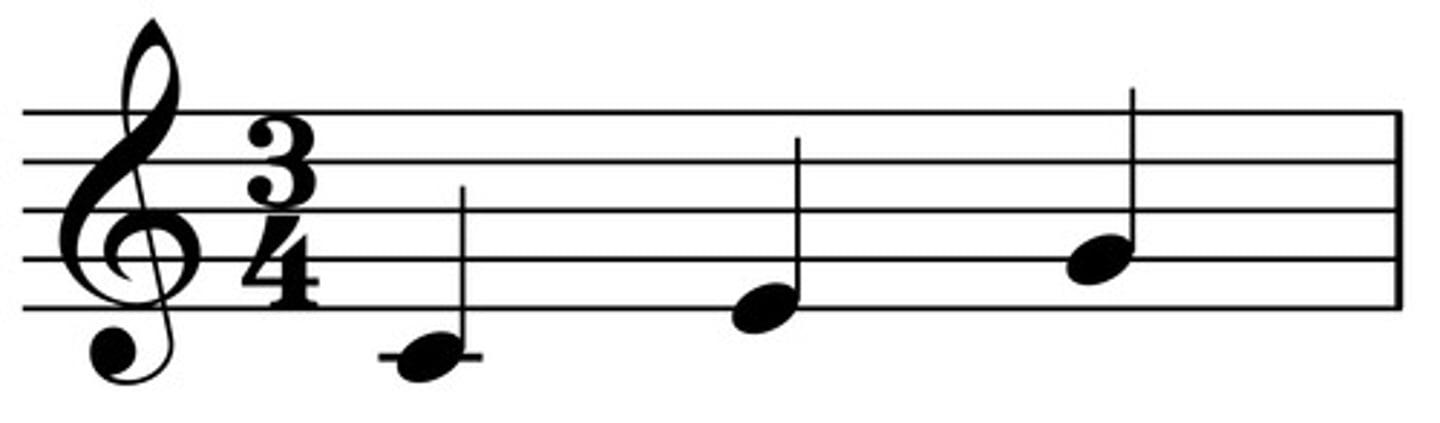

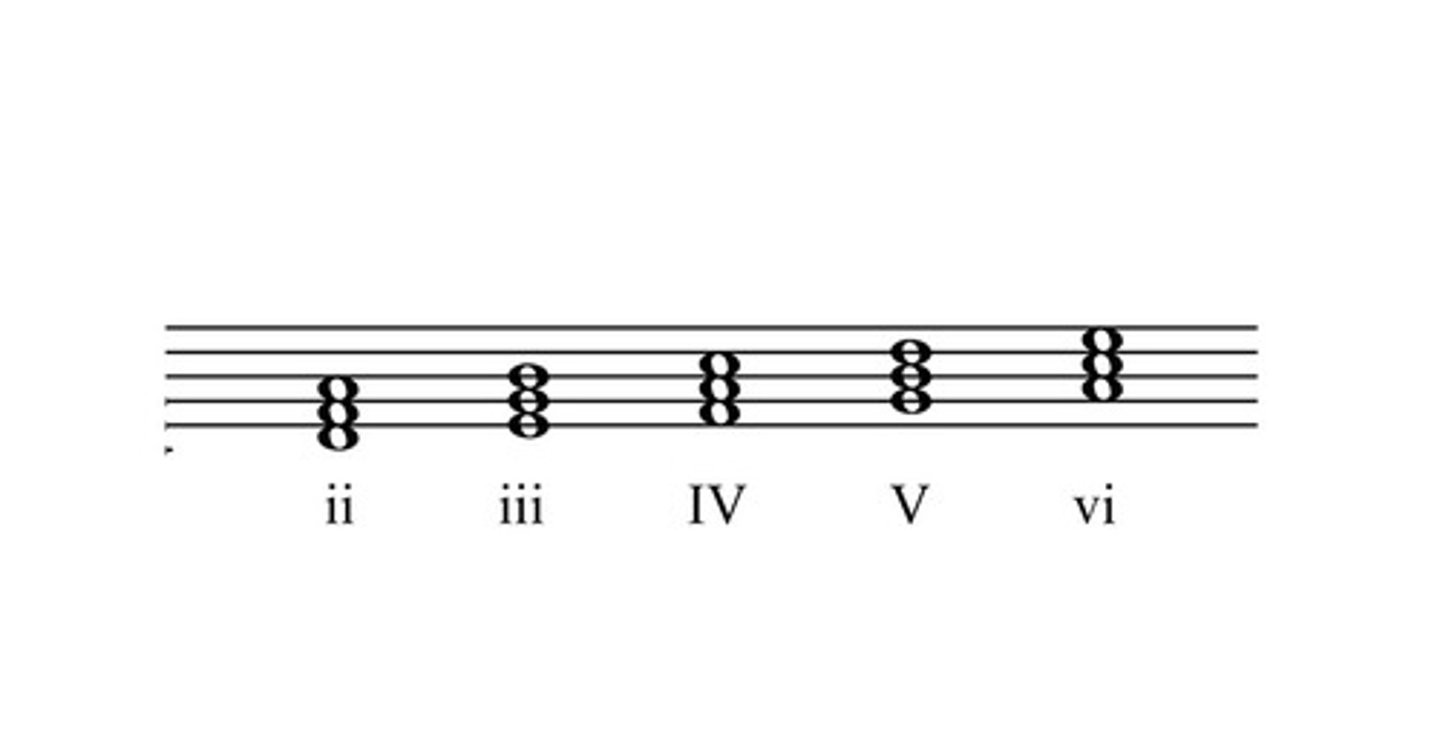
Primary chords
I, IV, V
