Biology Final exam flash cards
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
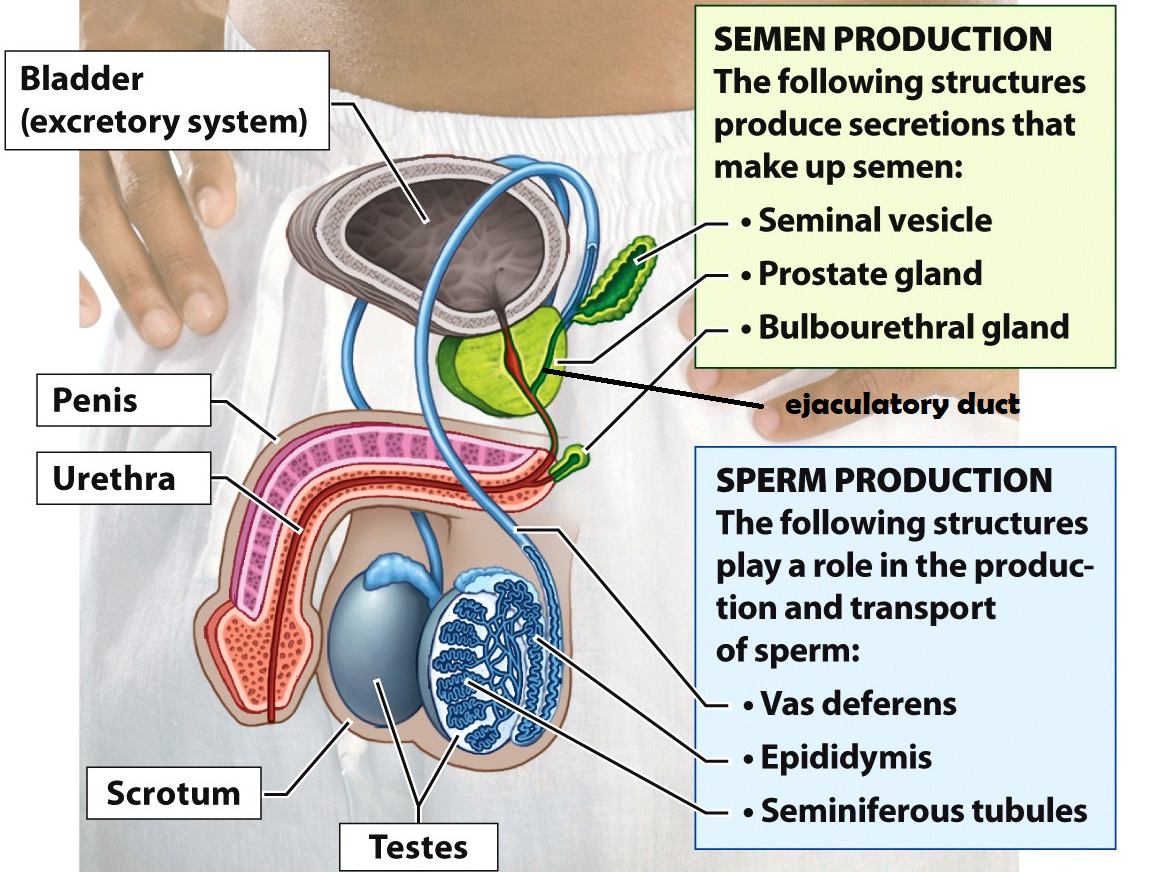
Testes
Organs that produce sperm cells
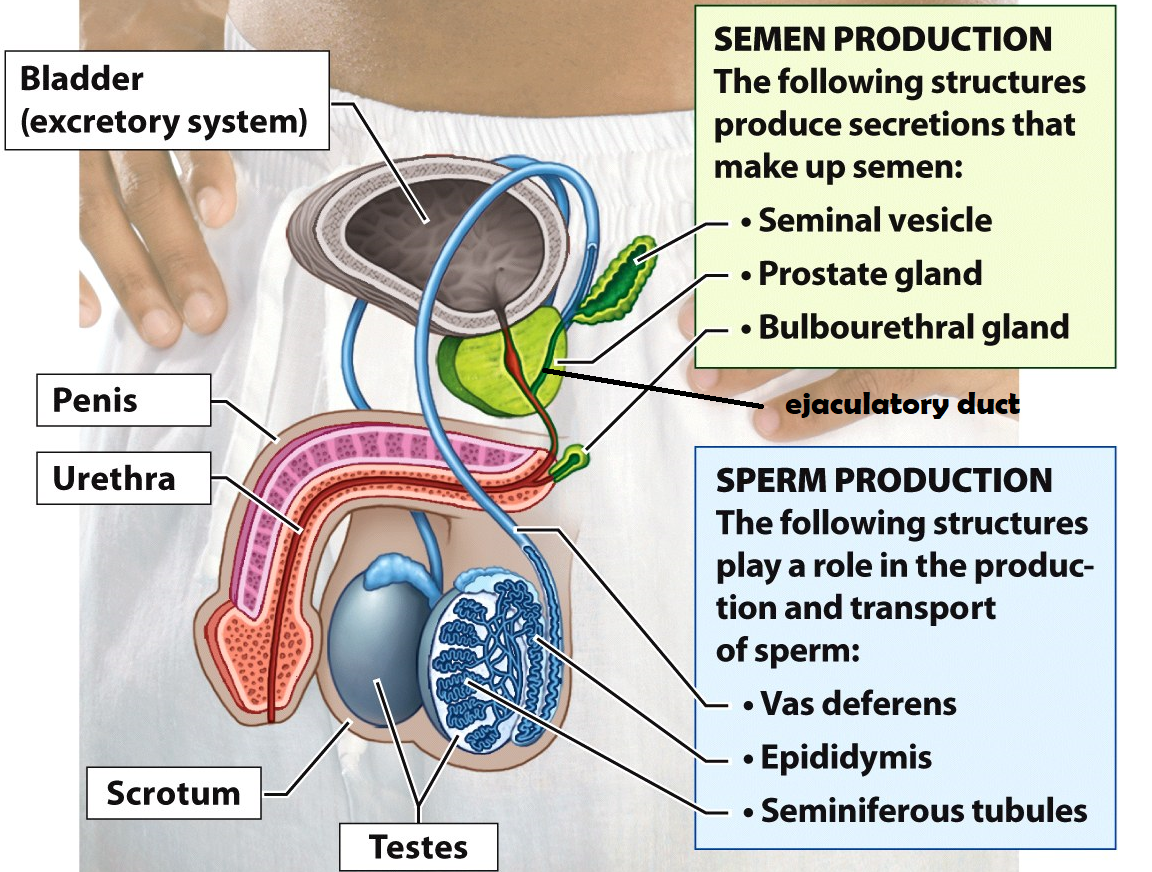
Epididymis
he site of sperm development & maturity
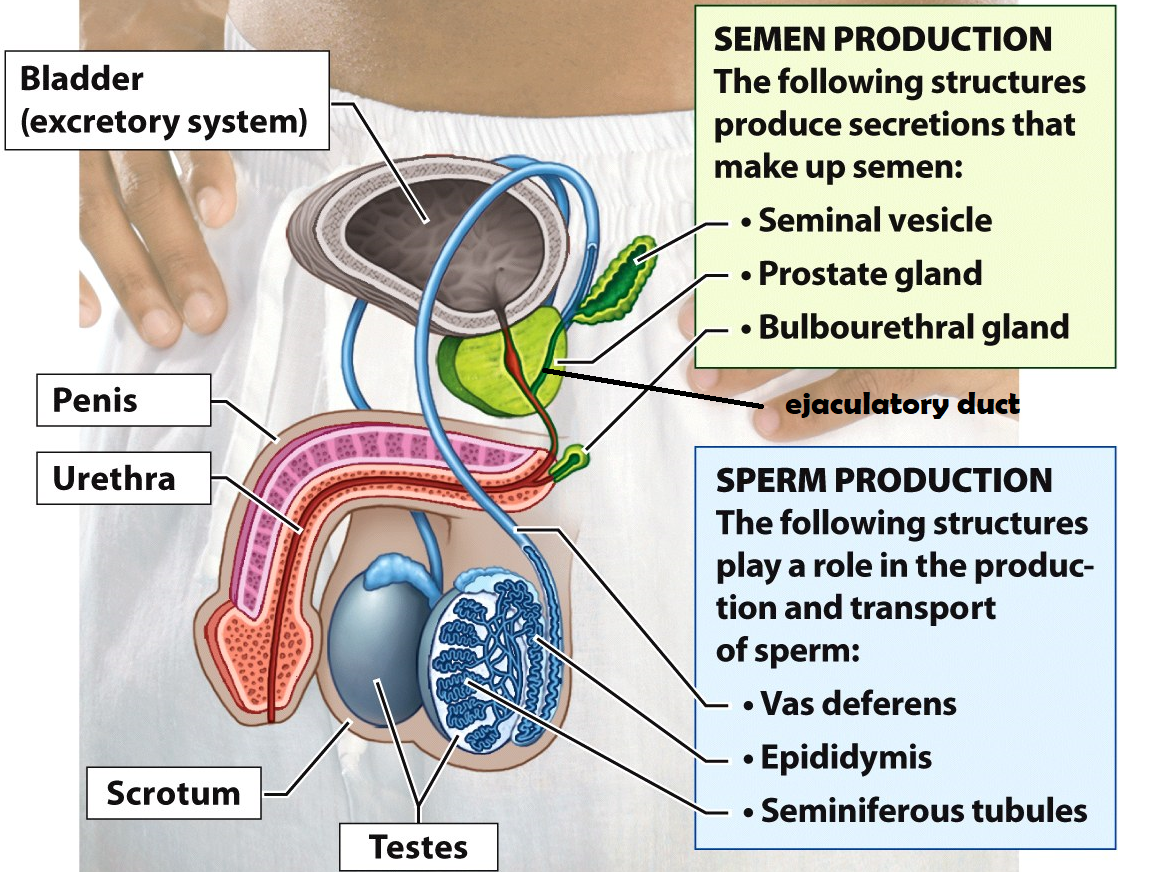
Vasa deferentia
tubes lined with smooth muscle that carry sperm out of the testes during ejaculation. This is also the site of a vasectomy
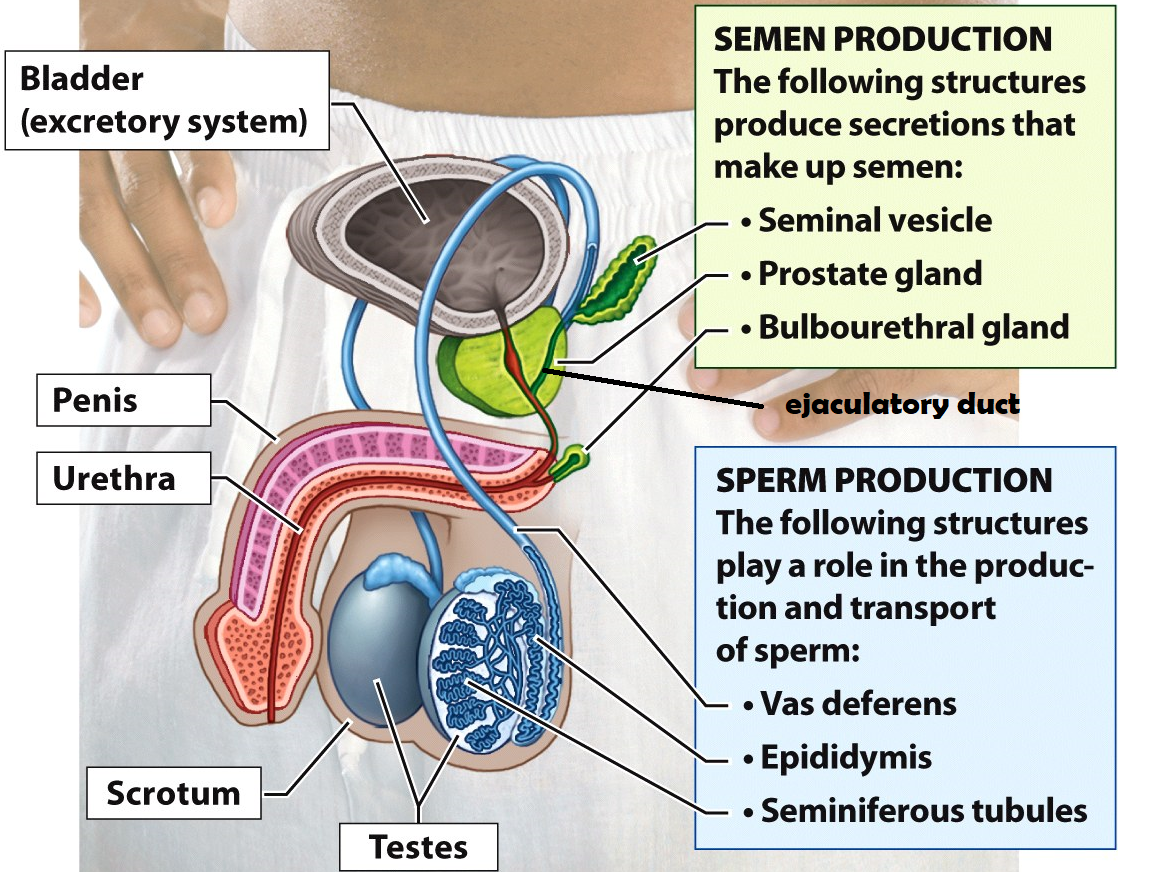
Seminal Vesicle
this structure adds fructose & prostaglandins to semen. Fructose serves as an energy source for sperm cells and prostaglandins induce contractions within the female uterus to propel sperm up to the Fallopian tubes
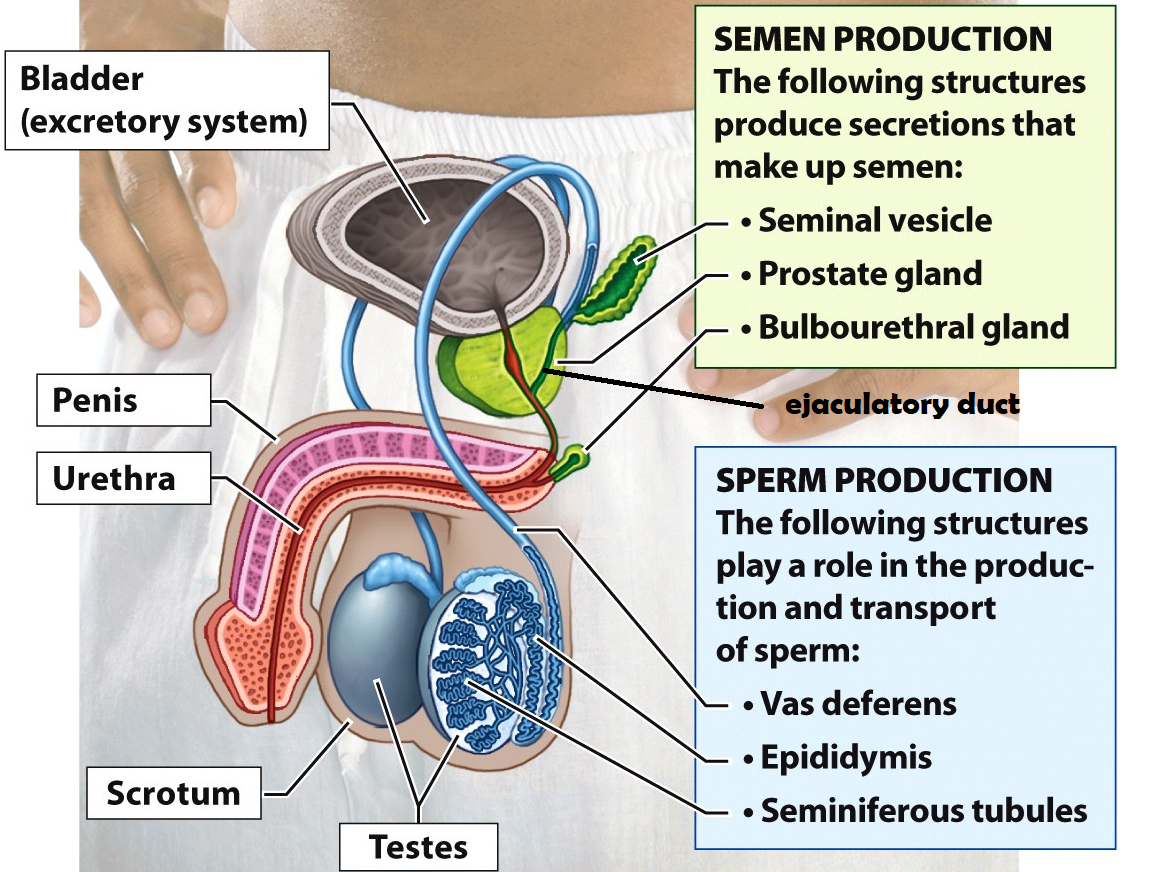
Prostate Gland
the structure adds an alkaline fluid to semen to protect sperm cells from the acidic environment of the female reproductive tract
