Articulations and Joint Classifications: Structure, Function, and Movements
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Articulation/Joint
Point of contact between two bones, between cartilage and bone, or teeth and bone.
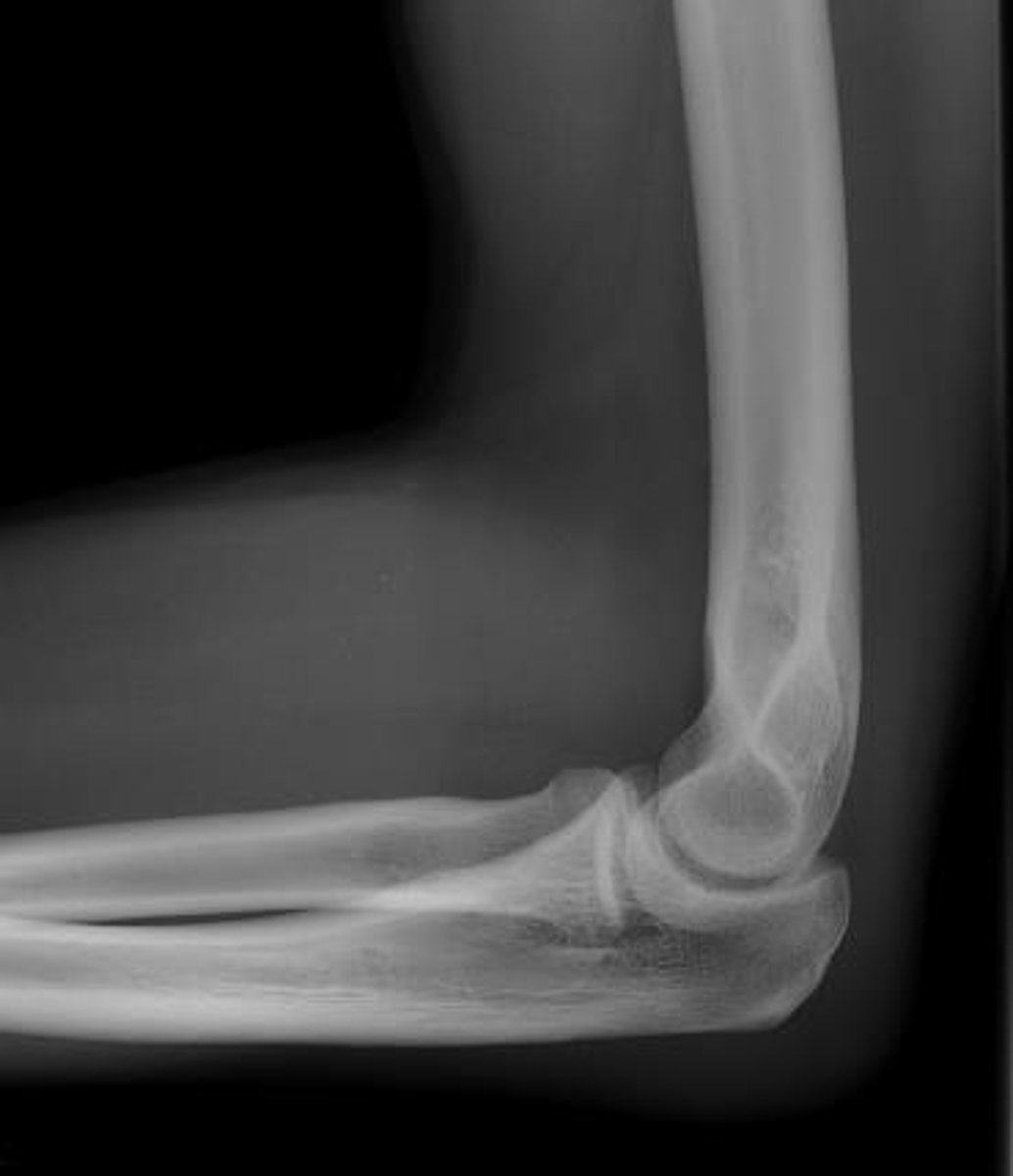
Ex: Elbow
Example of an articulation involving the Humerus and Ulna, and Humerus and Radius.
Ex: Skull bones
Example of articulations involving Frontal and Parietal bones.
Joints classification
Joints can be classified structurally and functionally.
Structural classification
Is there a joint cavity? What types of connective tissue are involved?
Functional classification
What degree of movement is permitted?
