romanesque
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Romanesque means,
the Roman style" or "descended from Roman
Romanesque architecture
-It is a direct modification of Roman architecture, and it owed something to Byzantine art It was a stye greatly inspired by Christianity
-With the decline of the Roman Empire, this was the first distinctive style to spread across Europe.
Geographical
- Romanesque
originated in W. Europe
(Italy,Germany, France, Spain)
Climatic
North (dull)
large windows to admit light
high-pitched roofs to ward off snow
South (sunny)
small openings to exclude dazzllng sunshine
Social
Establishment of feudal systems In which people were given land and protection by people of higher rank, and worked and fought for them In return.
Castles were built.
Religious
Christlanity was the chief source of education and culture
Religious enthusiasm found their material expression in the magnificent cathedral churches and monastic bulldings
Architecture was regarded as sacred sclence
PLAN
is the basic basilica.
crypt
beneath the altar housed the relics of a saint.
Small churches
are generally without aisles.
Large churches
are flanked by aisles and divided by an arcade.
Abbey churches and cathedrals
often had transepts.
Narthex
is the church's lobby.
Aisles
are passageways on either side of nave.
Nave
is the central part to accommodate the congregation.
Transept
is an area set crosswise to the nave forming a Latin Cross plan.
Apse
is the semi-circular, vaulted part
oriented on the east towards Jerusalem.
Ambulatory
is semi-circular passageway behind the apse.
Absidials
Are radiating side chapels for relics of saints.
(triforium)
above the aisle is the gallery
sexpartite vault
is a four-sectioned vault with an additional arch rib dividing it into six unequal parts.
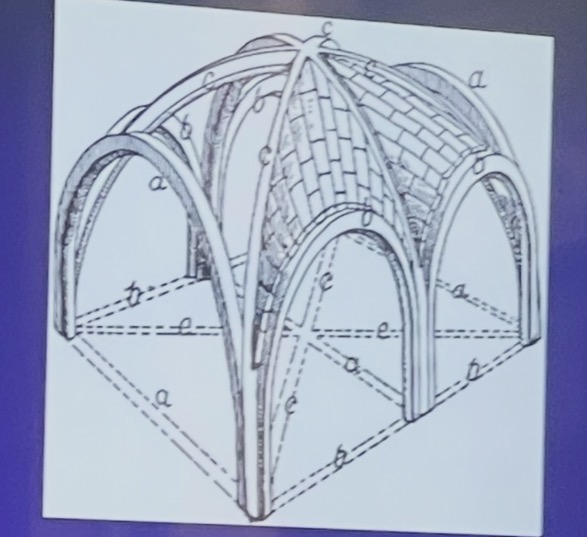
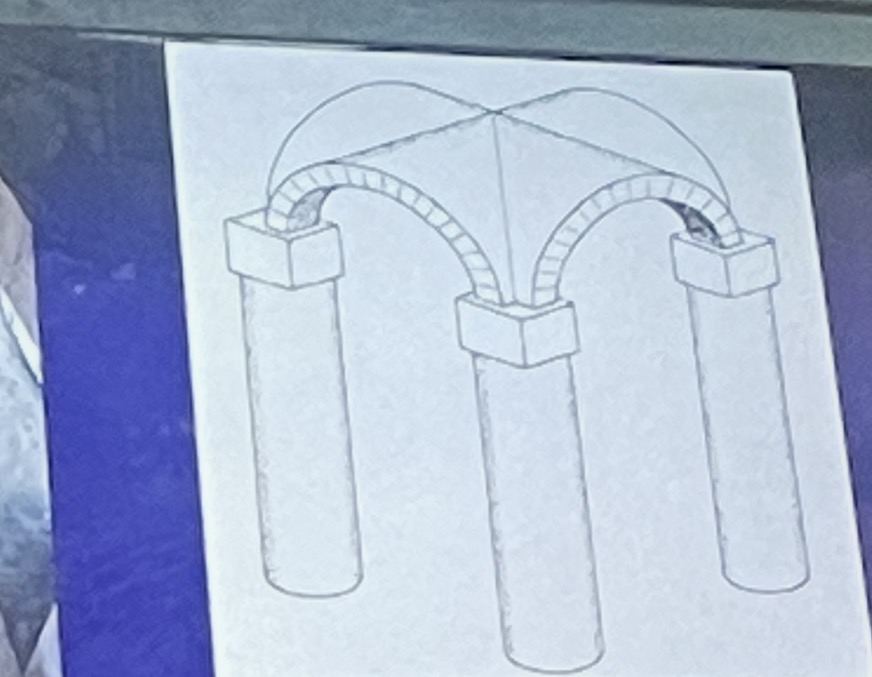
quadripartite vault
is divided into four sections of equal bays.