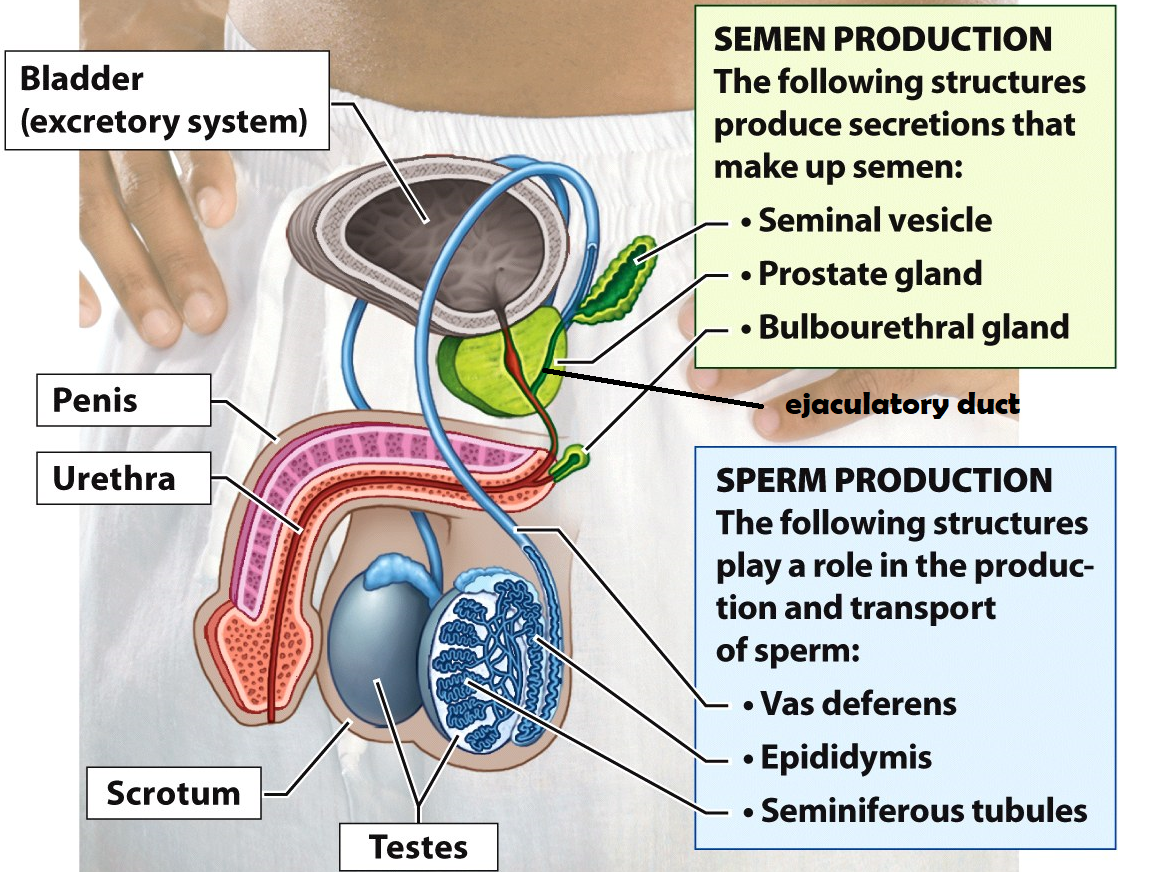
Bulbourethral Gland
this structure secretes mucus to lubricate the urethra before ejaculation. It produces “pre-ejaculatory” fluid
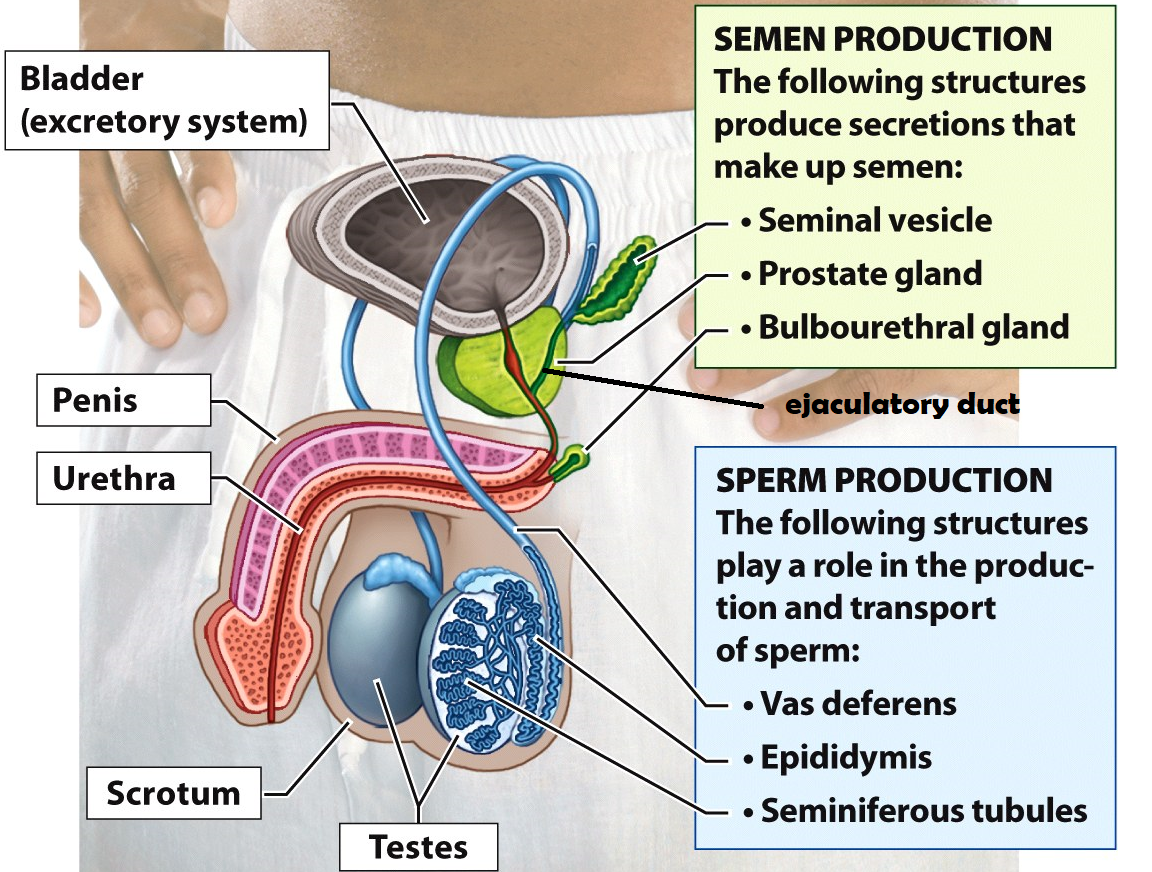
Urethra
a duct that carries semen or urine out of the body
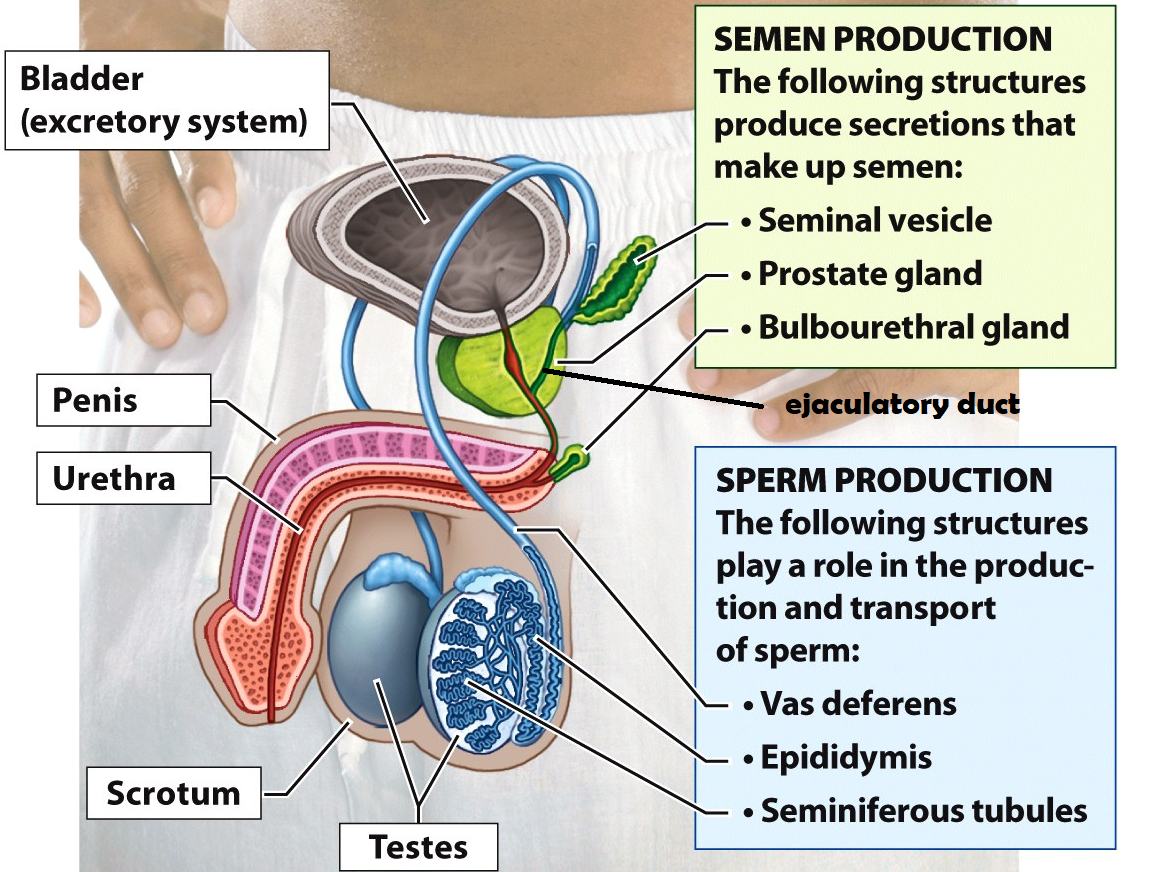
Penis
external male reproductive organ that deposits semen into the female vagina
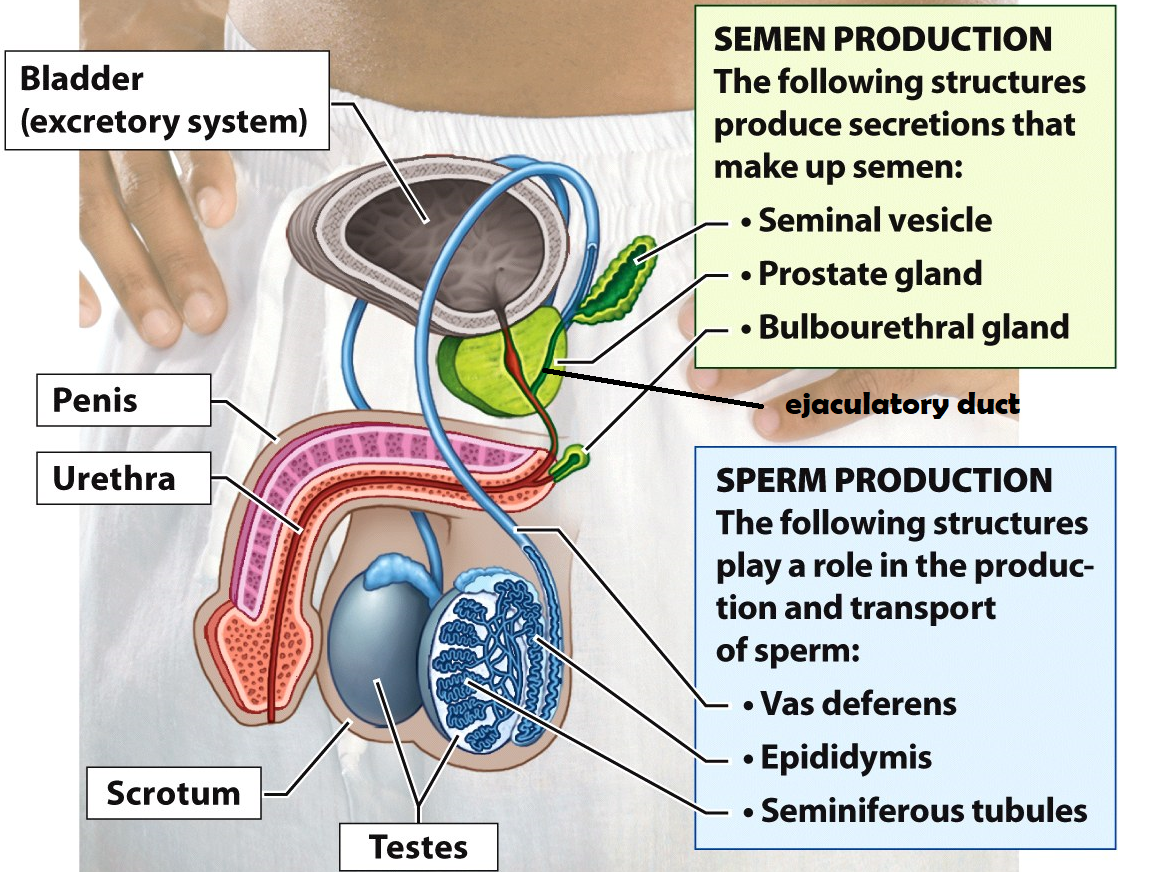
Scrotum
a sac of skin and muscle that holds the testes external to the body where the temperature is cooler for increased sperm survival
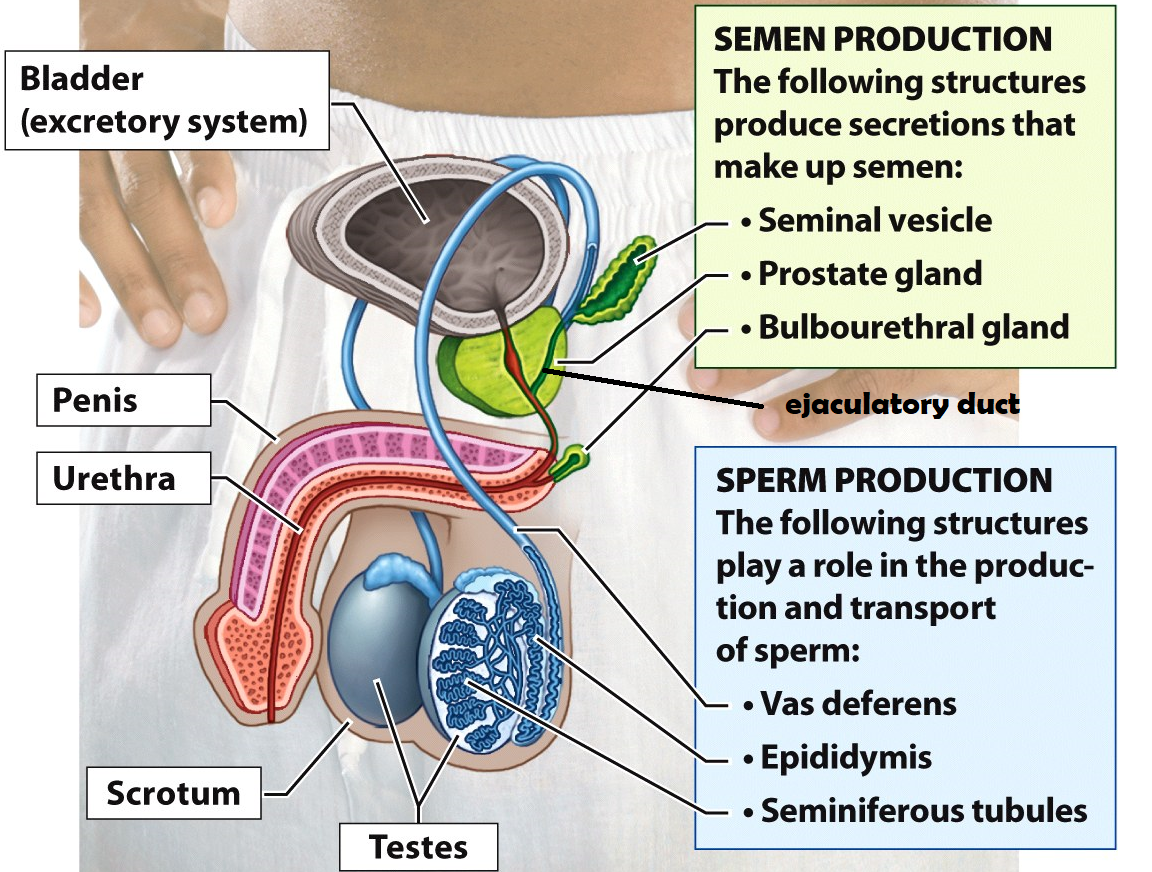
Bladder
Stores urine
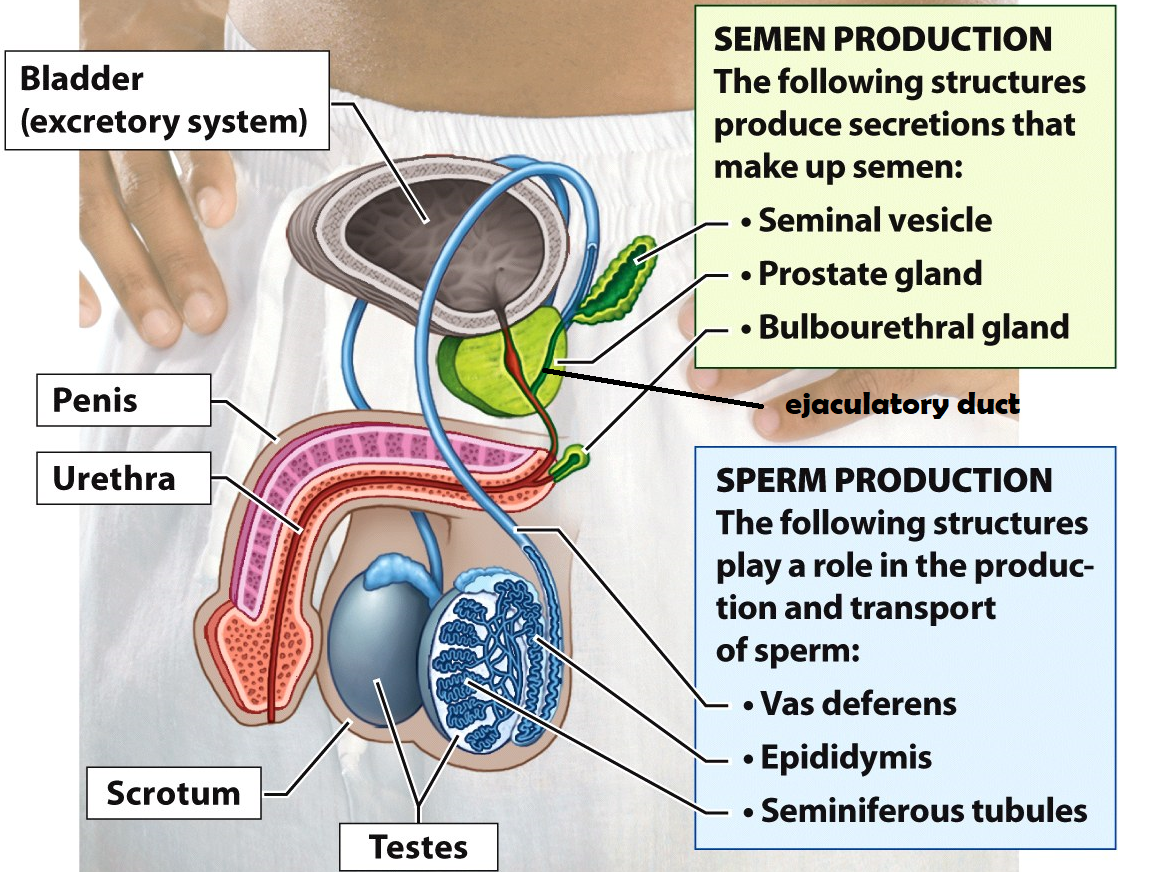
Ejaculatory duct
a tube that is formed when the vas deferens and seminal vesicle meet. Its function is to combine sperm from the testes, alkaline fluid from the prostate, and other fluids from the seminal vesicle before semen is ejaculated
