population ecology and growth
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
population
a collection of individuals of the same species living in the same geographic area
community
a collection of populations of species in a geographic area
ecosystem
individuals of the community & the environment in which it exists
ecosystem — biotic components
living organisms of the ecosystem
ecosystem — abiotic components
nonliving players in an ecosystem
eg. weather & nutrients
biosphere
entire life-containing area of a planet — all communities and ecosystems
niche
all the biotic and abiotic resources used by the organism
population density
describes how ,amy individuals are in a certain area
distribution
describes how populations are dispersed over that area
dispersion pattern — clumped
individuals live in packs that are spaced out from each other like schools of fish or herd of cattle

dispersion pattern — uniform
individuals are evenly spaced out across a geographic area, like birds on a wire

dispersion pattern — random
species are randomly distributed across a geographic area, like tree distribution in a forest

population ecology
study of the size, distribution, and density of populations and how these populations change with time
Size of the population, N, indicates how many individuals of that species are in a given area
demographers
study the theory & statistics behind population growth and decline
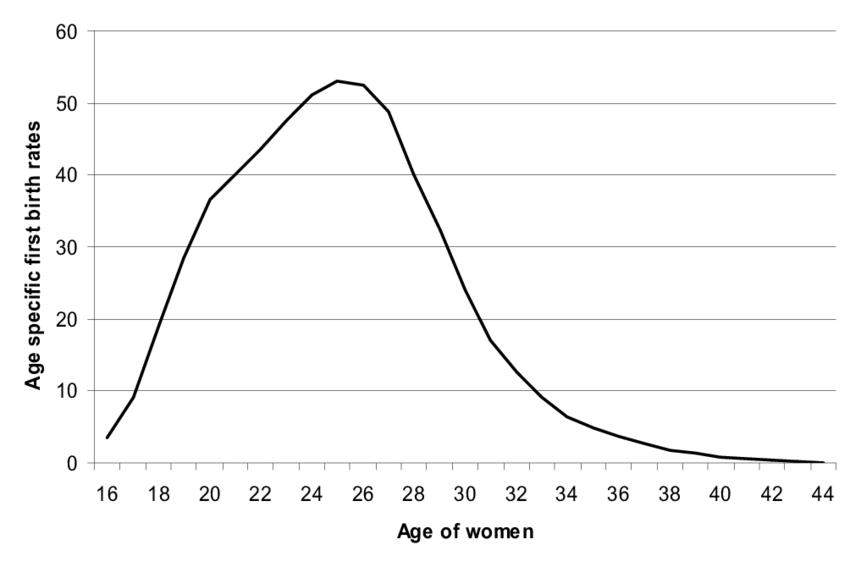
birth rate — make sure yk how to analyze/read the graph
offspring produced per time period. Highest among those in the middle of the age spectrum
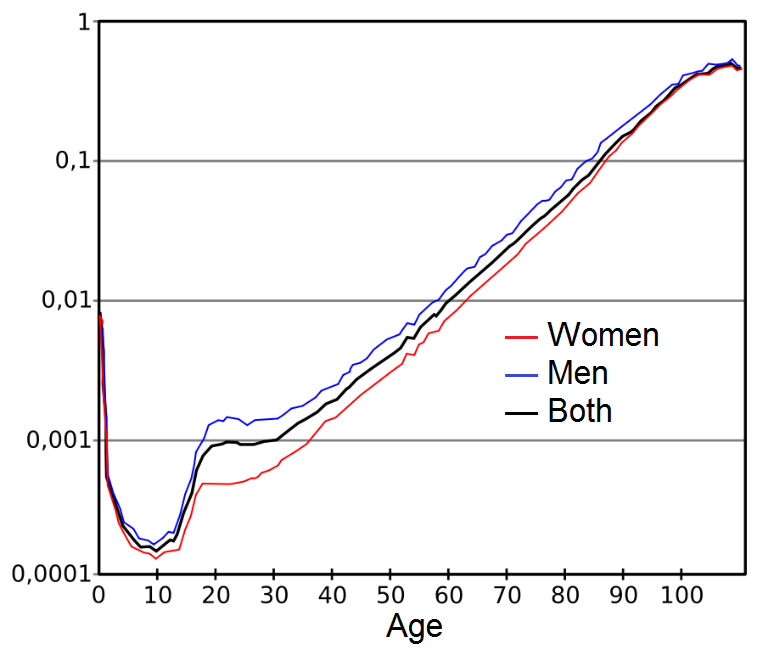
death rate — make sure yk how to analyze/read the graph
number of deaths per time period. Highest among those at 2 extremes of the age spectrum
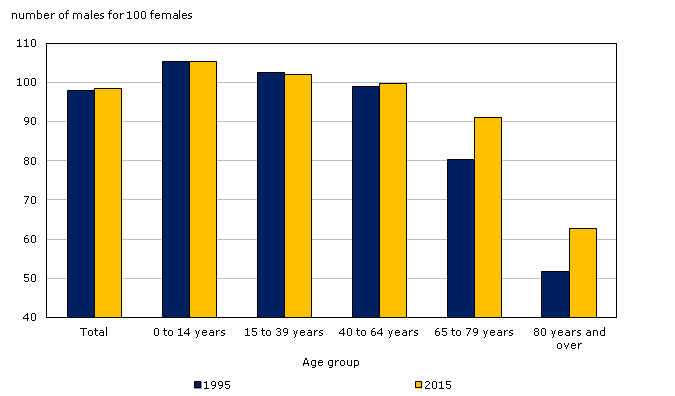
sex ratio — make sure yk how to analyze/read the graph
proportion of males & females in a population
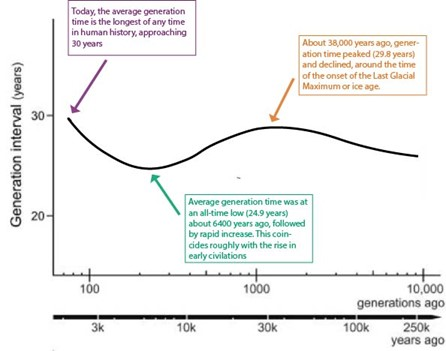
generation time — make sure yk how to analyze/read the graph
time needed for individuals to reach reproductive maturity
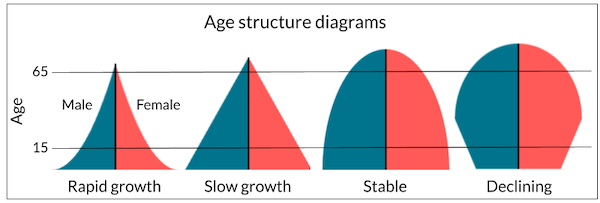
age structure — make sure yk how to analyze/read the graph
statistic that compares the relative numbers of individuals in the population from each age group
immigration rate — make sure yk how to analyze/read the graph