Synarthrosis
does not allow any movement
Amphiarthrosis
allows a small amount of movement
Diarthrosis
freely moveable
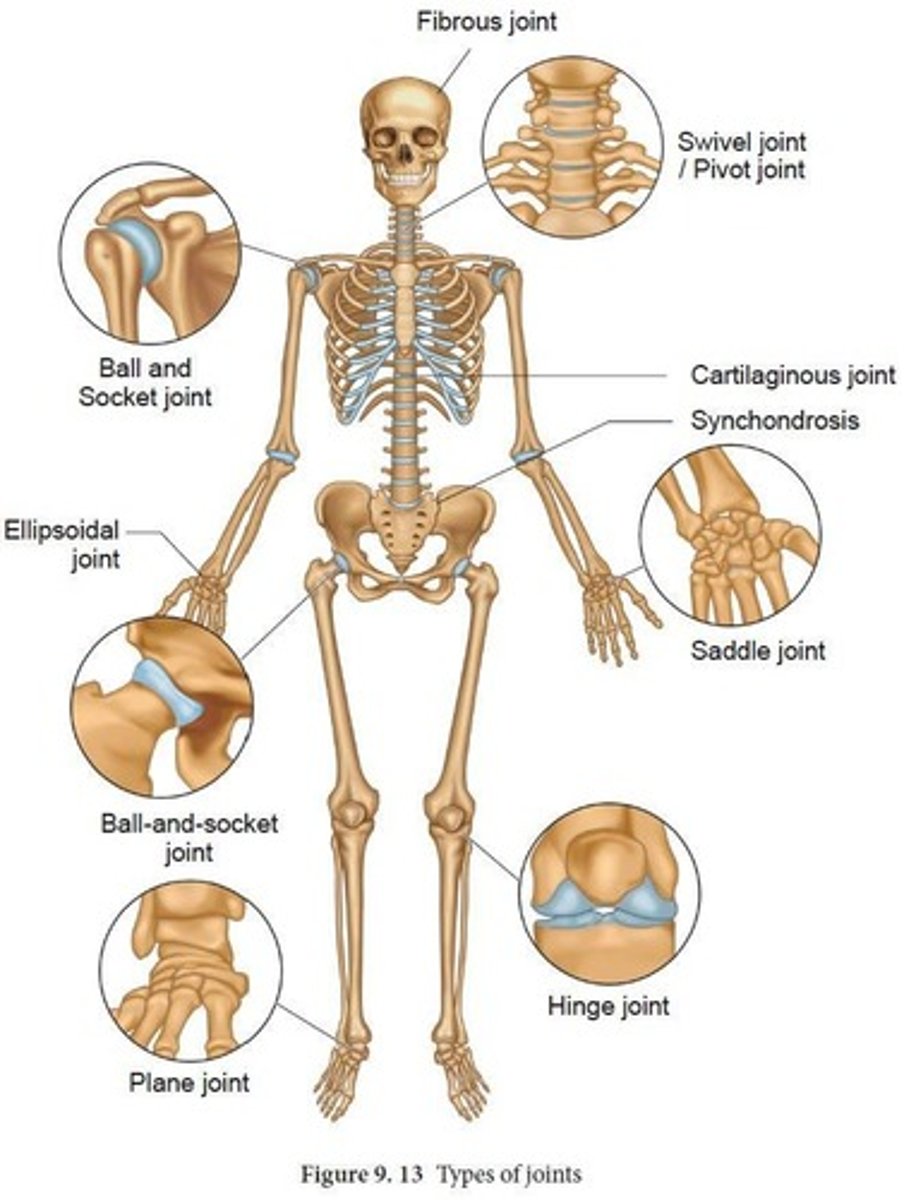
Fibrous Joints
contains dense regular collagenous CT with no joint space
Cartilaginous Joints
contains cartilaginous CT with no joint space
Synovial Joints
diarthrosis joints that contain a fluid-filled joint space between articulating bones
Fibrous Joint
held together by dense regular CT, very strong, collagen rich, and has no synovial cavity
Sutures
bones of skull with interlocking edges
Gomphosis
teeth
Syndesmosis
adjacent bones linked by strong membrane, e.g., tibia/fibula; radius/ulna
Cartilaginous Joint