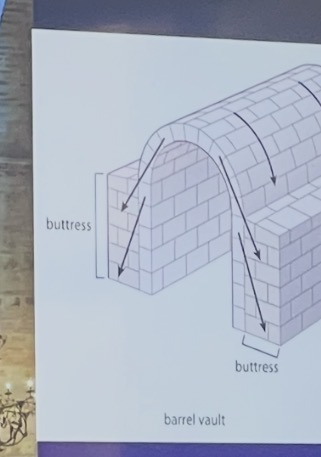
barrel vault
Squinches
achieve the same goal by bridging the corners of the square to form an octagonal base, in the case of an octagonal tower.
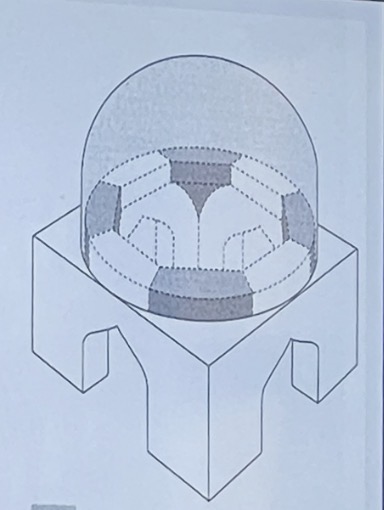
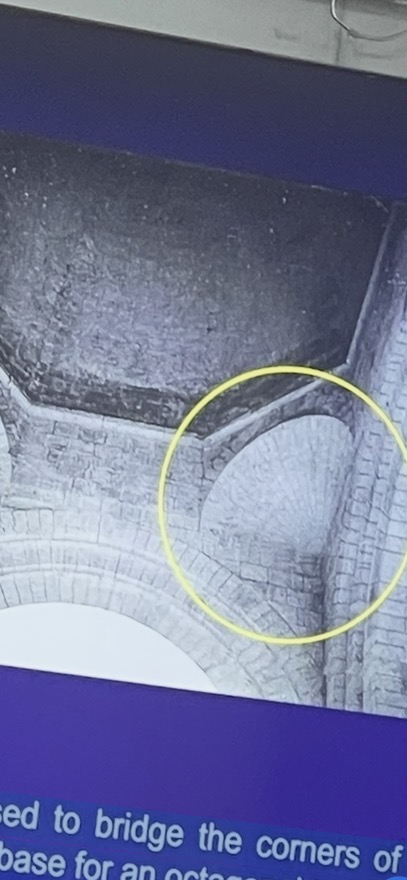
squinch
is used to bridge the corners of a square to form a base for an octagonal tower.

corbel table.
Corbels are in the form of projecting blocks of stones. A row of corbels is called a
lombard band
is a decorative blind arcade.
Fortified towns
protected by walls called fortifications
Monastery
establishment for monks or nuns
is a group of buildings designed as a self-sufficient community for the monks.
Monastic Village
The crusades
were a series of Holy wars launched by the Christian society of knights of Europe against Muslim aggression
Knights Templar,
founded to protect the Holy Places in Palestin
to safeguard the pilgrim routes to Jerusalem
oldest of the Western Christian military orders most skilled fighting units of the Crusades
Knights Hospitaller
founded during the late 11th cent. under Augustinian rule to protect and care forsick or injured pigtins to the Holy Land.
