Anat and Phys
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
Earn XP
Last updated 10:02 PM on 3/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
Define tissue
Groups of cells that are similar in structure and perform a common or related function
2
New cards
4 basic types of tissue
epithelial, muscle, nervous, and connective
3
New cards
Main function of epithelial tissue
Strong regeneration ability and will replace lost cells. These cells are inverted, but avascular, so nutrients are delivered through the basement membrane.
4
New cards
What are the two surfaces of epithelial tissue?
Apical and basal membranes
5
New cards
Define apical membrane
Upper area exposed to the environment or the cavity lining of internal organs. Surface may be smooth but usually microvilli are present.
6
New cards
Define basal membrane
Bottom surface. Connected to the basement membrane.
7
New cards
What is the basement membrane
Gives support and structure to epithelial cells. Made up of reticular and basal lamina. Acts as nutrients for epithelial cells since they are avascular.
8
New cards
Define reticular lamina
CT network of collagen proteins that support epithelium cells.
9
New cards
Define basal lamina
Non cellular adhesive sheet of glycoproteins secreted by the epithelium cells that serves as a selective filter and support structure.
10
New cards
Where are simple cells found
A single layer of single epithelial cells-inside the body
11
New cards
Where are stratified cells found
Multiple layers of epithelial cells-outside the body
12
New cards
Where are squamous cells found
Lungs, blood vessels, and skin
13
New cards
Where are cuboidal cells found
Kidneys/glands
14
New cards
Where are columnar cells found
Intestines
15
New cards
Name the types of epithelial cells
Simple squamous, simple columnar, simple cuboidal, pseudostratified columnar, stratified squamous-keratinized, stratified squamous- non-keratinized.
16
New cards
Define simple squamous
Relatively flat cells that line surfaces, may be further broken down into; endothelium, slick friction - reducing cells that line blood and lymph vessels. Mesothelium, found on serous membranes that line organs and body cavities
17
New cards
Define simple columnar
Line digestive tract from stomach through rectum. They function in absorption and secretion, two modifications, dense microvilli (brush border, increases surface area for absorption)
18
New cards
Define simple cuboidal
These cells function in absorption and secretion. They are rare in the body, forming walls of smallest ducts and many kidney tubules.
19
New cards
Define pseudostratified columnar
Ciliated version containing goblet cells line the respiratory tract. They function in mucous secretion to help trap pathogens and excretion.
20
New cards
Define stratified squamous keratinized
Thick layer of cells used for protection. Surface cells are constantly being replaced. Found on the external parts of skin and extend into every body opening. External skin is 4-5 of dead, keratinized skin cells.
21
New cards
Define stratified squamous non-keratinized
Internal skin surface is alive, wet/slick, and acts as a mucosal membrane.
22
New cards
What are the two types of glands and their main difference
Exocrine and endocrine. Their ducts are their main difference.
23
New cards
Define exocrine gland
Secrete their product onto body surfaces or into body cavities. Excrete via epithelium lined ducts. Some exocrine glands are; mucous, sweat, salivary, liver, pancreas.
24
New cards
Define endocrine gland
Ductless glands. Produce hormones. Excreted by exocytosis into intercellular space from there hormones travel via lymph or blood to target tissue. Pituitary
25
New cards
4 main types of connective tissue
Connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, and blood
26
New cards
Main functions of connective tissue
Binding and support, protection, insulation, and transportation of substances
27
New cards
3 main components of connective tissue
Ground substance, cells, and fibers
28
New cards
Why are glycosaminoglycans (GAG) so important?
GAG intertwines and traps water. This helps produce synovial fluid, but it cushions and lubricates joints. Ex: hyaluronic acid and glycosamine
29
New cards
3 types of fibers in connective tissue
Elastic, collagen, and reticular
30
New cards
Define elastic fiber
Certain connective tissues secrete Elastin, this is a rubber-like protein found where elasticity is needed, these will return to their original shape after being stretched or compressed (skin, lungs, blood vessel walls).
31
New cards
Define collagen fiber
Secretes a fibrous tissue called collagen, these proteins bind together to create a very dense high tensile strength matrix, Long white fibers that are very flexible and provide great tensile strength and resist stretching.
