iGCSE Edexcel Physics Solids, Liquids & Gases
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
a substance below the melting point is a...?
solid
less dense
there are less particles in the same volume, the particles are spaced out, similar mass
more dense
there are more particles in the same volume, the particles are very close to each other, larger mass
density
the mass per unit volume of a substance
state the equation linking density, mass and volume
density(kg/m³)=mass(kg)/volume(m³)
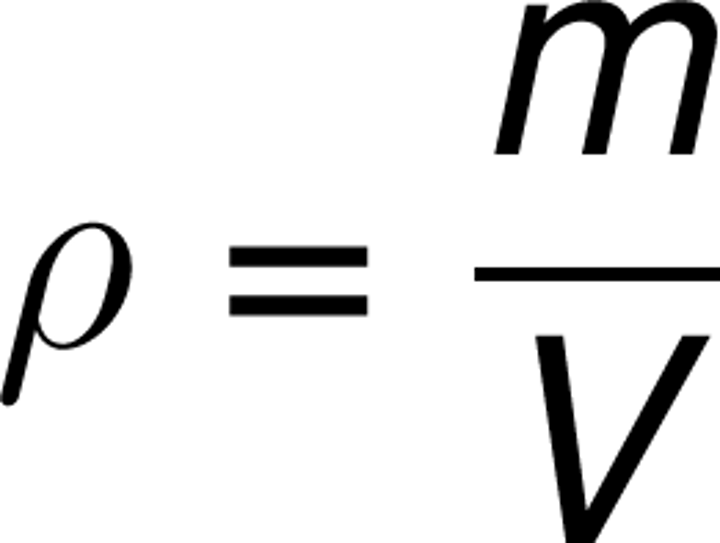
when will an object float?
density of object < density of medium

when will an object sink?
density of object > density of medium

state the equation linking force, pressure and area
pressure=force/area
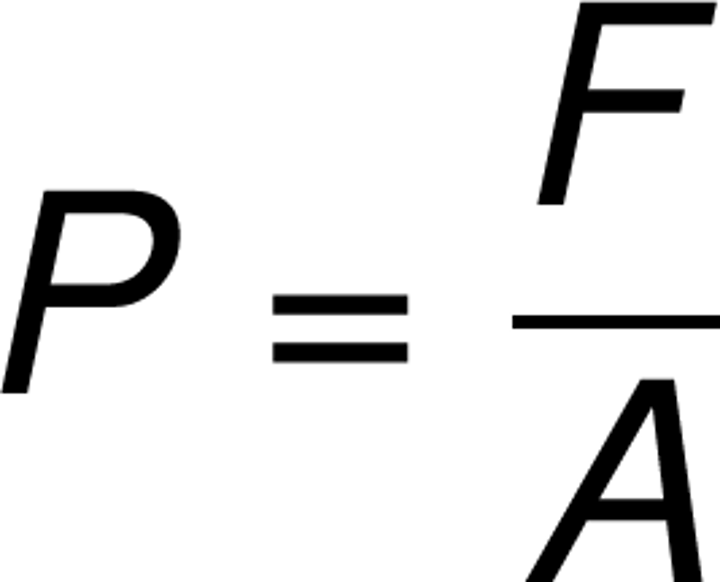
high pressure
const. F/small A
low pressure
const. F/large A
when does pressure in liquids increase?
