EH2 Lecture 1 - Changing Patterns of Health and Disease
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
The scientific study of human populations with reference to:
- size
- composition
- distribution across places
- processes through which they change
Define "demography"
by birth, by in-migration
How can an individual enter a population?
by death, by out-migration
How can an individual leave a population?
number of births per 1000 population (per year)
Crude birth rate
Because it is not age-standardised,
because it includes all individuals rather than women who can have children
Why is crude birth rate an inaccurate representation of fertility?
15-44
What age range is cosidered child-bearing age?
"The number of children per woman"
Total fertility rate (TFR)
Women need to have on average 2.1 babies to maintain population size based on births
What is the replacement rate?
Yes, as this is an age-standardised measure
Can TFR be used to compare population growth betweeen countries? why/why not?
Age-specific fertility rates are the number of children per woman in a specified age bracket. The TFR is the sum of all ASFRs.
What is ASFR
from the 1930s there was a large spike in TFRs until the late 50s where there was a large drop,
the mid to late 60s were stable,
there was a sharp drop between 1970 and 1980 and TFRs have since sat below the replacement rate, though increasing since the low of 2001
What have been the general trends in TFRs since the 1930s
Crude death rate (CDR),
Infant mortality rate (IMR),
child mortality rate
What are the 3 commonly reported categories of mortality rates?
Infant mortality rates are the deaths per 1000 live births in a given year before said individuals reach 1 year of age
Define IMR
Child mortality rates are the deaths per 1000 live births in a given year for children between 1 and 5 years of age. This is often reported together with IMR as deaths per 1000 live births for children aged 5 or below
Define child mortality rate
82%
What proportion of deaths under 5 years of age occur during infancy?
A country's level of health development
What are infant and child mortality rates good indicators of?
socioeconomic factors (housing, hygiene, sewage & waste disposal, nutrition, etc.)
Health care factors (poor access to primary health care and hospital services surrounding pregnancy and birth, immunisation, etc.)
Name two factors influencing infant and child mortality rates
62% occur during the neonatal period
Within infant mortality rates, during what stage do most deaths occur?
within 28 days from birth
