SSEP review
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
SSEPs
____ are the most common technique utilized for spinal cord monitoring in IONM
DCML (dorsal column medial lemniscus), fine touch, proprioception, vibration
SSEPs monitor the ___ pathway which is responsible for carrying information related to ____, ____, and ____ sensation
crude touch, pain, and temperature
Information regarding ____, ____, and ______ sensations are carried by the spinothalamic pathway and are not monitored by SSEPs
medulla
The DCML decussates at the ______
dorsal horn gray matter (spinal cord)
The spinothalamic pathway decussates at the _______
ipsilateral
Spinal cord injury to the DCML pathway results in ______ loss of fine touch, proprioception, and vibration below level of the lesion
contralateral
Spinal cord injury to the spinothalamic pathway results in ______ loss of crude touch, pain, and temperature below the level of the lesion
2, 3
The DCML pathway is made up of ___ synapses (medulla and thalamus), and __ orders of neurons
Fasciculus Gracilis
Lower extremity medial portion of DCML pathway
Fasciculus Cuneatus
Upper extremity lateral portion of the DCML pathway
contralateral
Each cerebral hemisphere of the postcentral gyrus contains somatosensory information for the _______ side of the body
rostral, caudal
Signals _____ to the site of injury will be affected, whereas signals ____ to the site would not be affected
technical, perfusion
peripheral SSEP loss can indicate ____ or____ issues
autodromic
ascending DCML pathways
antidromic
descending DCML pathway
reduced amplitude
Stimulation electrodes placed too close together can result in _________ due to shallow current flow and reduced efficacy through salt bridge formation
large artifacts
Stimulation electrodes placed too far apart can result in ________ due to increased impedance and would require more voltage
median
Stimulation sites for the _____ nerve
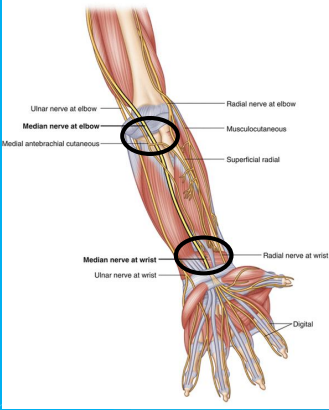
radial
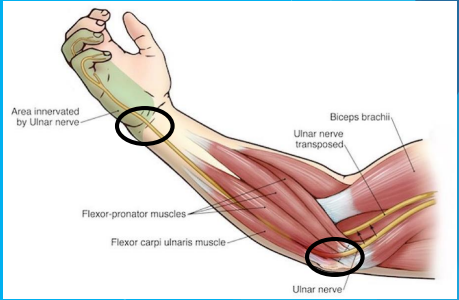
Stimulation sites for the _____ nerve
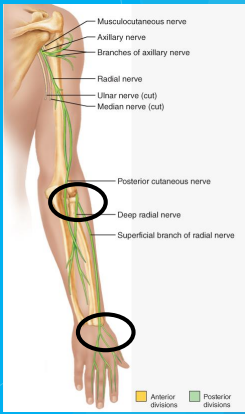
ulnar
Stimulation sites for the _____ nerve
median nerve
C5-T1 sensory roots (medial and lateral cords) of the brachial plexus
radial nerve
C5-T1 sensory roots (posterior cord) of the brachial plexus
ulnar nerve
C8-T1 sensory roots (medial cord) of the brachial plexus
200-500, 2.7-4.8, 15-40, 10-30
Recommended stimulation parameters for SSEPs includes:
Pulse width: ______ microsec
Rep Rate: _______ Hz (not integer divisible by 60)
Intensity: _____ mA (pad electrodes), ______ mA (needle electrodes)
CP
SSEP recordings are optimally done at the ___ line
active-reference