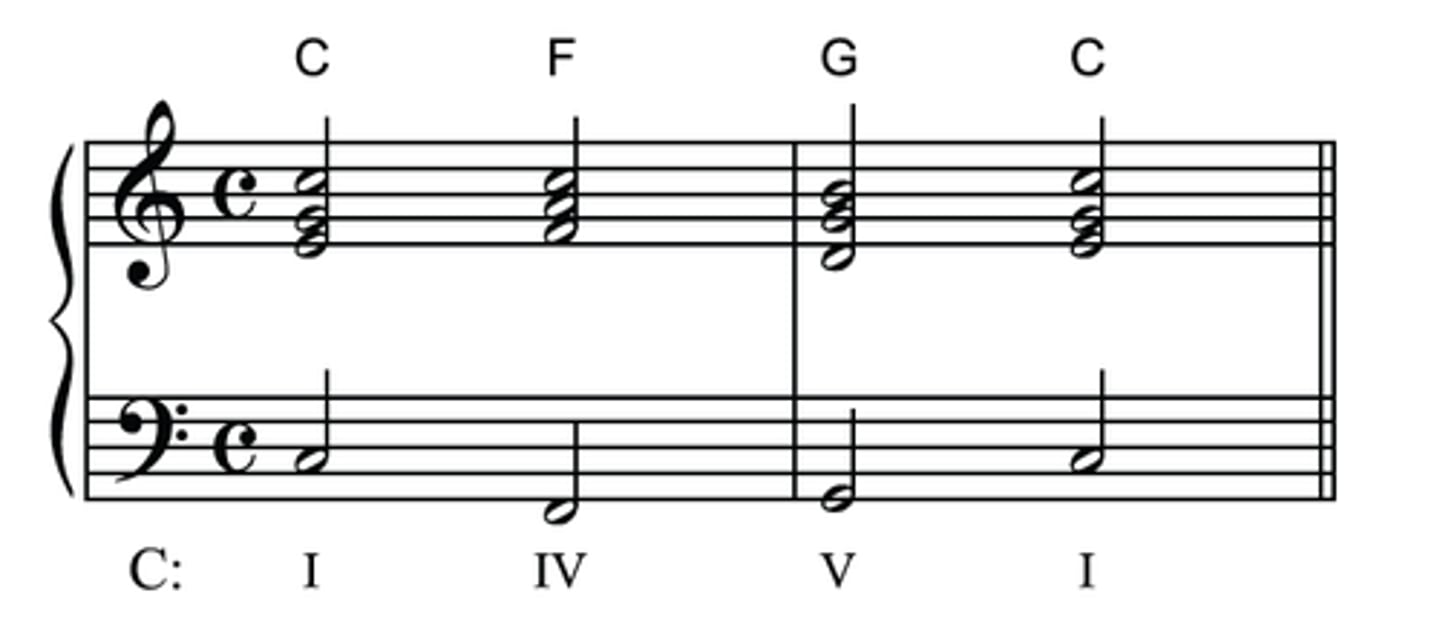
Secondary chords
II, III, VI
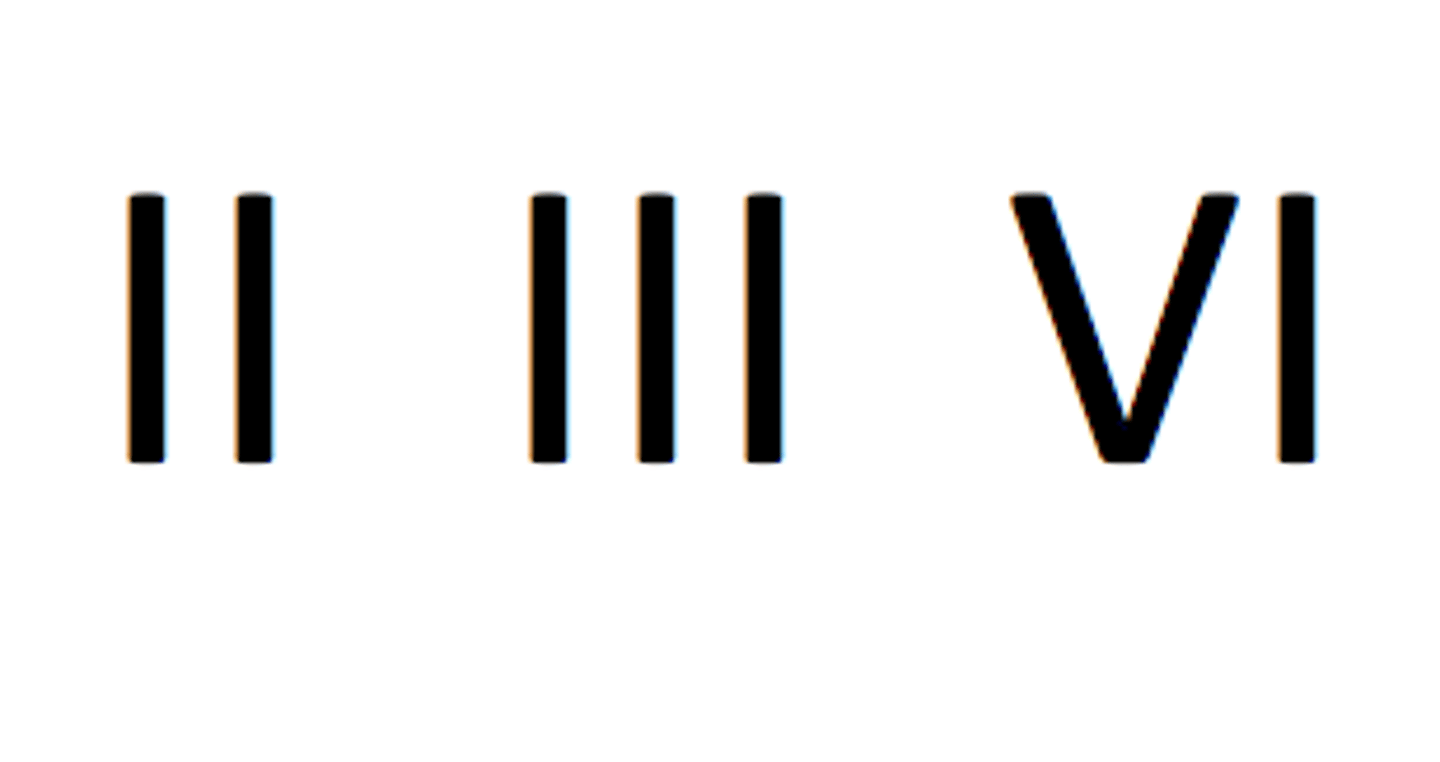