During what ages is an infant considered a neonate?
It allows for healthcare initiatives to target high risk areas/ages.
Why is knowing all these statistics surrounding child deaths important?
perinatal conditions,
congential abnormalitites,
signs, symptoms, abnormalities,
other causes
List 4 causes of infant death in descending percentage
Because they are not age-standardised. Age-specific death rates (ASDR) are a better representation of mortality trends in a population
Why are CDRs not a good reflection of the death rates of a population? What might be a better measurement?
Ischaemic heart disease (heart attacks),
Dementia and Alzheimer's,
Cerebrovascular Diseases (strokes),
trachea, bronchus, and lung cancer,
chronic lower respiratory diseases (eg emphysema)
What are the current 5 leading causes of death (current as of 2013)
fertility,
mortality,
migration
Which big 3 factors produce population stability and change?
Population pyramid
What is this data representation called?
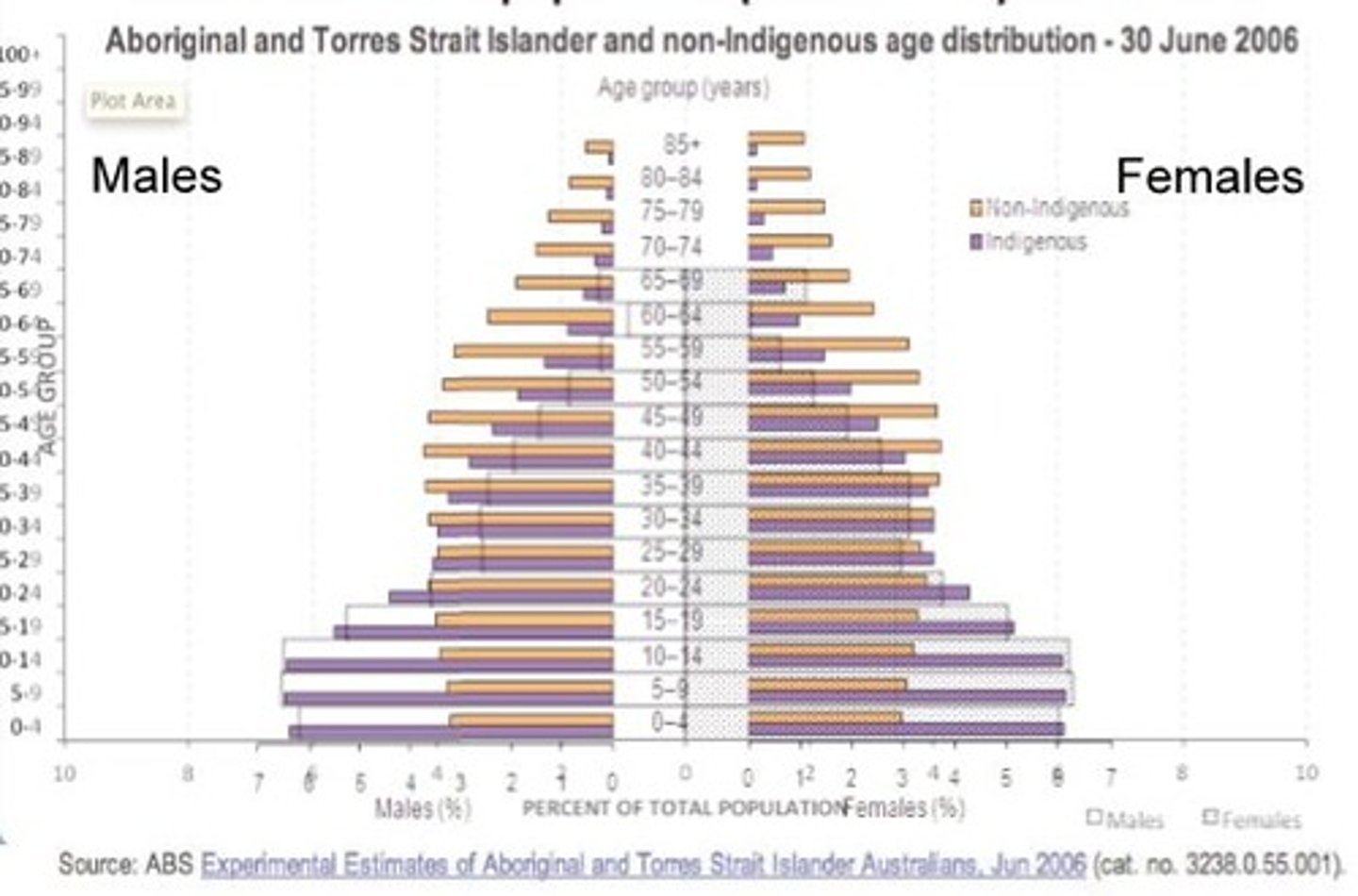
immigration
What is the current largest contributor to Australia's population growth?
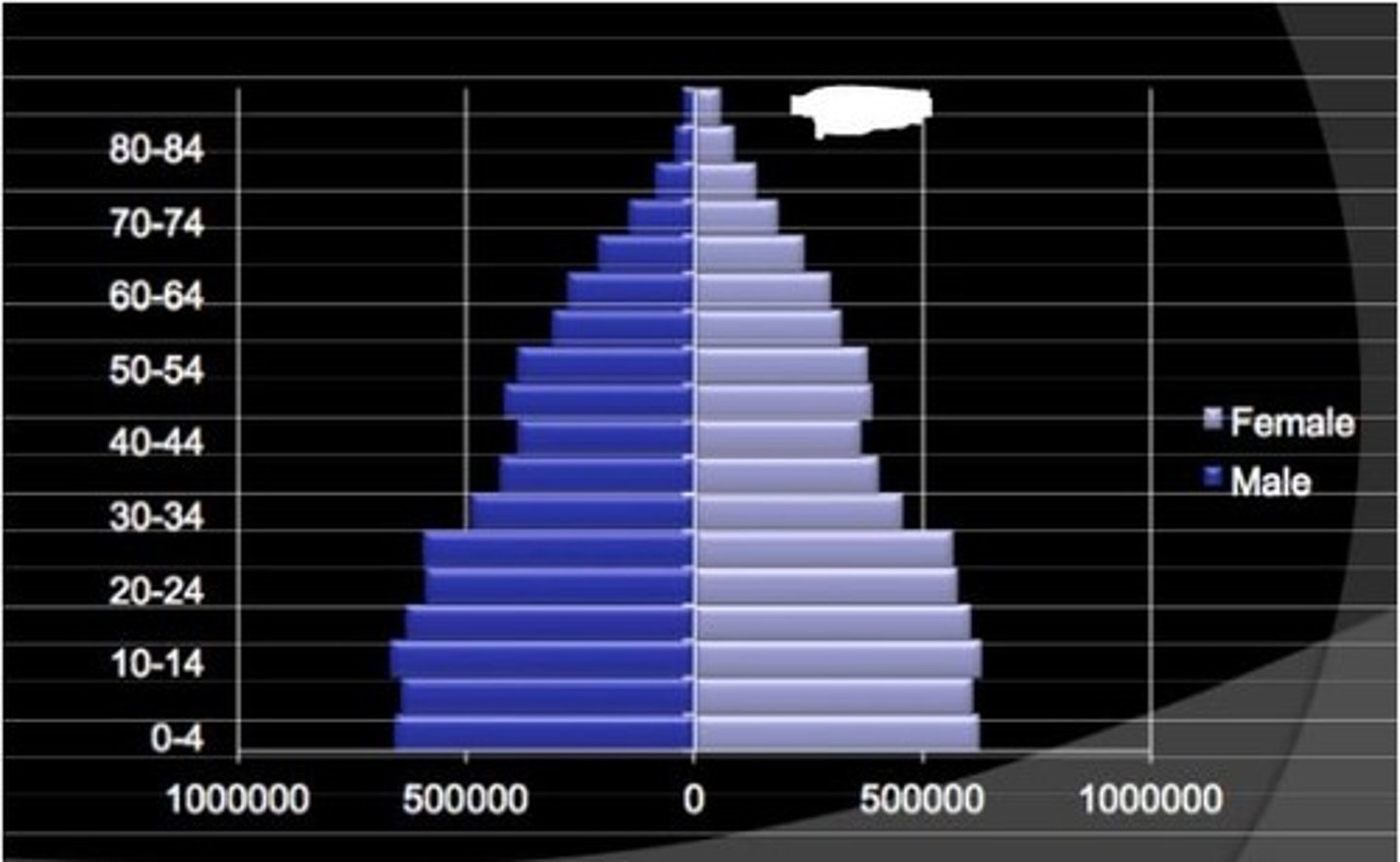
stable
What is this pattern called?
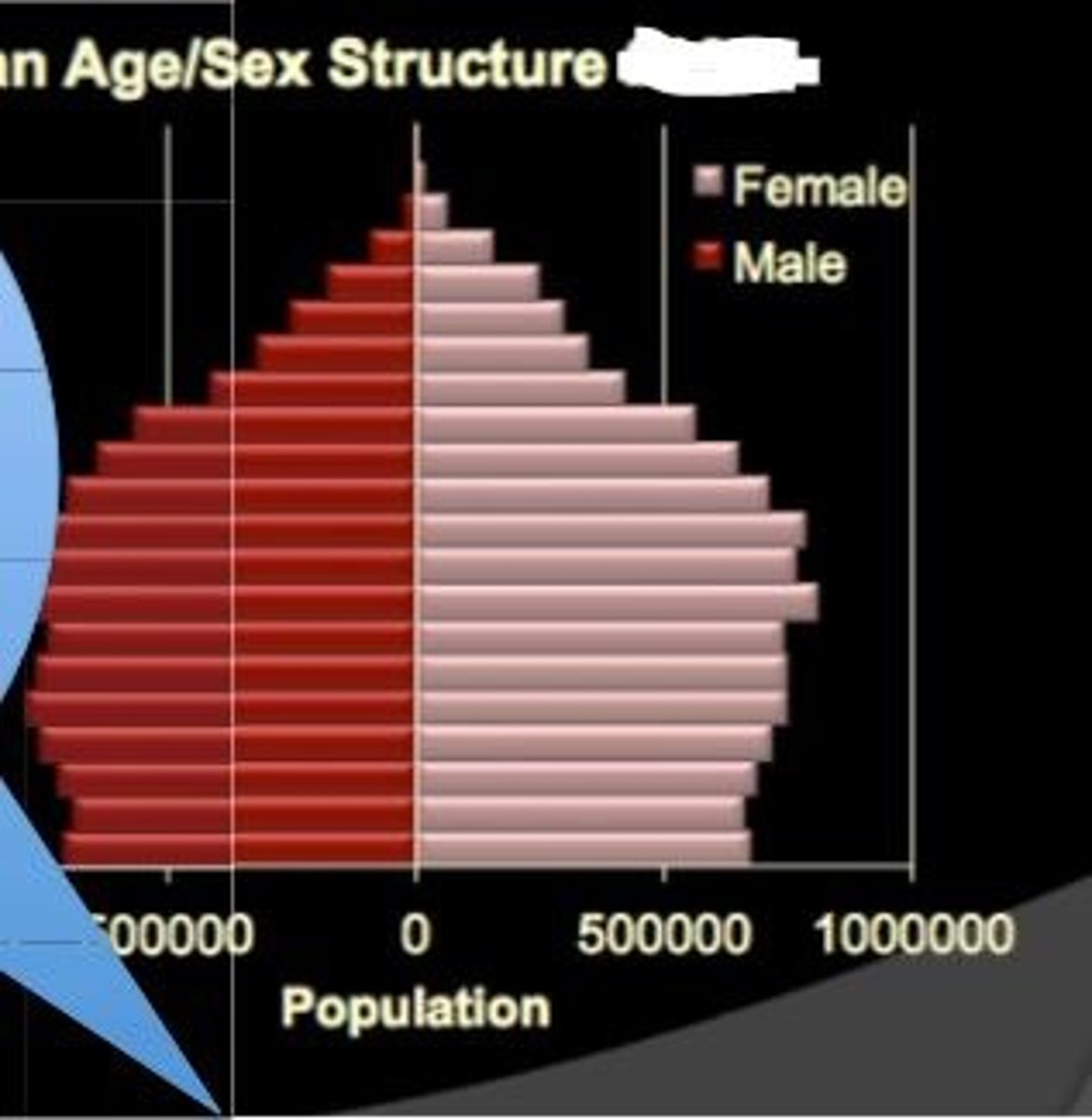
expanding
What is this pattern called?

