Pathology of the Respiratory System
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
180 Terms
upper airway (air entrance)
lower airway (tubes that move air deeper)
lung (air exchange)
What are the three major divisions of the respiratory system?
nasal cavity
paranasal sinuses
nasopharynx
gets the air ready before it goes straight to the lungs I.e. warms it, filters, adds moisture
What does the upper airway consist of? (3)
what is the purpose of this area of division?
larynx
trachea
bronchi
bronchioles
these are the tubes that move air deeper
what does the lower airway consist of? (4)
what is the purpose of this area of division?
bronchi
bronchioles
alveoli
air exchange
what do the lungs consist of? (3)
what is the purpose of this area of division?
thoracic cavity
thoracic cavity
mediastinum
this cross section shows the intricate anatomy of the respiratory system and the anatomic associations of w/ the components of the ______ ______.
this intricate association is important to consider because diseases affecting the _____ ____ or ___________ may also impact the respiratory system
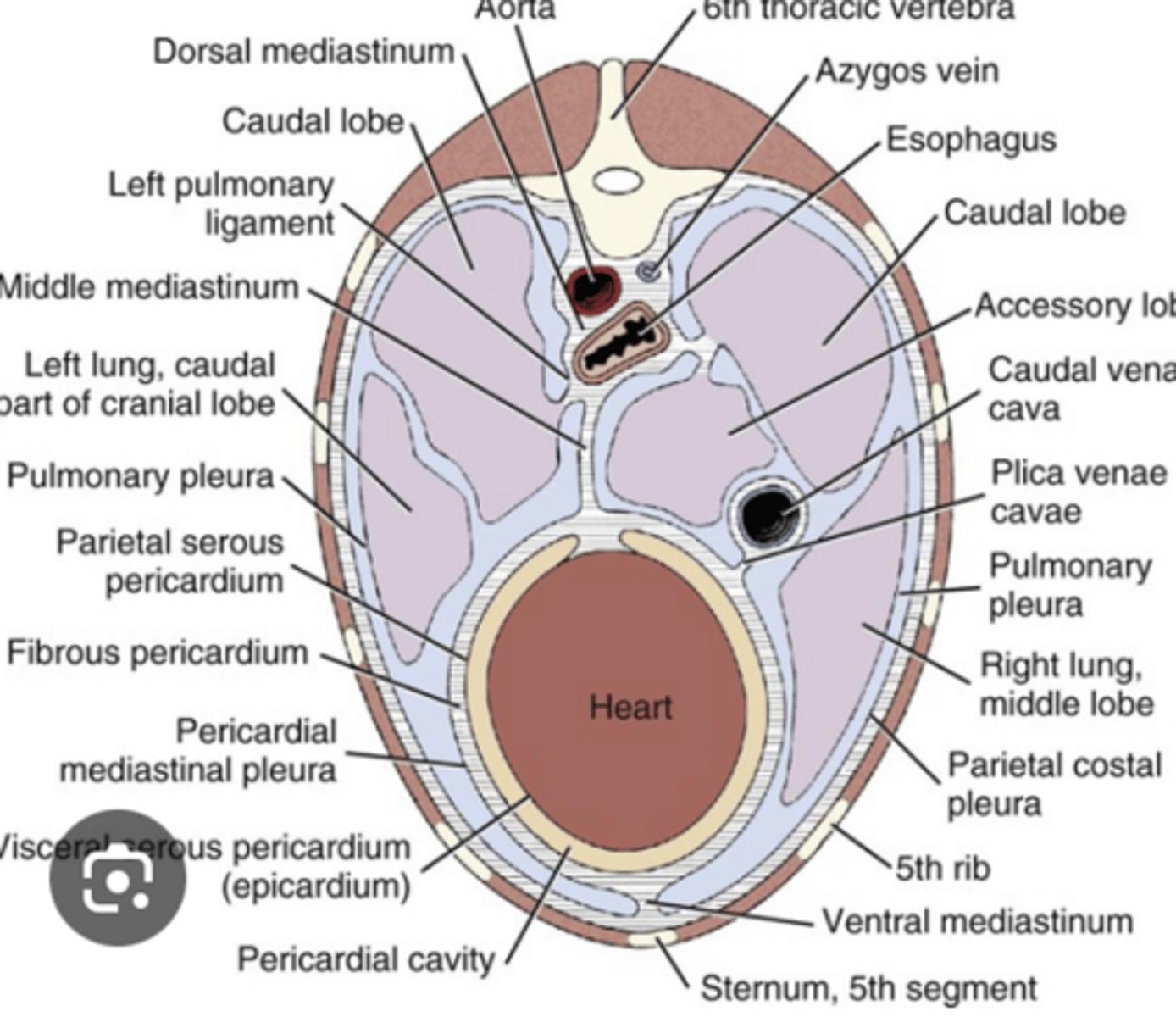
thoracic wall, mediastinum
It is important to remember that diseases affecting the _________ and _________ may also impact the respiratory system.
