Electronics - Chp 13
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Electrical conductor
materials that allow an electric current to pass through easily
Electrical insulators
materials that do not allow electricity to flow through them, they have high resistance
Semi-conductors
materials have resistance to electrical current between that of a conductor and insulator, can be used to control the flow of electricity; such as switching it on and off, or routing it in another direction
System
a combination of parts or components, working together to achieve a particular outcome, requires an input, process, and output
Input
causes the system to do something
Process
accepts the input and does something with it
Output
the result of the process
Electronic circuit
a system of electronic components that are connected together to perform a particular function
Switch
breaks or completes the circuit, stopping or allowing the flow of current, and changes the direction of motors
SPST switch
single pole, one switch can control a single circuit at a time
single throw, refers to the one output that can be powered
used to turn the circuit on and off

SPDT switch
single pole, one switch can control a single circuit at a time
double throw, refers to the two outputs that can be powered by one switch

DPST switch
double pole, one switch can control 2 circuits
single throw, refers to one output

DPDT switch
double pole, one switch can control 2 circuits
double throw, refers to the two outputs that can be powered by one switch
changes direction of the motor

DIP switch
row of on/off switches

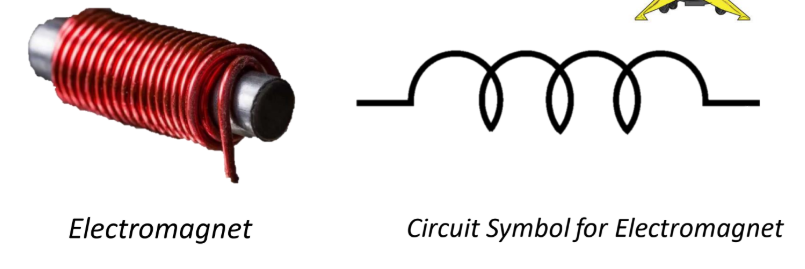
Electromagnet
made up of a copper coil wrapped around an iron bar
when the circuit is powered, the electromagnet is magnetised
Solenoid + Use
converts electric current into linear movement
a current passes through a coil of wire around an iron core
the iron core is magnetised and a metal bar is pulled into the centre of the coil
- solenoids are used to operate switches, or electronically lock doors
Relay + Use
electromagnet is magnetised and attracts the armature, which forces the switch contacts together
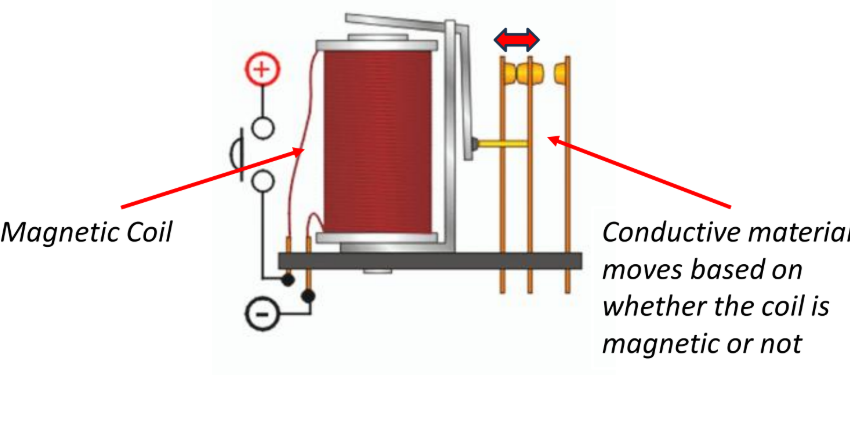
- used to safely turn on and off circuits that require very high electrical currents, opening and closing of security gates, raising and lowering high window blinds
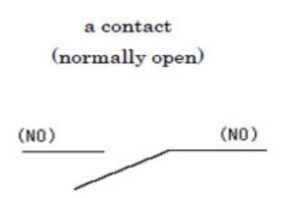
Electromagnet - a contact
normally open, off by default
when the coil is magnetised, it closes and conducts current
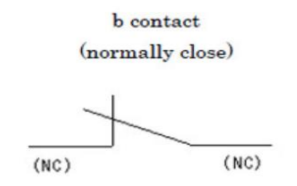
Electromagnet - b contact
normally closed, on by default
when the coil is magnetised, it opens and does not conduct current
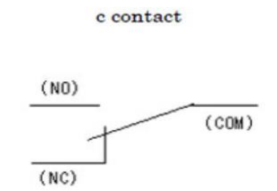
Electromagnet - c contact
a common switch is when a switch is connected to a NO (normally open) terminal and NC (normally closes) terminal, and it switches between the two when the coil is magnetised
Wire
used to connect the separate components in a circuit, connections between wires are made by soldering
Diode
semiconductor components which allow current to flow in one direction only
polarised component
Polarised component
it matters which way you connect them in a circuit, as they have an anode and a cathode
