ch. 18 - Endocrine System
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Endocrine System
Regulates cells using hormones, with wide effects and targets all cells
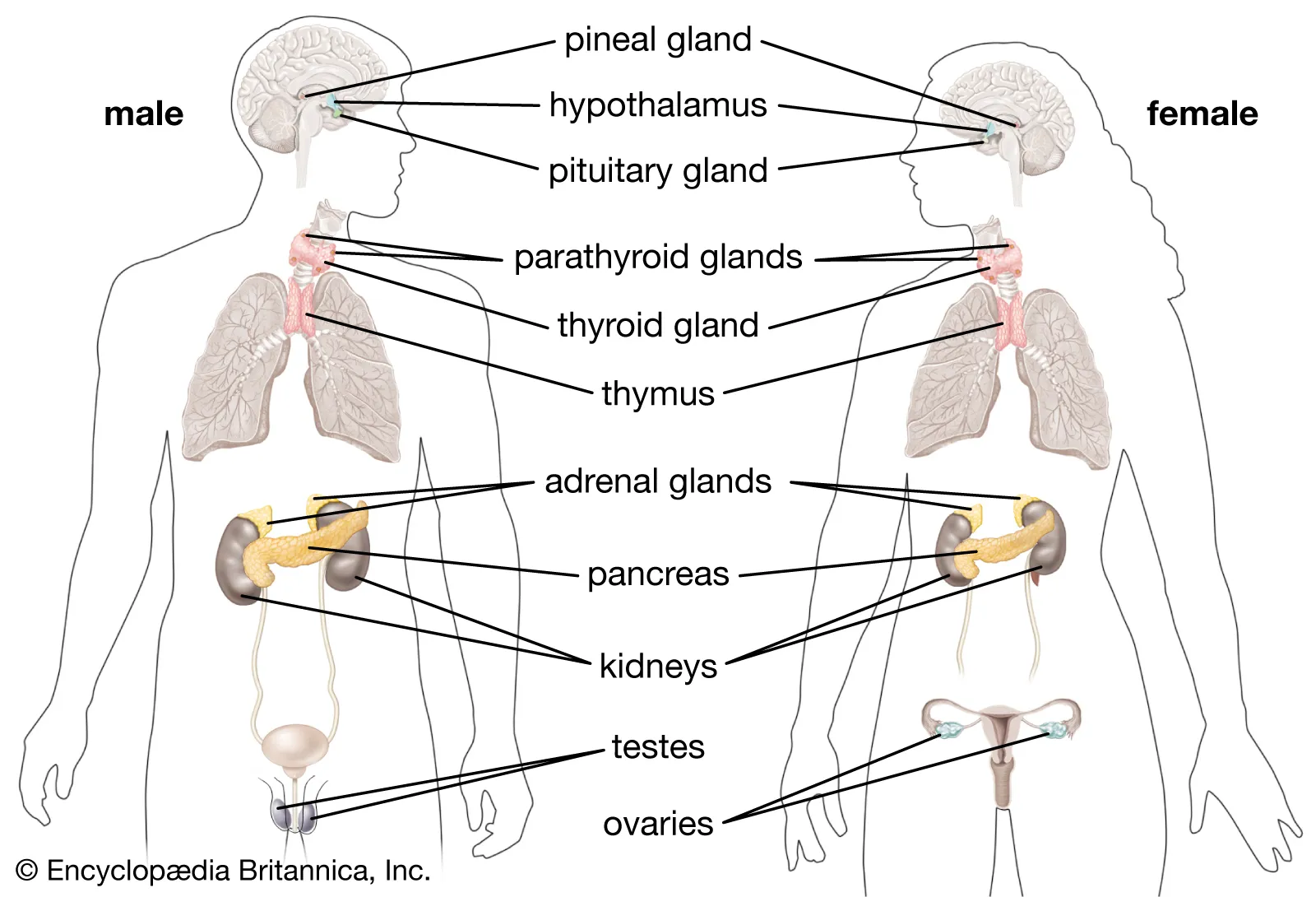
Endocrine Gland
Specialized organ making hormones, secreting into blood, without ducts
Exocrine Gland
Secretes products into ducts and into the body surface, not part of endocrine system
What are examples of exocrine glands?