A recording channel in which there is an electrode near the generation site (active) and an electrode further away (reference) to allow best common mode rejection/cancellation with the differential amplifier (highly sensitive)
Bipolar
A more specific recording channel in which the active and reference electrodes are both placed near the site of the generator (ex- most EMGs)
Erbs point, C5S or C2S, CPi or Fz, CPc
Recording sites (upper):
Peripheral: _____
Cervical: _____
Subcortical: _____
Cortical: _____
30, 500-1500, 5, 20-500, 10-100, 2-20
SSEP Recording parameters:
Filters: LFF- ____Hz, HFF-____ Hz
Recording epoch/sweep display: ____msec per division (50 msec total)
Average number of trials: _____ runs
Dynamic range/amplifier gain: ____mV/Div
Display gain: _____mV/Div
N20
Cortical upper obligate waveforms
N20, N18, P14, N13, N9
SSEP upper obligate waveforms
N18, P14
subcortical upper SSEP obligate waveforms
N13
cervical upper SSEP obligate waveforms
N9
peripheral upper SSEP obligate waveforms
Posterior tibial
Stimulation sites for the ____ nerve
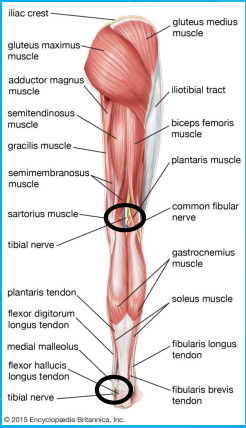
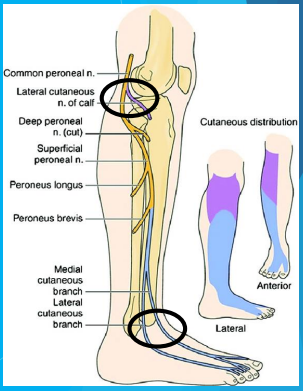
Peroneal
Stimulation sites for the ____ nerve
femoral
Stimulation sites for the ____ nerve
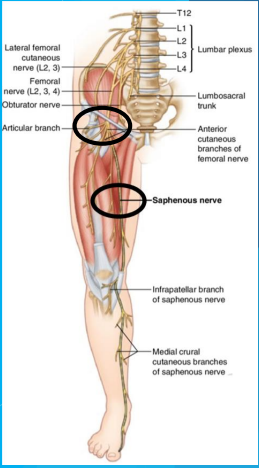
femoral nerve
L2-L4 sensory roots of the lumbar plexus
peroneal nerve
L4-S2 sensory roots of the lumbosacral plexus
Tibialis nerve
L4-S3 sensory roots of the lumbosacral plexus
200-500, 1.9-4.7, 20-50, 15-40
Lower SSEP stimulation parameters:
Pulse width: ____ msec
Rep-rate: ____ Hz
Intensity: ____mA (pad electrodes), ____ mA (needle electrodes)
pop fossa, T12 or L1, CPc or Fz, CPi or CPz
Lower SSEP recording sites:
Peripheral: _____
Lumbar point: _____
Sub-cortical: ______
Cortical: _____
10
Lower SSEP recording parameters change the sweep display to ____msec per division (100 msec total)
P37, N34, P31, N18, N8
Lower SSEP obligate waveforms:
P37
cortical lower SSEP obligate waveform
N34, P31
subcortical lower SSEP obligate waveforms
N18
Lumbar lower SSEP obligate waveform
N8
Pop fossa/peripheral lower SSEP obligate waveform
inhalational agents
SSEPs may be unreliable with _______ anesthesia regimen
specific to a sensory nerve root
Dermatomal Sensory Evoked Potentials (DSEPs) are similar to SSEPs except that the stimulation is delivered to a specific dermatome making it more ________ rather than a group of nerve roots and DSEPs have lower amplitudes
200-300, 1.9- 4.8, 30-40, 20-30
DSEPs stimulation parameters
pulse width: ____msec
Rep rate:______ Hz
Intensity: _____ mA (pad), ____ mA (needle)
the same
DSEPs have _______ recording parameters and anesthesia regimen to SSEPs