CASTLE
fortified structure of European innovation during the Middle Ages
Functions of a castle:
military
administrative
domestic
Motte and Bailey Castle
first type of a European castle
a motte is a mound of earth and a bailey is a courtyard surrounded by a wooden fence and a ditch
Rectangular Keep Castle
surrounded by thick walls and moat, this castle offered a better form of defence.
main feature is the stone keep with entrance on the second level to make it difficult for the invaders to enter.
Types of Mediaeval Castles
- Shell Keep Castle
a circular shell of stone wall with various buildings inside it and surrounded by a moat.

Types of mediaeval Castles
4. Concentric Castle
this combination of the shell keep and the rectangular keep offered the best protection
surrounded by a moat, it has double concentric walls in different levels and with features allowing archers to launch arrows
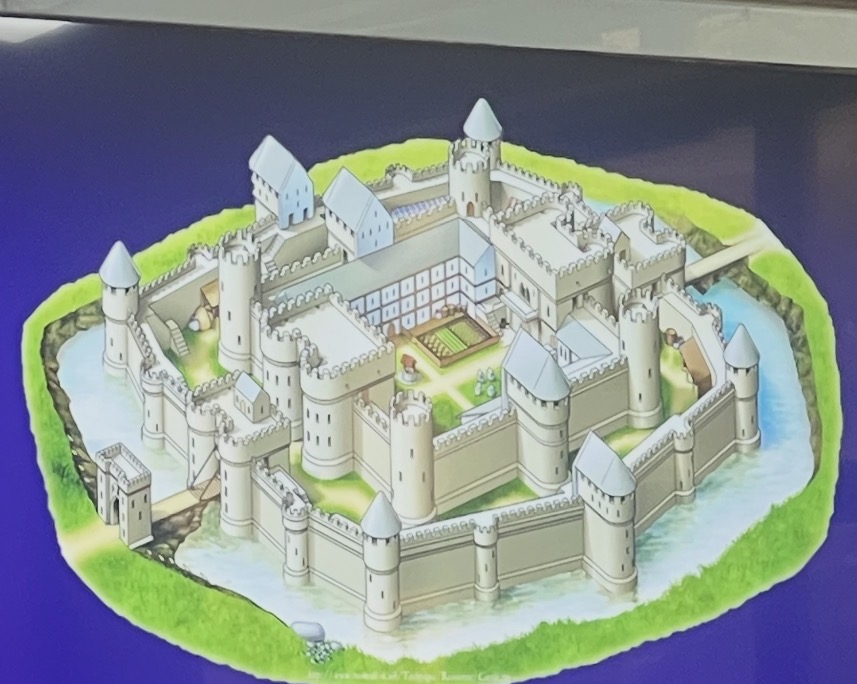

Keep or donjon
is the fortified tower or stronghold of a castle
Curtain walls
are the enclosing defensive walls of a castle.
Rampart
is a defensive earthen bank surrounding a castle.
Talus/Glacis
is a bold sloping thickness at the foot of walls as protection from undermining.
Towers
allow lookouts to see invaders easily.
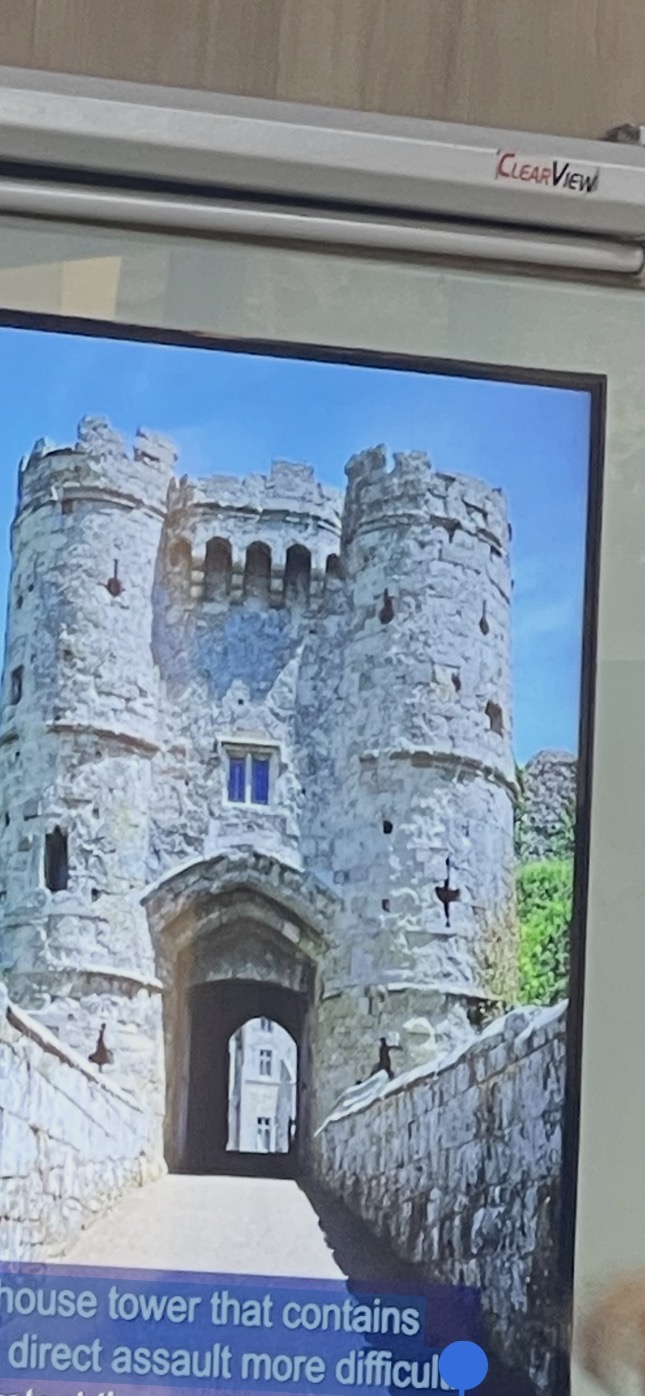
The barbican
