AFM 241 - Final Exam (W6-W12)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:13 PM on 8/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
1
New cards
W6: Define **Analytics**
resources that help generate customer insights, identify growth opportunities, and stimulate innovations, producing competitive advantage
2
New cards
W6: **Early (or first)** advantage/ability
the ability to capture critical data assets can be difference between a dominating firm and an also-ran
3
New cards
W6: **Differentiation** (competitive advantage)
(be better, by being different), key in dsitinguishing operationally effective data from those efforts that can yield true strategic position
4
New cards
W6: Define **Databas**e (data organization)
single table or a collection of related tables
5
New cards
W6: Define **Database management systems (DMBS)** (data organization)
Software for creating, maintaining and manipulating data (aka database software)
6
New cards
W6: Define **structured query language (SQL)** (data organization)
a language used to create and manipulate databases
7
New cards
W6: Define **Business Intelligence**
combining aspects of reporting data exploration and ad hoc queries and sophisticated data modelling and analysis
* infrastructure for collecting, storing and analysis data the business produced
* databases, data warehouses, data marts fall under BI
* infrastructure for collecting, storing and analysis data the business produced
* databases, data warehouses, data marts fall under BI
8
New cards
W6: Define **Data Analytics**
tools and techniques for analyzing data (OOLAP, stats, models, data mining)
9
New cards
W6: Define **BI Vendors**
create bI and analytical software purchased by businesses (via the cloud)
10
New cards
What does **analytics** use and how is it useful?
* data, information technology, statistical analysis, quantitative methods, and mathematical or computer based models
* helps managers gain improved insight about their business operations and make better, fact based decisions
* helps managers gain improved insight about their business operations and make better, fact based decisions
11
New cards
W6: Define **Metrics** (data analytics)
used to quantify performance
12
New cards
W6: Define **Measures** (data analytics)
numerical values of metrics
13
New cards
W6: Define **Discrete Metrics** (data analytics)
involve counting
* on time or not on time
* number or proportion of on time-deliveries
* on time or not on time
* number or proportion of on time-deliveries
14
New cards
W6: Define **Continuous Metrics** (data analytics)
measured on a continuum
* delivery time
* package weight
* purchase price
* delivery time
* package weight
* purchase price
15
New cards
W6: **Numerical Data** (data type)
data that consists of numbers and can be measured or quantified (discrete and continuous data)
16
New cards
W6: What are the two sub-topics of numerical data (data type)
1. interval
2. ratio
17
New cards
W6: What is **Interval** numerical data (data type)
* ordinal data but with constant different observations
* no true ‘zero point’
* ratios are not meaningful
* e.g., temperature readings or grades
* no true ‘zero point’
* ratios are not meaningful
* e.g., temperature readings or grades
18
New cards
W6: What is **Ratio** numerical data (data type)
* continuous values
* a natural ‘zero point’
* ratios are meaningful
* e.g., monthly sales or delivery times
* a natural ‘zero point’
* ratios are meaningful
* e.g., monthly sales or delivery times
19
New cards
W6: Categorical data (data type)
represents qualitative or descriptive characteristics. It consists of categories or groups that are mutually exclusive and do not have a numerical value.