- Saliva (salivary glands)
- Skin oil (sebaceous glands)
- Tears (lacrimal glands)
- Digestive enzymes (digestive glands of the stomach)
What is an example of a gland that had both exocrine & endocrine functions?
pancreatic gland
What are some organs that are not specialized endocrine glands, but produce hormones?
- kidneys
- heart
- stomach
- liver
- placenta
Paracrine hormones
hormones with local effects, affecting only some tissues
Endocrine hormones
hormones that secrete into the blood and affect cells at other locations in the body
Antagonistic Effect
Hormones producing opposite effects, e.g., insulin and glucagon
Synergistic Effect
Two different hormones that produce the same effect, e.g., testosterone and growth hormone
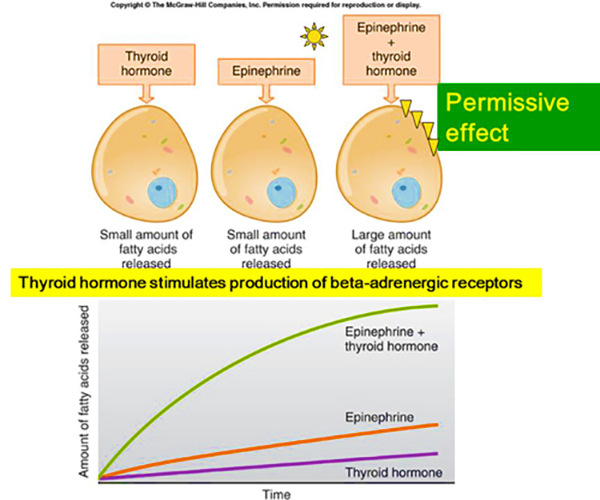
Permissive Effect
One hormone required for another to have an effect, e.g., thyroid hormone for GH
