Unit 1 Maternal Newborn
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
Uterus
Hollow, thick-walled organ; Centered in pelvic Cavity
Uterine Corpus/body
Upper layer of uterus
Uterine Corpus layers
Serosal Layer (perimetrium)
Muscular Layer (myometrium)
Mucosal Layer (endometrium)
Fundus
Rounded uppermost portion of uterus
Endometrium
Monthly renewal from menarche to menopause with absence of pregnancy
Cervix
Lower portion of uterus
Internal os
Opens to uterus
External os
Opens to vagina
Cervix Functions
Lubricate vagina
Act as passage from vagina to uterus
Acts as bacteriostatic agent
Provides alkaline environment to protect sperm
Uterine ligaments that support uterus
-Broad
-Round
-Ovarian
-Cardinal
-Infundibulopelvic
-Uterosacral
Isthmus
Part of fallopian tube next to uterus, site of tubal ligation.
Ampulla
Fertilization occurs here, next to isthmus
Fimbria
Funnel like enlargement with many moving fingerlike projections (frimbriae) reaching out to the ovary which helps to intercepting the ovum when released.
Fallopian tube functions
Transport ovum to uterus
Site for fertilization
Nourishing environment for ovum/zygote
Ovaries
-obtains three layers
-Store and develop follicles and secrete hormones: Estrogen and Progesterone
Female reproductive cycle (FRC)
Ovarian cycle (2 phases)
Menstrual (3 phases)
Take place simultaneously
Estrogen
-Secreted by ovary
-Controls women’s secondary sex characteristics (femaleness)
-Maturation of ovarian follicles
-Amount greatest during proliferative phase of menstrual cycle
Progesterone
-Hormone of pregnancy**
-Secreted by corpus luteum (inside ovary, little space that is created once follicle ovulates out of ovary)
-Helps thicken uterine lining to help embryo attach
-Greatest amount during secretory phase of menstrual cycle
Prostaglandins (PGs)
-Play a significant role in ovulation; helps release mature egg
–PGF vasocontricts (increases contractility)
–PGE vasodiolator (relax muscles)
Hypothalamus secretes:
gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) which causes anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH
FSH
Responsible for maturation of follicle (follicle will secrete estrogen as it matures)
LH
-Increases production of progesterone, release of mature follicle
-Surge 10-12 hrs before women ovulates
-Estrogen drops and progesterone rises when ovulation occurs
Ovarian cycle
2 phases
Follicular phase (days 1-14)
Graffian follicle (fluid filled sac with ovum in it) appears by day 14)
Under dual control of FSH and LH
Body temp increases after ovulation due to increased progesterone (24-48hrs after)
Luteal phase (15-28, fixed)
Begins when ovum leaves follice
If ovum fertilized and implants in endometrium, egg secretes hCG which trigger pregnancy test (best to take in morning with dilute urine).
Corpus luteum degenerates when fertilization does not occur
Menstrual Cycle (28 days, three phases)
-Menstrual phase (bleeding signifies start of cycle)
Some endometrial areas shed-bleeding
Estrogen levels low
Corpus luteum begins to degenerate
Small blood vessels rupture, and cells escape into stromal cells
Menstrual flow begins
-Proliferative phase
Increasing amounts of estrogen enlarge endometrial glands with peak before ovulation and Cervical Mucous thins
-Secretory phase—follows ovulation
Increased vascularity of uterus in preparation for fertilized ovum
Somatic cell
-any cell other than reproductive cells
-23 pairs, 46 chromosomes (diploid)
-22 autosomes (similar cells in males and females)
1 sex chromosome
Each human begins life as a:
single cell; fertilized ovum or zygote
Cells reproduce in a continuing process:
–Mitosis (growth and development)
–Meiosis (human production)
Mitosis
-Exact copies of original cell (somatic cells)