* e.g., gender (male/female), color (red/blue/green), and marital status (single/married/divorced). I
* e.g., gender (male/female), color (red/blue/green), and marital status (single/married/divorced). I
20
New cards
W6: What are the **two** sub-topics of categorical data (data type)
1. nominal
2. ordinal
21
New cards
W6: What is nominal data (data type)
* data placed in categories according to a specified characteristics
* no relationship between categories
* no natural order or ranking
* binary nominal data is where there are only two possible responses
* e.g., customer location or employee classification
* no relationship between categories
* no natural order or ranking
* binary nominal data is where there are only two possible responses
* e.g., customer location or employee classification
22
New cards
W6: What is ordinal data (data type)
* data ranked or ordered according to some relationship with one another that allows sorting
* no fixed units of measurement
* e.g., survey responses (poor, average, good, excellent) or college football rankings
* no fixed units of measurement
* e.g., survey responses (poor, average, good, excellent) or college football rankings
23
New cards
W6: Define Data warehouse
set of databases designed to support decision making in an organization
* aggregate enormous amounts of data from different operating systems
* structured for fast online queries and exploration
* aggregate enormous amounts of data from different operating systems
* structured for fast online queries and exploration
24
New cards
W6: Define Data mart
structured databased or databases focused on addressing the concerns of a specific problem or business unit
* e.g., increasing customer retention or improving product quality
* e.g., increasing customer retention or improving product quality
25
New cards
W6: Define **Data Lake**
allow for storage of data in both structured as well as unstructured (raw) formats)
* provide tools to pipe out data, filter it and refine it so it can be turned into information
* provide tools to pipe out data, filter it and refine it so it can be turned into information
26
New cards
W6: Define **Data Cloud**
cloud service that provides tools to extract transform and load (ETL) data from disparate sources into the cloud so it can be analyzed
* consider flexibility, scalability, cost-effectiveness and fault tolerance
* consider flexibility, scalability, cost-effectiveness and fault tolerance
27
New cards
W6: What are the **three big V’s** of big data
1. Volume
2. Velocity
3. Variety
28
New cards
W6: Define **Data Governance**
* rules and processes needed to manage data from creation to retirement
* Legal, Regulatory, Privacy, Information Security and Operation considerations
* Legal, Regulatory, Privacy, Information Security and Operation considerations
29
New cards
W6: What are things you need to consider **before** building a large scale data warehouse?
* clear vision with business focused objectives and issues
* communicate with executives and make sure they understand the payoff/ROI
* communicate with executives and make sure they understand the payoff/ROI
30
New cards
W6: What are the types of data analytics?

31
New cards
W6: What should you do when applying data analytics?
\

32
New cards
W6: Why does Business Analytics **matter** to A&F?
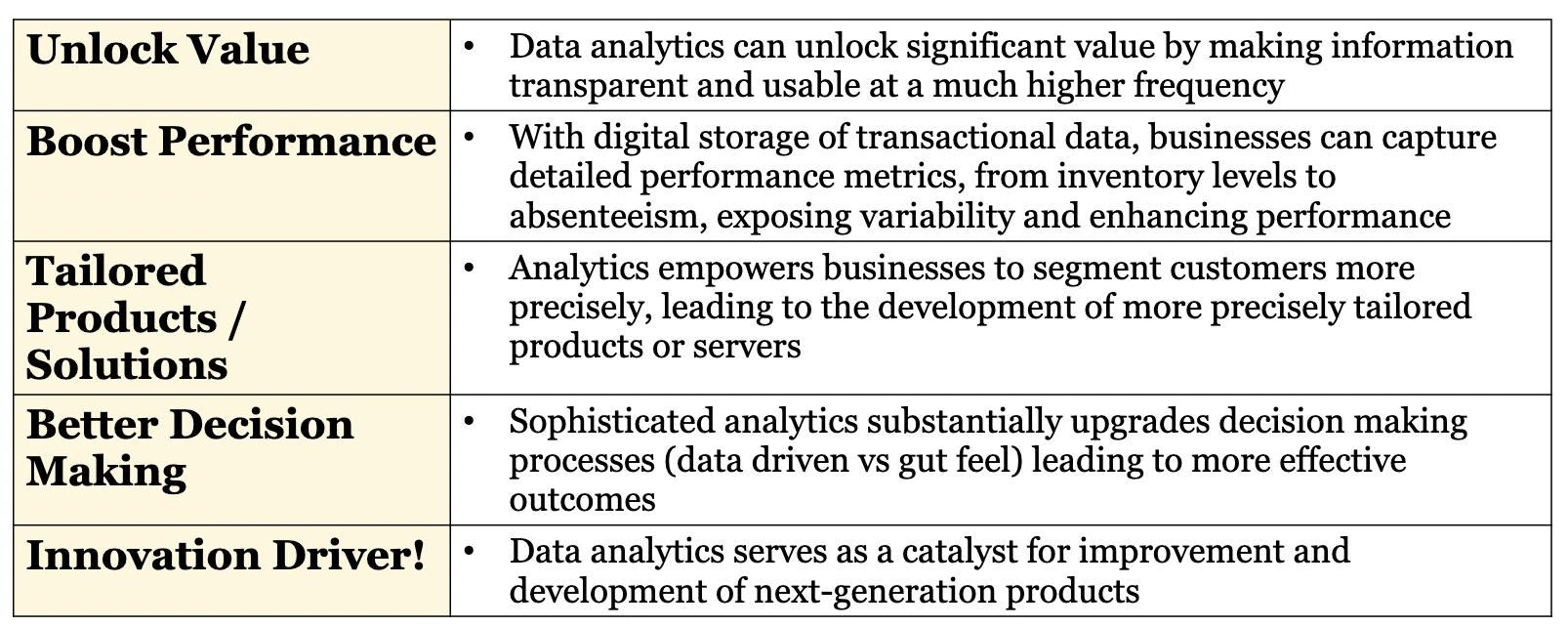
33
New cards
W6: What are the **differences** between data and information?
