Cardiovascular System Overview and Functionality
1/242
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
243 Terms
Superior vena cava
Major vein returning deoxygenated blood to heart.
Right atrium
Receives deoxygenated blood from body.
Tricuspid valve
Valves between right atrium and ventricle.
Right ventricle
Pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs.
Pulmonary semilunar valve
Prevents backflow into right ventricle.
Pulmonary trunk
Carries deoxygenated blood to pulmonary arteries.
Pulmonary arteries
Transport deoxygenated blood to lungs.
Lungs
Site for gas exchange in blood.
Pulmonary veins
Carry oxygenated blood from lungs to heart.
Left atrium
Receives oxygenated blood from pulmonary veins.
Bicuspid valve
Valves between left atrium and ventricle.
Left ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood to body.
Aortic semilunar valve
Prevents backflow into left ventricle.
Aorta
Major artery delivering oxygenated blood to body.
Vasculature
Network for blood transport and exchange.
Arteries
Carry blood away from the heart.
Veins
Bring blood back to the heart.
Capillaries
Tiny vessels for gas and nutrient exchange.
Diffusion
Movement of substances following concentration gradients.
Blood volume
Humans have about 5 liters of blood.
Double pump
Heart structure with two atria and two ventricles.
Pulmonary circuit
Pathway from heart to lungs and back.
Systemic circuit
Pathway delivering blood throughout the body.
Heart valves
Prevent backflow; ensure unidirectional blood flow.
Right ventricle function
Pumps blood into pulmonary circulation.
Normal pathway
Artery → capillary → vein blood flow.
Portal system
Artery → capillary → portal vessel → capillary → vein.
Pericardium
Tough outer layer surrounding the heart.
Myocardium
Muscle layer responsible for heart contractions.
Endocardium
Innermost layer lining the heart chambers.
Sinoatrial Node (SA node)
Heart's natural pacemaker located in right atrium.
Atrioventricular node (AV node)
Coordinates contraction between atria and ventricles.
Action potential
Electrical signal triggering muscle contraction.
Purkinje fibers
Conduct impulses to coordinate ventricular contractions.
Bundle branches
Transmit electrical impulses to ventricles.
SA Node
Primary pacemaker generating heart rhythm.
AV Node
Delays electrical signal between atria and ventricles.
