Comprehensive Guide to Joints: Types, Movements, and Structures in Anatomy
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Articulation
Site where two or more bones meet
Functions of joints
Give skeleton mobility and hold skeleton together
Functional classification of joints
Based on the amount of movement joint allows
Synarthroses
Immovable joints that can be fibrous or cartilaginous
Amphiarthroses
Slightly movable joints that can be fibrous or cartilaginous
Diarthroses
Freely movable joints that are all synovial joints
Structural classification of joints
Based on material binding bones together and presence/absence of joint cavity
Fibrous joints
Bones held together by dense connective tissue with no joint cavity
Cartilaginous joints
Bones joined by cartilage and lack joint cavity
Synovial joints
Bones joined by ligaments with fluid-filled joint cavity separating bone surface
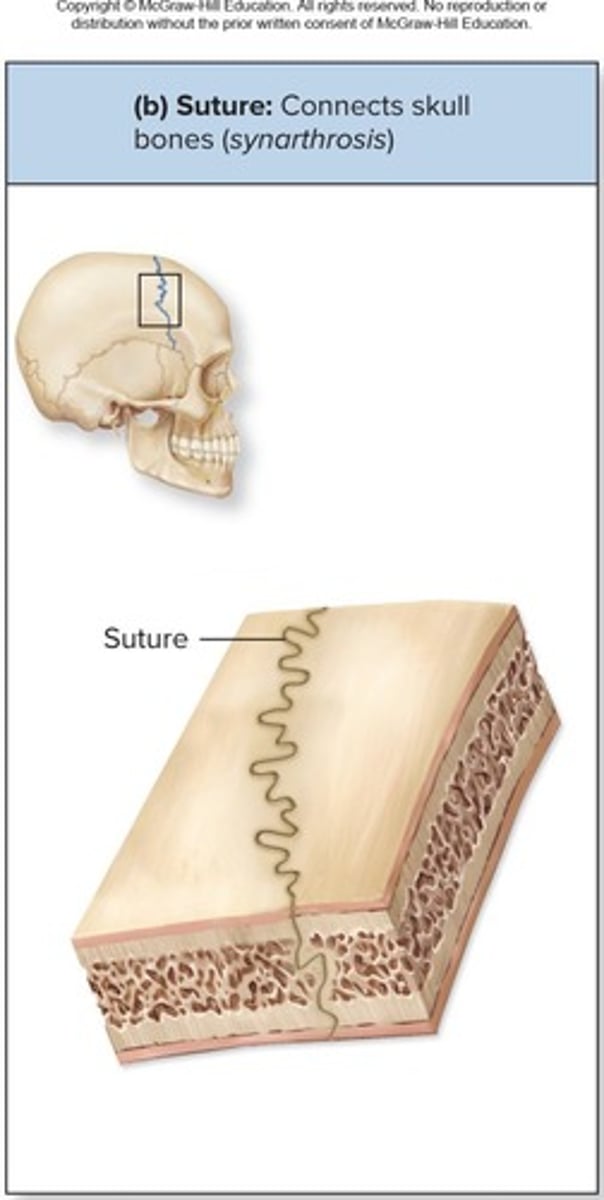
Fibrous Joints: Sutures
Rigid, interlocking joints that are immovable for protection of the brain
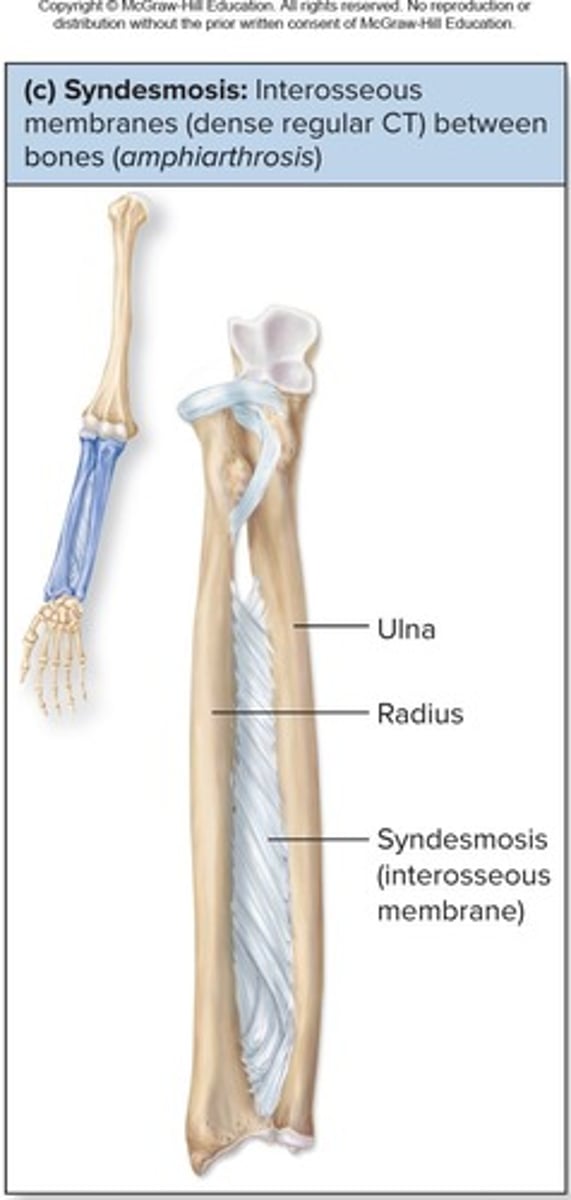
Fibrous Joints: Syndesmoses
Bound by interosseous membrane, allowing little to no movement
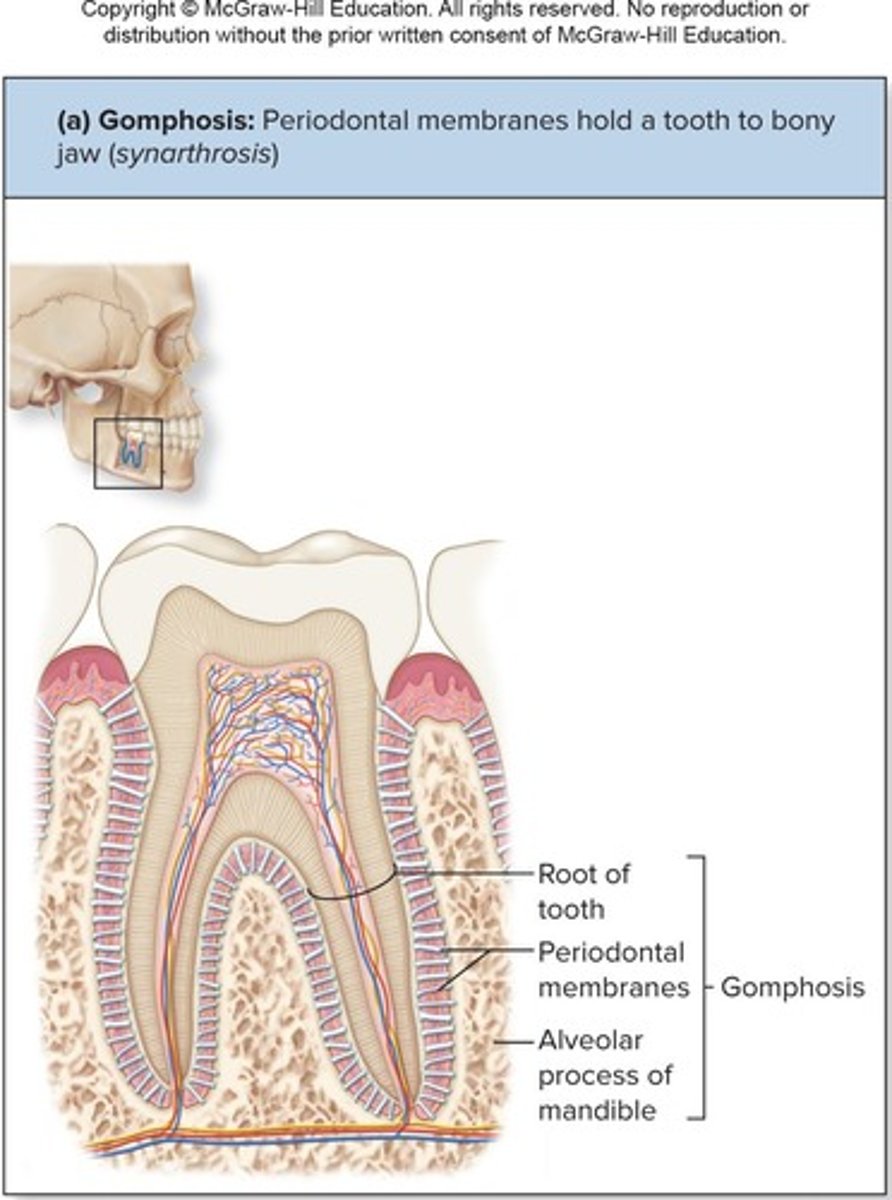
Fibrous Joints: Gomphoses