pressure in liquids increase with depth
celsius to kelvin
K=C+273
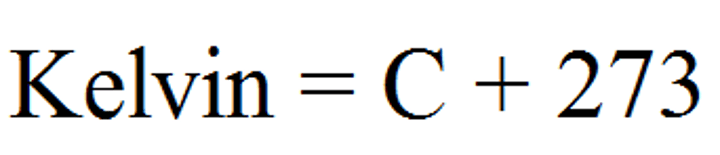
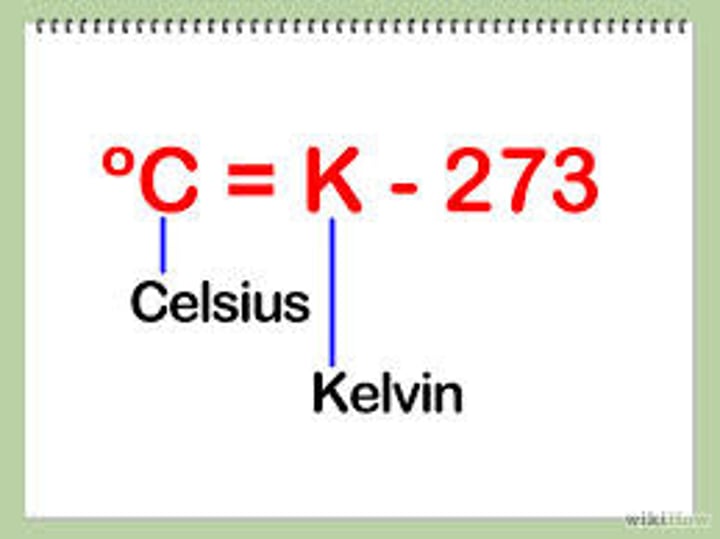
kelvin to celsius
C=K-273
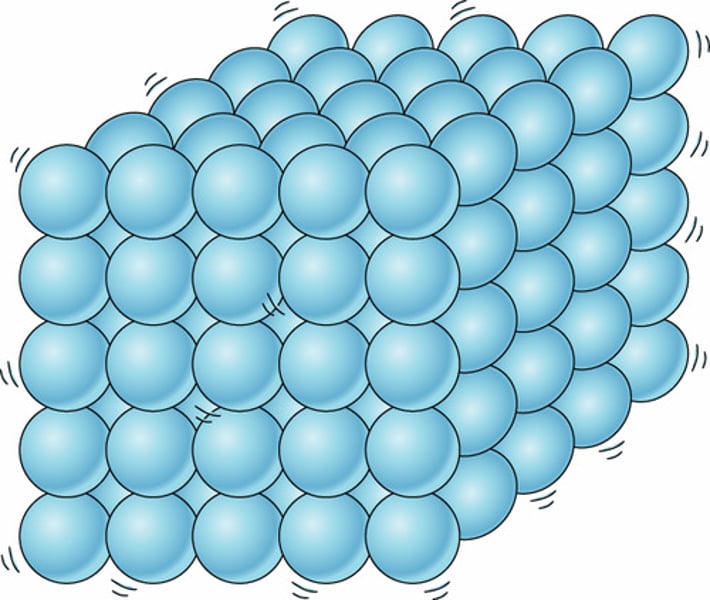
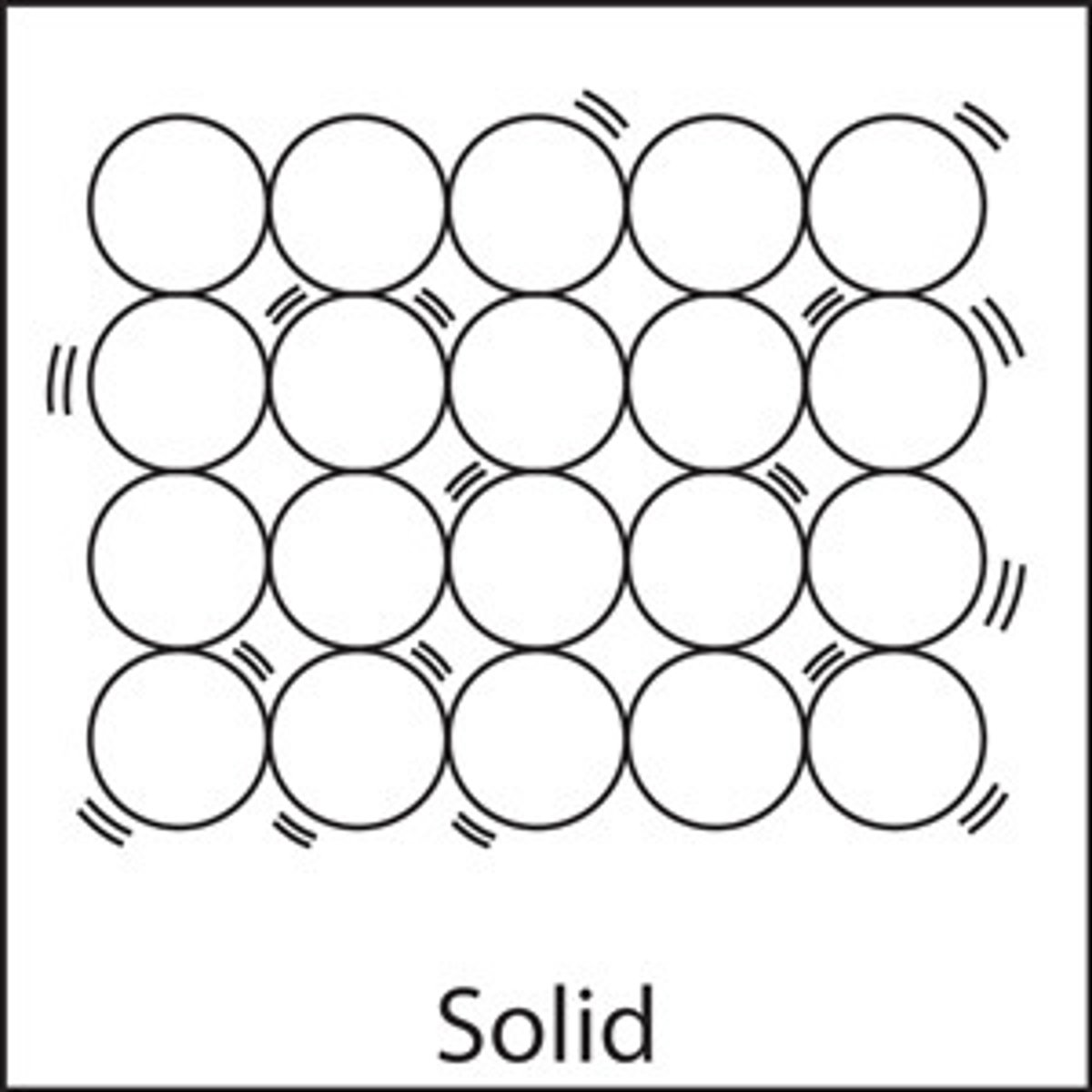
describe the movement of particles in solids
vibrate around their fixed position
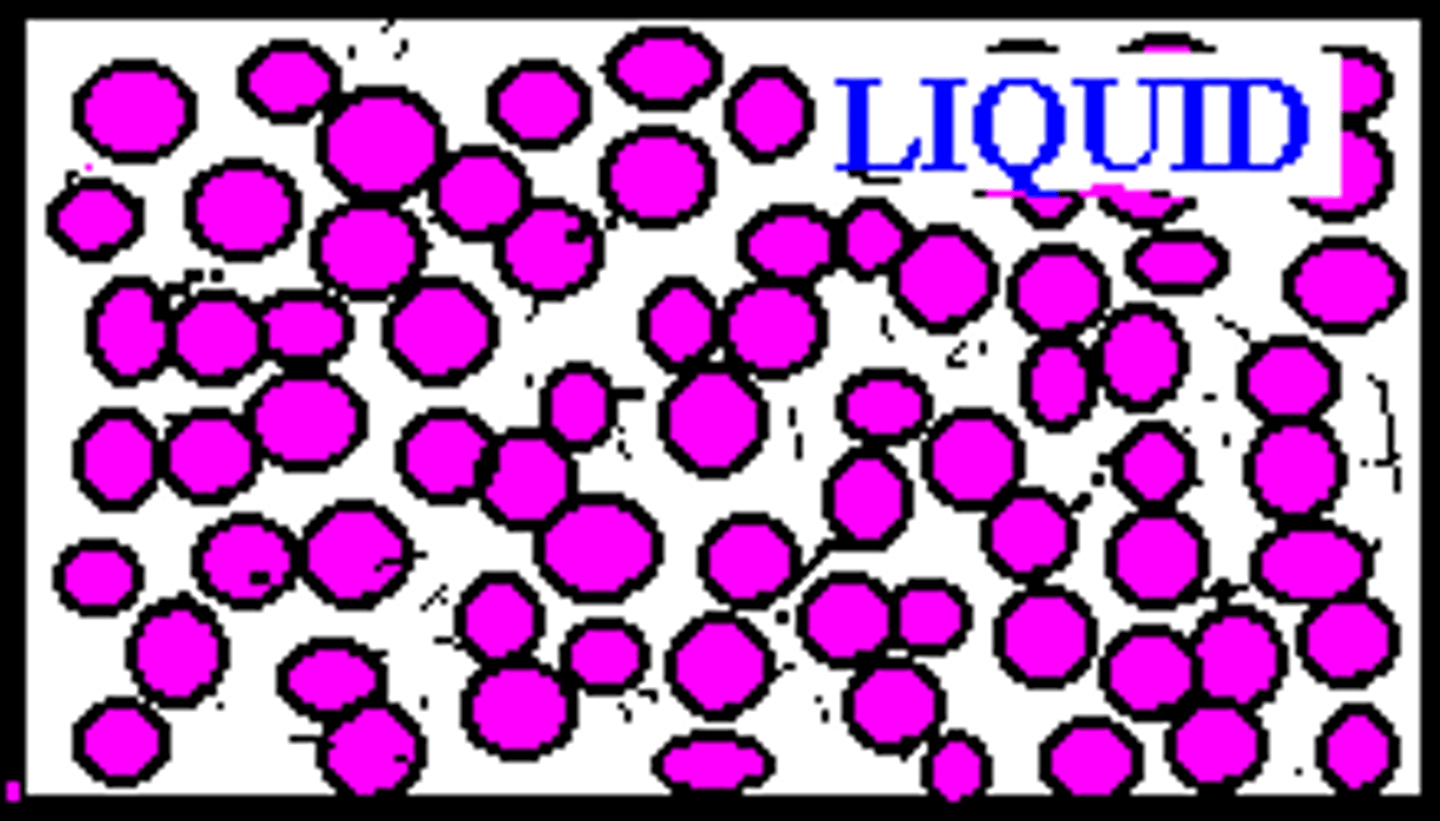
describe the movement of particles in liquids
slide or roll over each other
describe the movement of particles in gases
-move freely and fast
-move randomly
describe the spacing of particles in solids
-very short distances
-very close to each other
describe the spacing of particles in liquids
-short distances
-close to each other