contracting
What is this pattern called?
This term describes a shift from the 18th century from
pandemic and infectious diseases causing the majority of deaths to non-communicable diseases (ncd). This was more due to the conquest of infectious diseases, rather than the rise of degenerative disease.
This shifted the majority of deaths from the young to the old
Describe the epidemiological transition
tuberculosis,
organic heart disease,
diarrhoea,
senility,
bronchitis,
pneumonia
Name some of the main causes of death before the epidemiological transition
ischaemic heart disease,
dementia,
stroke,
lung cancer,
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD),
diabetes,
bowel cancer
Name some of the main causes of death since the epidemiological (aka health) transition
better living standards,
improvements in hygiene,
antibiotics,
mass immunisation,
progress of medical knowledge and skills
What are some of the contributing factors to the epidemiological shift?
1. age of pestilence and famine
2. age of receding pandemics
3. age of degenerative and man-made diseases
4. age of delayed degenerative diseases
5. age of emergent and re-emergent infections
What are stages 1 to 5 of the epidemiological transition model?
tuberculosis,
rubella (measles),
pertussis (whooping cough)
Name 3 re-emerging diseases
ebola,
legionaires diseases,
AIDS,
gastric ulcers (due to helicobacter pylori)
Name 4 "emerging" diseases
- doesn't account for emerging and re-emerging diseases
- doesn't account for co-existence of chronic and infectious diseases ("double-burden") and the relationship between them (eg. chronic diseases increases risk of infection)
-fails to recognise that degenerative diseases have always been present, but simply were noticed less
What are some of the flaws of the epidemiological transition theory?
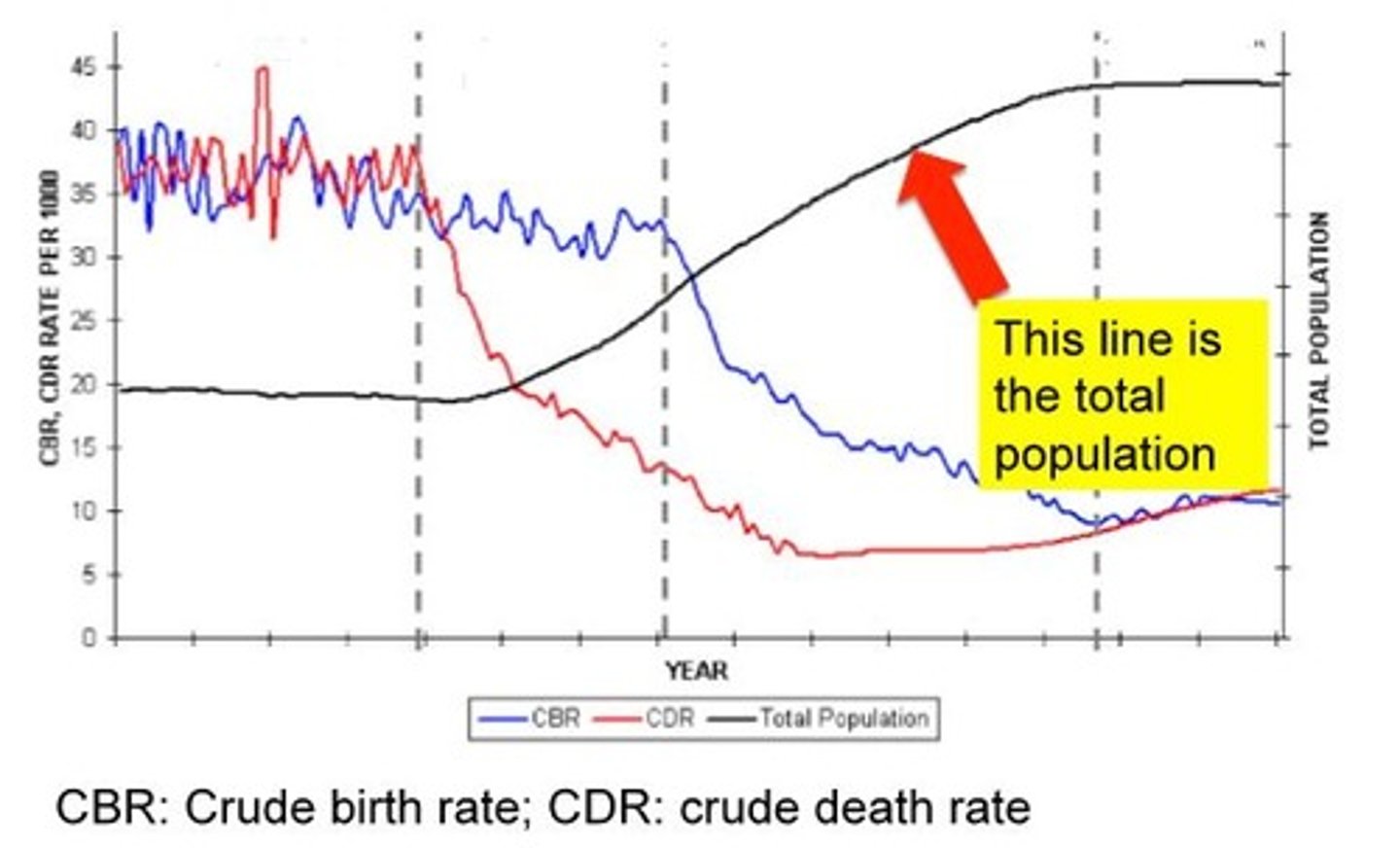