is a fortified gatehouse tower that contains a series of defences to make a direct assault more difficult.

Murder holes
were placed to protect the castle entrances
Machicolations .
are projecting parapets allowing floor openings (murder holes), through which molten lead, boiling oil or stones are dropped down below
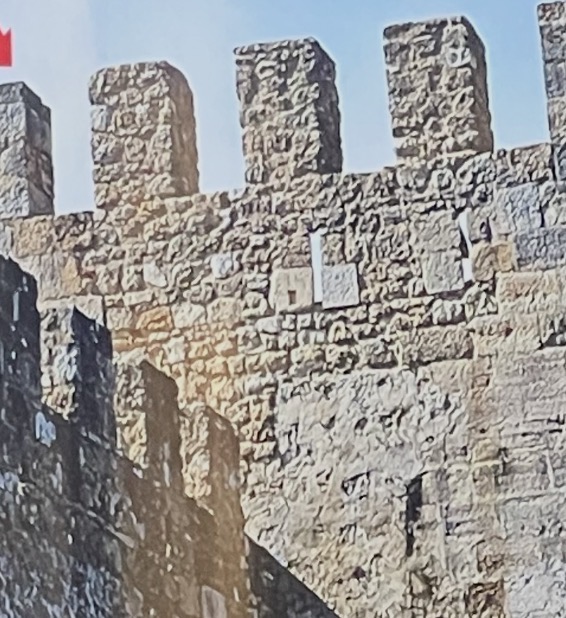
Crenellations (battlements)
are regular gaps in the parapet.
Merlons
are the upstanding parts of an embattled parapet between two crenels.

Arrow loops
are narrow openings set inside walls and towers enabling defenders to launch arrows.
Bailey or ward
is the enclosed courtyard area where the domestic buildings of the castle were.
A spiral staircase
going up clockwise gives added room for the defenders. Steps are uneven making it difficult for attackers.
Garderobe
is the castle's toilet."
3 TYPES OF CASTLES IN THE HOLY LAND
1. Pilgrim Forts
sited to secure the routes from coastal ports to Jerusalem
Coastal Fortifications
secure the sea links
due to the advent of powerful cannons and permanent artillery fortifications
Towards the end of the Middle Ages, castles tended to lose their military significance .
Castles became more important as residences and statements of power.
are narrow openings set inside walls and towers enabling defenders to launch arrows.
arrow loops