Atrioventricular Bundles
Conducts impulses from AV node to ventricles.
Purkinje Fibers
Distributes electrical impulses throughout ventricles.
Contractile Cells
Muscle cells generating force in heart.
Intercalated Disks
Connects adjacent cardiac muscle cells.
Desmosomes
Structures allowing quick electrical signal passage.
Gap Junctions
Facilitates synchronized heart muscle contractions.
Resting Membrane Potential
Stable voltage across cell membrane at rest.
Action Potential
Electrical impulse triggering muscle contraction.
Pacemaker Potential
Unstable resting potential in autorhythmic cells.
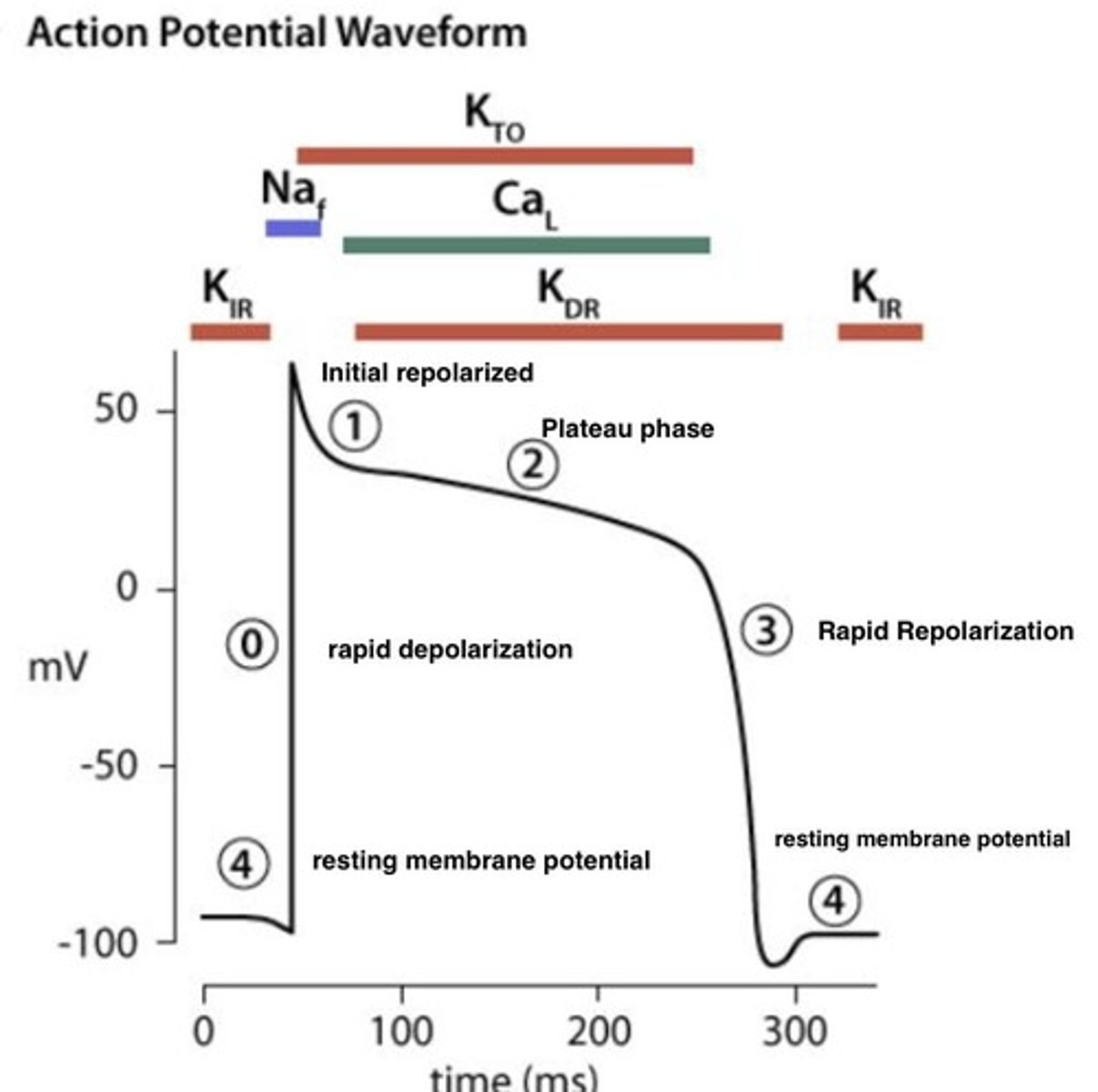
Rapid Depolarization Phase
Initial phase of action potential with Na+ influx.
Plateau Phase
Prolonged depolarization due to Ca2+ influx.
Repolarization Phase
Return to resting potential after contraction.
Tetanic Contraction
Sustained muscle contraction; dangerous for heart.
Calcium Ions (Ca2+)
Essential for cardiac muscle contraction.
Voltage-Gated Channels
Regulate ion flow during action potentials.
Apex Muscle Cells
First to contract, pushing blood upward.
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, abundant in cardiac cells.
Autorhythmic Cells
Generate and conduct electrical impulses autonomously.
Funny Ion Channels
Na+ channels contributing to pacemaker potential.
L-Type Calcium Channels
Open during plateau phase for prolonged contraction.
T-Type Calcium Channels
Transient channels aiding in rapid depolarization.
Ventricular Myofibrils
Contractile fibers in ventricular muscle cells.
Plateau phase
No tetanus occurs during cardiac muscle contraction.
L type voltage gated Ca2+ channels
Channels in conduction fibers for calcium influx.
SA Node
Initiates heartbeat by generating electrical impulses.
AV Node
Receives signal from SA node, activates septum.
Contraction of atria
Atria contract to push blood into ventricles.
Contraction of ventricles
Ventricles contract starting from the apex.
Atrioventricular valves
Valves that close during ventricular contraction.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Recording of electrical activity of the heart.
Einthoven's triangle
Triangle formed by limb leads for ECG.
Lead 1
Right arm (-) to left arm (+) configuration.
Lead 2
Right arm (-) to left leg (+) configuration.
Lead 3
Left arm (-) to left leg (+) configuration.