describe the spacing of particles in gases
-large distances
-far apart form each other
describe the order of particles in solids
-regular order
-regular pattern
-regular lattice
describe the order of particles in liquids
-irregular order
-irregular pattern
describe the order of particles in gases
-random
-no order
-no pattern
describe the forces of attraction between particles in solids
very strong forces
describe the forces of attraction between particles in liquids
strong forces
describe the forces of attraction between particles in gases
-weak forces
-no forces
melting/freezing point
every pure substance melts/freezes at a particular temperature

a substance beyond the melting point is a...?
liquid
boiling point
every pure substance boils at a particular temperature

a substance beyond the boiling point is a...?
gas
a substance below the boiling point is a...?
liquid
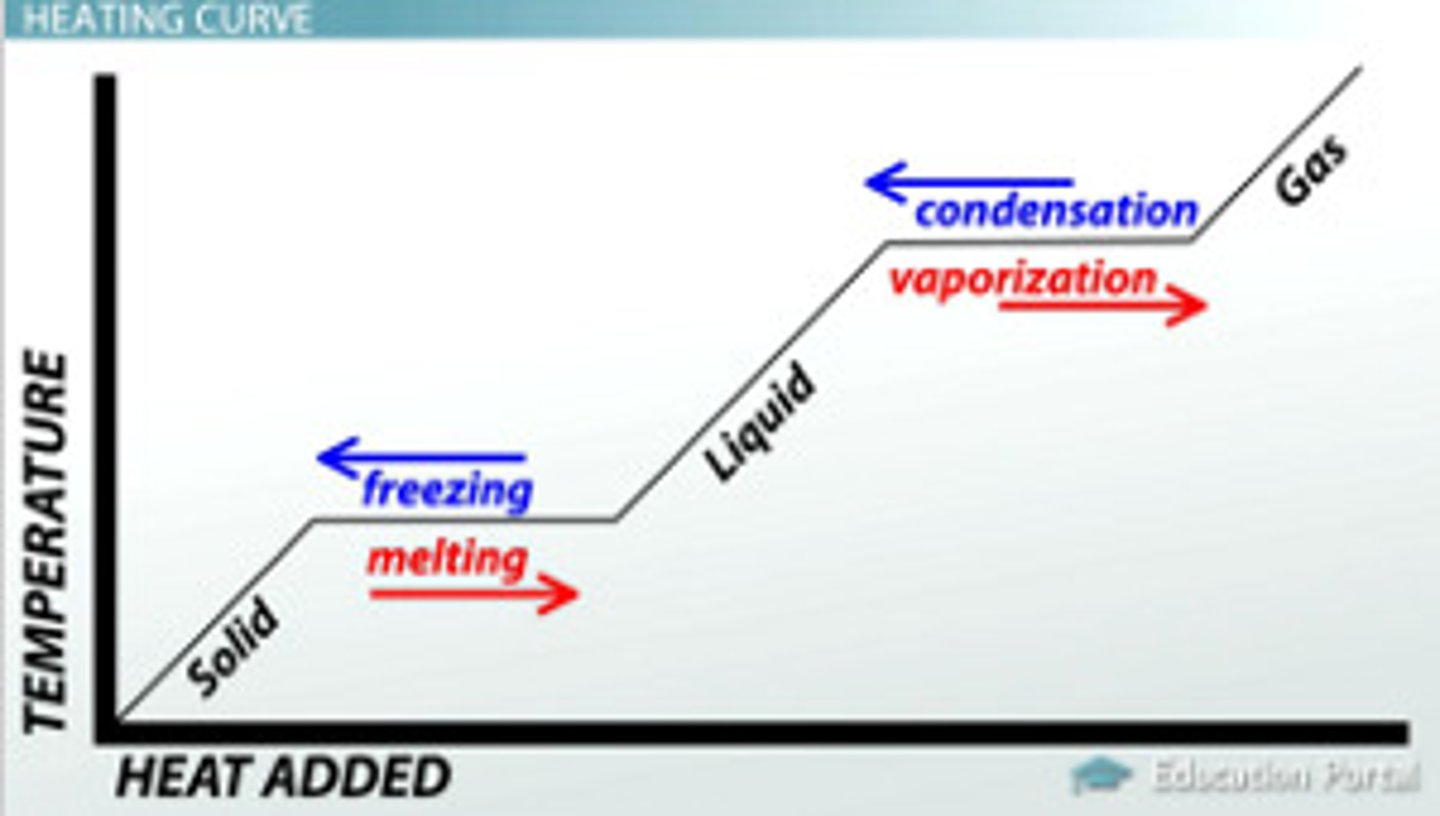
energy is taken in from the surroundings, temperature increases
melting, boiling/evaporation, sublimation
energy is given out to the surroundings, temperature decreases
deposition, condensation, freezing
heating curve
a plot of temperature versus time for a substance where energy is added at a constant rate
brownian motion
the random motion of a particle as a result of collisions with surrounding gaseous molecules
boyle's law
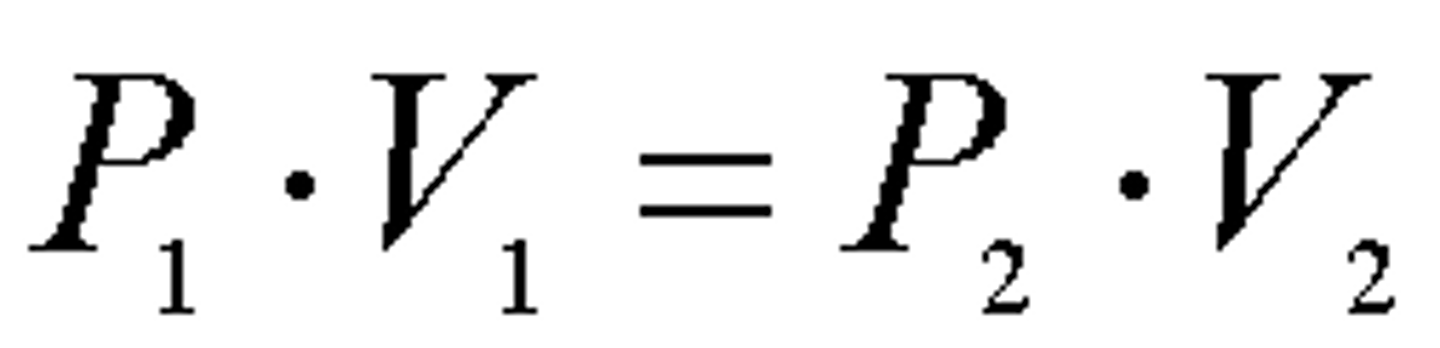
