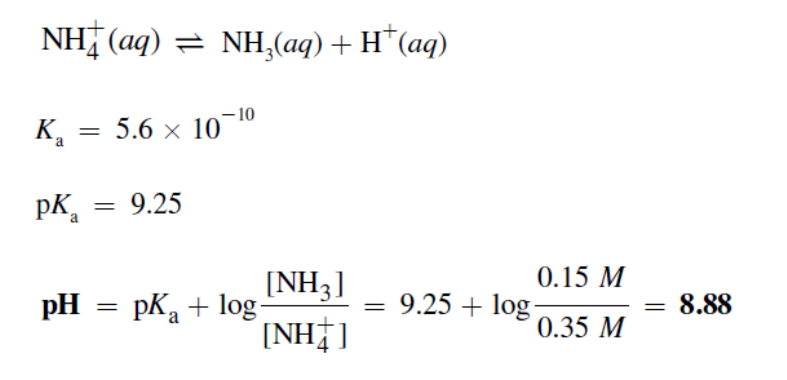G12E chemistry EOT T1
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is the ion-product constant of water?
Kw = 1×10-14 at 25C
What is the equation relating [H+] and [OH-] in a solution at a temperature of 25C?
Kw = [H+][OH-]
How do we find [H+] from the pH?
[H+] = 10-pH
How do we find the pH from [H+] ?
-log(H+)
How do we get pOH or pH?
14 - pH = pOH
14 - pOH = pH
What’s a buffer solution?
A buffer solution is a solution that resists change in pH when an acid or case is added to it.
What does a buffer solution consist of?
A weak conj. acid-base pair. Either:
A weak acid + conj. base
A weak base + conj. acid
What is an oxide?
a compound which is the result of the reaction between a metal or non-metal with oxygen.
Which groups of oxides are basic?
1 and 2 (except Be + O)
They react with water to make a basic solution.
Example in picture
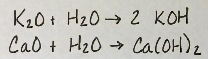
What makes a basic oxide?
It makes a hydroxide compound (or basic solution) when it reacts with water
What makes an acidic oxide?
Most acidic oxides are with nonmetals.
It forms an acidic solution when it reacts with water.
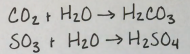
What happens when a basic oxide reacts with an acid and an acidic oxide reacts with a base?
They form an ionic compound and water.
Source:

What does it mean when something is amphoteric?
It means it has both acidic and basic properties.
Example: Water
Give an example of an amphoteric oxide.
AI2O3 (aluminum oxide)

What is a hydroxide?
element + OH
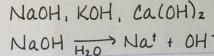
How does a neutral oxide form?
A neutral oxide is formed when the cation is from a strong base and an anion is from a strong acid.
Which groups make a basic hydroxide?
Group 1 and 2
Give an example of an amphoteric hydroxide
Al(OH)3
According to the periodic table, which directions does acidity increase in?
Acidity increases from left to right (due to electronegativity)
Increases from top to bottom (due to size)
What is the common ion effect?
The common ion effect describes the effect on equilibrium that occurs when a common ion (an ion that is already contained in the solution) is added to a solution. The common ion effect generally decreases solubility of a solute.
Basically, if you add another ion that already exists in the solution it makes it harder to dissolve. Like if you add too much tang to your water.