32
New cards
Define reticular fiber
Short and fine collagen fibers that are arranged in branching patterns, form a delicate network around vessels to offer support and within organs such as the liver, spleen and lymph nodes where they provide structural support
33
New cards
Mature cells of connective tissue proper?
Fibrocyte
34
New cards
Productive cells of connective tissue proper?
Fibroblast
35
New cards
3 categories of loose connective tissue
Areolar, reticular, and adipose
36
New cards
Define areolar
Honeycomb or web-like network of loose fibers that contains ground substance, a thick viscous fluid that surrounds cells. It is found in-between muscle fibers.
37
New cards
Define adipose
Chicken wire appearance. Cells filled with oil droplets (adipocytes). Takes up and releases fat. Brown adipose tissue contains many mitochondria. Adipose tissue contains a large number of capillaries for rapid storage and mobilization of lipids. Found in fat tissue
38
New cards
Define reticular-loose connective tissue
Forms a stroma or mesh-like supportive structure for many free blood cells. Found around blood cells. Ex: lymph nodes, spleen, liver
39
New cards
Most common type of loose connective tissue?
Areolar
40
New cards
Define dense regular-loose connective tissue
All run the same direction. Strength is in the direction that they run. Ex: tendons or ligaments. Tendons- strong and bendable connections.mLigaments-some elastic fiber
41
New cards
Define dense irregular-loose connective tissue
Found in the scalar of the eyes and fibrous joint capsules. Thick, irregularly arranged collagen fibers. Found where tension from all directions may occur- multiple directions.
42
New cards
What is unique to cartilage?
Cartilage is avascular, aneural and 80% water.
43
New cards
3 types of cartilage
Hyaline, elastic, and fibrous
44
New cards
Define hyaline cartilage
Covers the ends of long bones. Provides a springy pad that absorbs compression at the end of joints – not radial dense will not show up on ultrasound. Lots of collagen fibers.
45
New cards
Define elastic cartilage
Forms the skeleton of the ear and epiglottis. Just like hyaline, but contains more elastic fibers.
46
New cards
Define fibrous cartilage
Structural intermediate between hyaline cartilage and dense regular CT. Found where support and ability to withstand heavy pressure is needed- Intervertebral disc and menisci. If the hyaline cartilage is damaged in an adult, fibrous cartilage will act as a repair.
47
New cards
What type of cartilage is most common?
Hyaline
48
New cards
Mature cells of cartilage?
Chondrocyte
49
New cards
Productive cells of cartilage?
Chondroblast
50
New cards
Definition of a joint or articulation
A form of connection between bones. They provide stability to the skeletal system as well as allowing for specialized movement.
51
New cards
Inflammation of the joints is defined as?
Arthritis
52
New cards
6 types of joints?
Ball and socket, ellipsoid, plane/gliding, saddle, hinge, and pivot.
53
New cards
Function of synovial fluid?
Mainly lubricate the joint. But also, supplies nutrients to the hyaline cartilage, removes waste products. Synoviocytes are the main source of glycosaminoglycans in the synovial fluid
54
New cards
What are the cells of the bone?
Osteon, osteoclast, osteoblast, and osteocyte
55
New cards
Define osteon
Closely packed structural unit of bone that contains; lamellae, collagen fibers, VAN
56
New cards
Define osteoclast
Bone destroying, hydrochloric acid liberates the calcium
57
New cards
Define osteoblast
The primary bone cell that produce organic bone matrix of collagen fibers. Young bone cell
58
New cards
Define osteocyte
Mature bone cell
59
New cards
Define osteoid
Uncalcified bone. What osteoblasts lay down prior to calcification of the bone.
60
New cards
Functions of the bone
Support, protection, movement, mineral storage, and blood cell formation.