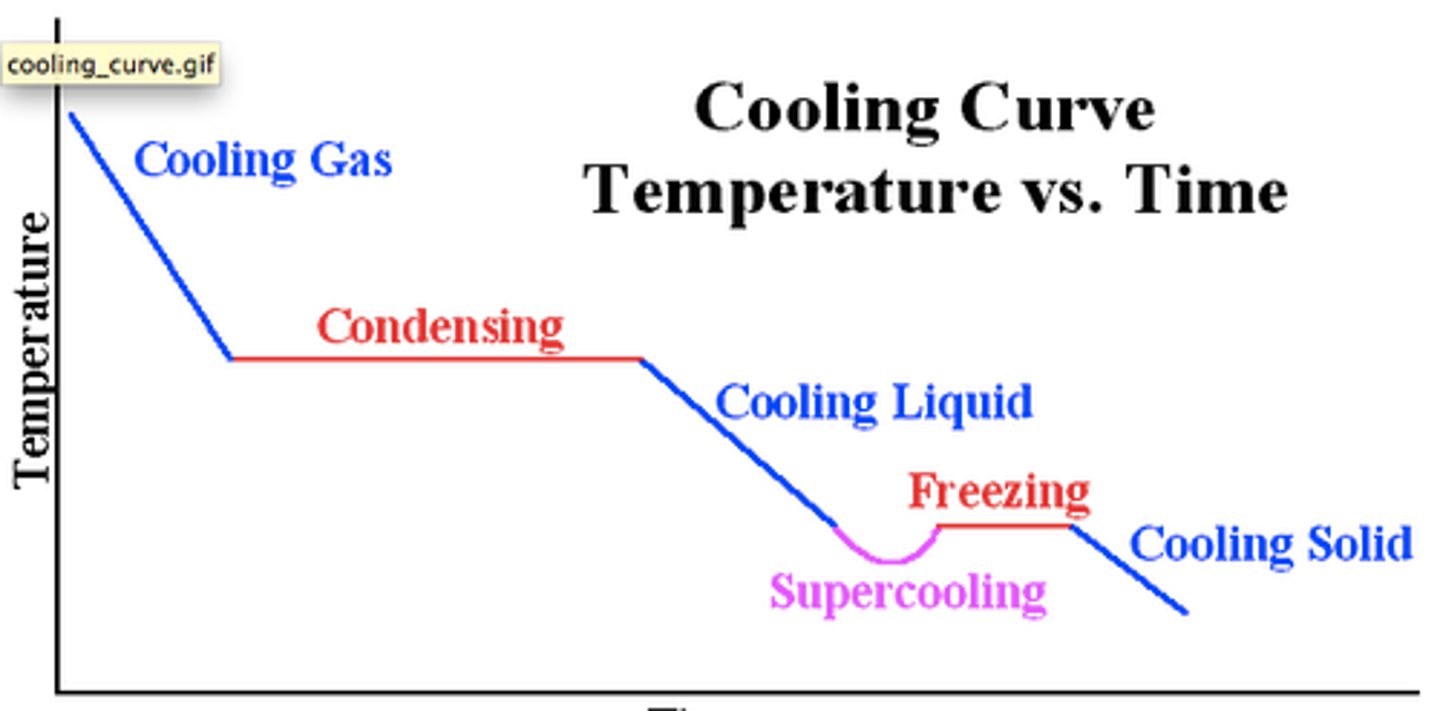
cooling curve
a line graph that represents the change of phase of matter, typically from a gas to a solid or a liquid to a solid
specific heat capacity
the energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kilogram of that substance by 1ºC (or 1K)
state the equation for change in thermal energy

what is the SI unit of pressure?
pascals (Pa) or N/m²

in solids, pressure acts in the direction of force. in which direction does pressure act in liquids or gases?
it acts equally in all directions
state the equation linking pressure difference, depth, density of liquid and gravitational field strength
pressure(Pa)=depth(m) x density(kg/m³) x g(m/s²)
explain why kelvin scale is used in science instead of celsius scale
kelvin scale is directly proportional with the average KE of the particles
what is absolute zero?
-273ºC or 0K when particles have no KE and do not move
explain the pressure of a gas in terms of the motion of particles
the particles move in random directions. when the collide with the walls of the container they exert force at a right angle to container. this causes pressure.
how does changing the temperature of a gas affect the velocity of the particles?
the higher the temperature, the more KE the particles have and therefore the faster the average velocity of the particles
how does temperature affect the pressure of a gas?