A homogeneous equilibrium
all species are present in the same phase
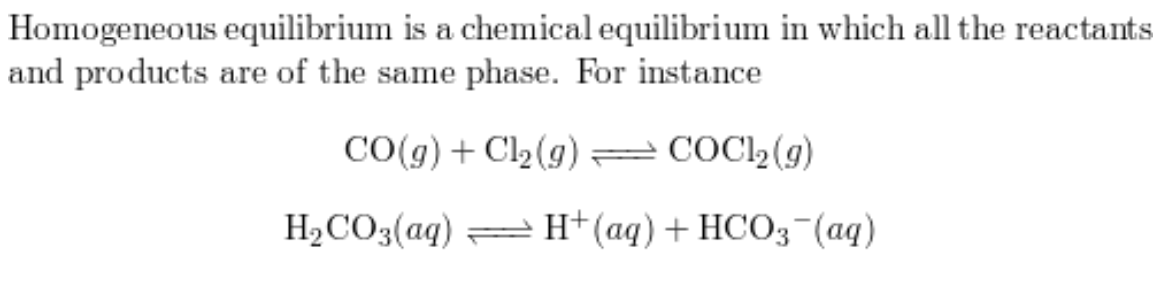
A heterogeneous equilibrium
species exist in more than one phase
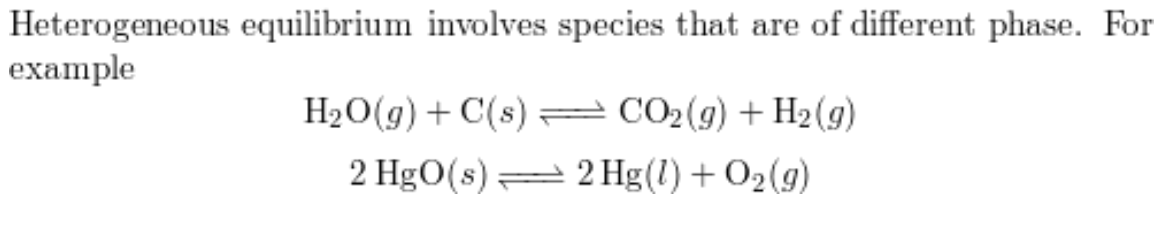
Le Chatelier's principle:
if a dynamic equilibrium is disturbed by changing the conditions, the position of equilibrium shifts to counteract the change to re-establish an equilibrium.
Basically, if stress is added to the equilibrium, the equilibrium will shift in response to the stress to remain balanced
According to Le Chatelier's principle:
What’ll happen if the concentration of the reactant increases?
Equilibrium will shift towards the decrease in the concentration of the reactants.
Equilibrium of the reaction shift towards the right.
According to Le Chatelier's principle:
What’ll happen if the concentration of the reactant decreases?
Equilibrium will shift towards the increase in the concentration of the reactants.
•Equilibrium of the reaction shift towards the left.
According to Le Chatelier's principle:
What’ll happen if If the product decreases?
Equilibrium of the reaction shift towards the right.
According to Le Chatelier's principle:
What’ll happen if If the product increases?
Equilibrium of the reaction shift towards the left.
As per Le Chatelier's principle, an increase in pressure or decrease in volume will ____?
At constant pressure, the addition of inert gas increases the volume, so it decreases the product formation.
At constant volume, the equilibrium remains undisturbed. It is because adding an inert gas at constant volume does not change the partial pressures.
What is a lewis base?
a substance that can donate a pair of electrons.
What is a lewis acid?
a substance that can accept a pair of electrons.
Shortcut for lewis acids and bases
Acid = Accepts
Base = Brings
Is CO2 classified as a Lewis acid/base?
Acidic, because of resonance
Is H2O a Lewis acid or base?
The oxygen in water has 2 lone pairs meaning that it’s a lewis base
Is I- a Lewis base or acid?
It’s a lewis base because it has excess electrons to donate.
Shortcut: if it’s a negative sign, it’s a lewis base. If it’s a plus, it’s a lewis acid.
Is NH3 a Lewis base or acid?
NH3 has a lone pair of electrons and is a Lewis base.
Is BCl3 a Lewis base or acid?
Acid. It’s electron deficient because it has a central atom

In the above reaction, 𝑨𝒍𝑪𝒍𝟑 is a Lewis acid and 𝑪𝒍−is a Lewis base.
Clue: If one has a sign, the other has the opposite label. E.g: if Cl- is a lewis base then AlCl3 is a lewis acid.

How does Ka determine the strength of an acid?
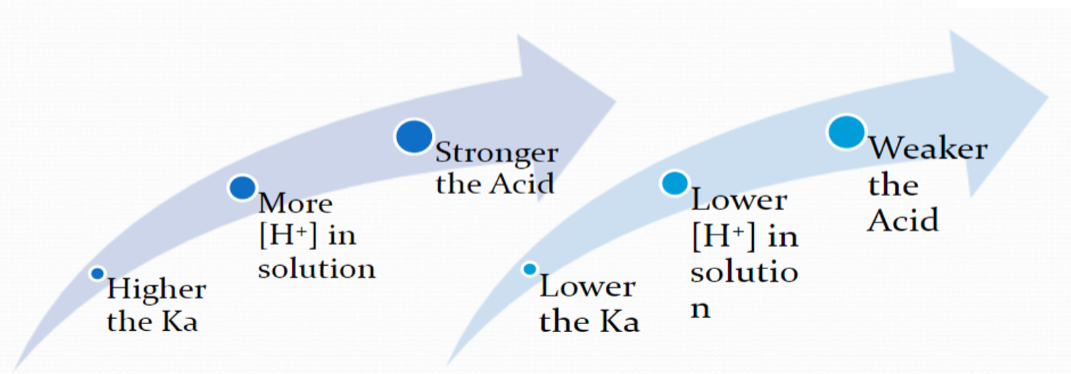
Ka formula (ice table)
Ka = [product]/[reactant]
What’s the formula for ionization % ?
(X (ice table) / [reactant initial concentration) x 100