What is an example of negative feedback involving hormones?
Cortisol secretion stimulated by ACTH, which then suppresses CRH production
What is an example of positive feedback involving hormones?
Uterine stretch stimulates oxytocin release, causing contractions and more stretching
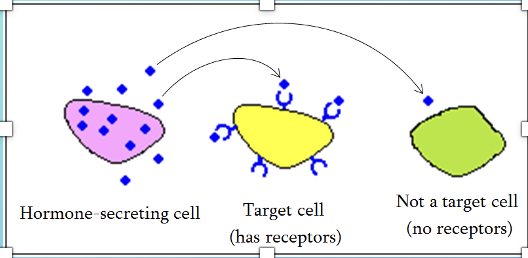
Target Cell
Cell with receptors for a particular hormone
What are 2 physiological processes examples regulated primarily by the endocrine system?
growth & metabolism
What hormones control growth?
GH (growth hormone), testosterone, & thyroxin
What hormones control metabolism?
insulin & leptin
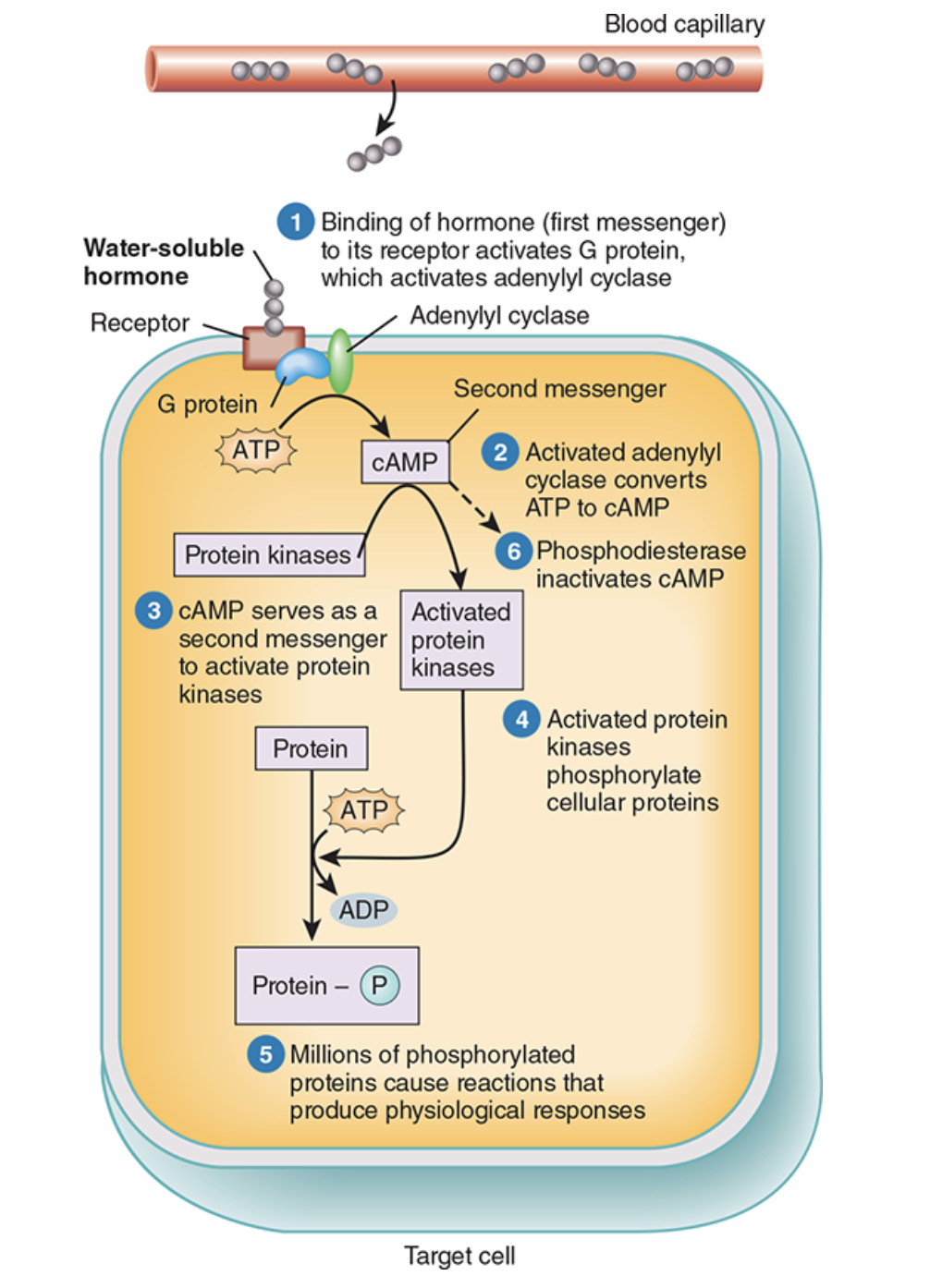
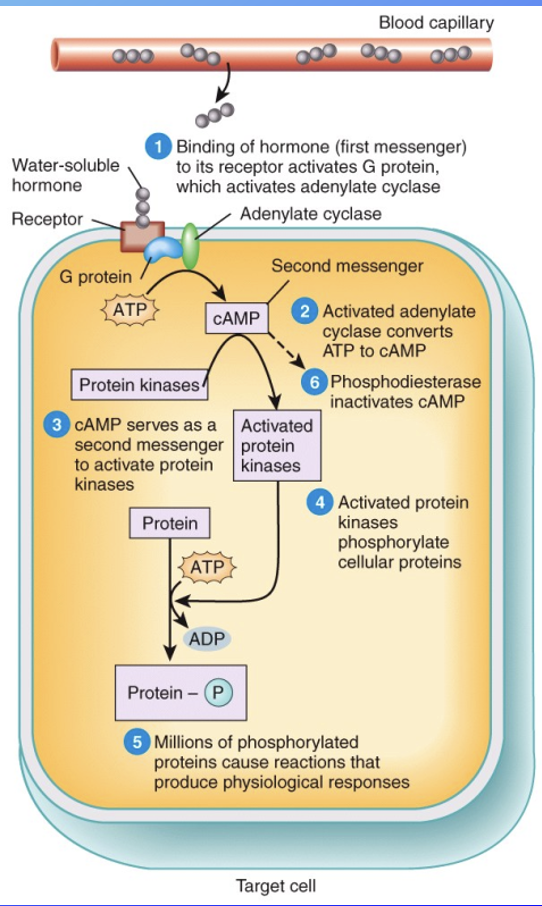
Water-Soluble Hormones
Hydrophilic (they cannot pass through the cell), bind to receptors on the outside of cell membrane, e.g., insulin & GH
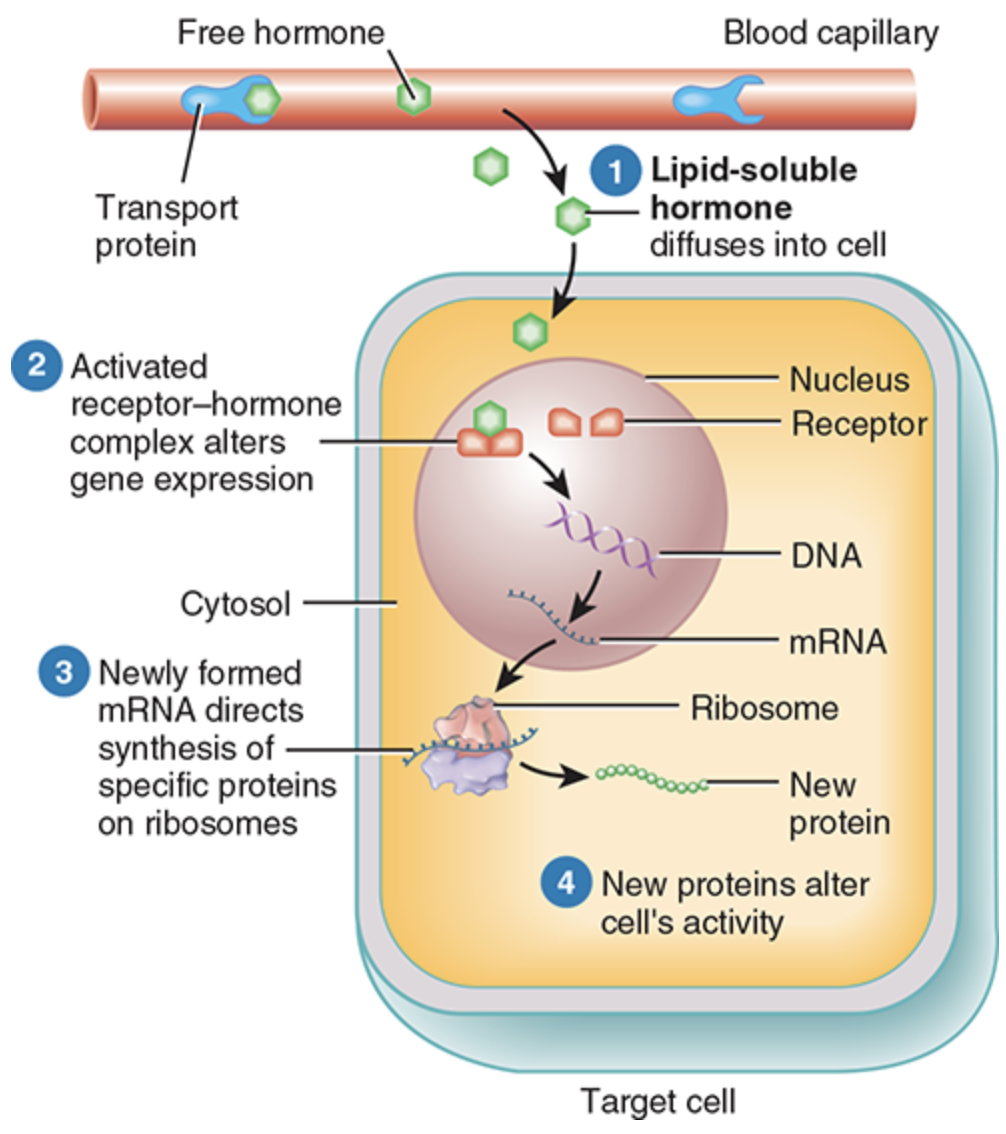
Lipid-Soluble Hormones
Hydrophobic, pass through cell membrane, bind to receptors inside the cell, e.g., steroid hormones, thyroid hormones
Hormone Receptor
Binds to a hormone for an action/response to take effect.
- located outside for water-soluble hormones and located inside the cell for lipid-soluble hormones
Protein hormone are made by
ribosomes on the rough ER
Steroid hormone are synthesized by
special enzymes, most located on the smooth ER
Second Messengers
special molecules made inside cells in response to hormone binding to its receptor, activating enzymes or membrane channels
Hypothalamus in relation to the endocrine system
Is the main link between nervous and endocrine system, controls the pituitary by secreting "release hormones" that are produced by special hypothalamic neurons called neuro-endocrine cells
Which hormones does hypothalamus produce?
- Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
- Oxytocin
- Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH)
- Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH)
- Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH)
- Prolactin-Inhibiting Hormone (PIH)
- Prolactin-Releasing Hormone (PRH)
- Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone (GHRH)
- Growth Hormone-Inhibiting Hormone (GHIH)
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
controls water excretion
Oxytocin
controls milk ejection and stimulates birthing contractions
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH)
stimulates secretion of Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH)
stimulates secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH)
stimulates secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin-Inhibiting Hormone (PIH)
is dopamine, suppresses secretion of prolactin
Prolactin-Releasing Hormone (PRH)
stimulates secretion of prolactin
Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone (GHRH)
also known as somatocrinin, stimulates secretion of growth hormone (GH)
Growth Hormone-Inhibiting Hormone (GHIH)
also known as somatostatin, suppresses secretion of growth hormone (GH)
Pituitary Gland
Releases hormones, with anterior and posterior parts
Anterior pituitary
secretes hormones that regulate a wide range of body activities, from growth to reproduction
Posterior pituitary
store and release hormones, does not synthesize
What are the pituitary hormones?
- Growth hormone (GH)
- Prolactin
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
- Oxytocin
Growth Hormone (GH)
promotes growth throughout the body
Prolactin
Controls milk production

Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
controls secretion of adrenocorticoid hormones
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Controls secretion of thyroid hormones
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) & Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
controls ovaries and testes functions
The posterior pituitary secretes 2 hormones. Which structure are these hormones synthesized?
Oxytocin and Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) are synthesized in the hypothalamus, then stored and released from the posterior pituitary gland.
Which 2 hormones is lactation regulated by?
prolactin & oxytocin
Which hormones play a role in stress response?
- Adrenalin (epinephrin) & Noradrenalin (norepinephrine): released during stress and enhance effects of sympathetic responses
- Glucocorticoids = Cortisol: controls glucose metabolism and long-term stress response
Produced in the adrenal gland
Thyroid hormones (T3, T4, Calcitonin)
regulate oxygen use and metabolic rate, cellular metabolisms, and growth and development
Thyroxin (T4)
has 4 iodines; regulates metabolisms, growth and development, and the activity of the nervous system
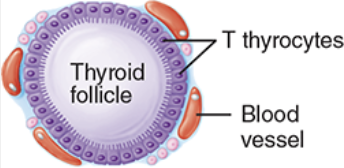
Triiodothyronine (T3)
a little stronger than T4, has 3 iodines; regulates metabolisms, growth and development, and the activity of the nervous system
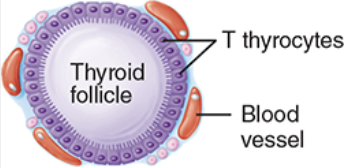
Calcitonin
lowers blood calcium and stimulates osteoblasts
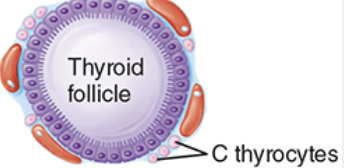
What are some common pathologies associated with the thyroid gland?
- Goiter: iodine sufficiency (swelling of the thyroid gland)
- Cretinism: thyroid insufficiency in babies
- Hypothyroidism: decrease of thyroid hormones production
- Hyperthyroidism: excessive thyroid hormones

Which 2 hormones are important for the regulation of calcium level
Calcitonin & Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
raises blood calcium and stimulates osteoclasts-bone resorption
Which endocrine hormones does the pancreatic gland make, and what are their roles?
Makes the endocrine hormones glucagon and insulin
- Glucagon: increases blood glucose levels
- Insulin: lowers blood glucose levels
Which hormone release is controlled directly by the sympathetic nervous system?
Epinephrine & Norepinephrine
Melatonin
Produced in the pineal gland, causes sleep and regulates circadian cycle
Which endocrine hormones are produced by gonads - testes and ovaries?
- Female=Ovaries
o Estrogen: development of oocytes, maintenance of female genital structures, and promote of secondary sex characteristics. Affects fluid and electrolyte balance and protein anabolism. Regulation of menstrual cycle.