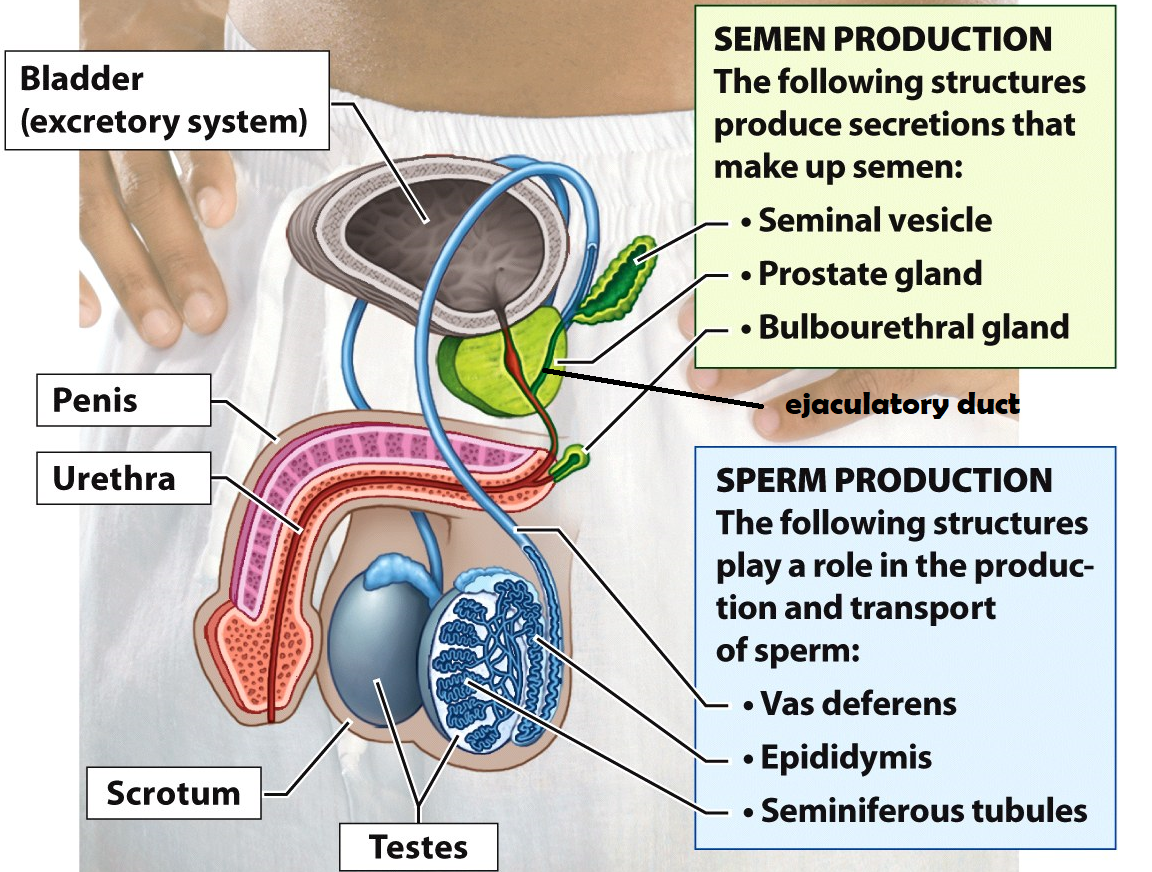
The pathway of sperm through the male reproductive system
Testes → Epididymis → Vas deferens → Ejaculatory duct in the prostate → Urethra → Penis
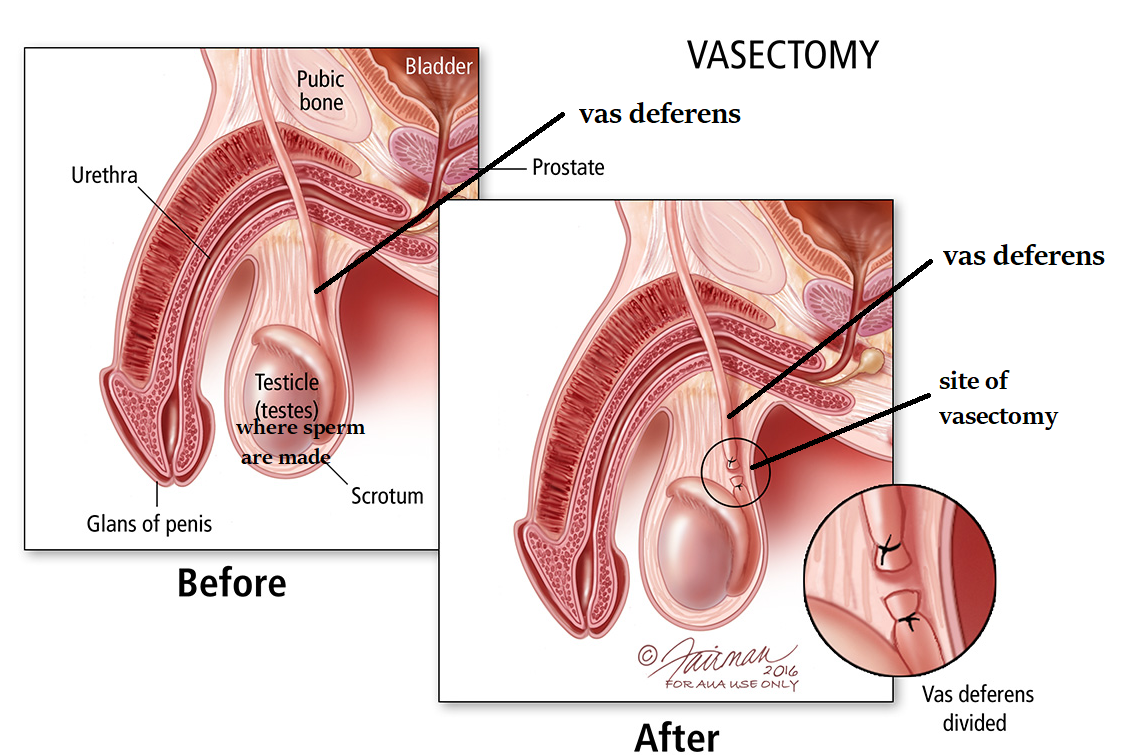
Vasectomy
This is a permanent form of birth control for men who do not want to have children. This procedure requires cutting and tying off the vas deferens to block and prevent the release of sperm cells during ejaculation
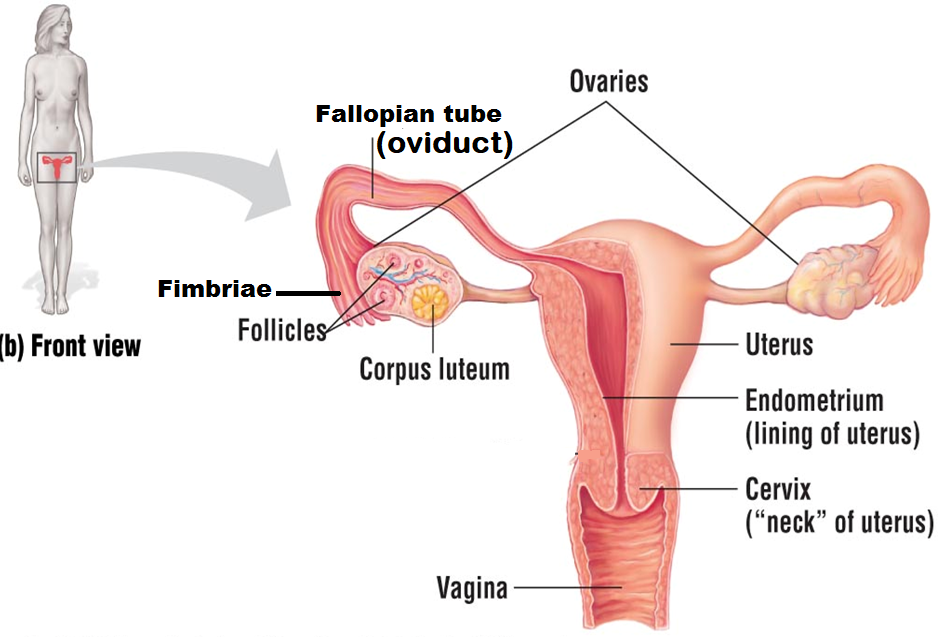
Ovaries
organs that produce and store eggs (oocytes). Females have two ovaries that alternate releasing a single egg once a month for one chance at fertilization
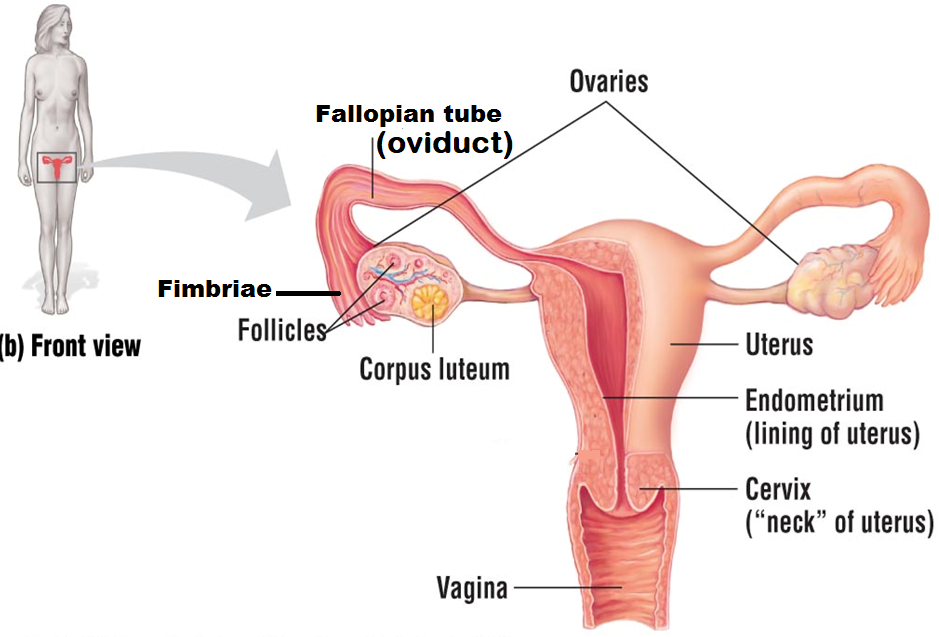
Follicle
a layer consisting of small cells; they surround, nourish, and protect a single egg
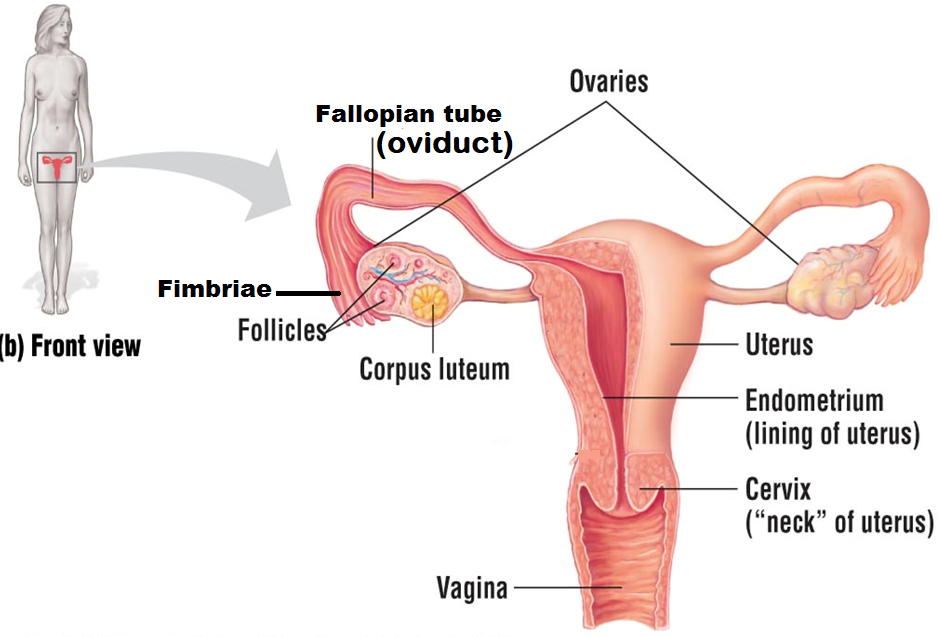