Peg-in-socket joints of teeth in alveolar sockets
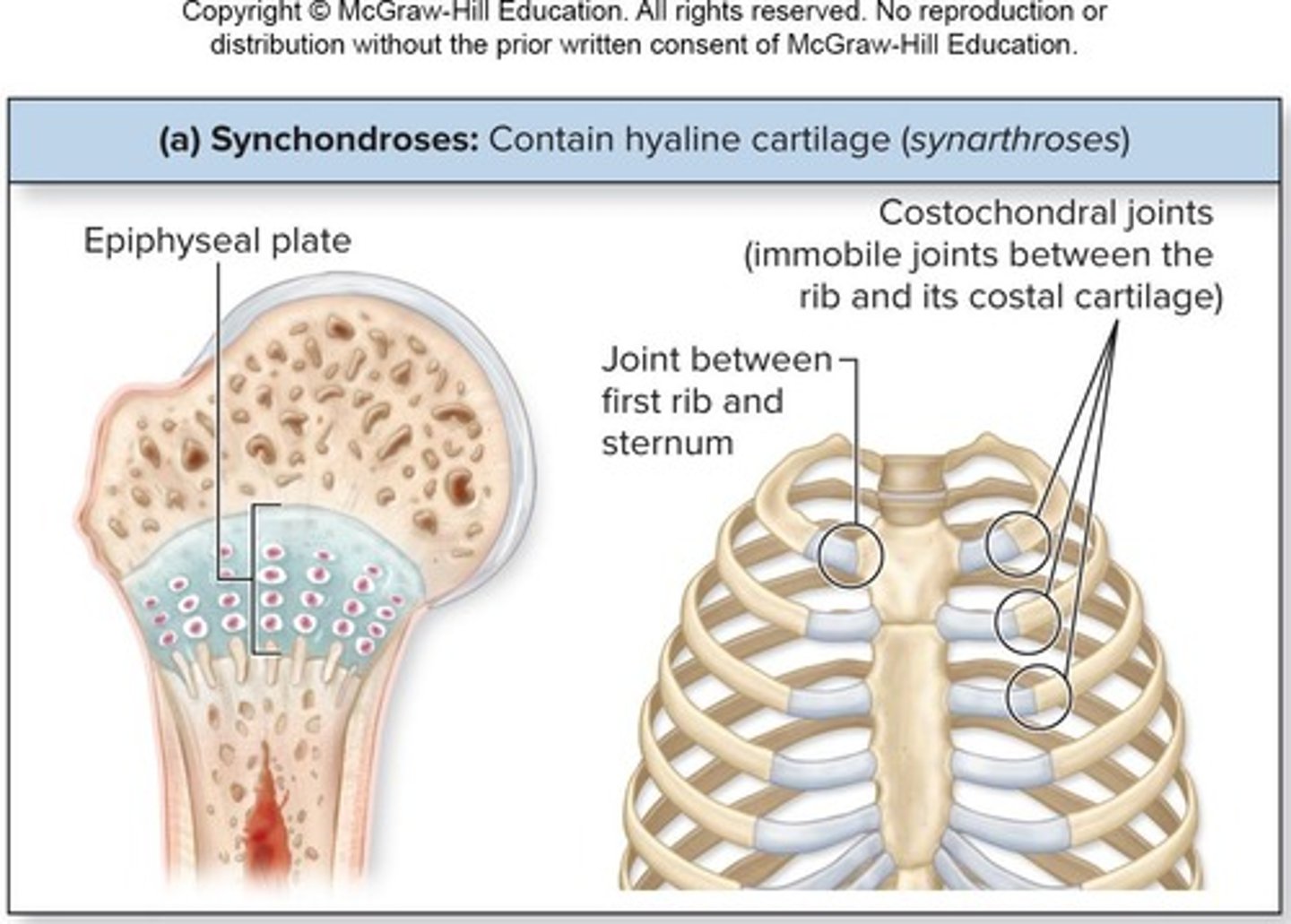
Cartilaginous Joints: Synchondroses
Bar/plate of hyaline cartilage unites bones and are all synarthrotic
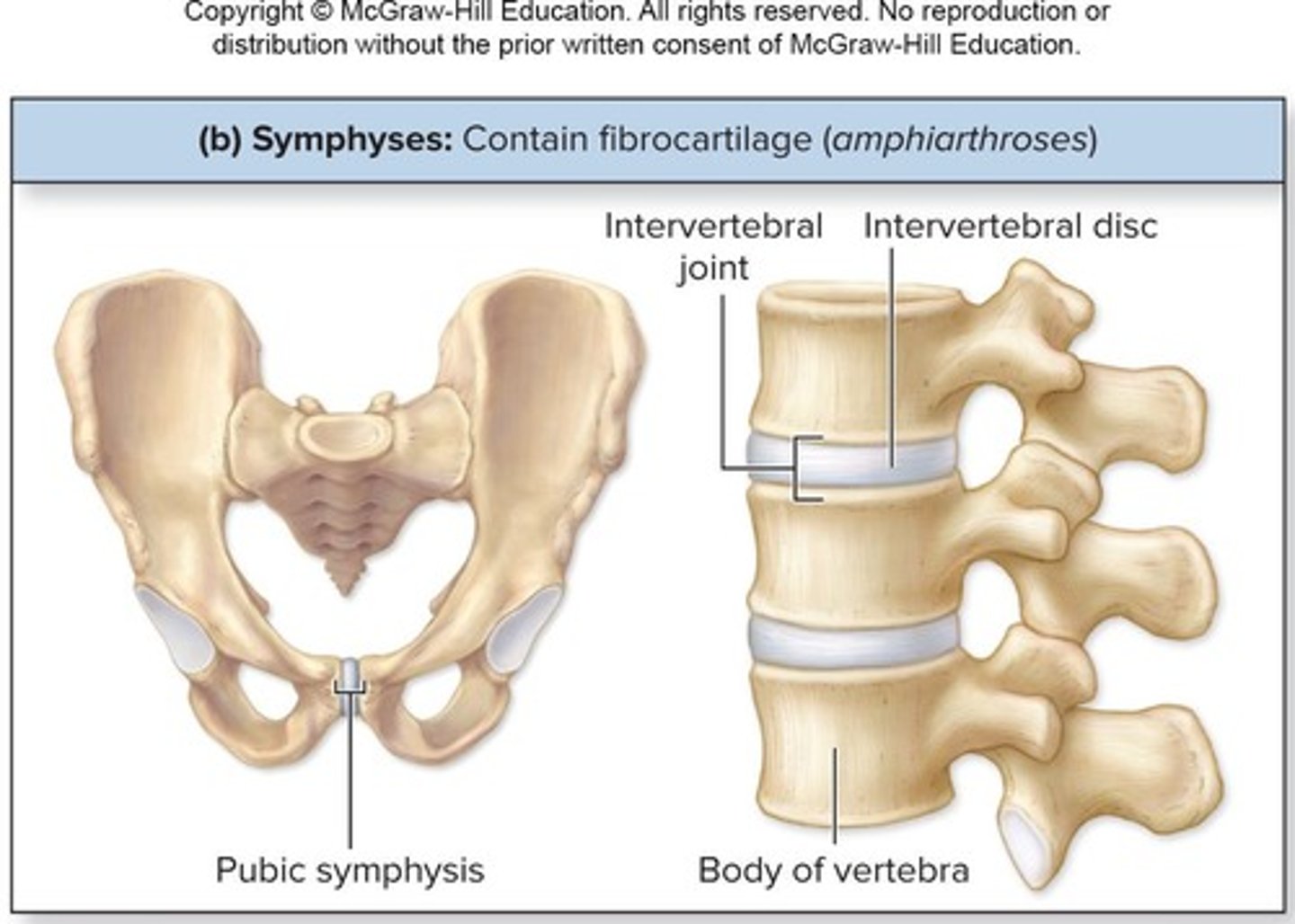
Cartilaginous Joints: Symphyses
Pads of fibrocartilage between articulating bones that allow slight mobility
Synovial Joints: Six Distinguishing Features
Include articular cartilage, joint cavity, articular capsule, synovial fluid, ligaments, nerves, and blood vessels
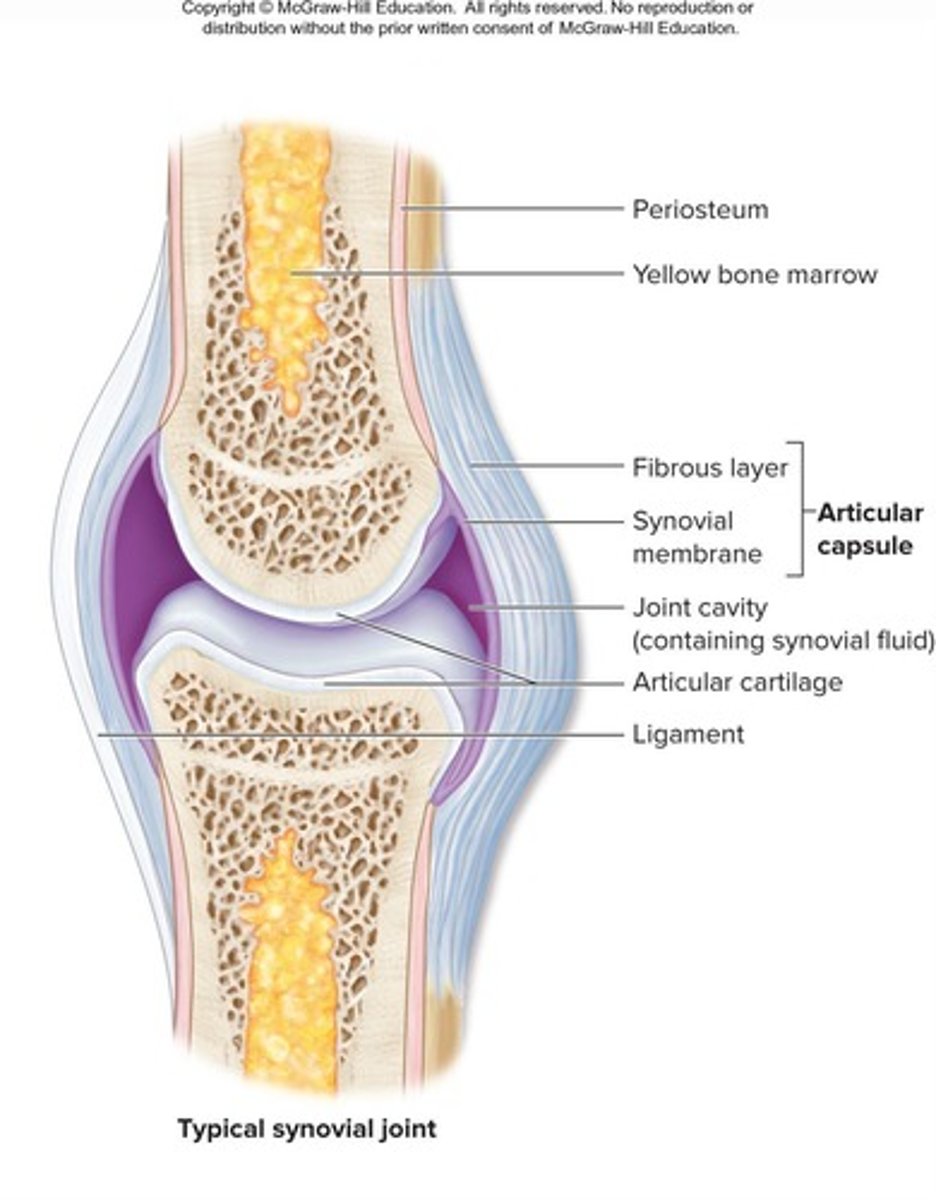
Articular cartilage
Hyaline cartilage on bone surface at joint that prevents crushing of bone ends
Joint (synovial) cavity
Small, fluid-filled potential space lined by synovial membrane
Articular (joint) capsule
Outer fibrous layer that strengthens joints to prevent bones being pulled apart
Synovial fluid
Viscous, oily substance that lubricates articular cartilage on articulating surfaces, nourishes and removes wastes from articular cartilage's chondrocytes, contains phagocytic cells to remove microbes and debris, and acts as a shock absorber.
Capsular ligaments
Thickened part of fibrous layer that reinforces synovial joints.
Extracapsular ligaments
Ligaments located outside the capsule of a synovial joint.
Intracapsular ligaments
Ligaments that are deep to the capsule and covered by synovial membrane.
Nerve fibers in synovial joints
Detect pain, monitor joint position, and stretch.
Capillary beds in synovial joints
Supply filtrate for synovial fluid.
Fatty pads
Cushioning material located between the fibrous layer and synovial membrane or bone, acting as protective packing material in joint periphery.
Articular discs (menisci)
Fibrocartilage structures that separate articular surfaces to improve the fit of bone ends, stabilize the joint, and reduce wear and tear.