held together by cartilage with moderate strength and no synovial cavity
Synchondrosis
bones are joined by hyaline cartilage, e.g., epiphyseal plate; ribs and sternum
Symphysis
bones are joined by fibrocartilage, e.g., pubic symphysis; intervertebral discs
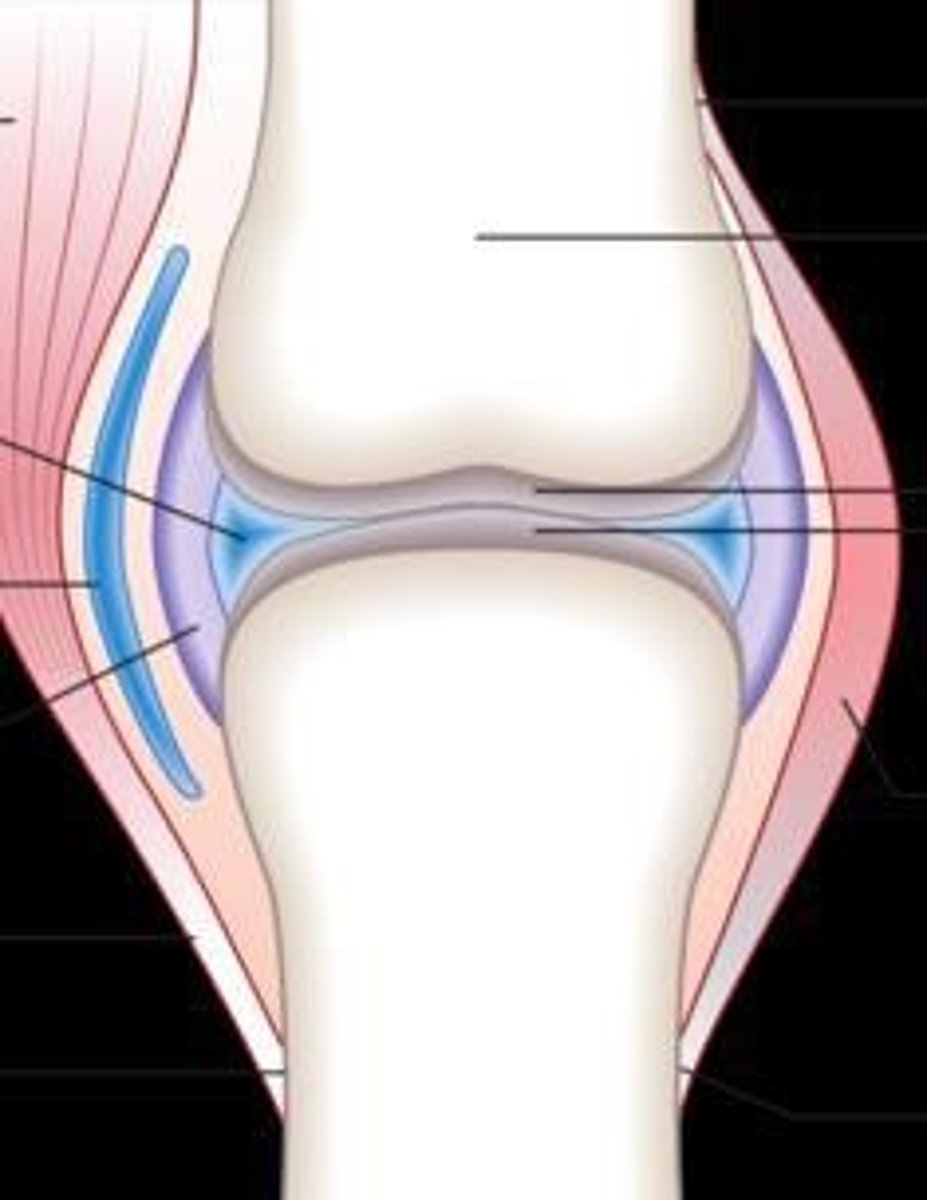
Synovial Joint
diarthrosis with synovial cavity and synovial fluid between bones, supported by ligament
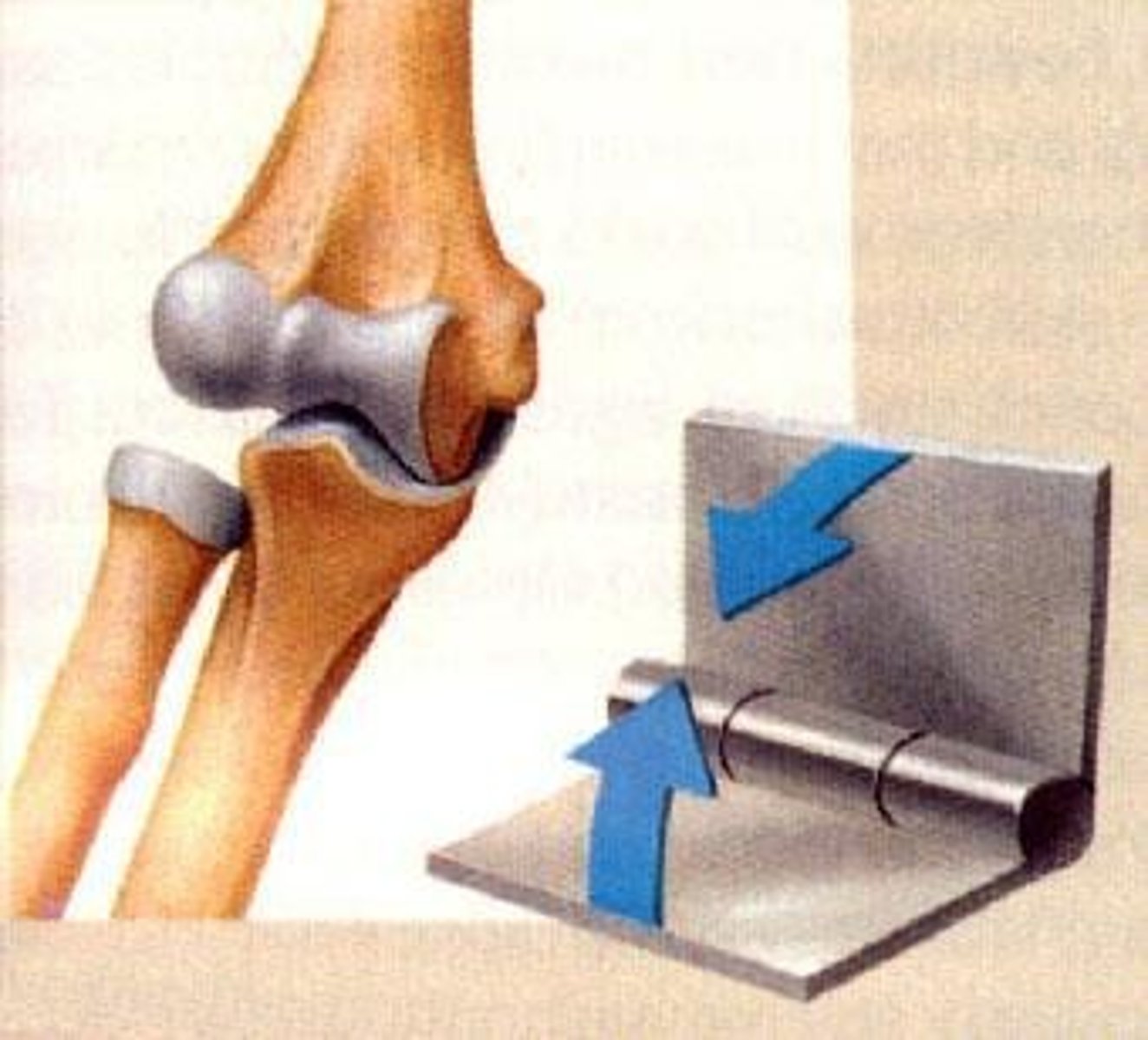
Hinge Joint
permit movement only in one plane, e.g., elbow; knee
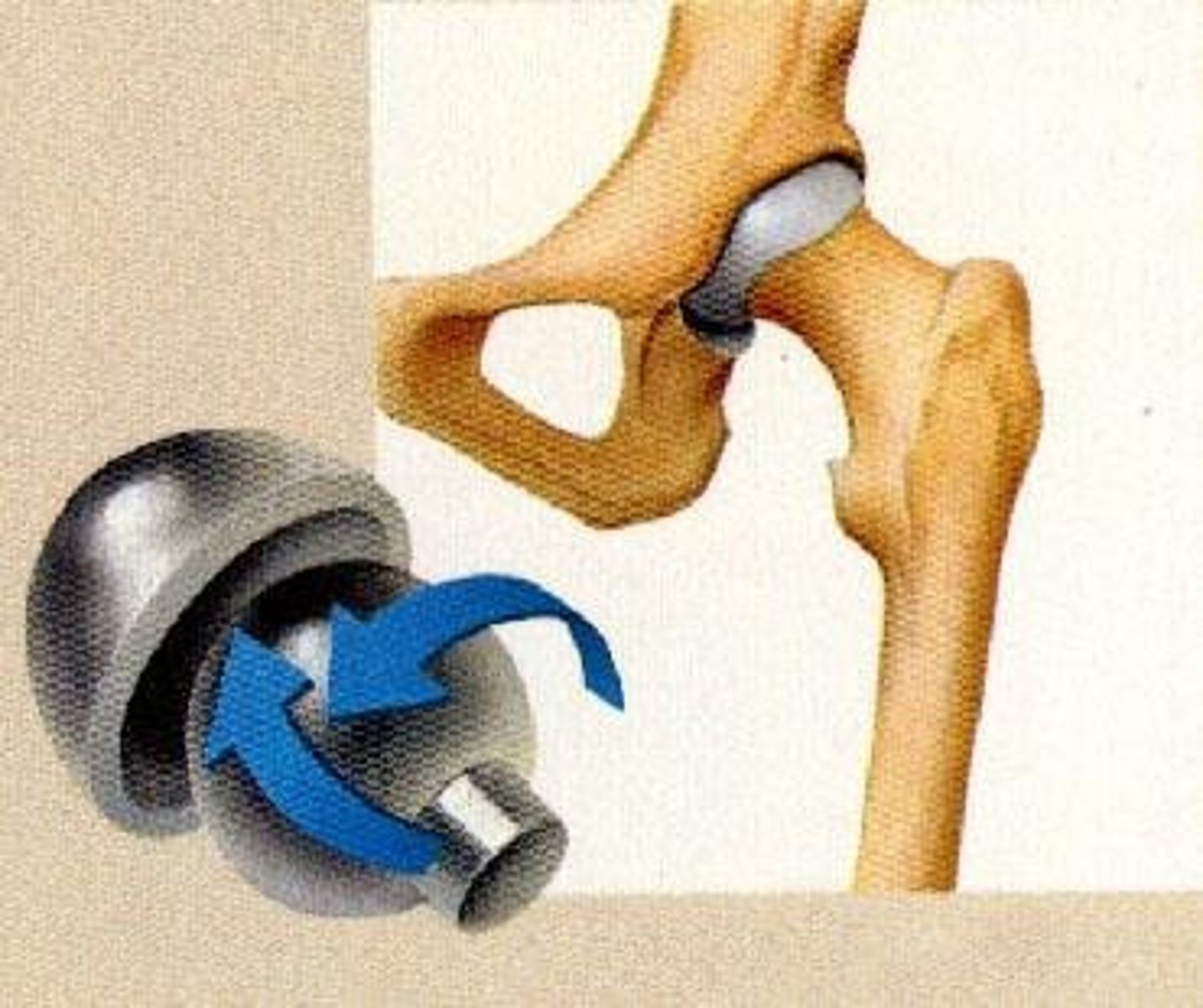
Ball and Socket Joint
allows a large range of motion, e.g., hip; shoulder
Articular Cartilage
cartilage found at the ends of bones to help protect the bone tissue