Corpus lutem
the structure that remains when the egg leaves the follicle during ovulation
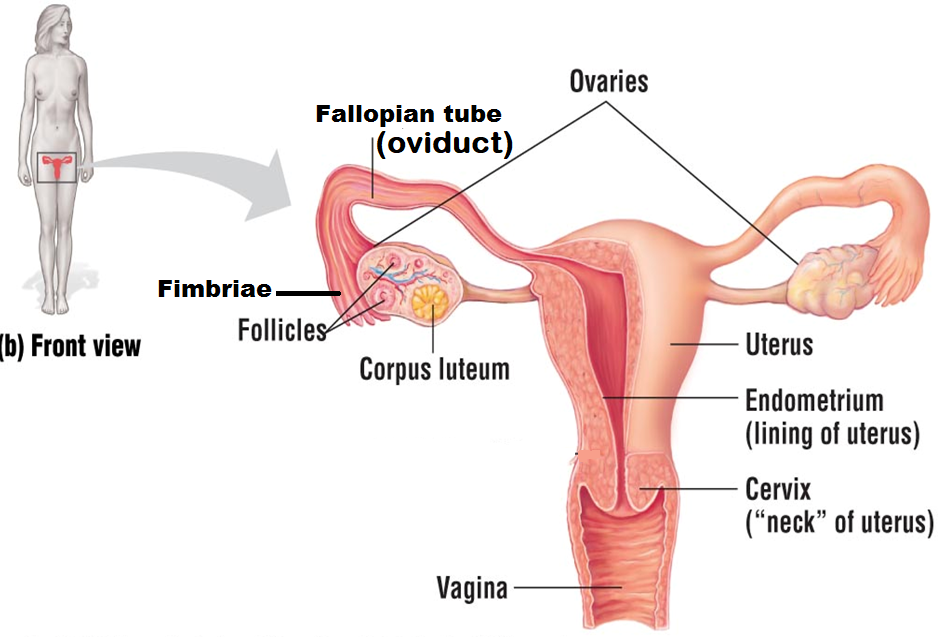
Fimbriae
finger-like projections found at the end of the Fallopian tube that help sweep the egg from the ovary into the Fallopian tube during ovulation
Fallopian tube (oviduct)
the structure that the egg is released into during ovulation. It is also the site of
fertilization and tubal ligation
Endometrium
the blood-rich tissue that lines the inside of the uterus. When a female becomes pregnant, the embryo implants into the endometrium, which will thicken to increase blood supply to the embryo. When a female is not pregnant, the endometrium thins and is shed during her menstrual cycle
Cervix
the neck of the uterus; it is also the site that must dilate (widen) during pregnancy
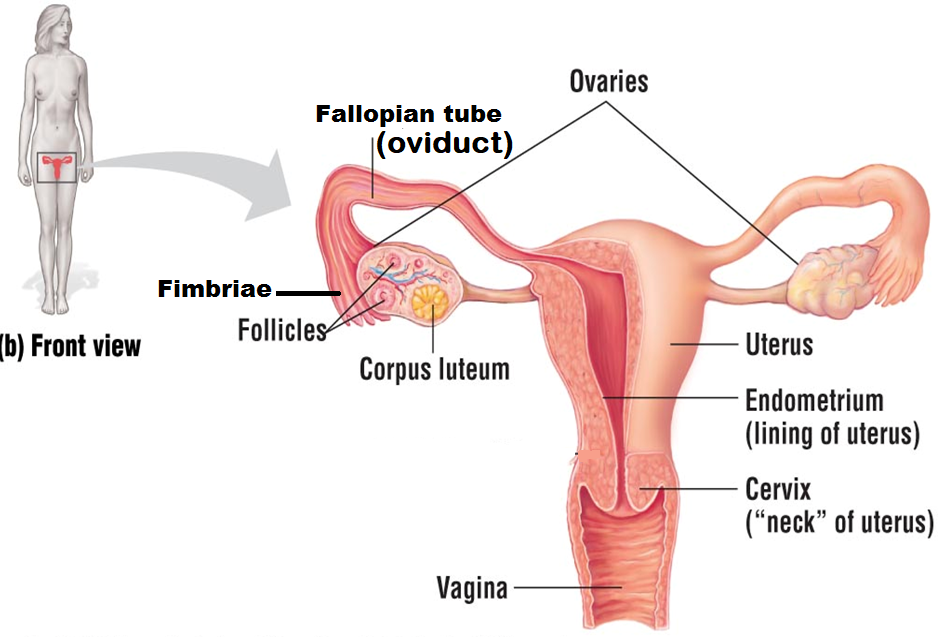
Uterus
