biology exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/101
Last updated 2:19 AM on 1/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
1
New cards
structural diversity
measure of different structures available as habitat
2
New cards
species diversity
measure of populations and variety of populations present
3
New cards
genetic diversity
measure of genetic characteristics within a species
4
New cards
villi
increase surface area in small intestine for absorption of monomers
5
New cards
carbs are broken down by…
amylase, sucrase/maltase/lactase (to become monosacchrides)
6
New cards
lipids are broken down by…
bile and lipase (to become glycerols and fatty acids)
7
New cards
protein is broken down by…
trypsin and erepsin (to become amino acids)
8
New cards
9
New cards
what does the liver do?
creates/synthesizes bile
10
New cards
accessory organs (digestive)
salivary glands, pancreas, liver, bile, gall bladder
11
New cards
what does the pancreas do?
releases enzymes to aid in digestion in the small intestine
12
New cards
4 stages of digestion
ingestion, digestion, absorption, egestion
13
New cards
macronutrients
carbohydrates, lipids, water, proteins
14
New cards
which side of the heart is oxygenated blood?
left
15
New cards
where does the lub dub sound come from?
lub - AV valves closing
dub - semilunar valves closing at end of contraction
dub - semilunar valves closing at end of contraction
16
New cards
healthy blood pressure
120/80
17
New cards
diastole
relaxation, filling phase of heart
18
New cards
systole
contraction, emptying phase of heart
19
New cards
what is the electrical pathway of the heart?
SA node → AV node → bundle of his → purkenje fibres
20
New cards
where does electrical impulse start?
SA node
21
New cards
path of blood through heart
22
New cards
function of veins
carry deoxygenated blood back to heart - VERY LOW blood pressure (have valves)
23
New cards
function of capillaries
transport blood, nutrients, and oxygen, single cell thick to allow for diffusion - LOW blood pressure
24
New cards
function of arteries
distribute oxygenated blood around body, carry blood away from heart - HIGH blood pressure
25
New cards
what is breathing controlled by?
the medulla oblonga
26
New cards
residual volume
volume of air that always remains in lungs
27
New cards
vital capacity
maximum amount of air that can be inhaled and exhaled
28
New cards
diaphragm movement during exhalation
relaxes (moves up)
29
New cards
diaphragm movement during inhalation
contracts (moves down)
30
New cards
where does gas exchange occur in humans?
the lungs and the body cells
31
New cards
archea
prokaryote, no nuclear membrane, unicellular, cell wall, heterotrough/autotrough, asexual reproduction
32
New cards
eubacteria
prokaryote, no nuclear membrane, unicellular, peptidoglycen cell wall, heterotrough/autotrough, asexual reproduction
33
New cards
protist
eukaryote, nuclear membrane, multicellular, mitochondria/some chloroplasts, no cell wall, autotrough/decomposer/heterotrough, mostly asexual
34
New cards
fungi
eukaryote, nuclear membrane, multicellular, mitochondria, unicellular (yeast)/multicellular, chitin cell wall, heterotrough, asexual/sexual reproduction through spores
35
New cards
plant
eukaryote, nuclear membrane, multicellular, mitochondria, chloroplast, multicellular, cellulose cell wall, autotrough, sexual/asexual reproduction
36
New cards
animal
eukaryote, nuclear membrane, multicellular, mitochondria, multicellular, no cell wall, heterotrough, sexual reproduction
37
New cards
cellular respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6H2O + 6CO2 + ATP
38
New cards
why are angiosperms successful?