This describes how births and deaths affect population growth over time. These are affected by social and economic factors. The model describes how developing populations move from high fertility and mortality patterns to stabilisation of both rates as they become more modern
Describe the demographic transition model
1. pre-industrial stage/pre-modern (high birth, high death, slow growth)
2. urbanising/industrialising (sharp population increase due to high births but falling death rates)
3. mature industrial (birth rates drop, death rates stabilise, some population growth)
4. post industrial (population stabilises with steadying death and birth rates at low levels)
Describe the graph and the 4 stages of the demographic transition model
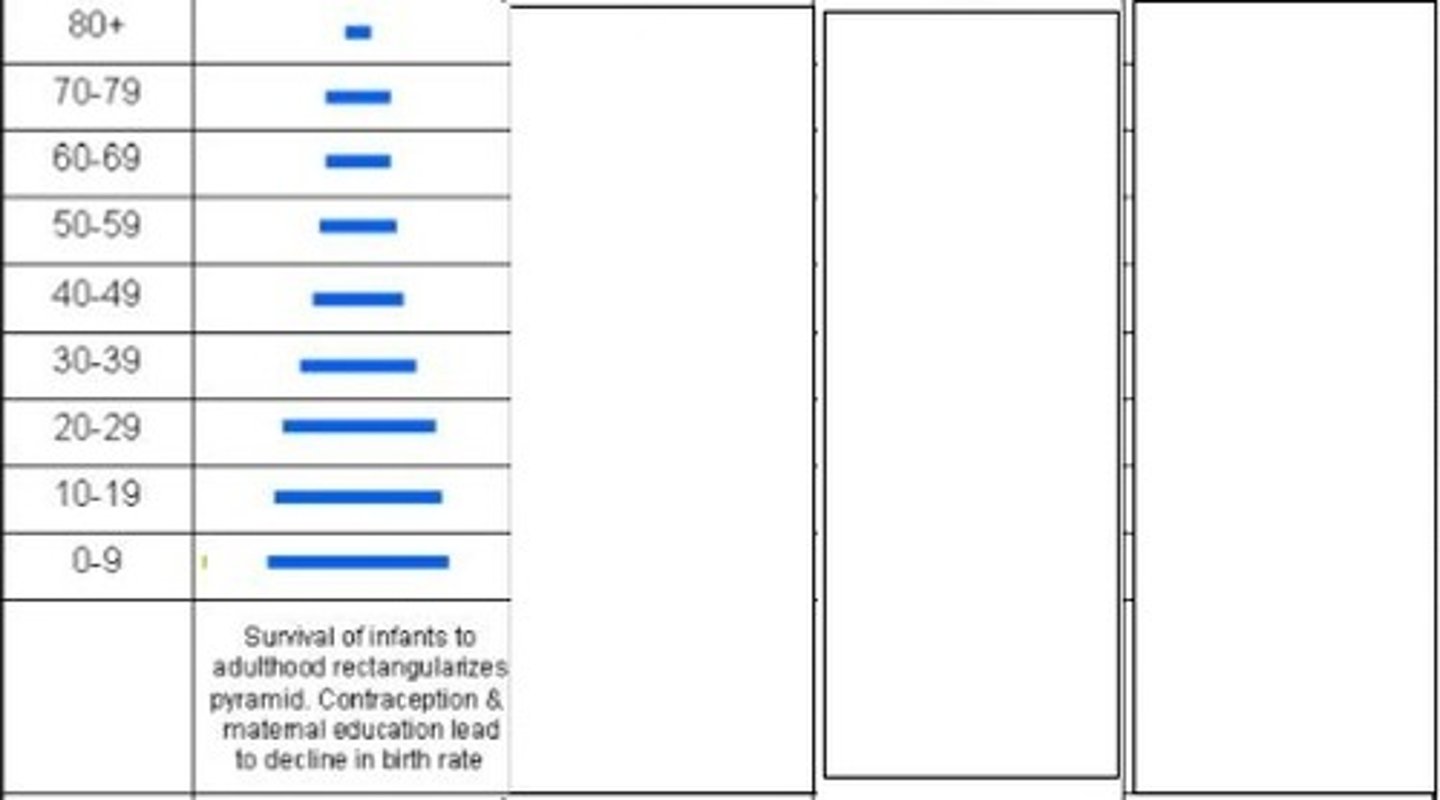
2 - industrialising
Which stage of the demographic transition model is represented here?
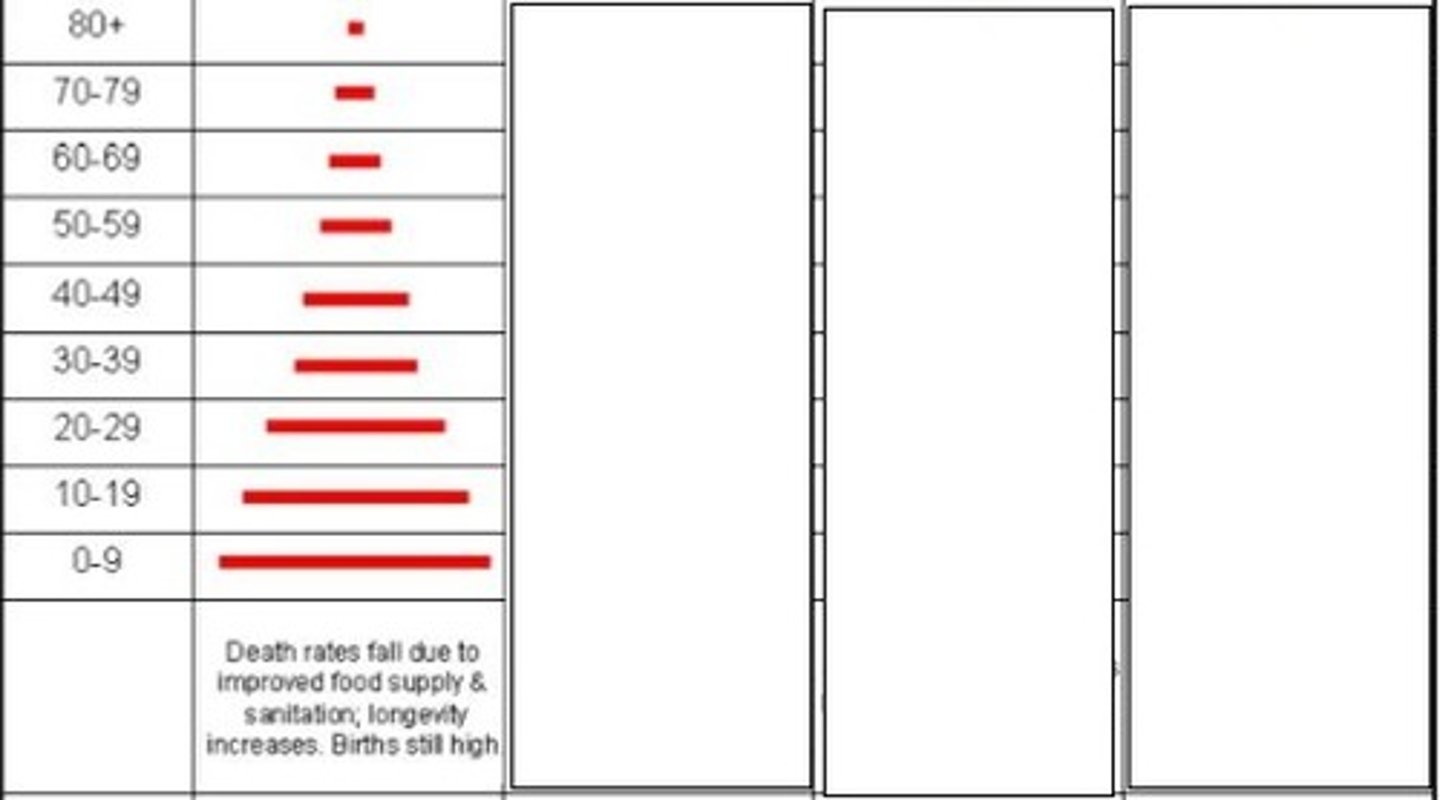
1 - pre-industrial
Which stage of the demographic transition model is represented here?