-Essential for growth, development, and tissue repair
-One-stage cell division
-Two daughter cells
-Makes growth and development possible
Gametogenesis- Meiosis
-Process by which germ cells (ovum and sperm) are produced
-Only half the genetic material of typical body cell
-Haploid number of cells to form full zygote (23)
Sperm and ovum unite to form:
Zygote
Ova are fertile for:
12 to 24 hrs after ovulation
Sperm are fertile for
72 hrs
Fertilization takes place in:
Ampulla; widest part just before it opens and connects to uterus
Sex of the zygote is determined at:
Fertilization
Implantation occurs:
7-10 days after fertilization
Blastocyst (ball of cells) burrows into:
Endometrium and endometrium in now called decidua
Body structures from primary cell layers (3 germ layers form 2 weeks after conception)
Embryonic Membranes (chorion and Amnion) Provide:
Protection
Nutrition
Waste removal
Gas exchange
Chorion:
-surrounds amnion, forms the fetal portion of placenta, site for early genetic testing
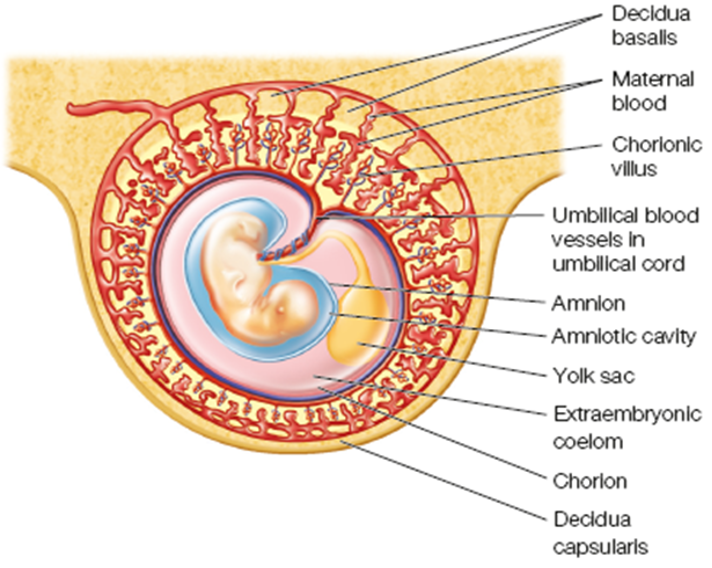
Amnion
Helps to form amniotic sac
Amniotic Fluid
Act as cushion
Temp regulation
permit symmetrical growth
Prevent embryo from attaching to amnion
Extension of fetal extracellular space
Yolk Sac
functions only in early embryonic life
Early nutrients
Forms primitive RBCs until embryo’s liver takes over (6 weeks)
Amniotic fluid contains
water, electrolytes, fats, carbs, fetal waste
Amniotic fluid Characteristics
▪Ph is slightly alkaline
▪Lanugo: fine baby hairs
▪Clear/faint yellow
▪Increases until 28 weeks to 700-1000ml
Oligohydramnios
amniotic fluid less than 400ml
Hydramnios
▪fluid greater than 2000mls
Umbilical Cord
Lifeline placenta to baby
–Body stalk fuses with embryonic portion of placenta
–Provides circulatory pathway from chorionic villi to embryo
▪One vein-delivers O2 to the fetus, two arteries delivers deoxygenated blood back to placenta (gas and nutrient exchange)
Wharton’s jelly
Connective tissue that attaches to blood vessels in umbilical cord that prevent it from collapsing in conjunction with high pressure blood.
Functions of fecal circulatory system
–Maintains blood flow to placenta
–Provides fetus with oxygen and nutrients
–Removes carbon dioxide and waste products
Fraternal twins
–Two ova and two sperm
–Dizygotic: two placenta and two amniotic sac
–Much more frequent than mono
–Just like two normal siblings, not the same
Identical Twins
–Single fertilized ovum
–Monozygotic: two babies, once placenta
–Considered a random event
–Congenital problems can occur (high risk, high rate of miscarriage)
•Originate at different stages
Placental development and functions
•After implantation cells differentiate, differentiation of fetal, trophoblast cells
•Forms week 3 and attaches to uterine wall
•Metabolic and nutrient exchange
Placenta Metabolic and transport activities
–Produces glycogen, cholesterol, fatty acids
Placenta endocrine functions
–Production of hormones
▪hCG
▪Progesterone
▪Estrogens
▪Relaxin
Placental immunologic properties
▪Exempt from immunologic reaction by the host
▪Hormones progesterone and hCG suppress cellular immunity during pregnancy
▪Prevent body from rejecting fetus
Development of FCS
-O2 blood flows through umbilical vein into abdominal wall of fetus
-Ductus venous: bypasses liver
-Foramen Ovale: passage from right to left atrium
-Ductus arteriosus: bypasses lungs; placenta assumes function
Fetal circulation delivers the highest available o2 concentration to:
the head, neck, brain, and heart and lesser to abdominal organs and lower body; hence, cephalocaudal development
Pregnancy duration
10 lunar months or 280 days
starts from beginning of last normal menstrual period and ends at birth
Most born within 10-14 days of calculated birth date.