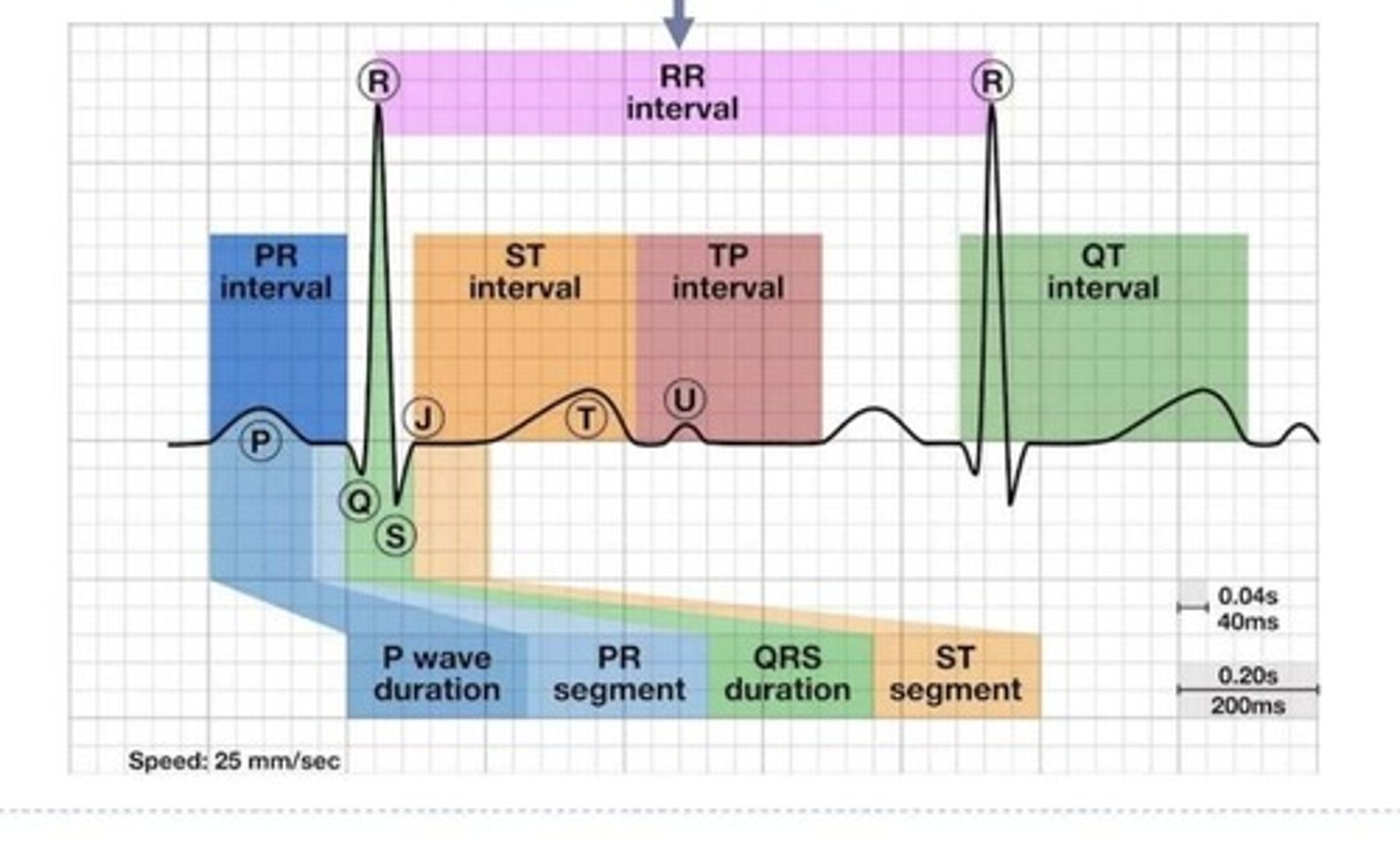
P wave
Represents atrial depolarization in ECG.
QRS complex
Indicates ventricular depolarization and atrial repolarization.
T wave
Represents ventricular repolarization in ECG.
PR interval
Time from atrial depolarization to ventricular depolarization.
PR segment
Time between end of atrial depolarization and ventricular depolarization.
ST segment
Time between end of ventricular depolarization and start of repolarization.
QT interval
Duration from ventricular depolarization to repolarization.
Isoelectric line
Baseline in ECG with no electrical activity.
Systole
Phase of contraction in the cardiac cycle.
Diastole
Phase of relaxation in the cardiac cycle.
Cardiac cycle
Sequence of events in one heartbeat.
******* diagram
Graphical representation of cardiac cycle events over time.
Ventricular pressure-volume changes
Changes during different phases of the cardiac cycle.