61
New cards
Label the osteon
Haversion canal, Volksman canal, periosteum, circumferential lamellae, blood vessels, spongy bones, osteon
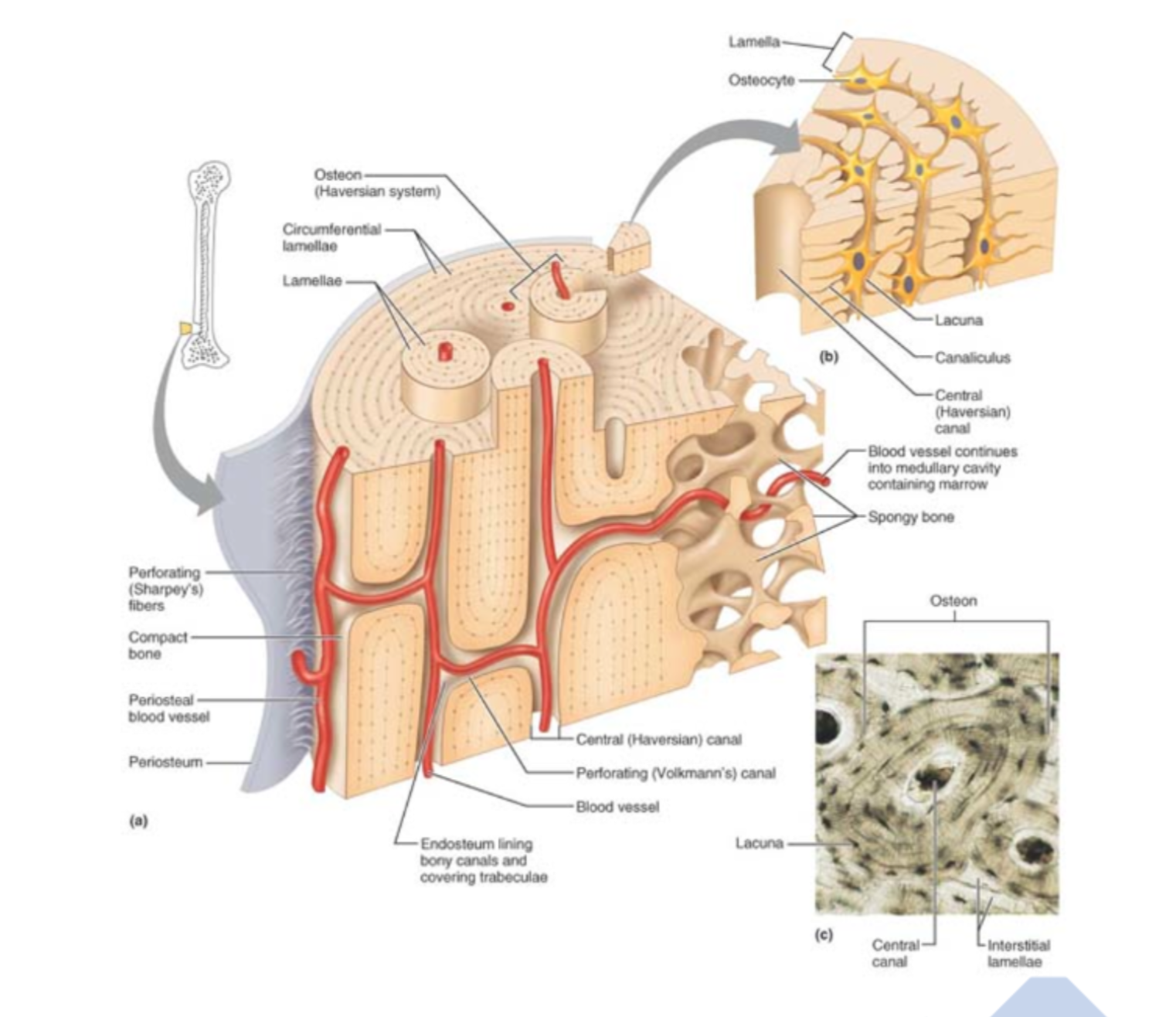
62
New cards
Define compact bone
The dense outer layer that looks smooth to the eye
63
New cards
Define spongy bone
Trabeculae honeycomb like structure found inside the long bone this is filled with red or yellow bone marrow
64
New cards
Define periosteum
Heavily supplied with nerve, lymph and blood. Enter diaphysis through nutrient foramen. Perforating (sharpey’s) fibers are collagen tuffs that secures periosteum to bone. Double layer membrane covering the bone
Outer layer is dense irregular CT
Inner osteogenic next to the bone contains bone forming (Osteoblasts), and bone destroying osteoclasts.
Outer layer is dense irregular CT
Inner osteogenic next to the bone contains bone forming (Osteoblasts), and bone destroying osteoclasts.