Joint Capsule
connective tissue that envelops/surrounds synovial joints
Synovial Cavity
space between bones containing synovial fluid
Synovial Membrane
lining of synovial cavity that secretes synovial fluid
Synovial Fluid
thick yolk-like fluid that helps reduce friction between cartilage, composed of hyaluronic acid and interstitial fluid
Nonaxial Movement
gliding movement only
Uniaxial Movement
movement in one plane
Biaxial Movement
movement in two planes
Multiaxial Movement
movement around all three planes
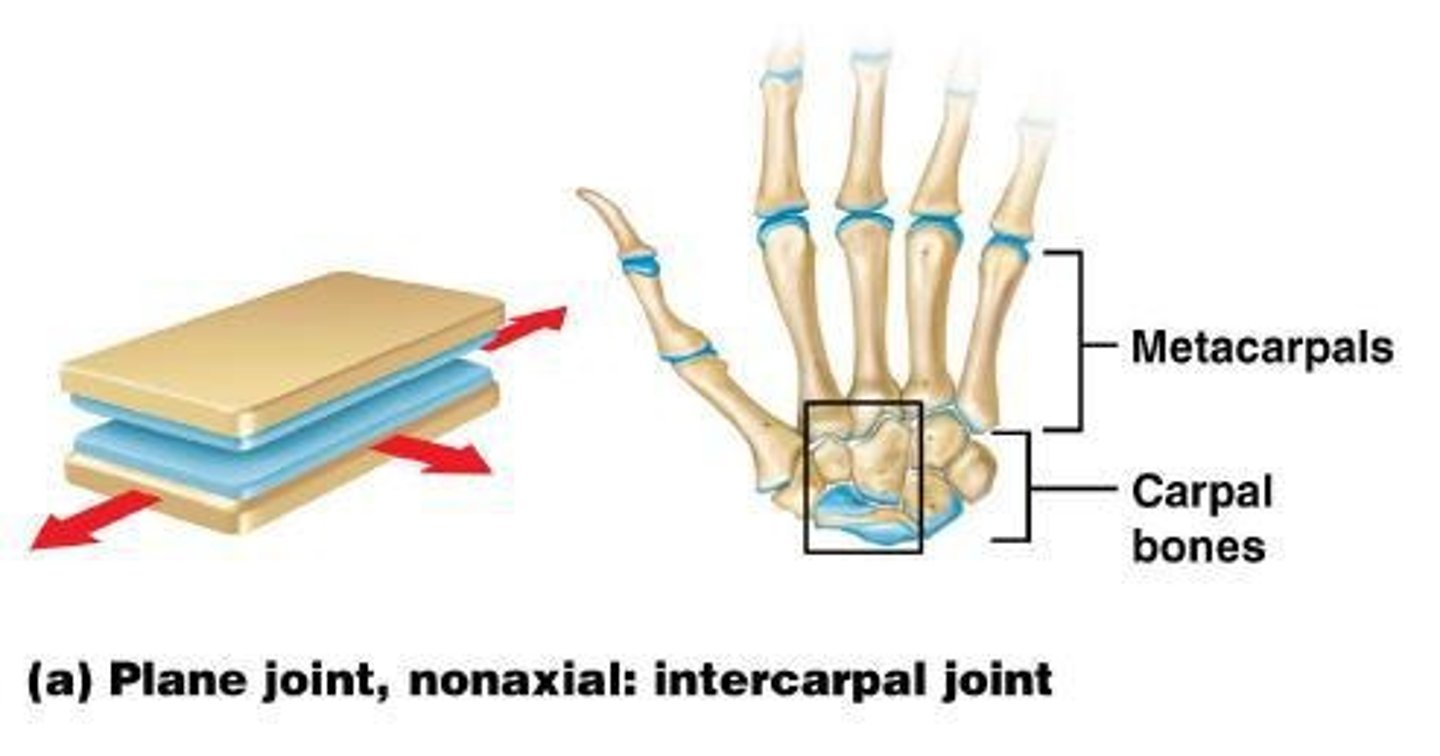
Planar Joint
gliding joints that allow short gliding movements, nonaxial
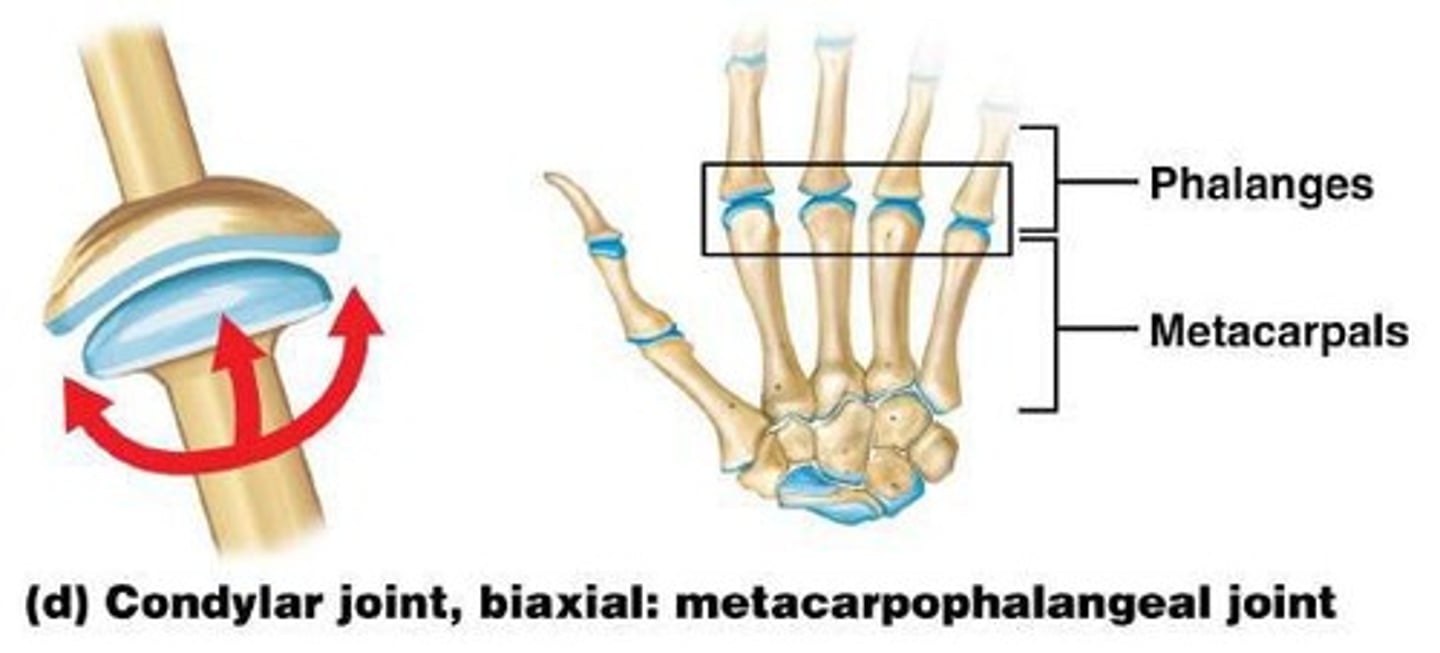