trachea
primary bronchi
2ndary lobar bronchi
tertiary segmental bronchi
bronchiole
respiratory bronchioles
alveolar ducts
alveolar sacs
alveoli
The respiratory tree is the branching system of airways within the lungs.
It starts from the ____
,which splits into 1°___________, then 2°________ and 3°__________.
these bronchi continue into smaller ________-> ____________ then even smaller into __________, __________ and finally ending in ________.
alveoli
what are the sites of gas exchange?
resistance
With each division in the respiratory tree, there is increased ________, which is important to remember in upper resp. diseases and pneumonia cases.
conductive/ transitional system
gas exchange system
vascular system
the three practical subdivisions of the respiratory system are:
conductive system
Which practical subdivision includes: nasal cavity, turbinates, paranasal sinuses, nasopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi
nasal cavity
turbinates
paranasal sinuses
nasopharynx
larynx
trachea
bronchi
What does the conductive system include? (name like 4 of the 7)
humidifies, warms, filters
The conductive system ________, ________ and _______ inspired air.
50-75
the conductive system accounts for ______-_________% of total respiratory resistance
(aka most of the work of breathing occurs here bc air is squeezed through the nose into small diameters, increasing resistance)
Turbinates
__________: Curved or scroll shaped bony structures protruding from the lateral walls and septum of the nasal cavity
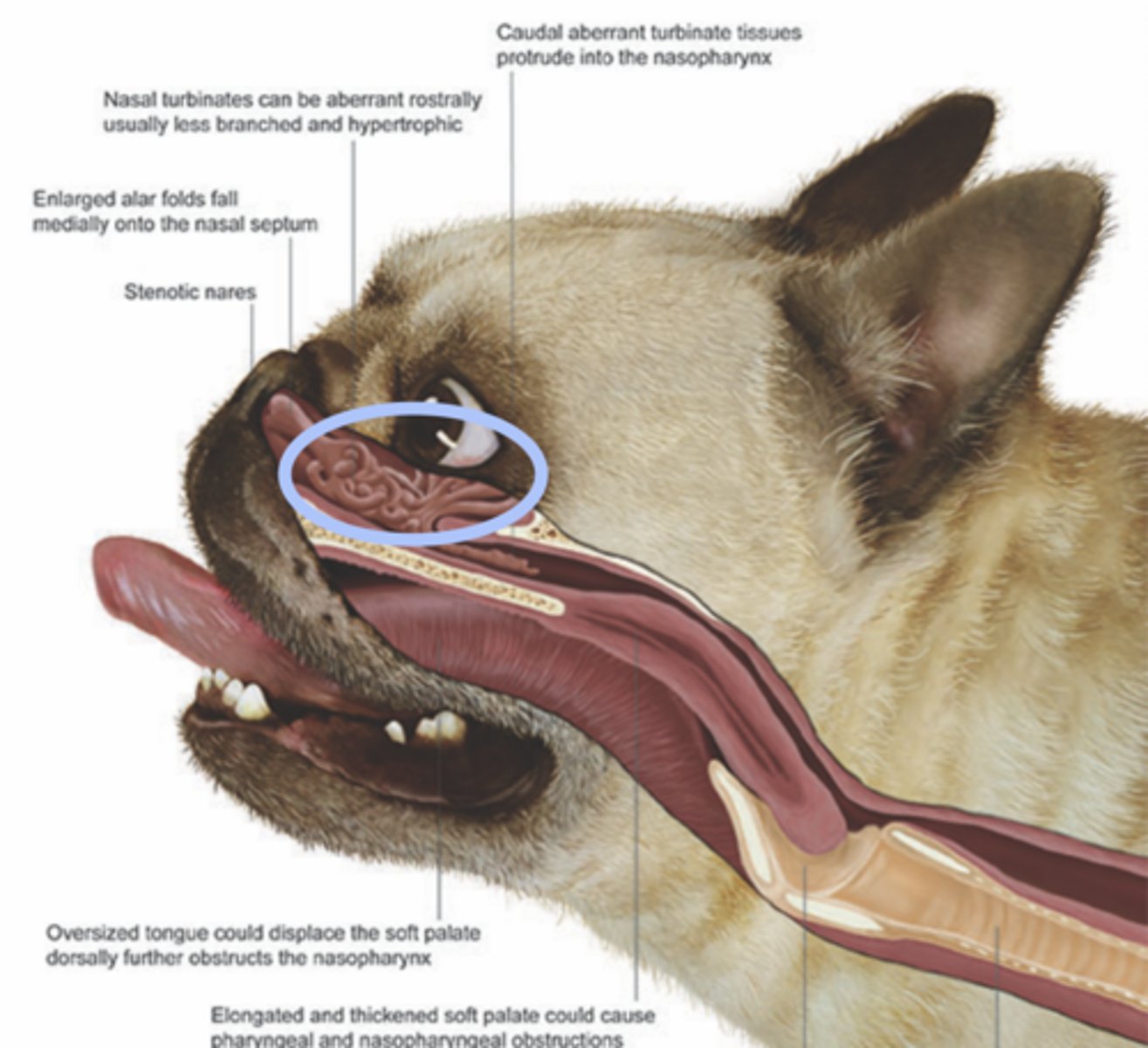
warming, humidifying, filtering
regulating nasal airflow
turbinates aid in _______, ________, and ______ inspired air as well as regulating _____________________
impaction of inhaled particles
(think such windy/bendy area is going to get things stuck in it, this is why when gunk is impacted, the reasoning for sneezing)
turbinates are also a major site of what?
paranasal sinuses
___________________: Air filled cavities in the facial bones
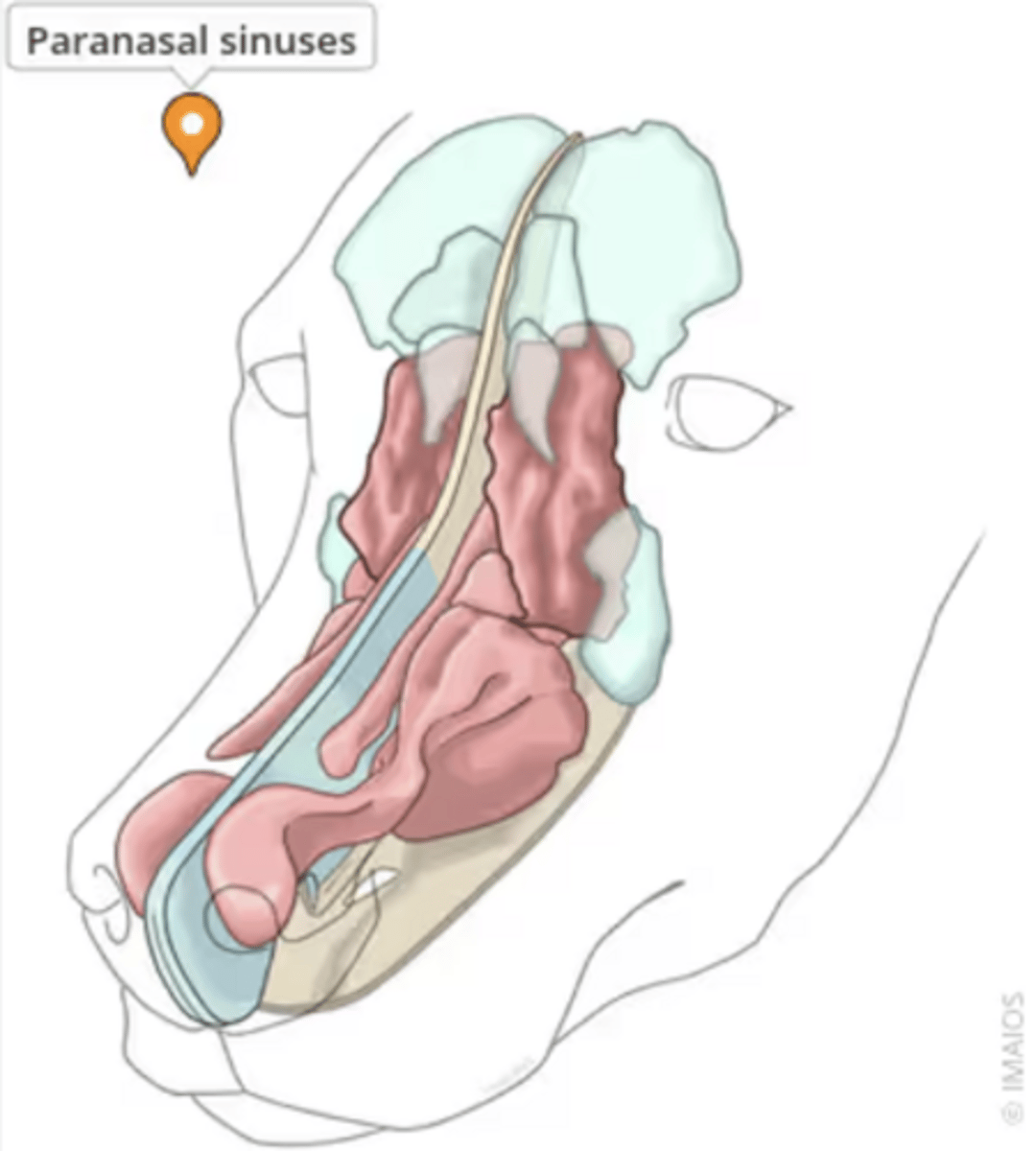
- decrease weight of the head (makes the head lighter, therefore easier to hold up)
- auditory (vocal resonance/ echo chambers)
- buffer against facial trauma (air cushions blows)
- insulate structures from temperature changes
What are the four functions of the paranasal sinuses?
doesn't drain well.... the openings close..... sinusitis
Because there are only small openings that communicate between the paranasal sinuses and the nasal cavity, what does this mean happens when the sinuses are inflamed?
vasodilation
_______________ is the hallmark of inflammation
horse
What species has six pairs of paranasal sinuses—the frontal, sphenopalatine and maxillary sinuses, and the dorsal, middle and ventral conchal sinuses
horses
molar roots are under the maxillary sinus so dental disease easily affects here
the maxillary sinus is specific to?
also, where does this sinus reside making what disease common here?
sinusitis
_____: refers to inflammation or infection of one or more of the paranasal sinuses
primary
[primary/secondary] sinusitis is defined as an infection in the sinus, usually bacterial in origin, which results in a buildup of pus within the sinus
secondary
[primary/secondary] sinusitis is an infection of the paranasal sinuses as a result of another primary cause, such as tooth root infection, bone fracture, or sinus cyst
secondary
Is primary or secondary sinusitis more common?
last four cheek teeth, the roots are within the maxillary sinuses
What are most likely to cause a secondary sinusitis in horses? And why?