they are forward biased and will only conduct electricity when the anode is connected to the positive terminal, and the cathode is connected to the negative terminal
they are reverse biased and will not conduct electricity if connected the wrong way around
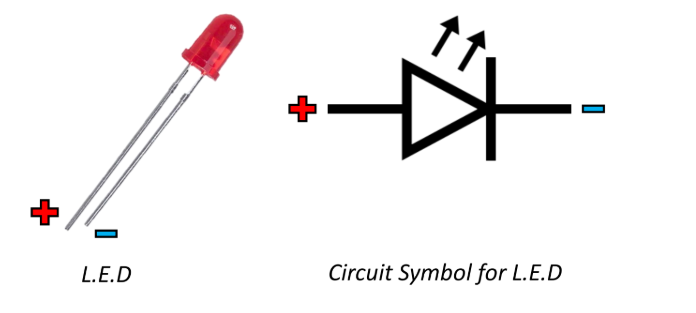
LED
light emitting diode, similar to diode but has a bulb in the middle which lights up when a current is passed through
the longer leg is the anode and the shorter leg is the cathode
the shorter cathode is next to the flat side of the LED
7 segment LED, is commonly used to form any number from 0-9
Capacitor
used to store electricity and then release it quickly
two pieces of metal are separated by an insulator
voltage is applied, and electrical charge is forced onto one plate and taken from the other
when the capacitor is fully charged it has the same voltage as the battery charging it
Capacitance
the measure of how much charge the capacitor can hold
What is capacitance measured in + with?
farads
multimeter
Capacitor Use
holds onto charge when the battery is disconnected, can be used in timing circuits
Types of capacitors + Functions
Fixed/non-electolytic/non-polarised capacitor
can be connected in any way in the circuit, usually very small
Electrolytic/polarised capacitor
forward biased, must be wired correctly
hold more cahrge thatn non-electrolytic capacitor, often used with resistors to create a time delay
Variable capacitor
capacitance can vary, usually by twisting a knob or screw, useful in adjustable timer devices
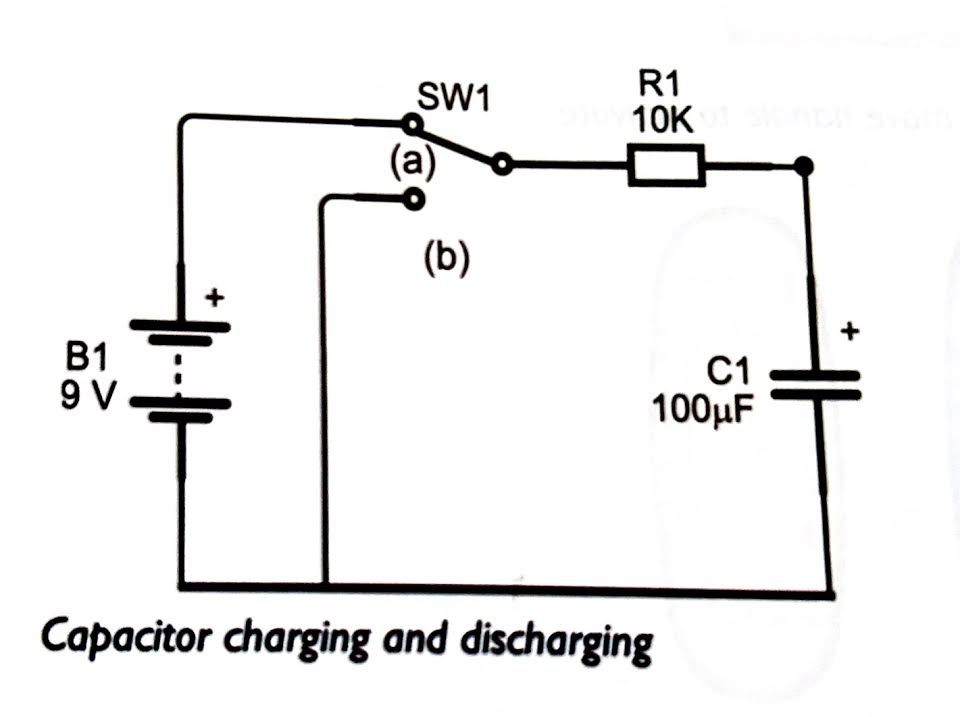
Capacitor circuit example:
switch is closed (position a), capacitor charges up until it reaches full capacitance
switch is opened (position b), resistor determines how quickly the capacitor discharges
Resistors
control the direction of current, divide, voltages, adjust signal levels, and slow down the current in a circuit
How to read the resistance on a resistor?


first band gives first digit
second band gives second digit
third band gives number of 0s
fourth band gives the tolerance
red is 2%
gold is 5%
silver is 10%
none is usually 20%
Resistor above
1000 × 0.05 = 50
Tolerance is between 1050-950 Ohms
What is the difference between a linear + non-linear resistor?
a linear resistance provides the same resistance once set
a non-linear resistor changes its resistance, eg changing it based on environmental factors; thermistor, light dependent resistor
Fixed resistor
resistance is set and cannot be changed
What is the difference between a variable resistor and a pentiometer?
physically the same, difference depending on how they are wired in the circuit
resistance can be adjusted by a knob, or using a screwdriver
when wired to centre terminal and one of the outer terminals, used as a variable resistor
when wired to all three terminals, centre takes in voltage
Variable resistors: Use
sets the sensitivity of the circuit
dimming switches
How does the resistance of an LDR change in different light levels?
light levels high → resistance low
light levels low → resistance high
Transistor
very sensitive electronic switches
they have three legs; emitter, base and collector
function as a high speed, automatic switch in a circuit or as an amplifier of current
Design a circuit which turns on a light when light levels are low
Design a circuit which turns on a light when light levels are high