* **Data**: raw facts and figured
* **Information**: data presented in a context so that it can answer or question or support decision-making
* **Knowledge**: insight derived from experience and expertise (based on data and information)
* **Information**: data presented in a context so that it can answer or question or support decision-making
* **Knowledge**: insight derived from experience and expertise (based on data and information)
34
New cards
Can you classify the data elements in this purchasing database?
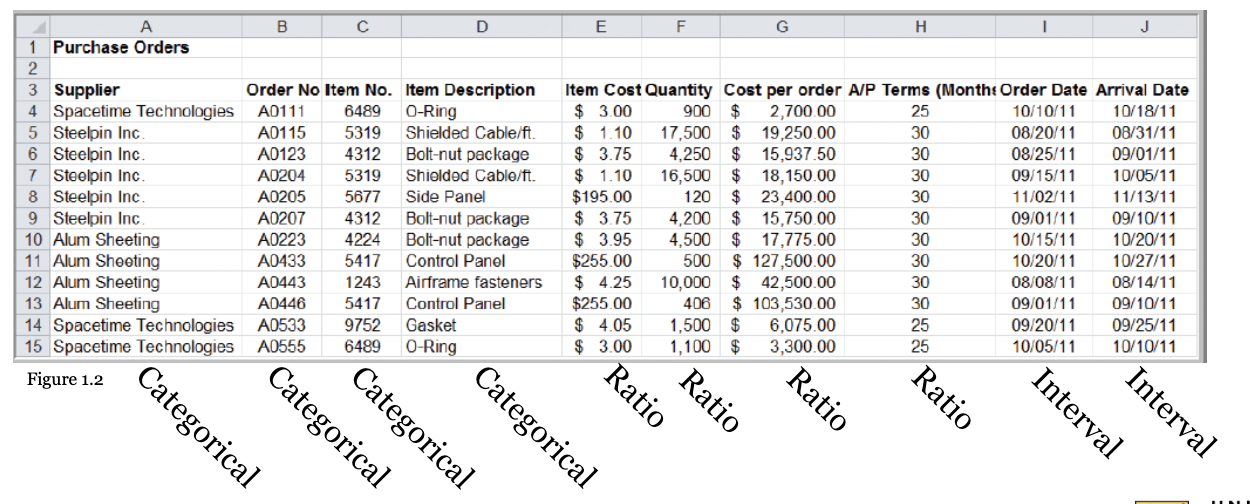
35
New cards
W6: Define **Big Data**
* the collections, storage and analysis of extremely large complex and often unstructured datasets that can be used by organizations to generate insights that would otherwise be impossible to make
* decision-making is data-driven, fact-based and enabled by:
* standardized corporate data
* access to third-party data sets through cheap, fast computing, and easier-to-use software
* decision-making is data-driven, fact-based and enabled by:
* standardized corporate data
* access to third-party data sets through cheap, fast computing, and easier-to-use software
36
New cards
W8: Define **Artificial Intelligence (AI)**
computer software that can mimic or __improve__ upon functions that would otherwise require human intelligence
* recall Moore’s Law - computer power doubles approx. every 2 years
* recall Moore’s Law - computer power doubles approx. every 2 years
37
New cards
W8: What are the **two major types** of artificial intelligence
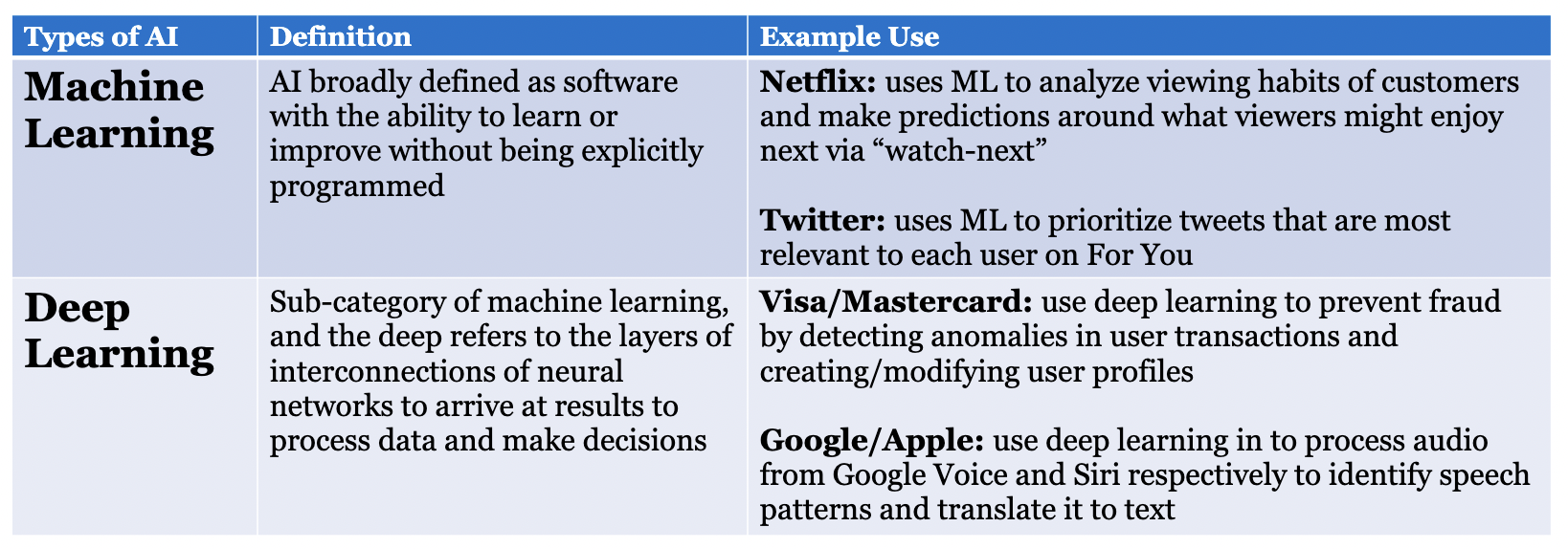
38
New cards
W8: What are the two sub-categories of the major AI types?