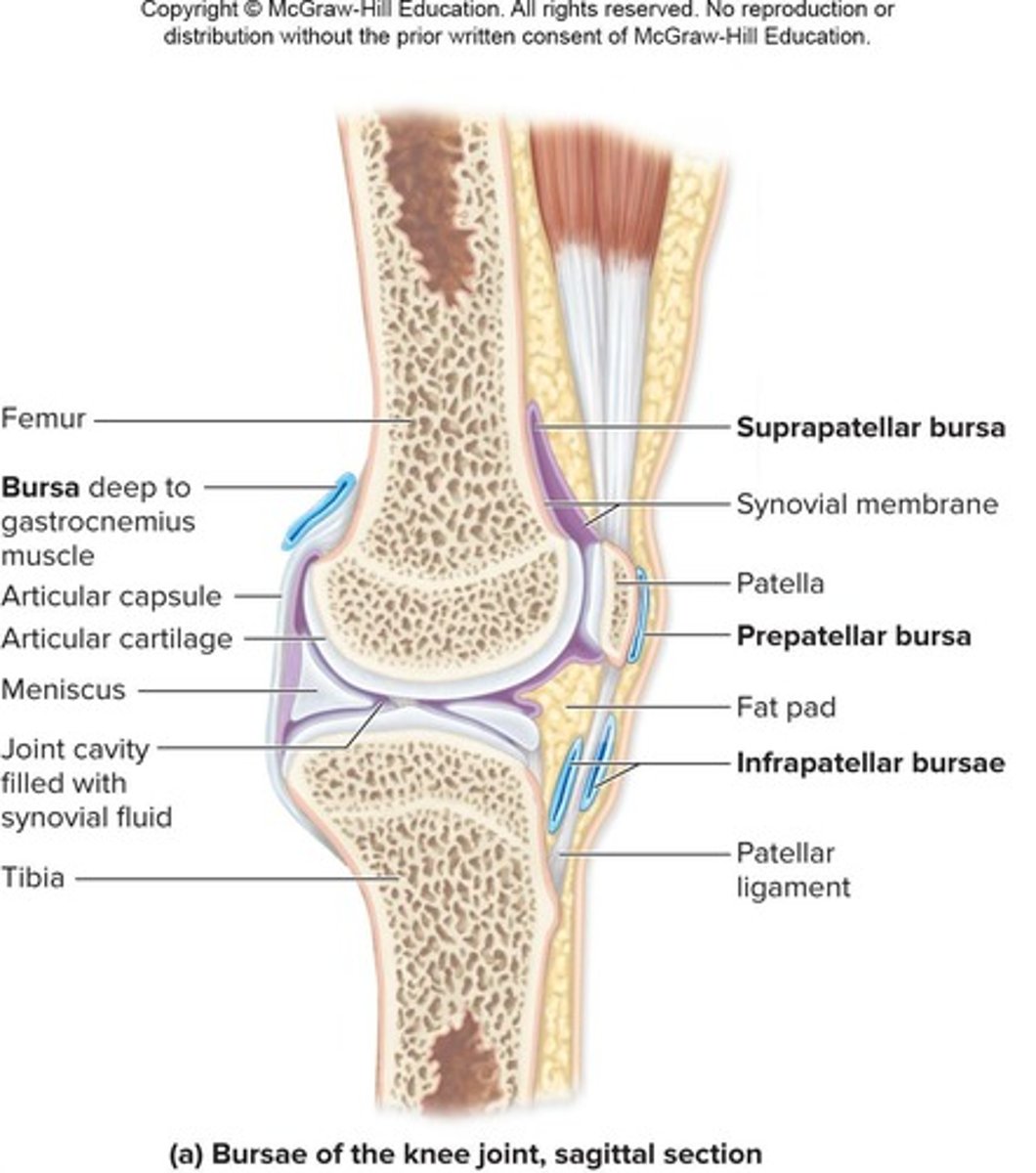
Bursae
Sacs lined with synovial membrane that contain synovial fluid, reducing friction where ligaments, muscles, skin, tendons, or bones rub together.
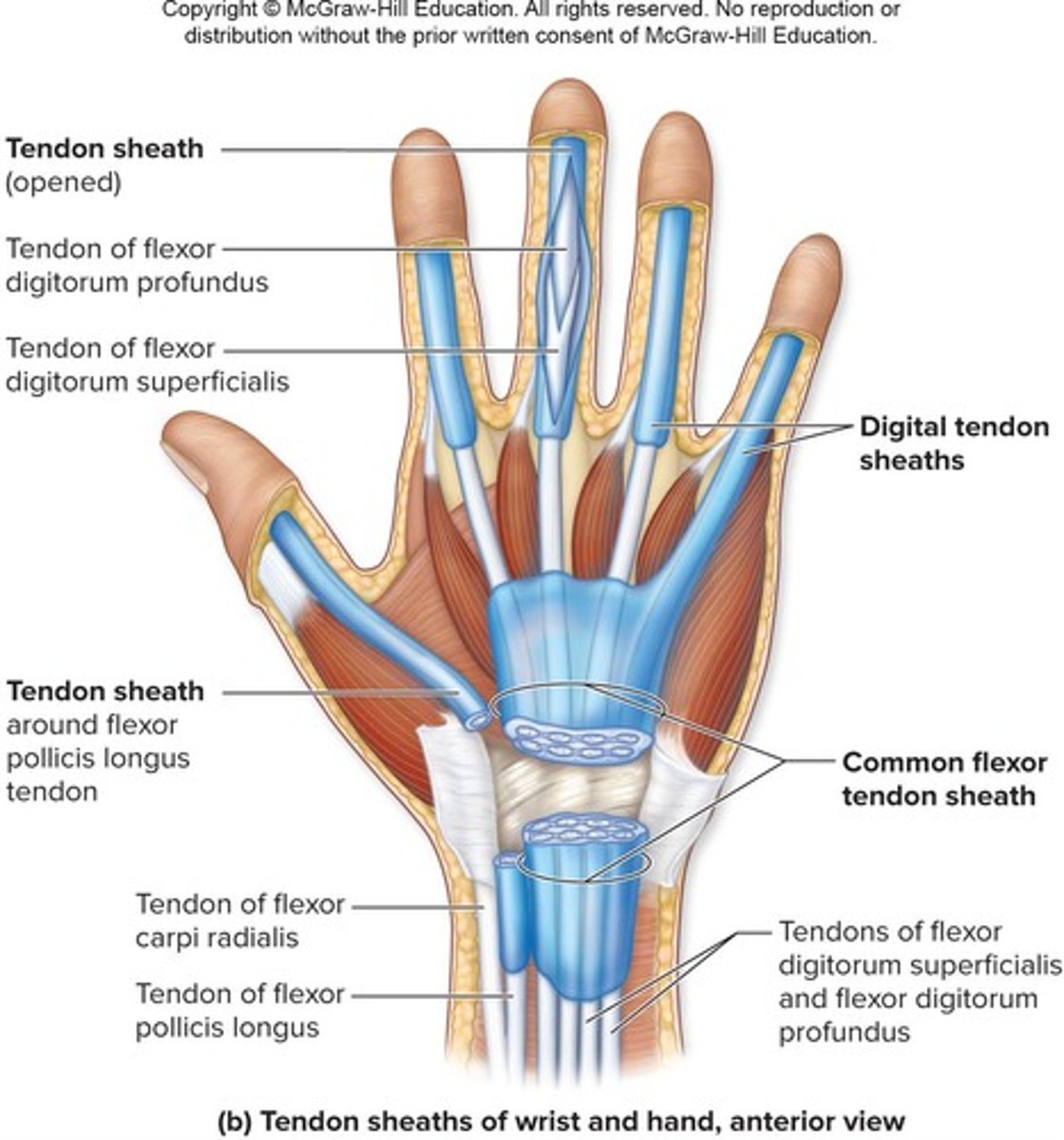
Tendon sheaths
Elongated bursae wrapped completely around tendons subjected to friction.
Stabilizing factors at synovial joints
Shapes of articular surfaces, ligament number and location, and muscle tendons that cross the joint.
Muscle tone
Keeps tendons taut and is extremely important in reinforcing shoulder and knee joints and arches of the foot.
Origin
Attachment point of a muscle to an immovable bone.
Insertion
Attachment point of a muscle to a movable bone.
Synovial joint movements
Movements occur along transverse, frontal, or sagittal planes.
Nonaxial movement
Slipping movements only, without rotation around an axis.
Uniaxial movement
Movement in one plane or axis.
Biaxial movement
Movement in two planes or axes.
Multiaxial movement
Movement in multiple planes or axes.
Plane joint
Articular surfaces are flat, allowing for limited side-to-side gliding movement in a single plane.
Hinge joint
Joint where a convex surface fits within a concave depression, allowing uniaxial movement like the hinge of a door.
Pivot joint
Joint where a bone with a rounded surface fits into a ligament ring, allowing uniaxial rotation on a longitudinal axis.
Condylar joint
Joint with an oval, convex surface articulating with a concave surface, allowing biaxial movement.
Saddle joint
Joint with convex and concave surfaces resembling a saddle shape, allowing biaxial movement.
Ball-and-socket joint
Joint where a spherical head of one bone fits into a cuplike socket, permitting multiaxial movement and is the most freely mobile type of joint.
Gliding movements
Two opposing surfaces sliding back-and-forth or side-to-side, allowing only limited movement in any direction.

Angular movements
Movements that increase or decrease the angle between two bones, including flexion, extension, hyperextension, lateral flexion, abduction, adduction, and circumduction.