Also known as the womb. It is the site of pregnancy
Vagina
site of sperm deposit; it is also known as the birth canal
The pathway of an egg through the female reproductive system
Ovary → Fallopian tube (where egg can be fertilized) → endometrium (where fertilized egg implants into the uterus
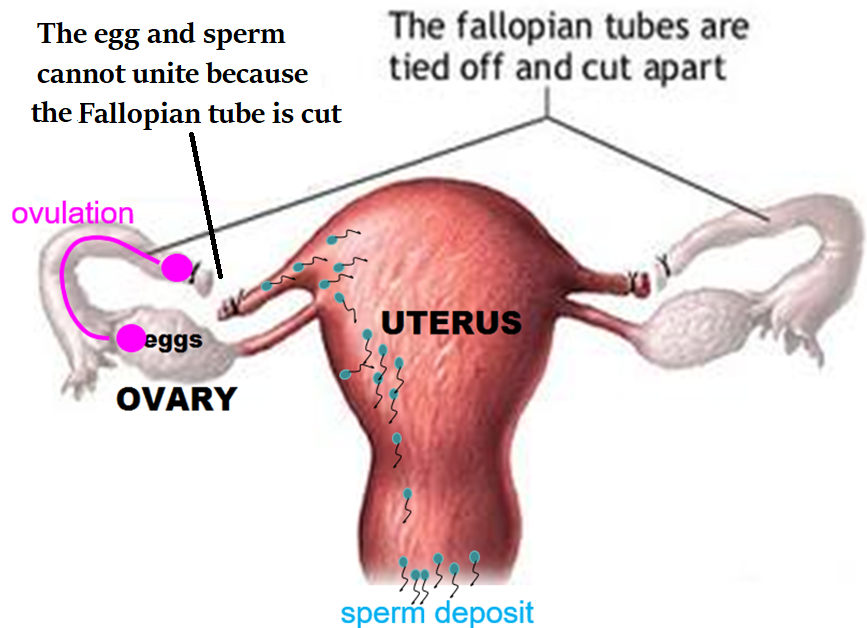
Tubal ligation
This is a permanent form of birth control for women who do not want to have children. This procedure requires cutting and tying off the Fallopian tube. The Fallopian tube is the site of fertilization, so when it is disconnected, the egg and sperm cannot unite, and no pregnancy occurs
First step of embryonic development
Ovulation
Second step of embryonic development
Fertilization and zygote formation
Third step of embryonic development
Cleavage
Fourth step of embryonic development
Implantation and hCG secretion
Fifth step of embryonic development
Primitive streak formation
Sixth step of embryonic development
Extra embryonic structures form
Seventh step of embryonic development
Gastrulation
Eighth step of embryonic development
Organogensis
Ninth step of embryonic development
Heart beats occur
Tenth step of embryonic development
Limb buds form
Eleventh step of embryonic development
SRY gene activates
Twelfth step of of embryonic development
Skeleton ossifies
Thirteenth step of embryonic development
Apoptosis of limb buds
Fourteenth step of embryonic development
Neurons generates action potentials (electrical signals) that allow skeletal muscles to contract
Ovulation
Once a month, a mature egg is released from the ovary where it is swept into the Fallopian tube via fimbriae. The egg has a 24-hour period to become fertilized by sperm that have traveled to the Fallopian tube following intercourse.