rate which individuals relocate into a given population
emigration rate — make sure yk how to analyze/read the graph
rate at which individuals relocate out of a given population
biotic potential
maxmimum growth rate of a population given unlimited resources, space, and lack of competition/predators. Rate varies by species
carrying capacity
maximum number of individuals that a population can sustain in a given environment
limiting factor — density-dependent factors
population's per capita growth rate to change—typically, to drop—with increasing population density
eg. competiiton w/ limited food
limiting factor — density-independent factors
affect per capita growth rate independent of population density. Examples include natural disasters like forest fires
population growth — exponential growth
population grows at a rate that makes a J-shaped curve. Population grows as if there are no limitations as to how large it can get (biotic potential)
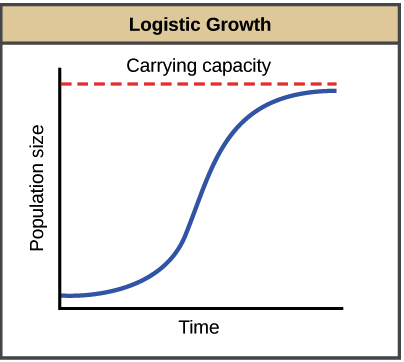
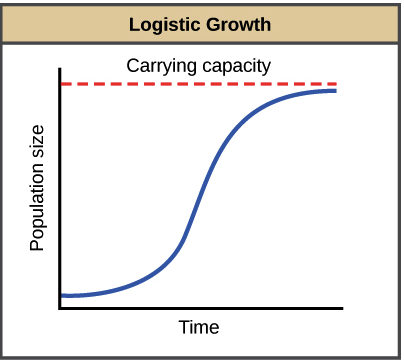
population growth — logistic growth
the population grows at a rate that creates an S-shaped curve. Limiting factors are responsible for S shape, putting a cap on the size to which the population can grow
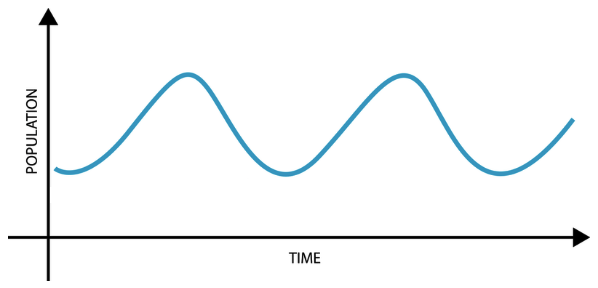
population cycle
when a population size dips below carrying capacity, it will later come back to the capacity and even surpass it. However, the population could dip below the carrying capacity as a result of some major change in the environment and equilibrate at a new, lower carrying capacity
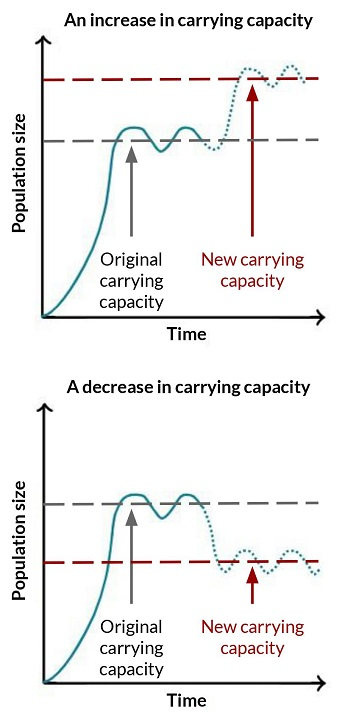
when population is over carrying capacity…
overpopulation due to resource availability. Resources will eventually decline, buildup of waste & disease occurs that drive population back down
when population is below carrying capacity…
resources replenish, allowing for increase in the birth rate & decline in death rate
population growth equation
(dN) / (dt) = B - D
dt = change in time
B = birth rate
D = death rate
exponential growth equation
(dN) / (dt) = rmaxN
N = population size
rmax = maximum per capita growth rate of population
logistic growth equation
(dN) / (dt) = rmaxN ((K - N) / K)
N = population size
rmax = maximum per capita growth rate of population
K = carrying capacity