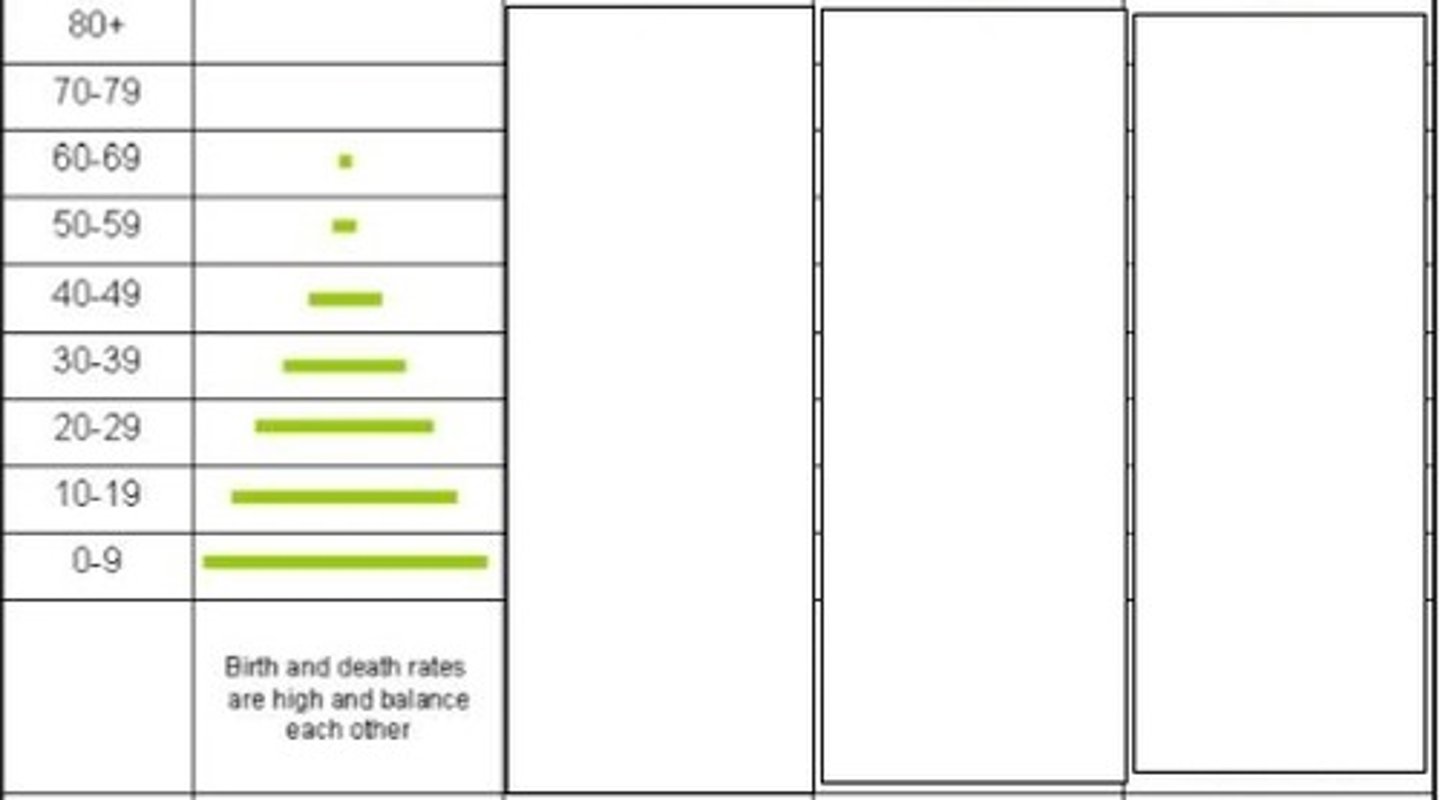
4 - post-industrial
Which stage of the demographic transition model is represented here?