Zygote
A fertilized egg
Cleavage and its purpose
Rapid cell division. It allows the number of cells in the embryo to increase. It’s goal is to lay the groundwork for mutlicellular. The embryo doesn’t get bigger, it just increases the number of cells it has inside.
Implantation
Baby hatches and burises itself under the endometrium.
hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin hormone)
A hormone made by the embryo that is made right after implantation. It tells the mother that she is pregnant. It is found in the urine and blood. It’s purpose is to ensure the endometrium is maintained and the menstrual cycle is prevented. If the hormone is not produces, the endometrium sheds and the embryo is lost
Primitive streak formation
The first signs the body is being forms. Establishes bilateral symmetry. (Meaning both the left and right side are the same)
Development of exttrambryonic structures
Found external to the developing embryo. Includes: Chorion, amnion, amniotic fluid, and umbilical cord.
Chorion
Outermost membrane around the embryo. It forms the placenta
Placenta
Attaches to the uterine wall, anchoring the fetus during pregnancy. It nourishes and maintains the fetus through the umbilical cord
Amnion
The inner membrane around the embryo that produce and stores ____ fluid
amnion fluid
A clear liquid that surrounds the fetus during pregnancy. During early pregnancy it is mostly water, but as the fetus develops it becomes yellowish. The fluid contains nutrients, hormones, and antibodies
Umbilical cord
A tissue that runs between the fetus and the placenta that is attaches to the uterus. It’s job is to bring oxygen and nutrients to the embryo while removing carbon dioxide and waste products from the embryo
Grasrtulation
The process describing the formation of the three germ layers: Endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm
Endodern
The innermost layer. It forms the skin, brain, and spinal cord
Mesoderm
The middle layer. It forms all muscles (skeletal, smooth, and cardiac), bones of the skeleton, and the cartilage and joints
Ectoderm
Outermost layer. It forms the digestive system, liver pancreas, and lungs
Organogenesis
A process where all of the embryo’s organs start to form
Heart beats
Circulate blood throughout the body. Blood supplies our cells with oxygen and nutrients
Limb buds
Structures that will eventually form arms and legs of the fetus
SRY gene (sex determining Region of Y
The Y chromosome contains a ____ gene that is activates in weeks 5 and 6 in the male embryos. In males, the wolffian ducts develop into vas deferns. In females, the Mullerian ducts develop into fallopian tube
Ossification
A process where an existing tissue in the body gets converted to bone tissue
Apoptosis
A process where the skin connecting the fingers and toes undergoes programed cell death, or apoptosis. The result is the formation of individual fingers and goes.
Action potential (electrical signals)
Neurons/nerve cells generate___________ which allow the contraction of skeletal muscle.
Purpose of steps 1-4 of the embryonic development
To make the baby and get it to the uterus
Purpose of steps 5-7 of the embryonic development
To create a line down the center of the body, secure the baby, and start making tissues
Purpose of steps 8-10 of the embryonic development
TO make body organs, get the heart pumping, and add arms and legs
Purpose of steps 11-12 of the embryonic development
Make the sex and the skeleton
Purpose of steps 13 and 14 of the embryonic development
Make you fingers and toes wiggle
Four steps of food processing
Ingestion
Digestion
Asorption
Elimination
Ingestion
The act of food intake
Digestion
Physically and chemically breaking down food
Absorption
Moving nutrients from the small intestine into the bloodstream for cell uptake
Elimination
Getting rid of any undigested materials
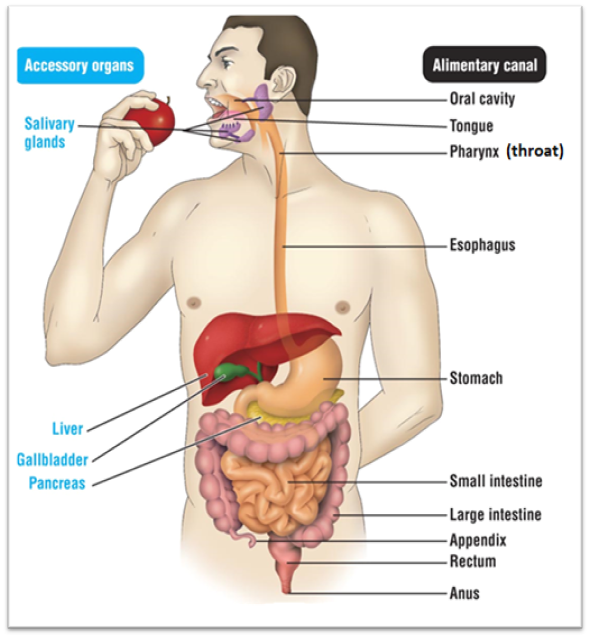
Oral cavity
Site of physical and chemical digestion. For physical, it includes the mouth, tongue, and teeth. Their function is to tear the food apart so it can be swallowed. A chemical uses digestive enzymes or other chemicals to break down food. One of its digestive enzymes is amylase. The salivary glands make this.