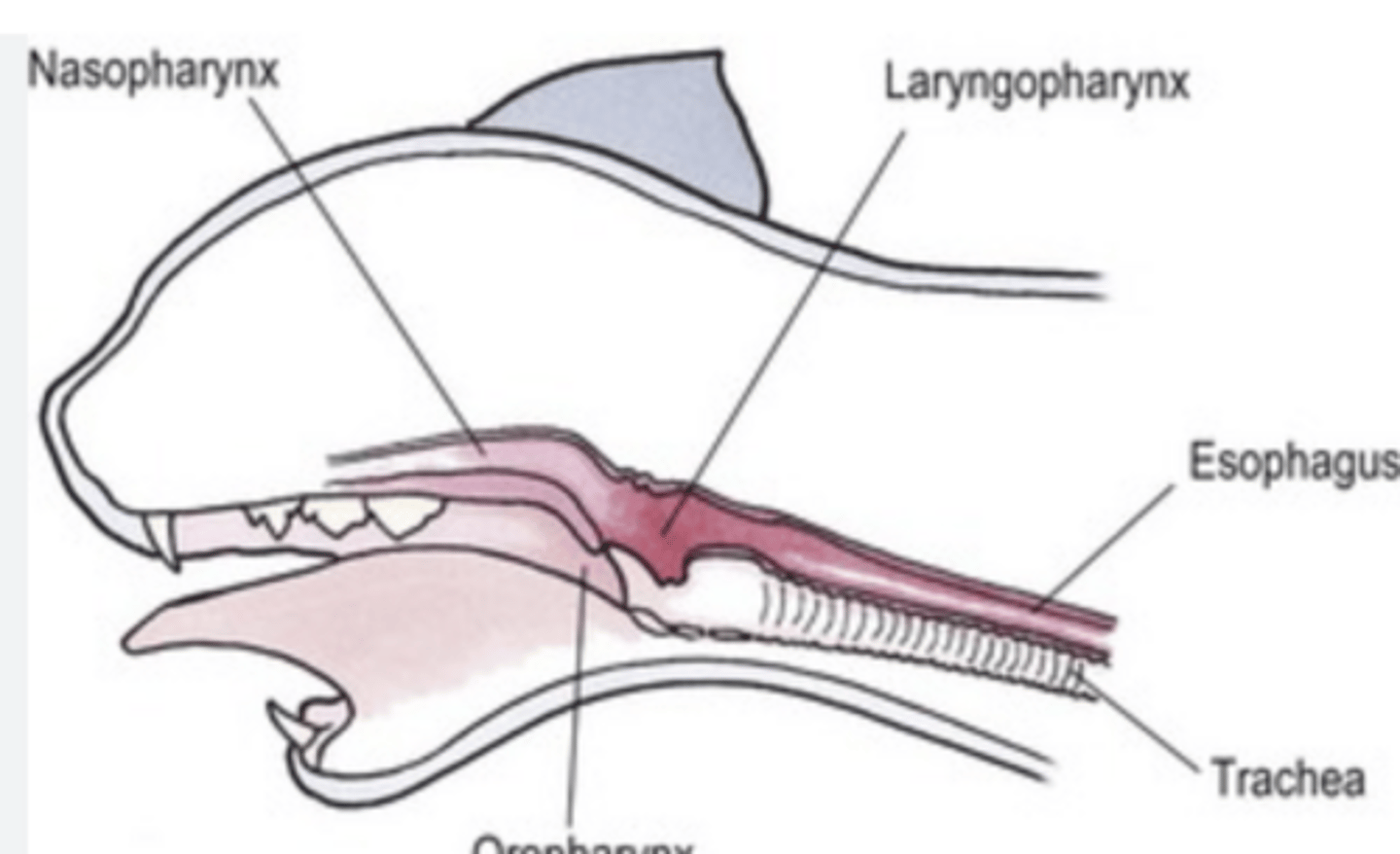
nasopharynx
______________:Mediates air passage from the nasal cavity to the larynx (connects the nose to the larynx)
eustacian tubes
middle ear
pressure equilibration
the nasopharynx is also the site where the ____________ connect to the _______ and allows for _______________
security checkpoint
immune cells
lympoid nodules/ MALT
the nasopharynx also acts as a __________ _______ as it is packed with ______ _______. specific aggregates of these immune cells are aka __________/ _______
lymphoid nodules, initiator and effector, pathogens
respiratory immunity in the nasopharynx is due to a large aggregate of ____________ in the submucosa. It acts as both a ______ and _______ site, and as a primary site for the colonization of ________>
larynx
_____________: separates the intestinal and respiratory tracts (its a "traffic cop" deciding air-> trachea, food-> esophagus)
is also and organ of phonation
aspiration of ingesta
increased airway resistance
Dysfunction of the larynx can lead to ____________
Narrowing of the larynx can lead to _________
c-shaped cartilaginous rings
the trachea is supported by _________ which maintain rigid structure and lumen size
main stem bronchi
the trachea divides into what?
mainstem bronchi
__________: is the terminal division of the trachea and entry into the pulmonaryy parenchyma
inversely, increase
diameter of the bronchi and resistance are ______________ related... so as diameter decreases, resistance will [increase/decrease]
air delivery
gas exchange
the transitional system is the area where ____ delivery transitions into _____ ______
(this zone includes very small brocnhi, bronchioles; and with each division, diameter decreases and resistance increases)
alveolar spaces
Where does air deliver transition into gas exchange?