65
New cards
Define endosteum
Delicate CT membrane that covers the trabeculae of spongy bone and lines the compact bone canals. Contains both osteoblasts and osteoclasts
66
New cards
How are bones classified?
By location (axial or appendicular) and shape.
67
New cards
Define axial skeleton
Skull, ribs, vertebral column
68
New cards
Define appendicular skeleton
Upper and lower limbs, pelvis, scapula
69
New cards
4 shapes of bone
Long, short, flat, irregular
70
New cards
Define long bone
longer than they are wide, shaft (diaphysis) plus two ends (epiphysis), named for their elongated shape not oval size
Ex: femur, humerus
Ex: femur, humerus
71
New cards
Define short bone
Cube type bones. Ex: sesamoid, knees, hock
72
New cards
Define flat bone
Thin, flattened, small curve. Ex: Scapula, sternum, ribs
73
New cards
Define irregular bone
All other types. Ex: pelvis, hips, vertebrae
74
New cards
Label part of the bone
diaphysis, metaphysis, epiphysis
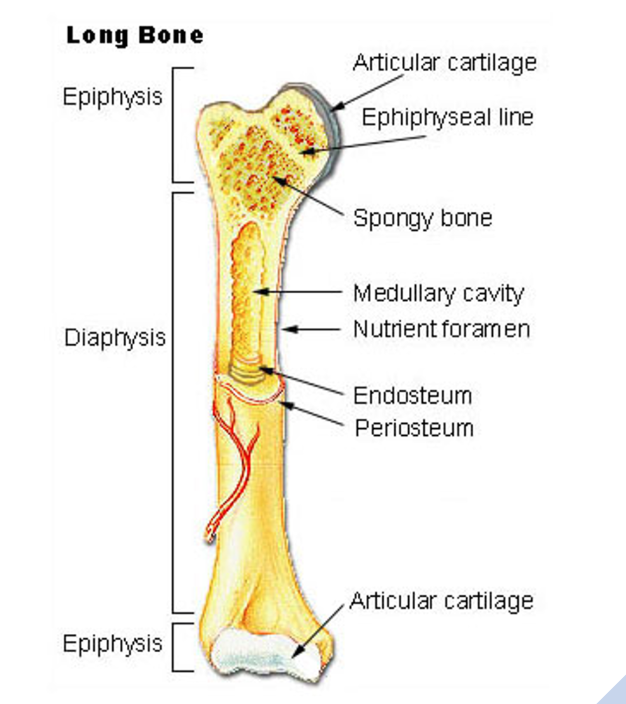
75
New cards
Define diaphysis
Shaft of bone, thick compact that surrounds a central medullary cavity, in adults the medullary cavity contains fat and is called the yellow bone marrow cavity
76
New cards
Define metaphysis
Portion of the bone between the epiphysis and diaphysis, in young growing animals it contains the epiphyseal plate (growth plate)
77
New cards
Define epiphysis
Bone ends, these tend to expand, exterior surface = compact bone, interior surface = spongy bone. Joint surfaces covered with hyaline cartilage, between diaphysis and epiphysis is the epiphyseal line (remnant of epiphyseal plate).
78
New cards
Define growth plate
The growth plate also known as the epiphyseal plate, is a disc of hyaline cartilage that grows during youth to lengthen the bone.
79
New cards
What hormones affect bone growth?
Growth hormone (GH) - anterior pituitary (most important stimulus of epiphyseal growth), thyroid hormone (modulates GH), sex hormones (estrogen and testosterone) 1st increase growth rate, then induce epiphyseal plate closure.
80
New cards
How do hormones affect bone growth?
If messed with, such as spay/neuter before puberty, the animal will grow taller than expected due to a lack of sex hormones to induce growth plate closure.
81
New cards
How are fractures classified?