Condyloid Joint
convex surface of one bone fits into a shallow, concave articular surface of another, biaxial
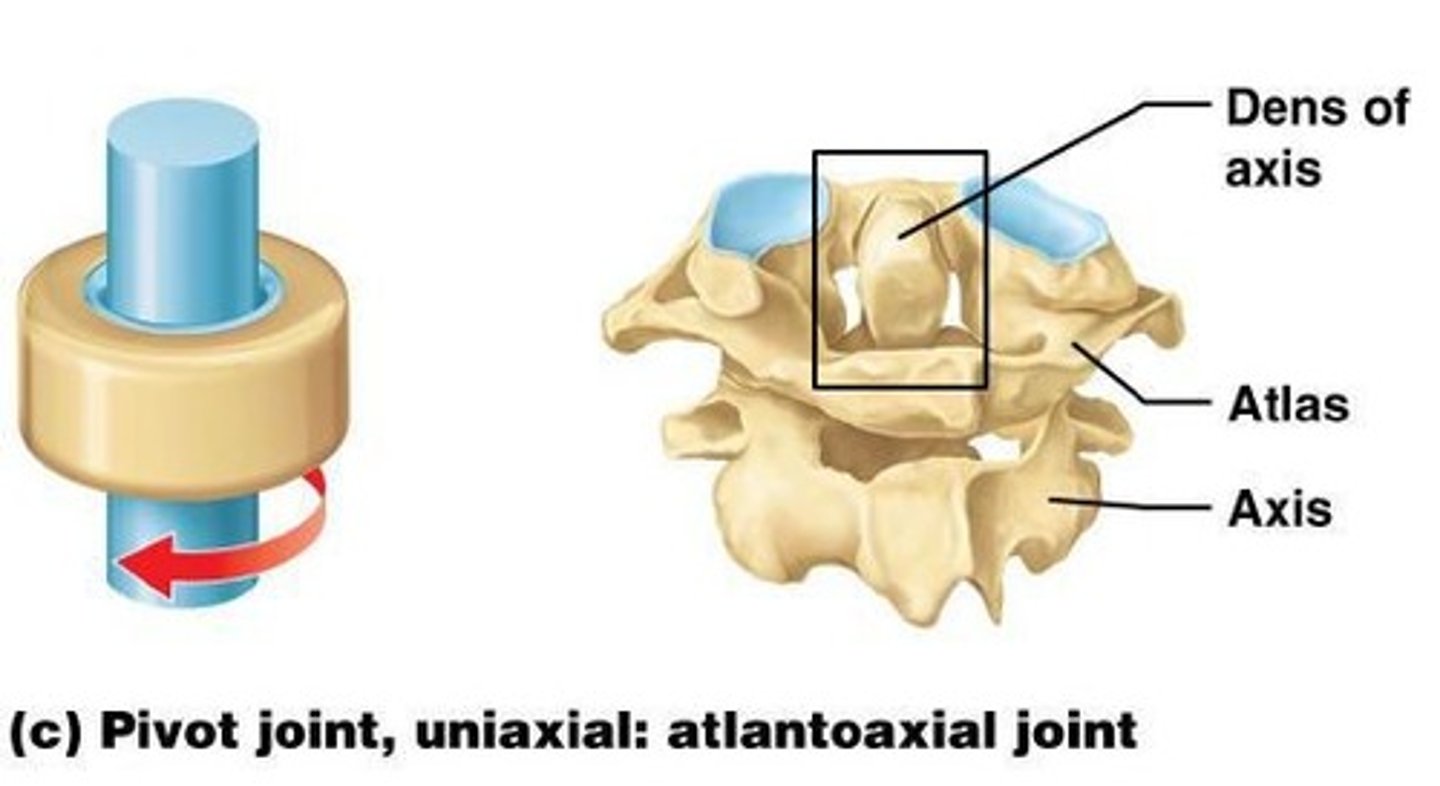
Pivotal Joint
round/pointed bone articulates with a ring formed by a bone/ligament, monoaxial
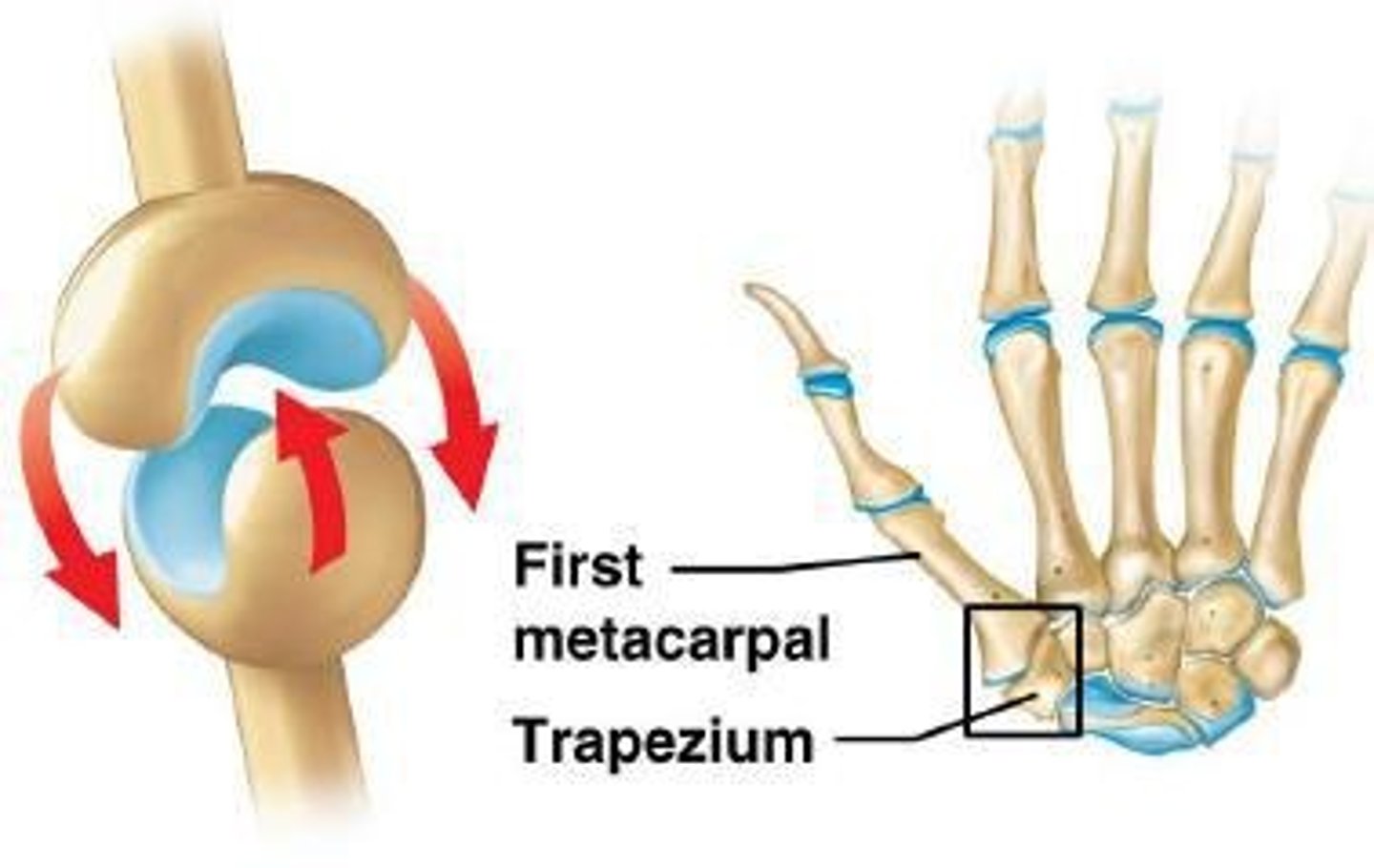
Saddle Joint
modified condyloid joint with biaxial movement in two planes
Suture
skull
Amphiarthrosis Joint
Slightly movable, connected by collagen fibers or cartilage
Fibrous Syndesmosis
Tibiofibular joint and Radioulnar joint
Diarthrosis Joint
Freely movable, mostly synovial joints
Sprains