- Male=Testes
o Testosterone: development of sperm; controls the growth and development of male genital organs, secondary sex characteristics, and body growth
What are all the major steroid hormones?
- Testosterone
- Estrogen
- Cortisol
- Aldosterone
- Androgen
- Progesterone
- Calcitriol
Testosterone
Develops sperm, controls growth & development of male genital organs, secondary sex characteristics, and body growth
Estrogen
Develops oocytes, maintains female genital structures, and promotes secondary sex characteristics. Regulation of menstrual cycle
Cortisol
Increases glucose levels in the blood, breaks down proteins, mobilizes fat, and suppresses inflammation
Aldosterone
retains Na+ ions in the body, excretes excess K+ ions into urine and retains water which increases blood pressure
Progesterone
helps prepare endometrium of the uterus for implantation of a fertilized ovum and the mammary glands for milk secretion
Calcitriol
regulates calcium and bone mineralization, activates vitamin D
Anabolic effect
energy-requiring reactions where small molecules are built into larger ones
Which hormones have anabolic effect?
- GH
- Testosterone
- Estrogen
- Insulin
Insufficient insulin results in
Diabetes Mellitus
Insufficient growth hormone results in
Pituitary Dwarfism
Too much growth hormone results in
Gigantism (adolescence) or Acromegaly (adult)
Insufficient ADH results in
Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes Mellitus
- "sugar diabetes" insulin deficiency or insulin resistance (cells not responding to normal amount of insulin.
o 2 Types of Diabetes Mellitus:
- Type 1 & Type 2: have different causes and different progression but have the same final result
Diabetes Insipidus