Position of bone ends after fracture: displaced (not lined up) or non-displaced (lined up)
Completeness: complete or incomplete
Orientation relative to long axis: linear, transverse, or oblique Skin penetration: open or closed
Completeness: complete or incomplete
Orientation relative to long axis: linear, transverse, or oblique Skin penetration: open or closed
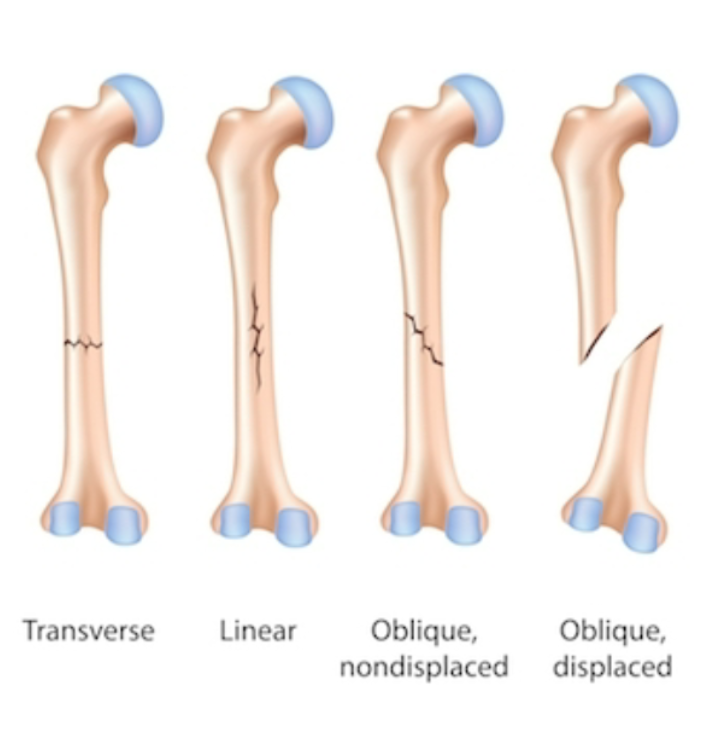
82
New cards
8 common fracture types
\
Comminuted- more than three pieces
Compression- the bone is crushed from impact, common in vertebrae
Spiral- occurs when excessive torque is placed on the bone Epiphysis- fractures involving the epiphyseal plate I-V. SALTER Harris
Depressed- depression of piece of skull from blunt force
Greenstick or Incomplete- happens in young soft bone in which the bone bends but does not completely break (calf and cattle guard)
Impaction- occurs when one piece of bone is forced down the center of the opposing piece (telescope)
Avulsion- piece of bone that is connected to a tendon/ligament which is torn off the main bone
Comminuted- more than three pieces
Compression- the bone is crushed from impact, common in vertebrae
Spiral- occurs when excessive torque is placed on the bone Epiphysis- fractures involving the epiphyseal plate I-V. SALTER Harris
Depressed- depression of piece of skull from blunt force
Greenstick or Incomplete- happens in young soft bone in which the bone bends but does not completely break (calf and cattle guard)
Impaction- occurs when one piece of bone is forced down the center of the opposing piece (telescope)
Avulsion- piece of bone that is connected to a tendon/ligament which is torn off the main bone
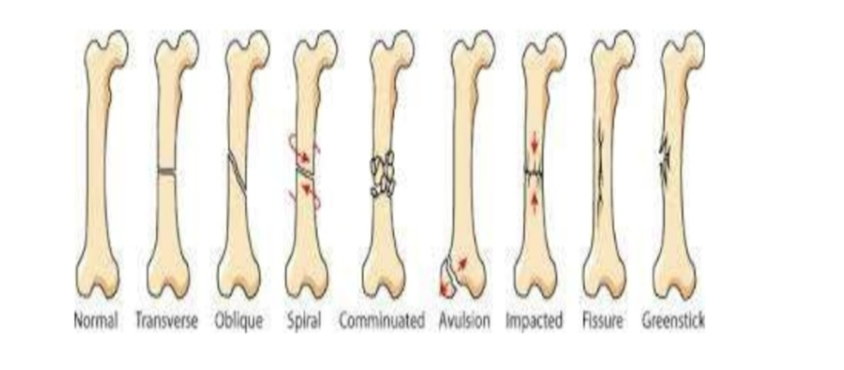
83
New cards
Treatment of fractures
Open Reduction- surgically open the fracture to visualize the repair (can be done with intramedullary pin, plates, screws, nails, wire)
Closed Reduction- this is done without opening the fracture site (can be done with a splint, cast, cross pins)
Closed Reduction- this is done without opening the fracture site (can be done with a splint, cast, cross pins)
84
New cards
Steps of fracture repair (treated or not)
Hematoma Formation (first 24 hours, very vascular)
Fibrocartilaginous callus formation (7 days)
Bony callus formation (up to 8 weeks)
Bone remodeling (in response to stress, Wolf's Law, remodels the bone as close to how it was before, up to 6 months)
Fibrocartilaginous callus formation (7 days)
Bony callus formation (up to 8 weeks)
Bone remodeling (in response to stress, Wolf's Law, remodels the bone as close to how it was before, up to 6 months)
85
New cards
Define osteomalacia/rickett’s
“Rubber Bones,” lack of calcification of the bones, Ca and/ or Vitamin D deficient
86
New cards
Define osteoporosis
Osteoclast activity out paces Osteoblast activity (breaking down bone quicker than it is laid down), diet related, hormone imbalances, vitamin D deficiency
87
New cards
What are biphosphonates?