Harmonic progression
the sequence of chords in a piece
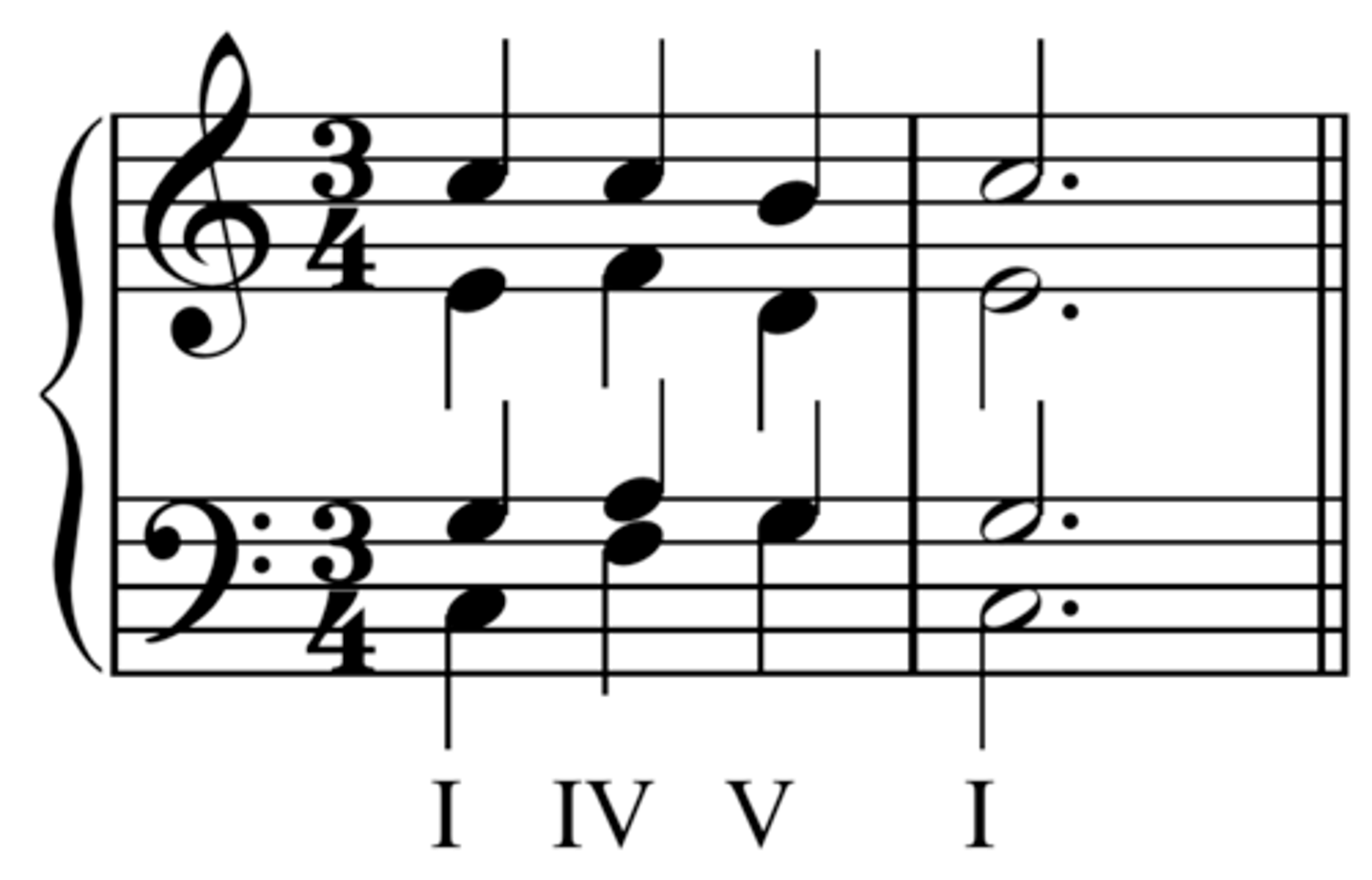