lack of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
o Common symptom is increased thirst
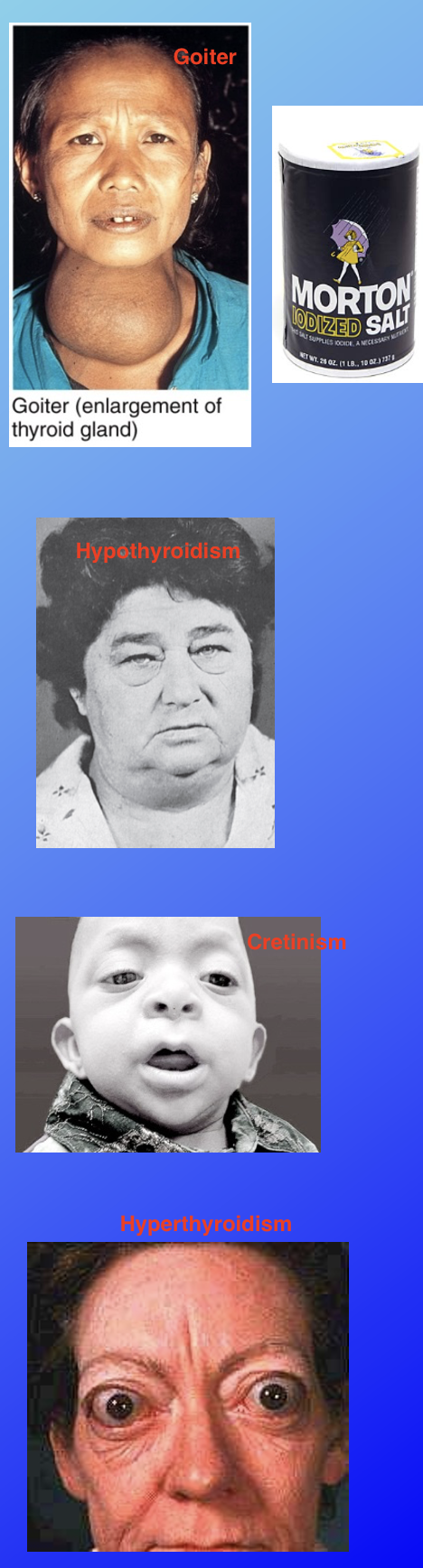
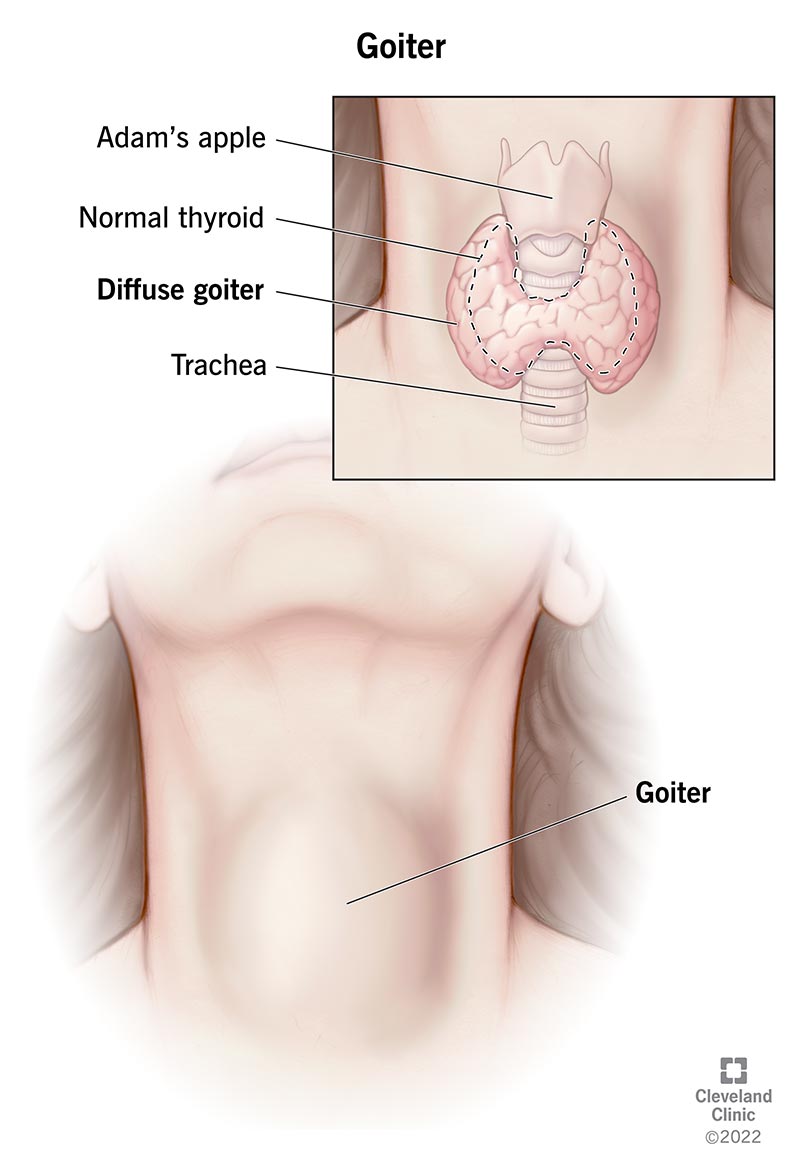
Goiter
Enlarged thyroid gland; a large lump on the neck due to iodine insufficiency
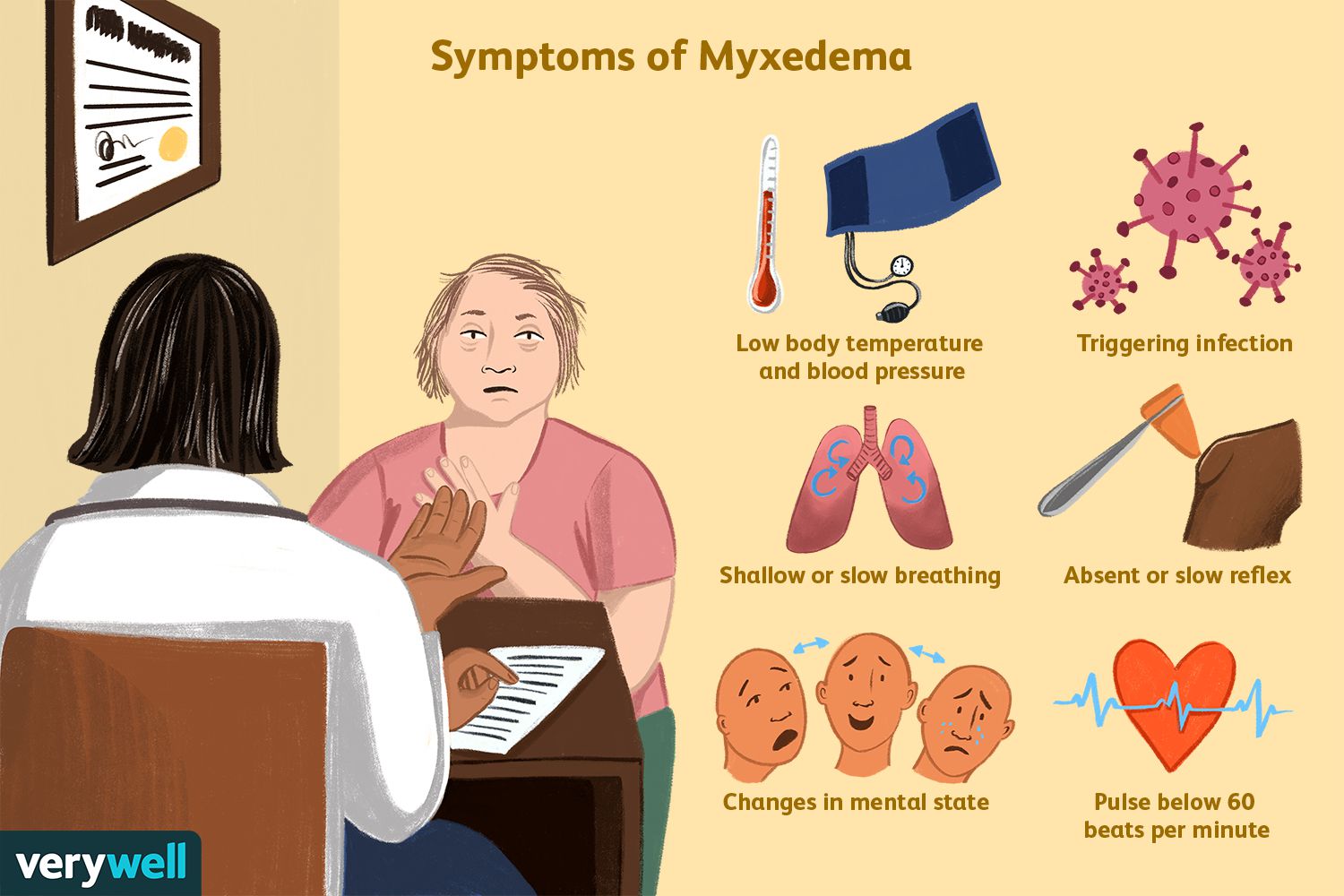
Myxedema
Hypothyroidism (decrease of thyroid hormone production) in adults, causing symptoms of slow heart rate, low body temperature, and weight gain, sensitivity to cold, muscle weakness, dry hair and skin, etc..
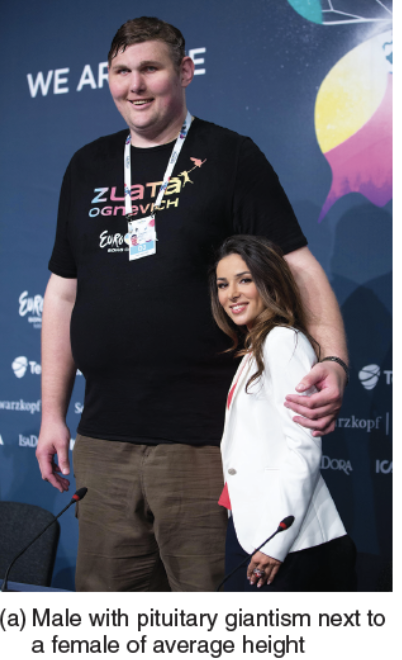
Gigantism
Excess growth hormone in childhood/adolescence, causing extreme height but proportionately build

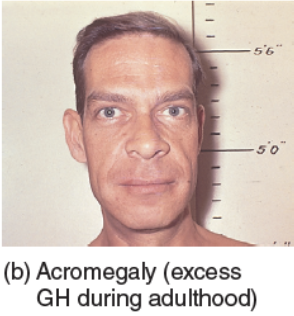
Acromegaly
Excessive growth hormone production in adults, causing bone and tissue overgrowth. - A person will have crude facial features, large jaws, heavy forehead, large nose, lips and ears.