Treats osteoporosis by inhibiting osteoclast activity.
Tiludronate disodium - Tildren- not usda approved
Clodronate disodium - Osphos- usda approved for only horses
Tiludronate disodium - Tildren- not usda approved
Clodronate disodium - Osphos- usda approved for only horses
88
New cards
SALTER Harris
For epiphyseal plate fracture
S- slip
A- above
L- beLow
TE- Trough Everything
R- cRushed
S- slip
A- above
L- beLow
TE- Trough Everything
R- cRushed
89
New cards
Hormone control of bone remodeling
Parathyroid hormone made in the parathyroid gland. Calcitonin produced by the parafollicular cells in the thyroid gland.
Decreased blood calcium levels will cause the release of parathyroid hormone which will activate osteoclast activity.
Increased blood calcium levels will turn off parathyroid hormone and release calcitonin which will inhibit bone reabsorption and encourage hydroxyapatite (inorganic portion of bone) deposition.
Decreased blood calcium levels will cause the release of parathyroid hormone which will activate osteoclast activity.
Increased blood calcium levels will turn off parathyroid hormone and release calcitonin which will inhibit bone reabsorption and encourage hydroxyapatite (inorganic portion of bone) deposition.
90
New cards
List ***four*** functions of epithelial tissue and where they occur.
Protection- Skin
Absorption- Gut
Filtration- Kidney
Excretion- Kidney
Absorption- Gut
Filtration- Kidney
Excretion- Kidney
91
New cards
All epithelial tissue comes in three basic shapes: 1.) __*2.) ---- 3.)*__ ________ each of these shapes can be represented as simple, stratified or pseudostratified.
Cuboidal, Squamous, Columnar
92
New cards
The epithelial cells that line the inside of the mouth and the esophagus are __**____**__whereas __**_____**__ make up the cells of the external skin.
stratified squamous non-keratinized and stratified squamous keratinized
93
New cards
__ cells line hollow urinary organs and are unique because they allow bladder to __ from a 6 cell thickness to a __ cell thickness.
Transitional, expand, 3
94
New cards
__**___**__ cells line the respiratory tract. They contain __**___**__ cells which produce mucus.
Pseudostratified columnar, goblet
95
New cards
__**___**__ cells can be found lining the digestive tract and have __**_____**__ which help with absorption.
Simple columnar and cilia/microvilli
96
New cards
Glands, which are lines with epithelial tissue, come in two forms. Mucous glands are examples of __**___**__ glands, which excrete their product via __**__.**__
Exocrine and ducts
97
New cards
The adrenal gland is an example of an ____ gland which secretes its hormone product by __**____**__ into the blood.
Endocrine and exocytosis
98
New cards
The fibrocyte is the mature cell for __**_____**__
Connective tissue proper
99
New cards
Where do chondrocytes get their nutrients from and why?
They get their nutrients from synovial fluid because they are avascular
100
New cards
What is the most common type of cartilage found in the body? What does it look like? Where is it found? If it is damaged, how is it repaired?
Most common: Hyaline
It looks like a smooth, glossy surface.
It is found on the ends of long bones within articular joints with collagen fibers.
If it is damaged, it will turn into fibrocartilage
It looks like a smooth, glossy surface.
It is found on the ends of long bones within articular joints with collagen fibers.
If it is damaged, it will turn into fibrocartilage