Medial rotation
Turns anterior surface of bone medially
Lateral rotation
Turns anterior surface of bone laterally
Pronation
Medial rotation of forearm so palm of hand posterior
Supination
Lateral rotation of forearm so palm of hand anterior
Dorsiflexion
Talocrural (ankle) joint bent so the dorsum (superior surface) of foot moves toward the leg
Plantar flexion
Talocrural joint bent so dorsum pointed inferiorly
Eversion
Sole turns laterally at intertarsal joints of foot
Inversion
Sole turns medially at intertarsal joints of the foot
Protraction
Anterior movement from anatomic position
Retraction
Posterior movement from anatomic position
Depression
Inferior movement of a body part
Elevation
Superior movement of a body part
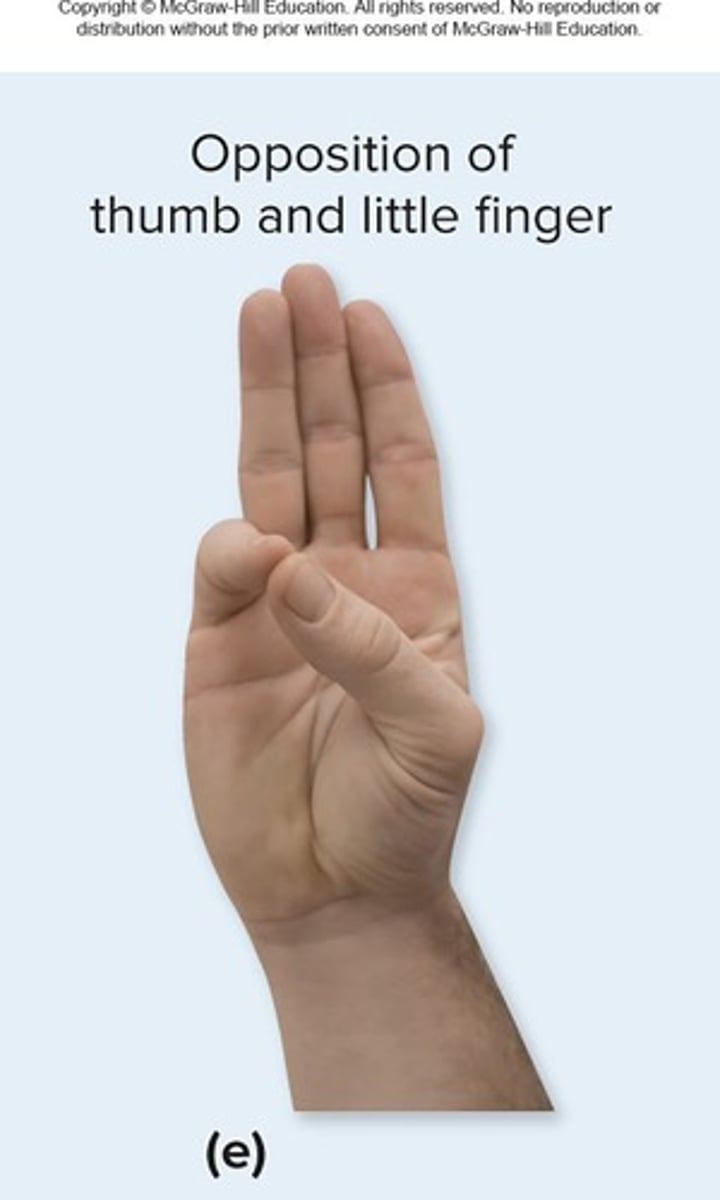
Opposition
Movement of thumb toward tips of fingers at carpometacarpal joint

Reposition
Opposite movement of opposition
Gliding joint
Joint allowing side-to-side (lateral excursion) grinding of teeth
Articular disc
Partitions joint into two parts forming two synovial cavities
Fibrocartilaginous glenoid labrum
Encircles socket of shoulder joint
Ulnar collateral ligament
Stabilizes medial side of the elbow joint
Radial collateral ligament
Stabilizes joint at lateral surface of elbow
Anular ligament
Surrounds the neck of the radius, binding head of the radius to the ulna
Iliofemoral ligament
Ligament providing support for anterior articular capsule of hip joint
Ischiofemoral ligament
Intracapsular ligament posteriorly located in hip joint
Pubofemoral ligament
Triangular thickening of capsule's inferior region in hip joint
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
Prevents hyperextension and anterior displacement of tibia
Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
Prevents hyperflexion and posterior displacement of tibia
Femoropatellar joint
Plane joint
Allows gliding motion during knee flexion
Lateral and medial tibiofemoral joints
Femoral condyles with lateral and medial menisci of tibia
Allow flexion, extension, and some rotation when knee partly flexed
Quadriceps femoris muscle tendon
Passes over knee's anterior surface, surrounds patella
Patellar ligament
Extends from patella to tibial tuberosity
Fibular collateral ligament
Reinforces lateral surface of joint
Extends from femur to fibula
Prevents hyperadduction
Tibial collateral ligament
Reinforces medial surface of joint
Extends from femur to tibia
Prevents hyperabduction
Medial Meniscus and Lateral Meniscus
Deep to articular capsule within knee joint
C-shaped fibrocartilage pads on top of tibial condyles Cushioning between articular surfaces
Change shape to conform to articulating surfaces Partially stabilize joint medially and laterally