flowers allow for gamete transfer, produce fruit to allow for seed dispersal, variety of seed dispersal methods
39
New cards
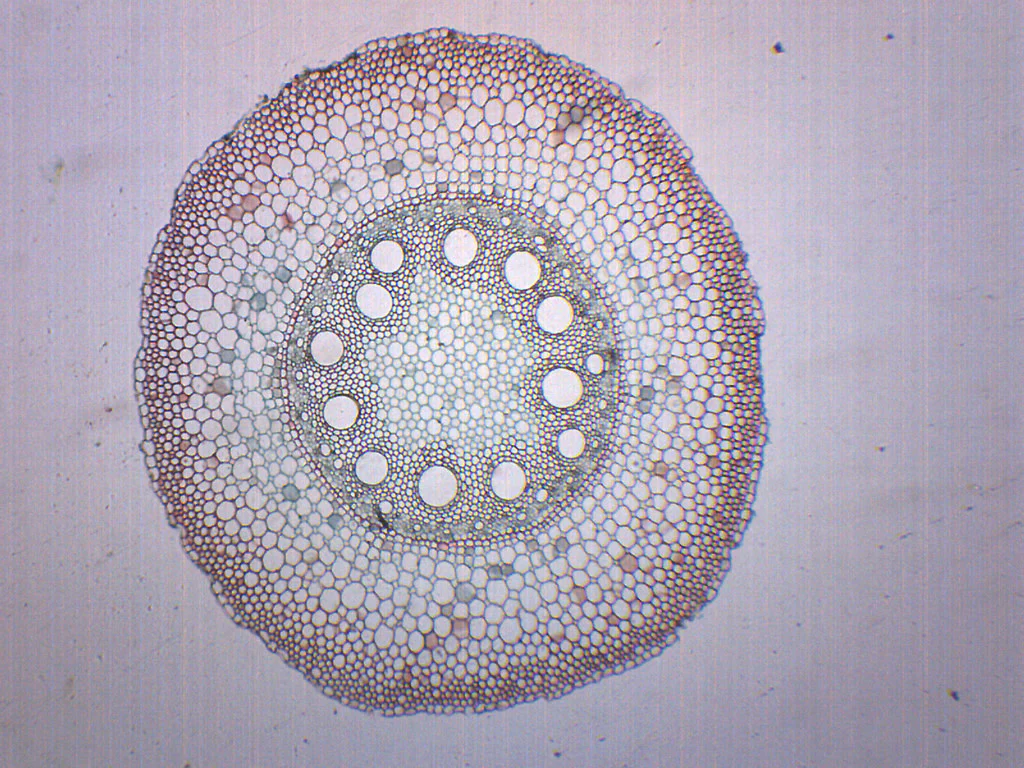
\
monocot root
40
New cards
monocot flower
petals in multiples of 3
41
New cards
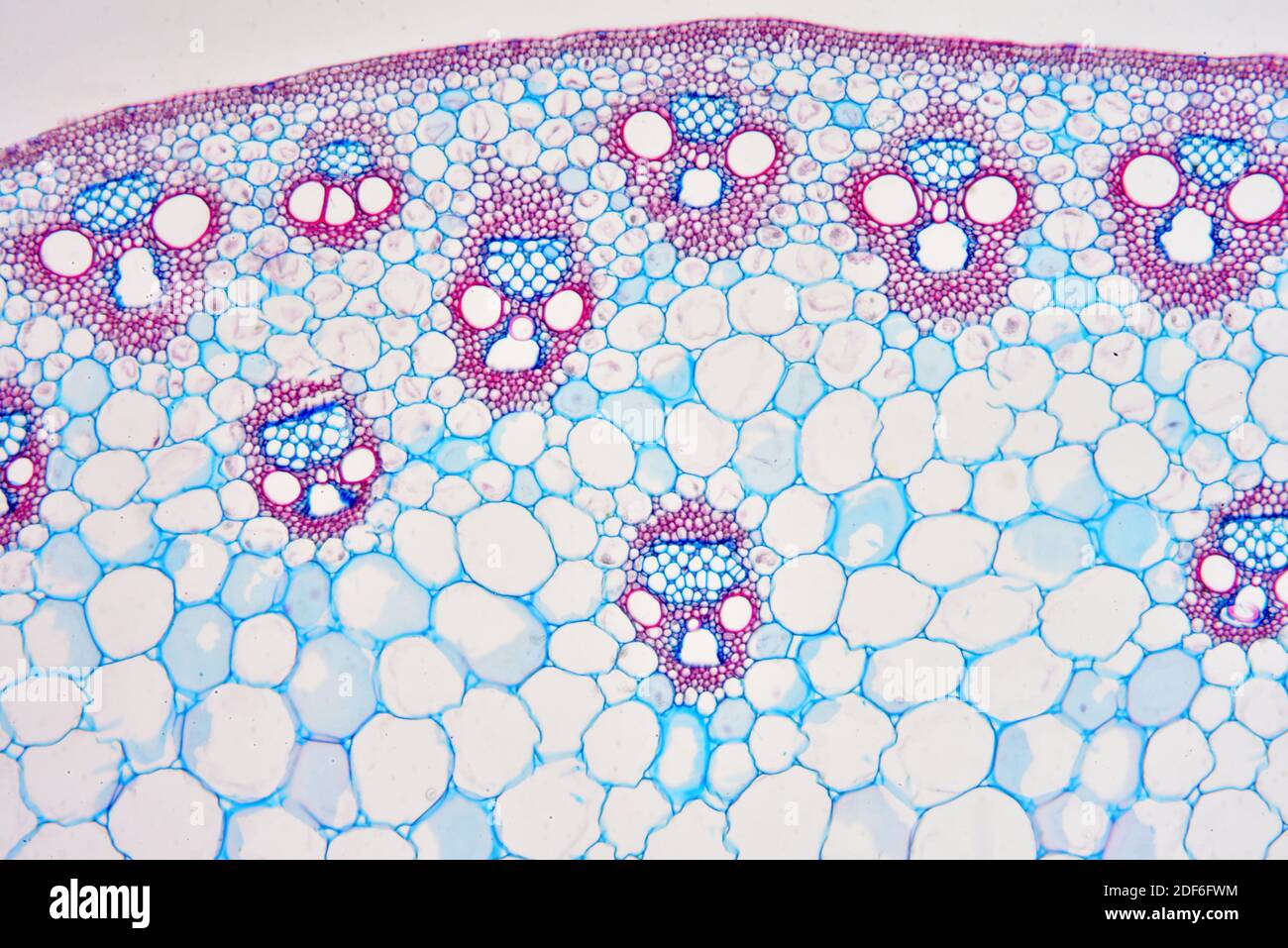
\
monocot stem
42
New cards
monocot seed
one cotyledon (leaf in seed)
43
New cards
monocot leaf
veins spaces evenly, parallel, long and narrow leaves
44
New cards
monocot pollen
one pore/furrow
45
New cards
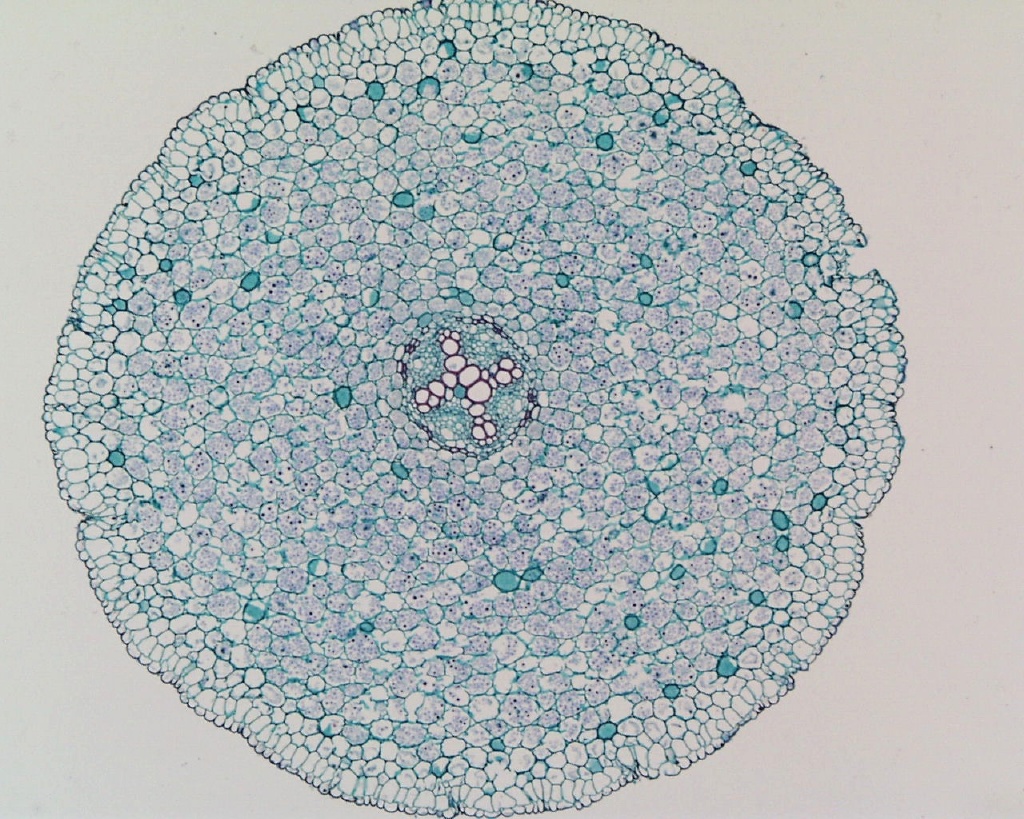
dicot root
46
New cards
dicot flower
4 or 5 petals
47
New cards
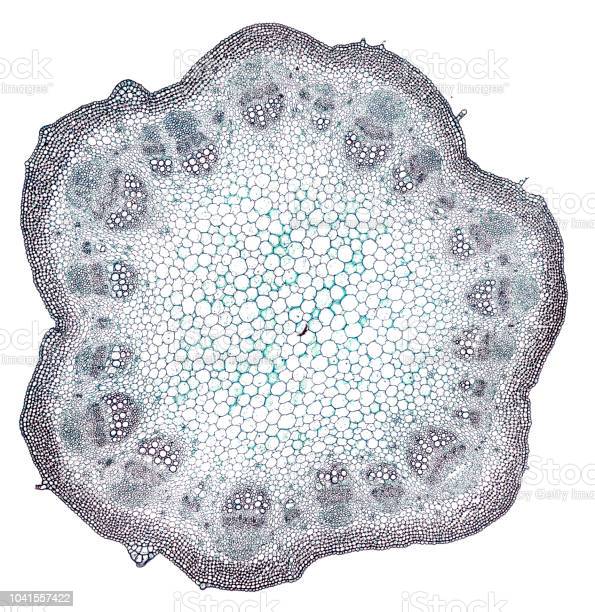
dicot stem
48
New cards
dicot seed
two cotyledons (leaf in seeds)
49
New cards
dicot leaf
branched veins, stomata found mostly along bottom of leaves
50
New cards
dicot pollen
three pores/furrows
51
New cards
meristematic tissue
in plants, allows for growth (APICAL + LATERAL)
52
New cards
apical meristems
type of meristematic tissue, at root and shoot tissues, grow vertically
53
New cards
lateral meristems
at locations other than root/shoot, grow around diameter
54
New cards
dermal tissue
protective coverings
55
New cards
cuticle
waxy layer, protects plants from disease, pests, water loss (dermal tissue)
56
New cards
stomata
on lower side of leaf, allows water vapour in and out (dermal tissue)
57
New cards
guard cell
controls size of stomata (dermal tissue)
58
New cards
root hairs
allow for absorption, protection, etc., (dermal)
59
New cards
vascular tissue
allows for transport through plants
60
New cards
xylem
carries water/dissolved ions up from roots
61
New cards
phloem