Injuries to ligaments ranging from slight (caused by overstretching) to serious (caused by tearing), e.g., tearing the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) of the knee
Arthritis
A group of inflammatory or degenerative diseases of joints that occur in various forms, characterized by swelling of the joint, pain, and stiffness
Gouty arthritis
Build up of uric acid
Osteoarthritis
Degenerates surface
Rheumatoid arthritis
Autoimmune disease causing inflammation to synovial membrane
Angular Motion
movement changes angle between bones
Flexion
decreases angle, e.g., movement of forearm towards face
Extension
increases angle
Lateral flexion
bending toward the side
Abduction
lateral movement of limb away from midline
Adduction
medial movement of limb towards midline ('add' together)
Rotational Motion
Bone turns on its own long axis
Lateral Rotation
limb rotates away from midline
Medial Rotation
limb rotates towards midline
Pronation
medial rotation of forearm
Supination
lateral rotation of forearm
Depression
inferior movement of body part, e.g., downward movement of mandible to open mouth
Elevation
superior movement of a body part, e.g., Closure of mouth or shrugging of shoulder
Dorsiflexion
movement of dorsal surface of foot or toes toward shin
Plantar Flexion
pointing toes inferiorly, e.g., ballerina on her toes
Inversion
soles of feet turned medially
Eversion
soles of feet turned laterally
Protraction
anterior movement of body part, e.g., sticking jaw (mandible) forward
Retraction
posterior movement of body part, e.g., moving mandible backwards
Fovea
small, pit-like depression
Fossa
shallow depression; in bone, often serves as articular surface
Olecranal
posterior elbow
Popliteal
posterior knee
Sural
calf
Calcaneal
heel
Vertebral
posterior midline
Gluteal
butt
Coronoid Fossa
Anterior-medial depression for coronoid process of ulna
Olecranon Fossa
Posterior depression for olecranon process of ulna
Ulna
Bone of the forearm, medial to radius
Trochlear Notch
articulates with trochlea of humerus
Olecranon Process
prominent posterior bump
Coronoid Process
inferior lip of trochlear notch