Most organs are formed by:
8 weeks gestation
•Two weeks pregnant at fertilization
Heartbeat at:
4 weeks
Fetal circulation at:
6 weeks
8-12 weeks (10 weeks)
Fetal heart tones can be heard by doppler
16 weeks
Baby’s sex can be seen and the fetus looks like a baby
20 weeks
Heartbeat heard with fetoscope
quickening
baby has regular schedule
hands can grasp
24 weeks
increasing activity
fetal respiratory movement begins
baby makes sucking movements
28 weeks
eyes open and close
baby can breath
baby is 2/3 final length
32 weeks
has fingernails and toenails
less red an wrinkled
subcu fat is being laid down
38+
baby fills total uterus
baby gets antibodies from mother
Factors influencing fetal development
•Quality of sperm or ovum and Genetic Code
•Adequacy of intrauterine environment
•Teratogen
—Any agent that can cause development of abnormal structures in an embryo
–Effects depend on:
▪Maternal and fetal genotype
▪Stage of development during exposure
▪Dose, duration of agent
•Organs formed primarily during embryonic development which makes them extremely vulnerable to teratogen
•Maternal nutrition/lifestyle (folic acid important to reduce neural tube defects)
Normal uterus change through pregnancy
-Enlargement
-Thickening of walls (endometrium)
-Increase in vascular and lymphatic system to support baby
-Braxton hicks contractions
Braxton hicks contractions
Irregular contractions which differs them from labor contractions. Occur early on and throughout pregnancy
Cervix changes
-Mucous plug formation; prevent microorganisms from entering cervical canal
-Increase in vascularity leading to Goodell sign and Chadwick sign
Goodell sign
Cervical softening to allow baby to pass through
Chadwick sign
Bluish-purplish discoloration
Ovary changes
-Cease ovum production during pregnancy
-HCG maintains corpus lutem
-Secrete progesterone unitl placental production is sufficient (11 weeks)
Vaginal changes
-Hypertrophy
-increased vascularization
-Hyperplasia due to estrogen
-+ secretions, loosening of connective tissue
-Increased blood flow
Breast changes; occur after first missed period
-Glandular hyperplasia and hypertrophy—> Tender breast
-Darkened areola and superficial veins prominent
-Montgomery glands form
-Striae may develop
Colostrum
Antibody rich yellow secretion
Converts to mature milk 2-3 days following childbirth
Tidal volume and o2 consumption ___
Increases and changes from abdominal to thoracic to compensate for baby’s growth
Mild dyspnea is ___ Tachypnea is ___
Normal, NOT
Lightening
Term for when baby drops at around 40 weeks
___ and ___ are common during pregnancy (Nasal)
Rhinitis and epistaxis
Blood volume increases ______ and ___ of maternal blood is contained in the uterus.
40-50% and 1/6, blood volume peaks at third trimester
There is a _____ in systemic and pulmonary vascular resistance which allows___
decrease, more blood to reach uterus and placenta.
Pulse will ___ during pregnancy, typically ___
Increase, 10bpm
Femoral venous pressure ___ causing ____
Rises, venous congestion aka edema in lower extremities
Mom needs to avoid lying on ___ to prevent _____ aka______
back, vena cava syndrome, supine hypotensive syndrome
Pt. may develop ____ as blood volume increases ____ but erythrocyte only increases ___
Anemia, 40-50%, 25%
Pt. may experience several symptoms related to uterine pressure including:
Acid reflux, heartburn, bloating, constipation, hemorrhoids
N/V during ___ caused by ___ and usually gone by ___
1st trimester, Hcg (released by fertilized egg), 2nd trimester
Gallbladder and gastric emptying may be slow leading to:
Cholelithiasis and IBS; encourage high fiber and low fat diet
Urinary changes:
GFR increased and glycosuria not uncommon
Skin and hair changes
Hyperpigmentation
Facial chloasma (subside after pregnancy) (melasma gravidarum)
Striae
Vascular spider nevi
Decreased hair growth
Hyperactive sweat and sebaceous glands
Linea Nigra-common
Pelvic joints relax leading to:
Waddling gait
Center of gravity changes leading to
Lordosis
Diastasis Recti
Separation of abdominal muscle; not painful
Eye changes
Decreased intraocular pressure
Thickening of cornea due to fluid retention; may affect contact fit; returns to normal after pregnancy
CNS Changes
Reports of decreased attention, concentration, and memory
Sleep problems common in pregnancy
Recommended to gain _______, if underweight gain ___ if overweight gain ___
25-35 lbs, more, less
Biggest weight increase occurs during ___ of pregnancy as baby is growing faster
Second Half
Insulin resistance becomes common second half of pregnancy due to increased ___ demands and ___ demands
fetal and carb.