harmonic rhythm
The speed at which the chords change
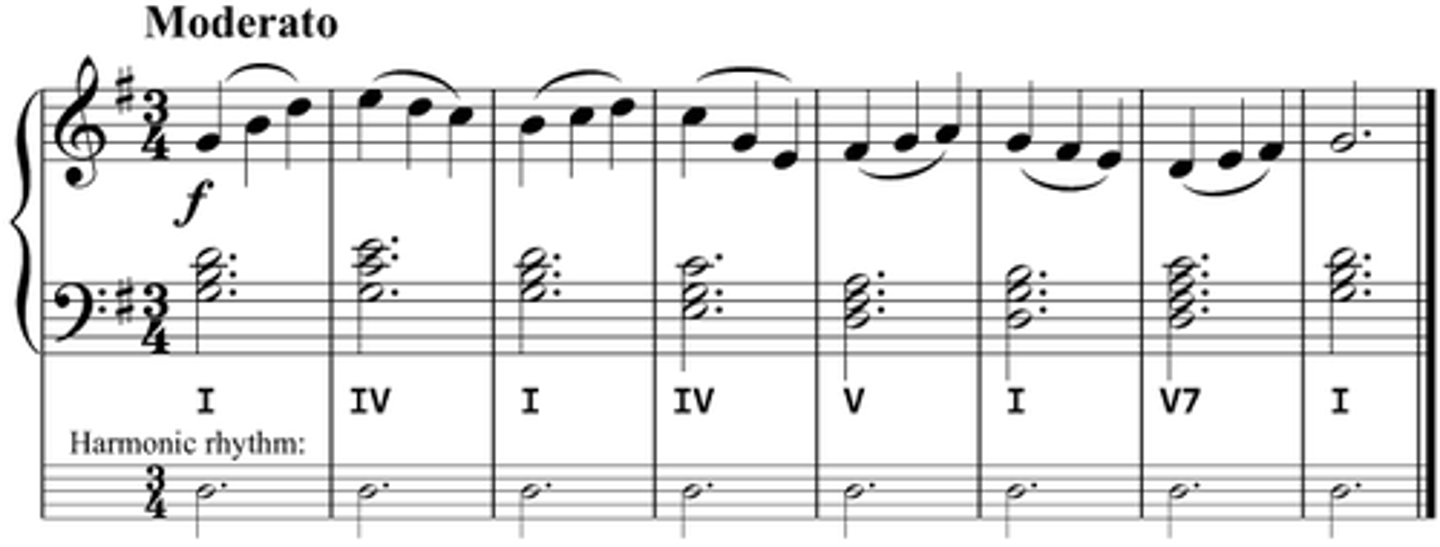

