𝘤𝘶𝘭𝘵𝘶𝘳𝘦 𝘶𝘯𝘪𝘵
1/135
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms

match the type of diffusion with the graphic
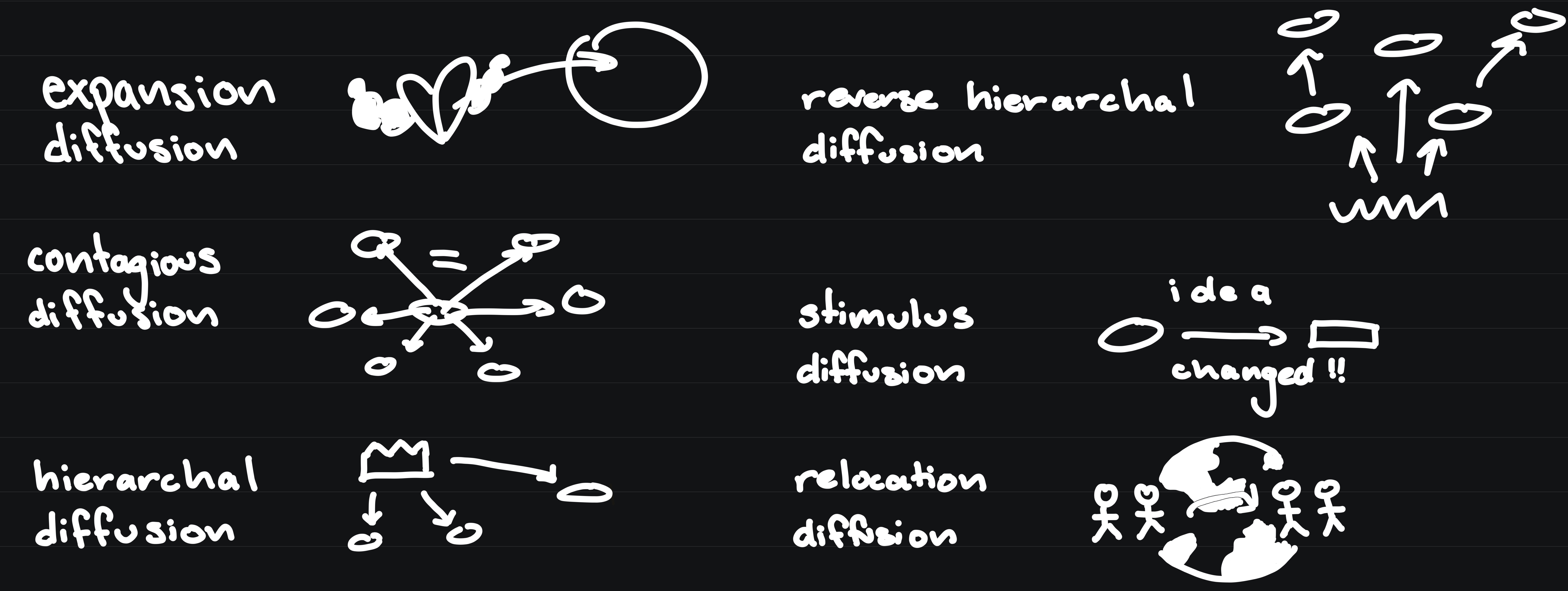
placelessness
doesn’t envoke emotional response; lakcs style
placemaking
process of a community coming together and transforming public places // ex. festivals, community gardens, etc
diaspora
dispersion
cultural divergence
individuals become separated from different aspectts of culture - may lead to abandonment
cultural convergence
different cultures merge (ex. mcdonalds)
protolanguage
deepest part of language organization, before language family. before written records of language. the roots
cultural landscape
the visible material landscape that cultural groups create as they inhabit the earth // ex. the great wall of China, Stonehenge, neighborhoods, parks, sacred places, farms and ranches, etc.
hierarchal diffusion
spread of an idea/innovation from one key person or node of authority/power // ex. celebrities promoting brands, gov., etc.
centrifugal force
things that pull people apart

introvert architecture
concealing architecture; emphasis on privacy
physical geography is optimal for that culture group // ex. Nazis use this idea to expand their “optimal” German culture. after war, ideologies like this persisted in racism creating xenophobia