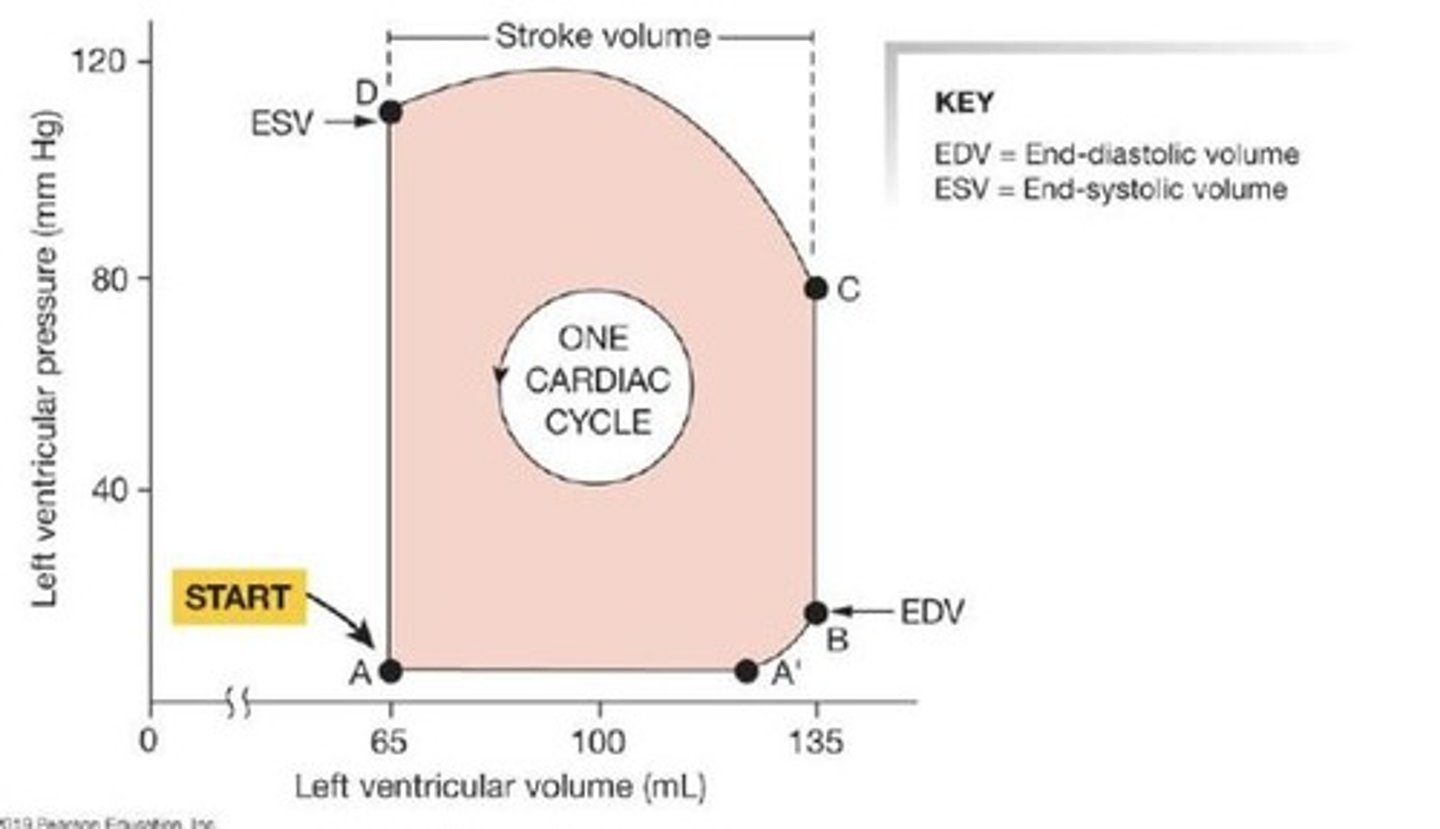
Ejection fraction
Percentage of blood ejected from ventricles.
Stroke volume (SV)
Volume of blood ejected during ventricular systole.
End diastolic volume (EDV)
Volume in ventricles at end of diastole.
End systolic volume (ESV)
Volume remaining in ventricles after contraction.
Cardiac output (CO)
Volume of blood pumped by each ventricle per minute.
Cardiac Output (CO)
Volume of blood pumped per minute.
Stroke Volume (SV)
Volume of blood ejected per heartbeat.
Heart Rate (HR)
Number of beats per minute.
Parasympathetic System
Reduces heart rate via vagus nerve.
Sympathetic System
Increases heart rate and contractility.
Vagus Nerve
Innervates heart, releases acetylcholine.
Cardiac Nerve
Innervates heart, releases norepinephrine.
Tonic Control
Maintains resting heart rate at 70 bpm.
If Channels
Increase Na+ and Ca2+ permeability.
Frank-Starling Law
SV increases with increased EDV.
Preload
End diastolic volume returning to heart.