Modulation
moving from one key to another
Pedal note
note held as the harmony changes (either a tonic or dominant pedal)
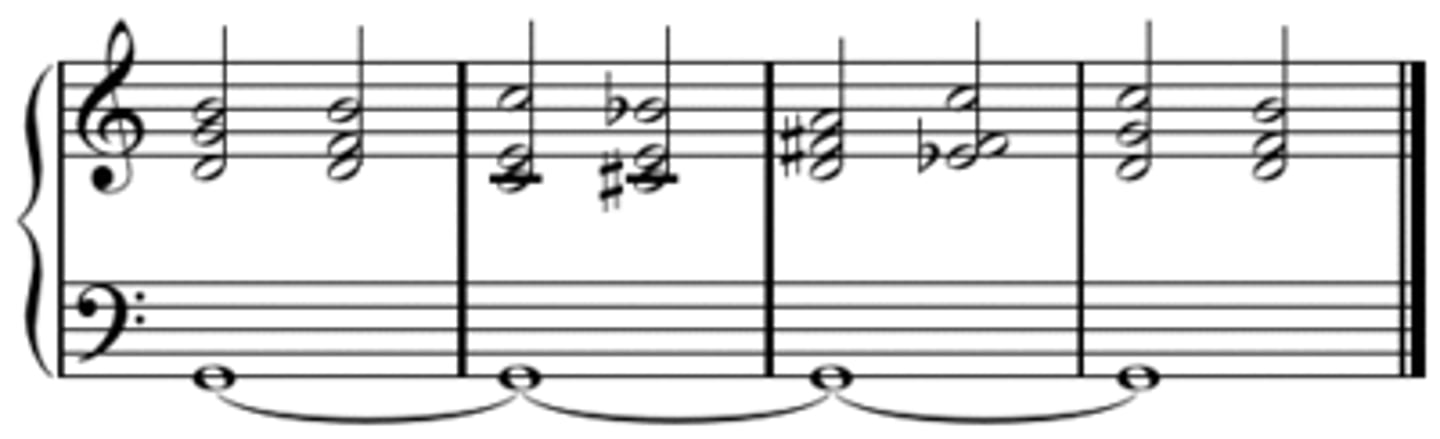