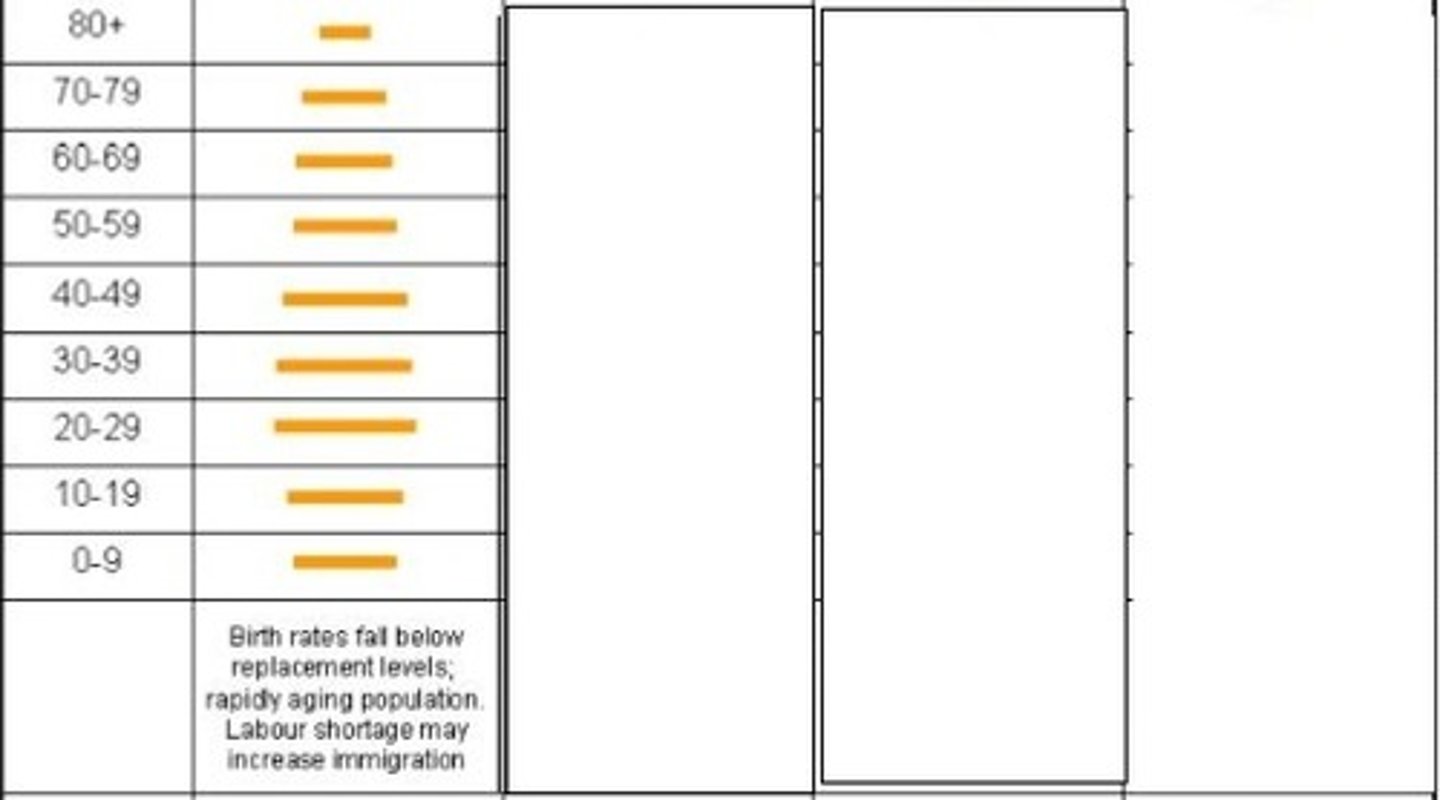
3 - mature industrial
Which stage of the demographic transition model is represented here?
high birth rates, high death rates, high infant mortality, high out-migration
Comment on fertility, deaths, migration, and infant mortality trends for developing countries
low fertility, low death rates, in-migration from less developed countries, low infant mortality
Comment on fertility, deaths, migration, and infant mortality trends for developed countries
lowering fertility rates
Which demographic trend is hardest to explain?