transports sugars synthesized in leaves to storage
62
New cards
ground tissue
makes up bulk of young plants, fills space between other tissues
63
New cards
how do you know seeds are living?
produce sugars, cellularly respire
64
New cards
stamen
male reproductive part of flower, contains anther and filament
65
New cards
pistil
female reproductive part of flower, contains stigma, style, ovary, ovuole
66
New cards
taproot
found in dicots
67
New cards
fibrous root
found in monocots, no main root
68
New cards
DNA full name
deoxyribouncleic acid
69
New cards
human cells have __ chromosomes
46
70
New cards
nitrogenous bases
adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine
71
New cards
there are __ pairs of chromosomes in humans
23
72
New cards
why do cells divide?
to grow, to repair, to reproduce
73
New cards
mitosis
asexual reproduction of cells to create identical daughter cells
74
New cards
interphase
DNA is duplicated, still in form of chromatin. centrioles replicate
75
New cards
early prophase
chromatin condenses, nucleolous disappears, spindle fibres form, nuclear membrane breaks down
76
New cards
late prophase
nuclear membrane is gone, spindle fibres attach to chromosomes, centrioles move to poles
77
New cards
metaphase
chromosomes line up in centre
78
New cards
anaphase
(apart) spindle fibres pull sister chromosomes apart
79
New cards
telophase
cleavage furrow forms, chromosomes uncoil within respective nuclear membranes
80
New cards
cytokinesis
cell splits, creates two identical cells
81
New cards
meiosis
one cell creates 4 genetically different haploid cells
82
New cards
prophase I