What is the quadratic formula?
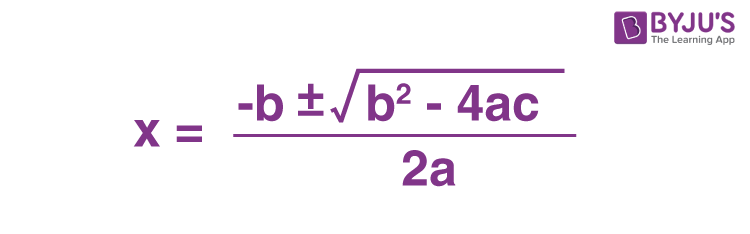
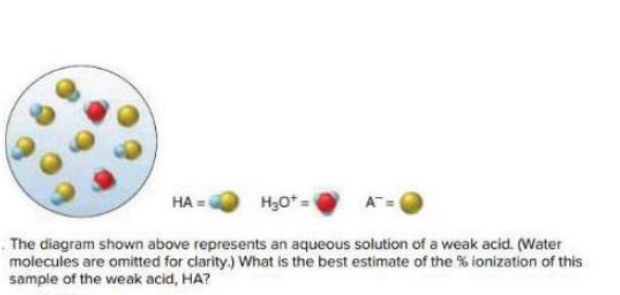
How do we find the ionization percentage from the total and the ionized from an illustration:
example:
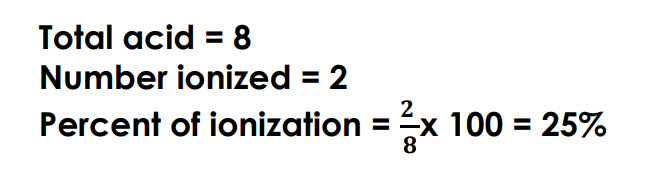
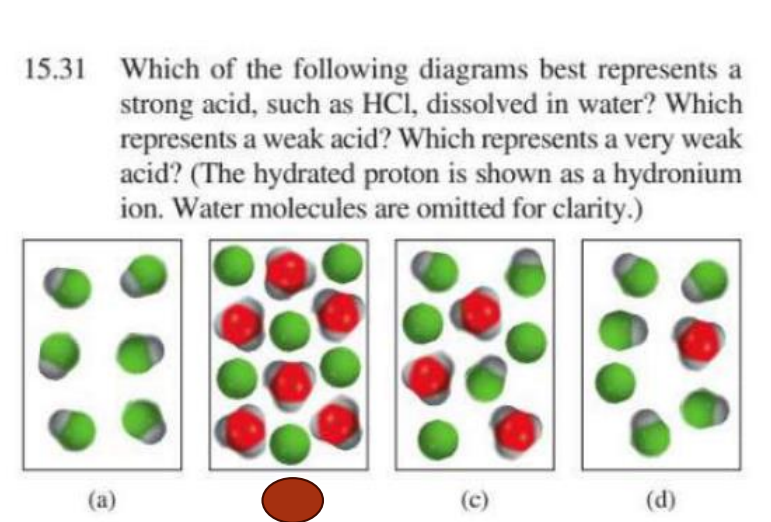
Explain why B is the correct answer here
B has an equal number of red and green indication total ionization (100%) which is a property of a strong acid
Shortcut for writing conjugate base
thanks chat gpt