increasing temperature increases the average kinetic energy of particles so they move faster. therefore particles collide harder and more frequently. this increases the pressure
state an equation linking initial pressure, final pressure, initial temperature and final temperature
P₁/T₁=P₂/T₂
explain how changing the volume of a gas affect the pressure of a gas
volume and pressure are inversely proportional assuming temperature and mass of the gas is kept constant. therefore as volume decreases pressure increases; as volume increases pressure decreases
state an equation linking initial pressure, initial volume, final pressure and final volume for a gas
P₁V₁=P₂V₂
state 2 assumptions you should make while using this equation: P₁V₁=P₂V₂
-fixed mass
-fixed temperature
give an example of how unwanted energy transfer while heating can be reduced
through using insulation, which prevents energy being transferred to the surroundings
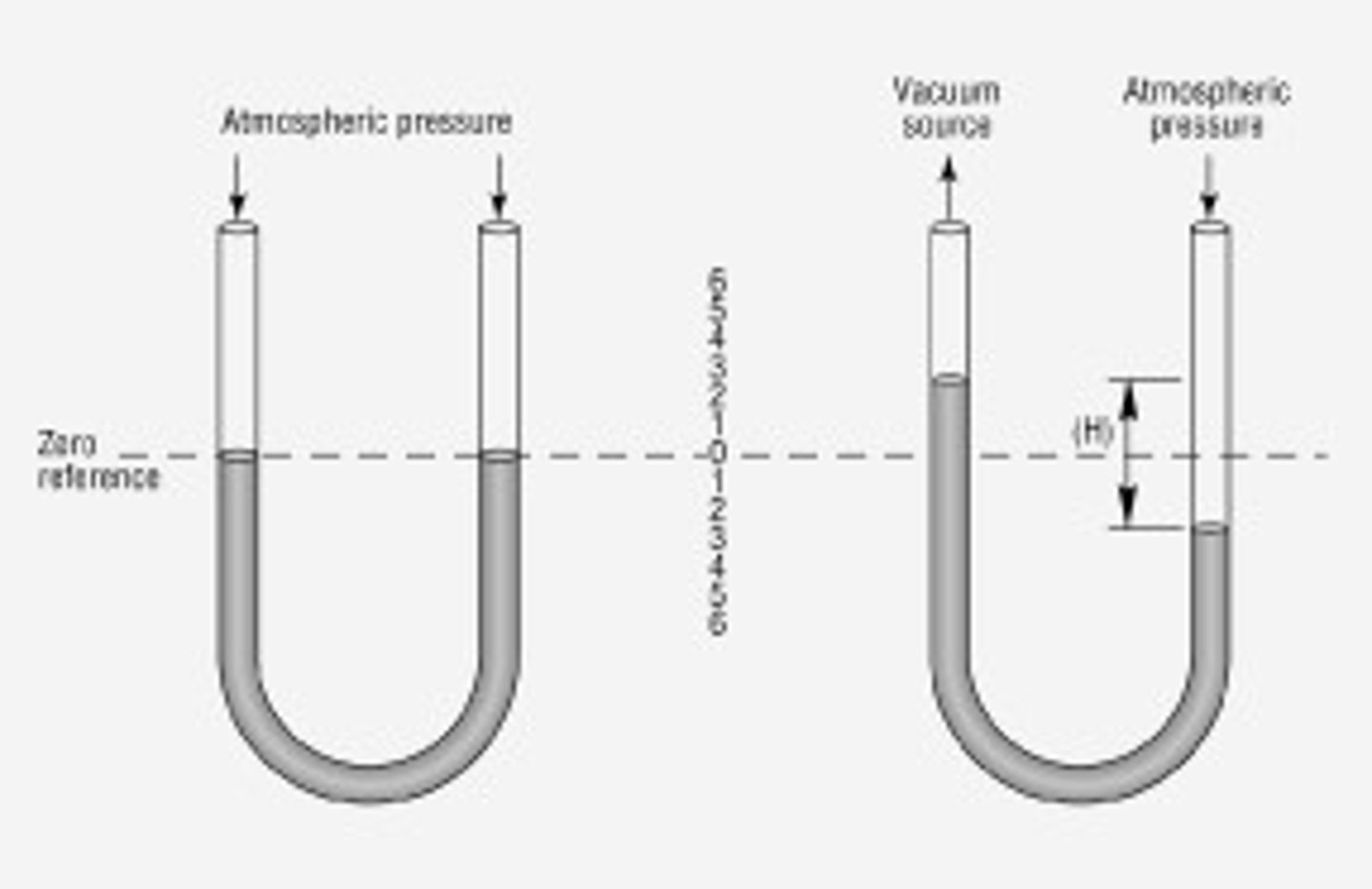
manometer
a device used to measure the pressure of a fluid. it consists of a U-shaped tube filled with liquid. the height of the liquid on either side of the tube can be used to determine the pressure difference
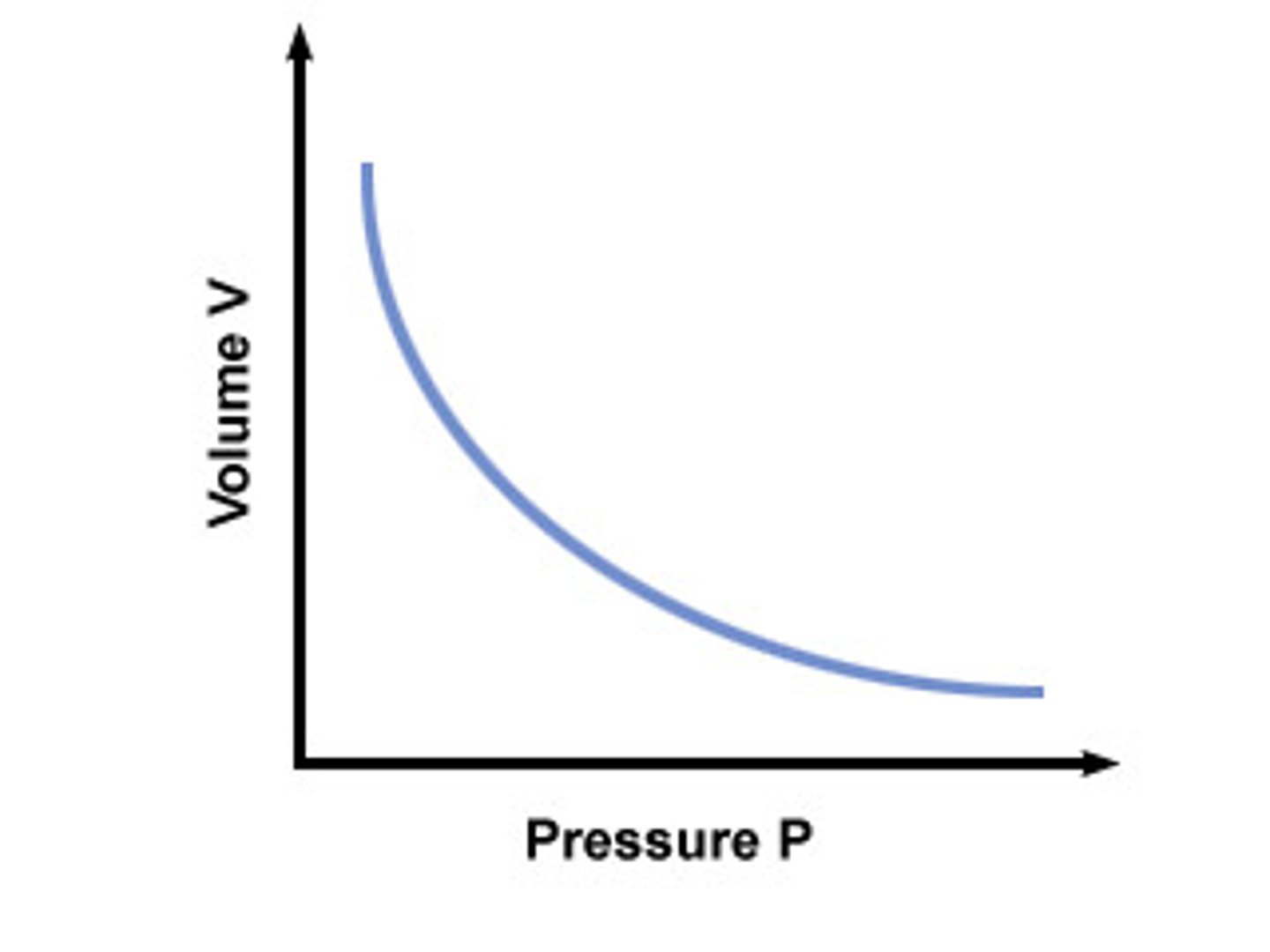
what does boyle's law state?
the pressure of the fixed mass gas is inversely proportional to the volume, as long as the temperature is kept constant
what does pressure law state?
the pressure is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature as long as volume is kept the same