chromatin condenses, nucleolous disappears, spindle fibres form, nuclear membrane breaks down (+ CROSSING OVER occurs, chromosomes exchange genetic info)
83
New cards
metaphase I
chromosomes line up on either side of the plate
84
New cards
anaphase I
homologus chromosomes are pulled to either side of cell (sister chromosomes STAY TOGETHER)
85
New cards
telophase I
nuclear membrane begins to reform, chromosomes decondense
86
New cards
cytokinesis (meiosis)
two new NON IDENTICAL cells form
87
New cards
interphase II
only centrioles are replicated, not DNA
88
New cards
prophase II
nuclear envelope begins to break down, chromosomes condense
89
New cards
independent assortment
homologus chromosomes like up randomly along metaphase plate in metaphase I, sister chromatids assort randmly in metaphase II
90
New cards
abnormal meiosis
chromosomal errors such as change in chromosome number/changes in structure - can cause down syndrome, turner syndrome, etc.,
91
New cards
nondisjunction in meiosis I
homologus chromosomes don’t separate in first division
92
New cards
nondisjunction in meiosis II
sister chromatids fail to separate in 1 of 2 cells
93
New cards
gene
codes a trait, portion of DNA
94
New cards
allele
version of a trait (i.e., blue eyes)
95
New cards
genotype
genetic expression of trait
96
New cards
phenotype
physical expression of trait
97
New cards
Gregor Mendel
father of genetics, predicted genes existed
98
New cards
incomplete dominance
blend of two traits (red + blue = purple)
99
New cards
codominance
both traits appear at once (red + blue = red and blue stripes)
100
New cards
9:3:3:1
ratio of phenotypes as a result of two heterozygous carriers mating, using a dyhibrid cross