MI - Friday Quiz unit 3
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
G0
Dormant cell phase
cells is still metabolically active
Temporary or permanent
Caused by
DNA repair
Little/no growth signals
Maturity (I.E. Neurons)
Proto-oncogene
Healthy gene that regulates cell growth, division, and apoptosis
Oncogene
Mutated proto-oncogene that is overactive
causes uncontained cell division and tumor formation
Tumor suppressor genes
produce proteins that inhibit cell growth/division
Control division
Identify and repair mutated DNA
Apoptosis
Risk factor: Genetic
Genetic predisposition
specific gene
hereditary
Risk factor: Biological
Sex, Age, Race, etc
Risk factor: Environmental:
Diet, Exercise, Habits, etc
Healthy vs cancer cell morphology
Healthy
uniform
Higher cytosol volume
Cancer
unorganized
irregularly shaped nucleus/multiple nuclei
lower cytosol volume
How does p53 regulate cell division
Activates genes to slow/inhibit cell growth or trigger apoptosis when the cell is stressed
low oxygen
DNA damage
etc
Its protein can also activate repair factors
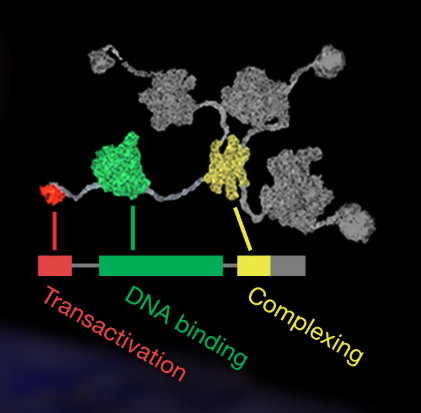
Structure of tp53
Transactivation Domain: allows tp53 to activate other genes after binding to their regulatory regions. Recruits enzymes that transcribe RNA.
DNA Binding Domain: responsible for tp53’s ability to bind to genes regulatory sequences. Checks for mutations. Most tp53 mutations are found here
Complexing Domain: Brings 4 tp53 molecules together so they become active
What happens when tp53 is mutated?
It cannot bind to DNA or halt cell division
Why might apoptosis occur?
Cell damage
Maintaining cell balance
Growth
Internal apoptosis pathway
Happens within mitochondria
When stimulus occurs the antiapoptotic BCL class is inhibited
results in increased membrane permeability
Cytochrome C is then released into the cytosol and forms a DISC (Death Inducing Signaling Complex)
External apoptosis pathway
Regulated by immune cells binding to a TNF receptor. The binding causes a capase cascade that kills the cell.
What do microarrays measure
mRNA expression
What are microarrays used for
determining which genes aren’t being expressed properly
Why are microarrays used with pearson correlation coefficient
determine how similar the genetic expression is in two or more individuals.
Human carcinoembryonic antigen (CEACAM6)
codes for a protein located in the extracellular matrix
cell cycle regulation, particularly with adhesion between cells
When over-expressed, it becomes an oncogene, because it leads to unregulated cell division and inhibits cellular death.
Cytochrome P450 (CYP1A1)
codes for a protein that is located in the endoplasmic reticulum
protein catalyzes reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesizes cholesterol, steroids, and other lipids
expression of this protein is induced by some polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), some of which are found in cigarette smoke
Sufactant protein B (SFTPB)
codes for proteins that assist breathing and is not involved in the regulation of the cell cycle.
SRY
codes for a protein located in the nucleus
protein is testis-determining factor (TDF), which initiates male sex determination
X-ray
noninvasive
electromagnetic radiation
dense structures and dyes appear white
structures like fat, muscle, and fluid appear black
examines bones, teeth, lungs, breasts, heart, blood vessels, and the digestive tract
uses ionizing radiation which can increase risk of developing cancer
X-ray: Pros and Cons
Pros
noninvasive
inexpensive
Cons
ionizing radiation
contrast material can cause allergic reaction
Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT Scan)
Noninvasive
series of X-ray views taken from many different angles are combined to produce cross-sectional images of the bones and soft tissues
examines the chest, abdomen, pelvis, spine, and other skeletal structures
ionizing radiation
Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT Scan): Pros and Cons
Pros
noninvasive
image bone, soft tissue, and blood vessels all at the same time
able to be performed with implants
Cons
ionizing radiation
contrast material reaction
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
noninvasive
uses magnets and radio waves instead of radiation
images of soft tissue
cross sectional images
examine the brain, spine, joint, abdomen, blood vessels, and pelvis
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Pros and Cons
Pros
noninvasive with almost no risk
no exposure to ionizing radiation
images of the soft tissue structures of the body are more likely to identify and accurately characterize diseases than other imaging methods
contrast materials are less likely to cause reactions
Cons
implants may pose a risk
confined space →claustrophobia
Bone scan
noninvasive
nuclear image testing
examine the skeleton to detect abnormalities
uses tiny amounts of radioactive materials called tracers (radionuclides)
Bone scan: Pros and Cons
Pros
noninvasive
extremely sensitive to abnormalities and variations in bone metabolism
can scan the entire skeleton
Cons
cannot determine cause of bone metabolism abnormalities
tracers used produce a small amount of radiation exposure