Drone
Low help note

Inverted pedal
when the pedal note is higher than the main tune

Baroque period
1650 - 1750

Baroque composers
Bach, Handel, Vivaldi, Purcell

Baroque orchestra
Mainly strings, small amount of woodwin, very basic brass (no valves), percussion consists of 1 or 2 timpani, harpsichord
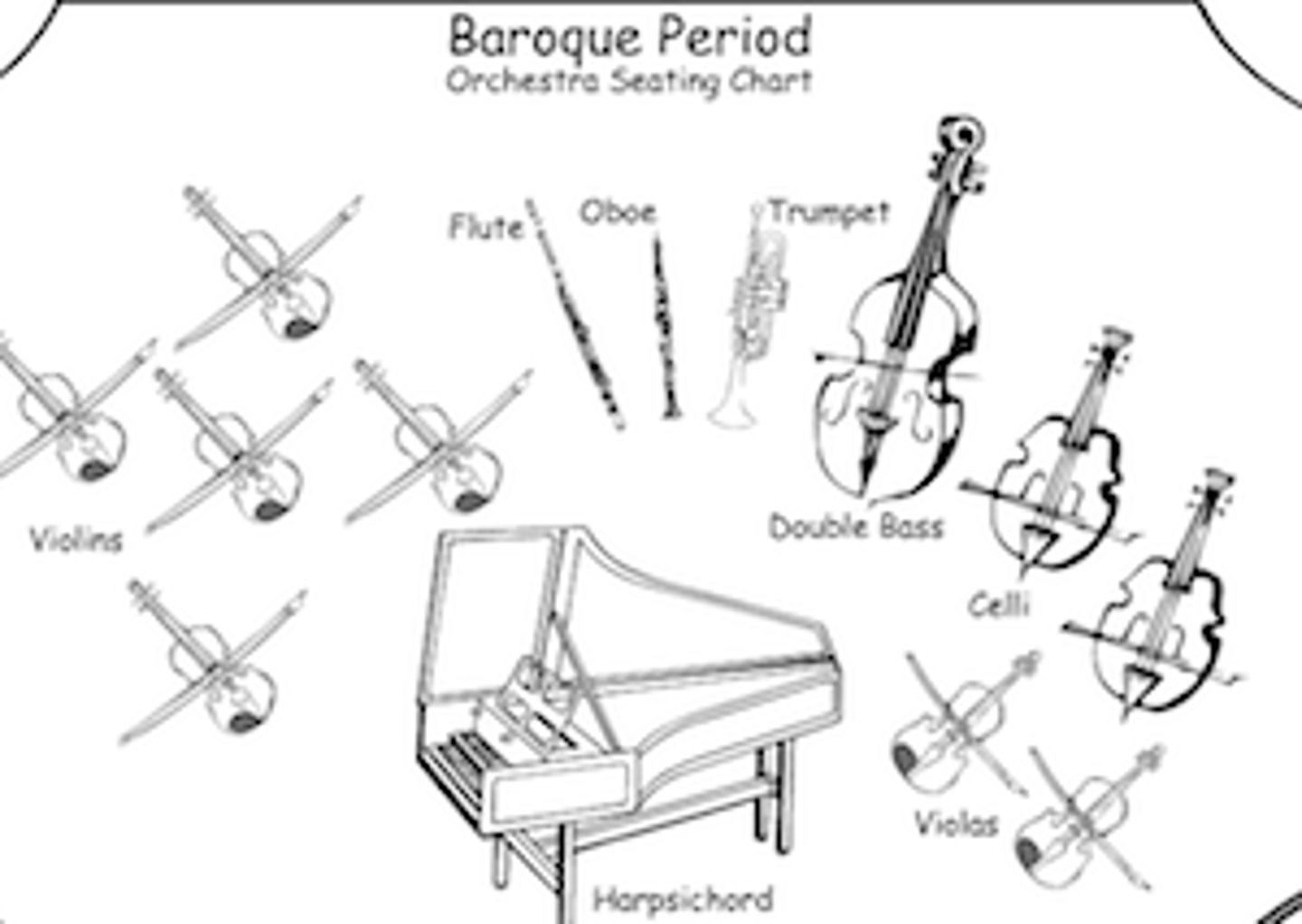
Baroque Prominent structures/forms
Ritornello Form, Sonata, Concerto Grosso, Canon and Fugue, Opera, Oratorio