bronchioles
_________: "are the small squishy air tubes before the air sacs". they are not supported by cartilage, so the diameter canchange with lung inflation
false; they have no cartilage so the diameter can change with lung inflation
true/false: bronchioles are supported by cartilage so that their small size doesn't change with changes in airflow
small, high
large, low
aka as a functional unit, there are thousands of bronchioles creating a large surface area
individually, bronchiole diameter is _____ and resistance is ________. But as a functional unit, cross sectional area is ______ with ______ resistance... what does this mean?
true
true/false: widespread damage is necessary to increase resistance to airflow in the bronchioles
its there is very little peribronchiolar connective tissue (so it doesn't limit the inflammation)
bronchioles are a common site of inflammation/ impaction... why?
acini
gas exchange occurs in the _______
respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar space
the acini consists of branching ______ into _______ and _______
fluid accumulation, exudate
damage to the acini will lead to ________ or _______ filling the alveolar spaces or interstitium
acinus
the fundamental functional unit of gas exchange in the lung is the?
blood gas interface
where oxygen and carbon dioxide transfer occurs between air and blood.
gas exchange
respiration
the acinus is a complex, branching structure maximizing surface area for _____ _____, AND forms the crucial interface for ______.
ventilation, perfusion, diffusion
Gas exchange happens over thin barriers through ________ (breathing), _________(blood flow), and ________ (moving gases down their pressure gradients)
terminal bronchiole, alveolar ducts, alveoli
The mammalian gas exchange system originates with each _____________, opening into ________ and a collection of __________
O2
CO2
4microns
the alveolar wall is paper-thin, allowing ____ and _____ to cross easily. its estimated to be about _______ thick
4
hypoxic
It is important to note that the entirety of the alveolar wall is approximately _____ microns thick.
PATHOLOGY ALERT: if the alveolar wall gets thicker, inflammed, filled with fluid, oxygen cannot cross and the animal becomes _____
- type I pneumocyte (thin flattened cells on the surface important for diffusion)
-type II pneumocyte (cubodial cells in the corners producing surfectant)
- basment membrane
- capillary endothelim
what is in the alveolar wall (wall important for gas exchange) (4)
capillaries
Alveoli are wrapped in a dense network of ____________, creating an enormous surface area for gas exchange
pores of Kohn
Adjacent alveoli have connections via small openings, called _______, that allow for collateral airflow and equalization of pressure between alveoli
increased surface area of the membrane
Increased alveolar pressure difference (PA-Pa)
Increased solubility of the gas
Decreased membrane thickness
What four things can increase the diffusion of gas across alveolar membranes?
bronchial circulation
pulmonary circulation
the vasculat system is also of importance not just for gas exchange but bc they lungs must be nourished too. there are two arterial supplies to the pulmonary system, these being __________ and _________
bronchial
________: circulation that arises from the thoracic aorta (oxygenated) and intercostal arteries. supplies the trachea, to the bronchi, to the respiratory bronchioles
pulmonary
_____________: circulation that arrives via the pulmonary artery (unoxygenated) from the right heart. the circulation for gas exchange
bronchial circulation
Which of the two arterial supplies to the pulmonary system brings OXYGENATED blood to the lung tissue to keep it working?
pulmonary circulation
Which of the two arterial supplies to the pulmonary system brings UNOXYGENATED blood to the lung tissue for gas exchange?
thoracic aorta and intercostal arteries
trachea, bronchi
The bronchial circulation arises from the _________ and ________ and supplies the ______ and __________ to the level of the bronchioles
False: PULMONARY circulation is the largest capillary bed in the body
True/false: the bronchial circulation is the largest capillary bed in the body
filter
due to the small diameter of the capillaries, the pulmonary circulation serves as a sort of blood __________
deliver blood for gas exchange
filter small thrombi
trapping of leukocytes
What are three functions of the pulmonary circulation (3)
pulmonary capillaries
___________________: tiny vessels surrounding alveoli where gas exchange occurs
shortness of breath, heart strain
pulmonary hypertension: High blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries, leading to _______ and ________
blockage
pulmonary embolism: a _______ in the pulmonary arteries, often by a blood clot
pressure, congestion
heart failure can cause increased _______ in the pulmonary system, leading to ________
pleura
_______: Covers the lungs, thoracic structures and thoracic wall.
fluid, blood or lymphatic supply
The pleural spaces contain small amounts of _________ but no direct _______ or ______________
(kinda a stretch on the wording I know. but whatever)
mediastinum
___________: Anatomic space bordered by the sternum, pleural surfaces of the lungs, diaphragm and vasculature
thoracic cavity
in some species, the mediastinum completely divides what?