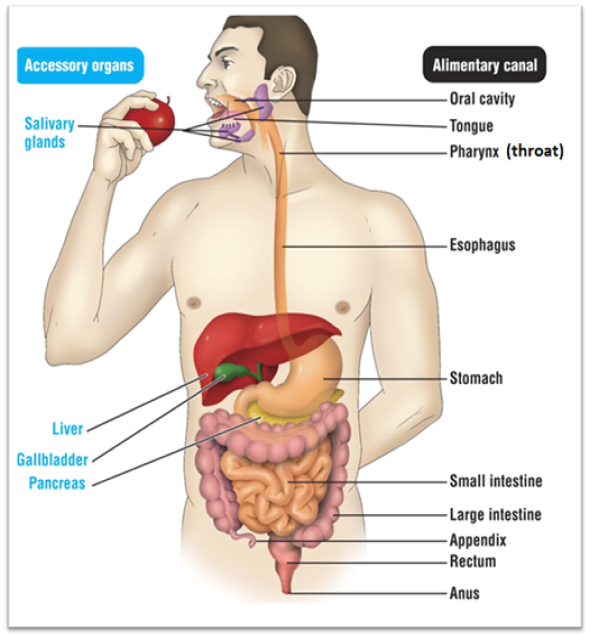
Pharynx
Also known as the throat. it’s function is to bring the food down to the esophagus
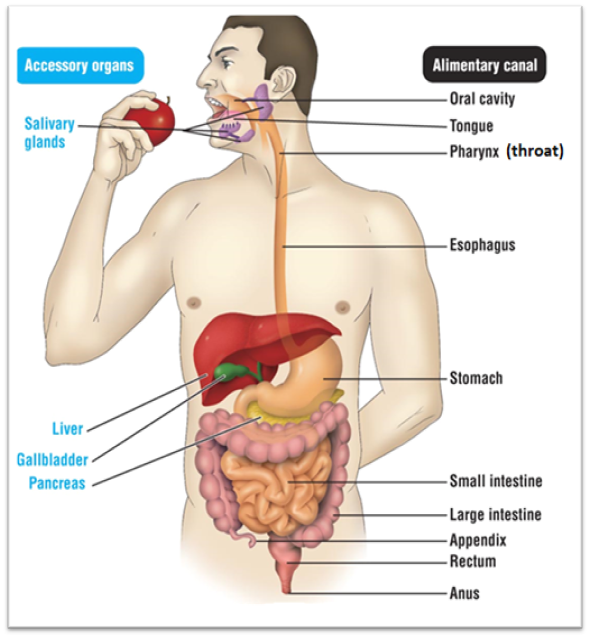
Esophagus
The pathway the food take to get from the mouth to the stomach
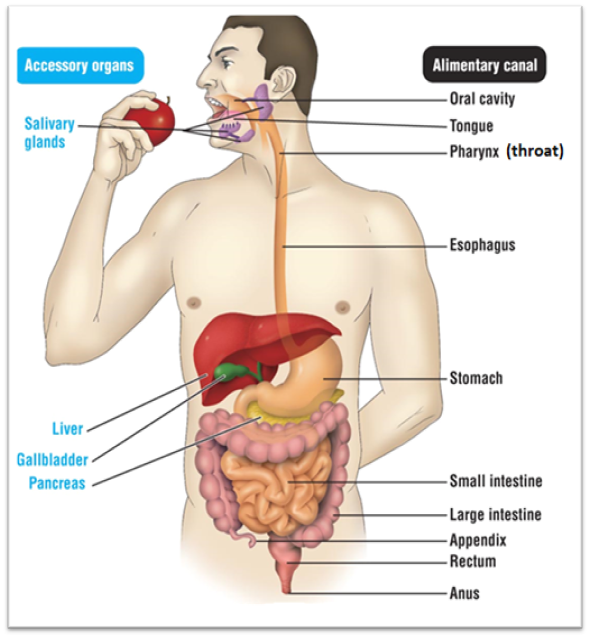
Stomach
Continues with chemical digestion of food. It exposes the food to it’s acid. After the acid is mixed with food, it creates an acid chyme. The organ creates a digestive enzyme called pepsin
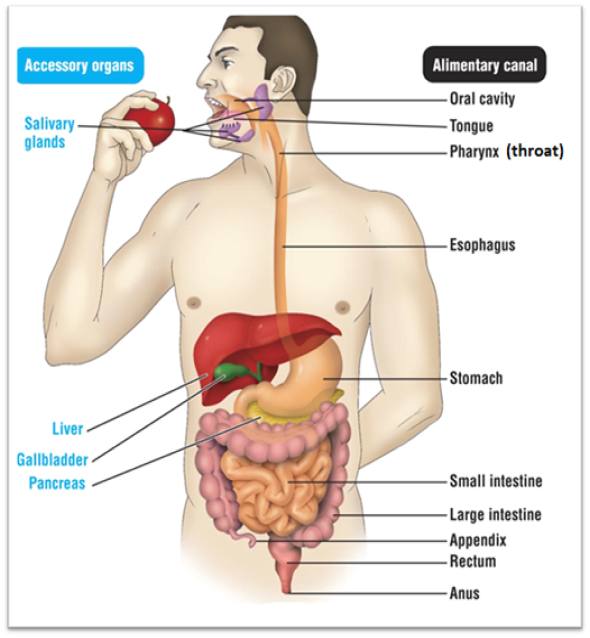
Small intestine
Has two functions. Function #1 is that it serves as the last place of chemical digestion. Relies on chemicals from the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas to complete food breakdown. It gets bile from the liver and gall bladder. The organ adds several chemicals that help with digestion. These chemicals are: Sodium bicarbonate, trypsin, pancreatic amylase, pancreatic lipase, and nuclease. It’s second function is to absorb the majority of nutrients and 90% of water
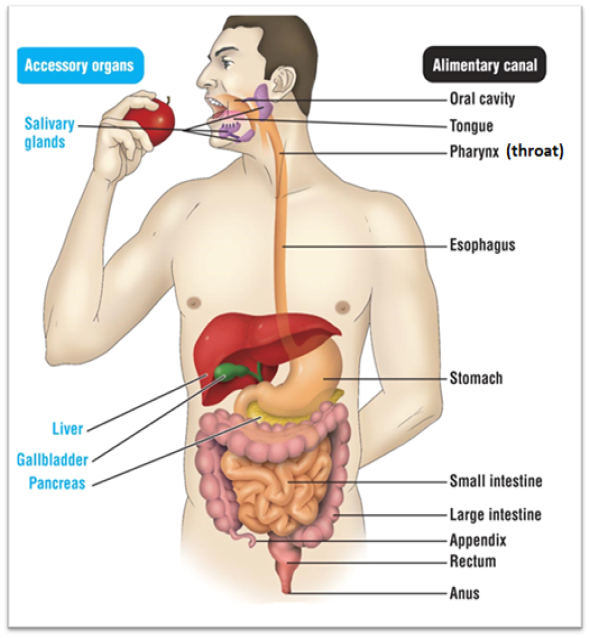
Large intestine
Absorbs remaining 1% of water, where you start to form poop. It produces vitamin K and B
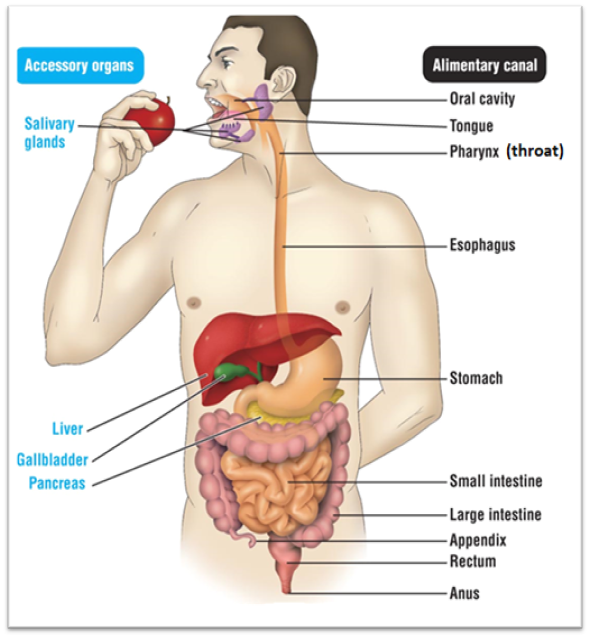
Rectum
Stores undigested materials (Examples are: solid waste, stool, feces, fecal matter, poop)
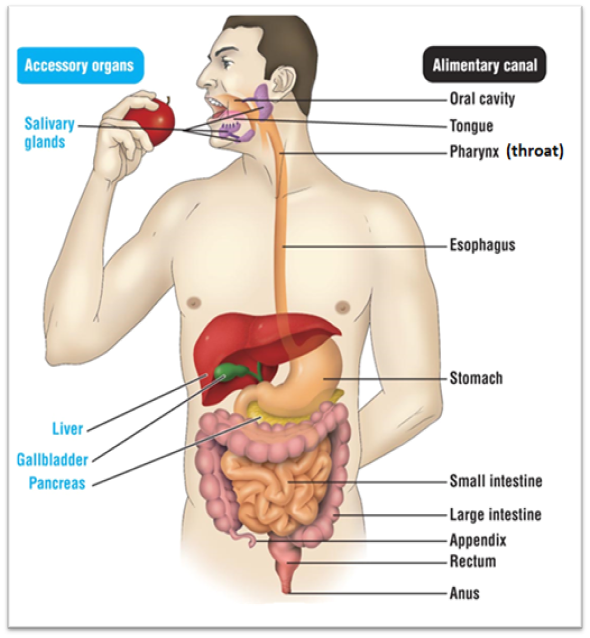
Anus
Eliminates poop
Gastric bypass
The leading way of rapid weight loss Bypassing the small intestine. The small intestine absorbs our macros. Has different procedures. Restrictive procedure, malabsorptive procedure. Side effects include: absorbing fewer nutrients and vitamins; need add supplements; may need a higher dose of medications due to decrease absorption; your baby will weight six pounds instead of seven.
Gastric sleeve
A shorter medical procedure. It is a better option for people with a heart and lung condition. less time is spent under general anesthesia. It’s a restrictive only procedure, it decrease stomach size.
lap band
Temp procedures with usual temp. No major invasive surgery is involved. Uses a medical device to restrict stomach size. It is restrictive but temporary.
GLP-1 injections
Glucagon-like peptide-1
Gastroparesis
Slowing down of digestion
Pathway for food through digestive system
Oral cavity → pharynx → esophagus → stomach → small intestine →large intestine → rectum → anus
Bile
Helps with liquid/fat digestion. The liver makes this enzyme and the gall bladder stores it
Stomach acid
Breaks down all macro molecules (protein, carbs, lipids, and nucleic acid). Produces by the stomach
Sodium bicarbonate
Neutralizes acid in the small intestine. Produces by the pancreas
Pepsin
A stomach acid that breaks down proteins. Produced by the pancreas
Trypsin and chymotryspin
Two chemicals that help with digestion. Their goal is to finish of digestion. They are produced by the pancreas
Nuclease
A chemical that breaks down the DNA of all plant and animal food. Produced by the pancreas
Salivary amylase
Breaks down carbohydrates in the mouth. Produced by salivary glands
Pancreatic amylase
Breaks down carbohydrates in the small intestine. Produced by the pancrease
Pancreatic lipase
A stomach acid that breaks down all fat molecules. produced by the pancreas
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Caused by hormonal imbalance that leads to irregular periods and unpredictable ovulation. fluid filled sacs may be seen in the ovaries
Endometriosis
A condition where tissue that is similar to the endometrium grows outside the uterus. symptoms include heavy periods and painful menstrual cramps
Uterine fibroids
Tumors that grow in the wall of the uterus. Most of these tumors and non-cancerous, symptoms include heavy and prolonged periods