Baroque features
Use of harpsichord, Terraced dynamics, predominantly strings in the orchestra, lots of ornamentation, basso continuo, polyphonic texture,contrasts in dynamics, dovetailed phraising

The classical period
1750 - 1820

classical composers
Mozart, Haydn, Beethoven (bridge composer)

Classical prominent structures/forms
Sonata form, concerto, symphony, minuet and trio, opera, oratorio
Classical key features
mainly homophonic textures, light clear texture, major/minor tonality ( mainly diatonic ), use of alberti bass, more varied dynamics including crescendos and diminuendos, clear cut phrases of 4 or 8 bars, clear cadence points ( perfect and imperfect ), predominantly tonic / dominant harmony, the emotion of the piece is carefully controlled

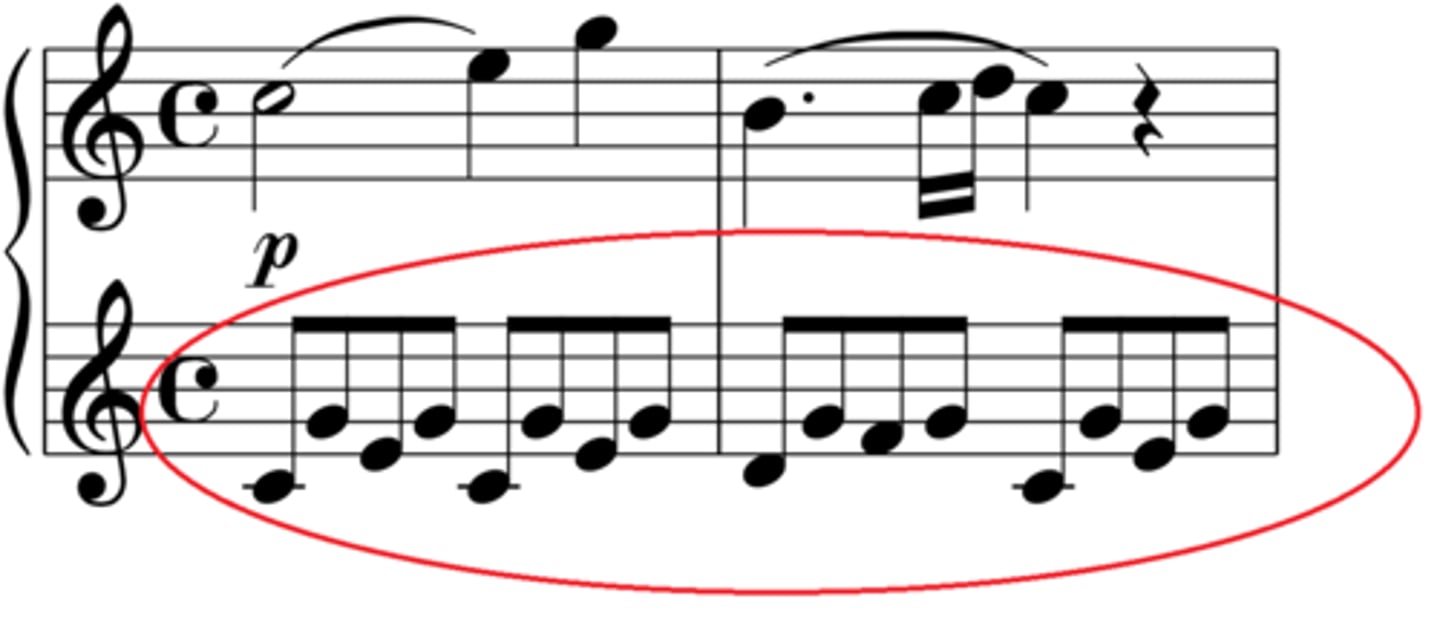
Alberti bass
Broken chord or arpeggiated accompaniment, where the notes of the chord are presented in the order lowest, highest, middle, highest and then repeated. pattern helps to create a smooth, sustained, flowing sound