guttural pouch
________: A ventral diverticulum of the Eustachian tube.
cooling of blood in the internal carotid, pressure equalization
Allegedly, the guttural pouch is essential for _______________ in the __________ and __________________
right: cranial, middle, caudal, accessory;
left: cranial and caudal
What are the lung lobes in a dog/cat/cow?
right:______________________
left:________________________
right: cranial, middle, accessory;
left: cranial and caudal
What are the lung lobes in a horse?
right:______________________
left:________________________
pulmonary lobule
__________________: Clusters of 3-5 terminal bronchioles with their acini form this
collateral ventilation
________: "the ventilation of alveolar structures through passages or channels that bypass the normal airways"
For our purposes, this would mean that if one lobule of the lung is infected with something, it could spread to other lobules
true
true/false: cattle and pigs have extensive lobulation due to abundant connective tissue... which means that if one lung lobule is infected with something, it's a lot less likely for the infection to spread to other lobules
olfactory neuroepithelium (smell receptors)
stratified squamous (in the nose to be tough)
ciliated pseudostratified respiratory epithelium (push secretions)
The entire respiratory tract is covered by epithelium... what are the three kinds?
epithelium
(olfactory neuropithelim, stratified squamous, ciliated pseudostratified respiratory epithelium)
submucosal gland
cartilage
smooth muscle
What are the 4 cells types in the conductive and transitional systems?
________: lines the entire tract
_______: secretes layer of mucociliary escalator
_______: for support
_____: support and pliability
olfactory neuroepithelium
___________: present in portions of the nasal cavity that contain specialized cells that bind to odorants to enable sense of smell
odors
chemical to electrical
relay
olfactory neuroepithelum functions to:
◉ detect ________
◉sensory transduction converting the _________ signals into ________
◉ neural r____
limited
so if damaged, lose smell receptors
olfactory neuroepithelial cells have a ______regeneration capacity. what does this mean?
cytochrome p450
some metabolites are more toxic than the full inhalant
the olfactory neuroepithelium, contains ______ which aids to metabolize inhalants... breakdown the chemicals we breathe in (to decode) why might this be a bad thing?
stratified squamous epithelium
what type of epithelium covers the nares?
injury
stratified squamous epithelium is resistant to ___________
ciliated epithelial cells
what type of epithelium covers 95% of the conductive system and is a vital part of the mucociliary escalator?
metaplasia squamous epithelium
cilia
mucociliary escalator
ocassionally ciliated epithelial cells can be damaged so extensively that the cells die and are replaced with ___________ _________ _______. this replacement and occurrence results in loss of ______, and decreased function of the __________ ________.
squamous epithelium, chronic irritation
metaplasia of the respiratory epithelium to ____________ can occur in instances of ___________
cilia, mucociliary escalator
in chronic irritation, when the epithelium becomes squamous, this results in a loss of ________ and decreased function of the __________
club cells (non-ciliated)
________: considered the stem cells of the upper and lower respiratory tract. these cells secrete a thin protein rich fluid and are metabolically active
bronchioles
stem cell
metabolically active
to be a bottom mucus layer bc cilia need a slippery surface to work properly
club cells are doind in the small _______ where the airways get thin and delicate. they are considered to be a ________ _____ of the upper and lower respiratory tract since they are ________ _____
club cells secrete a sol layer- bottom mucus layer, for why?
metabolically
oxidazes (CYp450)
* gotta be aware of the breakdowns though
Club cells have efficiency for being _________active, containing ____________ to detoxifiy compounds
1) alevolar epithelium
2) macrophages
3) endothelium
4) fibroblasts
the cell types in the gas exchange system are: (4)
type I and type II pneumocytes
alveolar epithelium, a cell type in the gas exchange system, contains what two types of cells primarily?