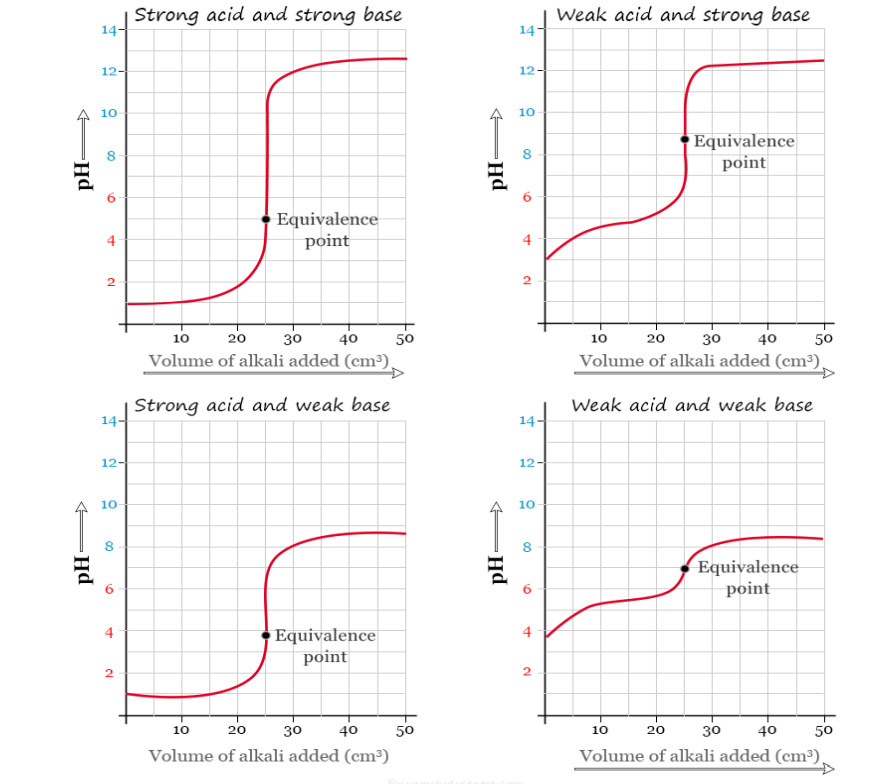
Explain how an acid-base indicator works in a titration.
A noticeable pH change occurs near the equivalence point of acid-base titrations and an indicator can be used to signal the end of a titration.
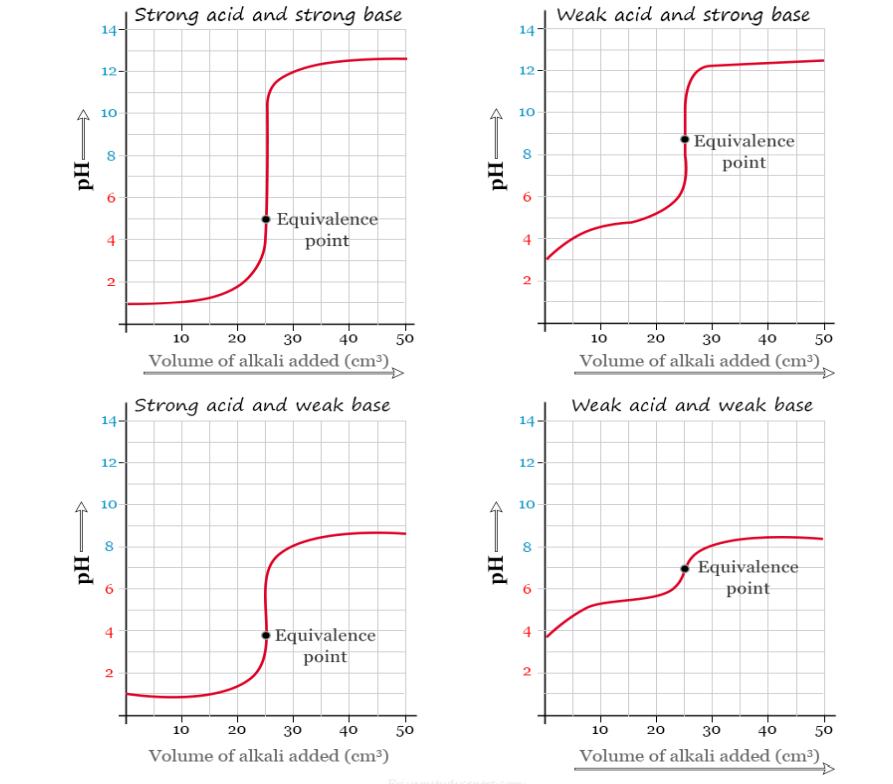
What are the criteria for choosing an indicator for a particular acid-base titration?
When selecting an indicator for acid-base titrations, choose an indicator whose pH range falls within the pH change of the reaction.
Examples of diprotic acids
Examples of such acids are carbonic acid 𝑯𝟐𝑪𝑶𝟑, sulfuric acid 𝑯𝟐𝑺𝑶𝟒 and chromic acid 𝑯𝟐𝑪𝒓𝑶𝟒.
What’s a diprotic acid?
An acid that is capable of donating two protons to other atoms are called diprotic acids.


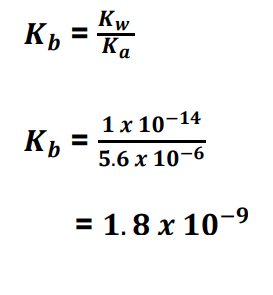
Brønsted-Lowry acid
A Brønsted-Lowry acid is any substance (molecule or ion) that can donate a hydrogen ion.
Brønsted-Lowry base
A Brønsted-Lowry base is any species that can accept a hydrogen ion (𝑯+)
Brønsted shorcut
Brønsted acids give away protons, while bases grab them.