The romantic period
1820 - 1900
Romantic composers
Tchaikovsky, Brahms, Chopin, Liszt

Romantic prominent structure/forms
opera, symphonic poem, theme and variation, lieder, programme music, piano concerto

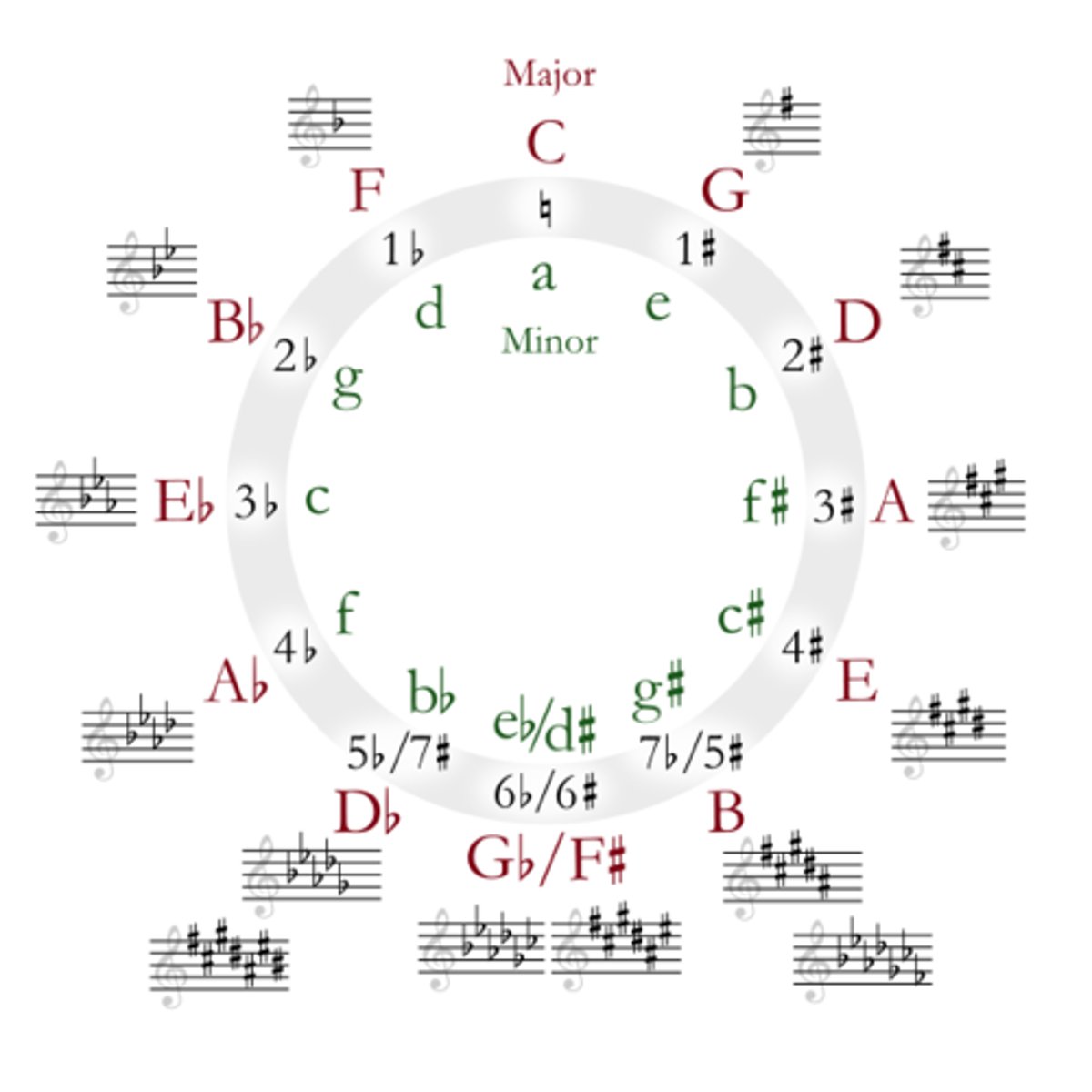
circle of fifths
keys or tonalities ordered by ascending (for sharp keys) or descending (for flat keys) intervals of a fifth
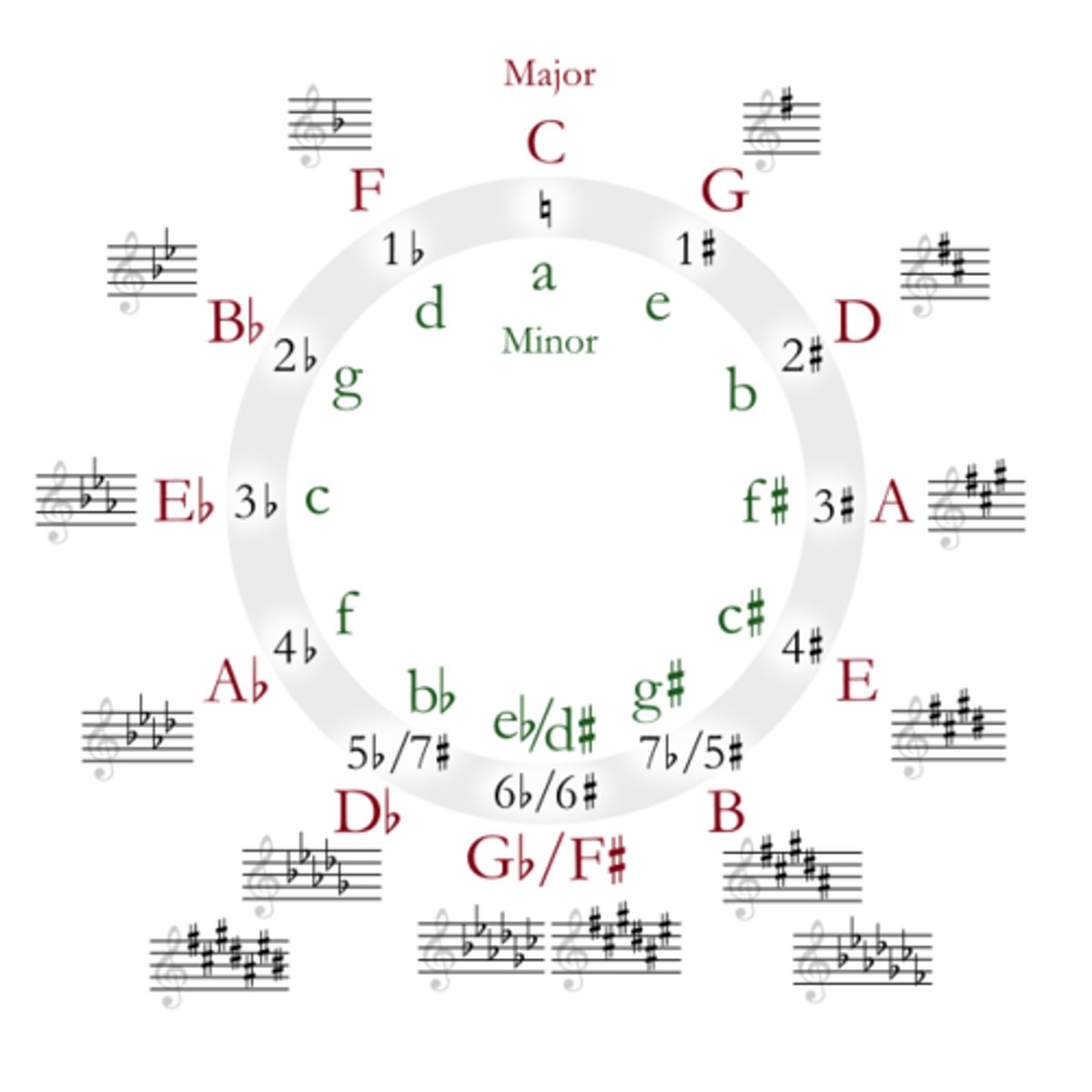
Romantic key features
huge orchestra using a huge range of percussion instruments as well as auxiliary instruments, dramatic contrasts between moods and the music, unusual modulations to keys you wouldn't necessarily expect though still using major and minor keys, a wider use of chromatic notes to add warmth and expression to the music, irregular phrase length, use of rubato