1. **Supervised Learning**
1. algorithms trained by specific examples and classifications
2. e.g., Gmail email spam filters learn to classify emails as “spam” or “not spam” by recognizing patterns and features in emails
2. **Unsupervised Learning**
1. algorithms that are not fed a pre-determined result
2. e.g., Facebook’s “People You May Know” feature, uses ‘clustering’ to identify patterns in user data without being told what to look for
1. # of connections with people who attend the same school as you
39
New cards
\
W8: Define **Graphic Processing Unit** (GPU)
W8: Define **Graphic Processing Unit** (GPU)
designed for specific tasks like handing large blocks of data simultaneously (parallel process)
* more efficient in intense AI computations
* more efficient in intense AI computations
40
New cards
W8: Define **Central Processing Unit** (CPU)
more general, handles sequential processing tasks
41
New cards
W8: Define **Neural Network**
\

42
New cards
W8: Define **Expert Systems**

43
New cards
W8: What is an **algorithm**
set of instructions that tell a computer system what to do
* AI uses algorithms in its process but can modify and improve it based on data it encounters
* AI uses algorithms in its process but can modify and improve it based on data it encounters
44
New cards
W8: Define **Generative AI**
describes AI that can be used to create new content, including text, audio, images, video, code and simulations
* sub category of machine learning
* sub category of machine learning
45
New cards
W8: Define **Large Language Models** **(LLM)**
* specifically trained to generate human like text
* learn from statistical patterns in language
* a prediction model
* learn from statistical patterns in language
* a prediction model
46
New cards
W8: Define **Pre-Trained Transformer (GPT)**
a specific type of LLM that basically predicts the next word in a sentence based on statistical patterns
* don’t actually comprehend the meaning of text put in front of them
* strength in being able to consider context from both past and future inputs simultaneously
* don’t actually comprehend the meaning of text put in front of them
* strength in being able to consider context from both past and future inputs simultaneously
47
New cards
W8: What are **Tokens**
* concept in LLMs
* represents a word or part of a word
* in LLM, process text by breaking it down into tokens - words or chunks of characters
* 1 token corresponds to 4 characters of text (\~75% of a word)
* represents a word or part of a word
* in LLM, process text by breaking it down into tokens - words or chunks of characters
* 1 token corresponds to 4 characters of text (\~75% of a word)
48
New cards
W9: Define **Autopilot**
allows AI to make __all__ the decisions
* e.g, Tesla autopilot has the vehicle making all of the decisions without human intervention
* e.g, Tesla autopilot has the vehicle making all of the decisions without human intervention
49
New cards
W9: Define **Co-pilot**
involves AI __assisting__ humans in making information decisions
* e.g., co-pilot in a Tesla vehicle involves the driver being in control, while Tesla’s software features assist in various ways
* e.g., co-pilot in a Tesla vehicle involves the driver being in control, while Tesla’s software features assist in various ways
50
New cards
W9: Why should we treat LLM as a co-pilot?
* imperfect and make mistakes
* as a result of going beyond its training data or misinterpreting a prompt
* cannot be left unattended
* not humans
* tools - require proper use to get the most out of them
* LLM outputs should be a starting point not end point
* as a result of going beyond its training data or misinterpreting a prompt
* cannot be left unattended
* not humans
* tools - require proper use to get the most out of them
* LLM outputs should be a starting point not end point
51
New cards
W9: Define **Hallucination** (in terms of LLM)
* perceptions of something that is not actually present
* many reject this term because it misrepresents what’s happening and suggest AI has human like features
* the model generates information or details that are not present in the input or the original context. It involves the model creating content that goes beyond the actual data it has been provided or the knowledge it has learned.
* many reject this term because it misrepresents what’s happening and suggest AI has human like features
* the model generates information or details that are not present in the input or the original context. It involves the model creating content that goes beyond the actual data it has been provided or the knowledge it has learned.
52
New cards
W9: Define **Confabulation** (in terms of LLM)
* Confabulation can happen when a language model generates responses that seem coherent but are factually incorrect, misleading, or nonsensical. It's one of the challenges in working with large language models, as they can generate text that sounds good on the surface but may not be accurate or reliable.
53
New cards
W9: Define **Prompt Engineering**
optimizing textual input to effectively communicate with large language models
54
New cards
W9: How will roles like software engineering change?

55
New cards
W9: What are important factors when creating an effective prompt?
* choosing your words deliberately
* think about sentence construction
* correct grammar (avoid confusing LLM)
* be precise - give clear constraints in the prompt
* think about sentence construction
* correct grammar (avoid confusing LLM)
* be precise - give clear constraints in the prompt

56
New cards
W9: Define the **Value Chain**
a set of activities through which a product or service is created and delivered to customers
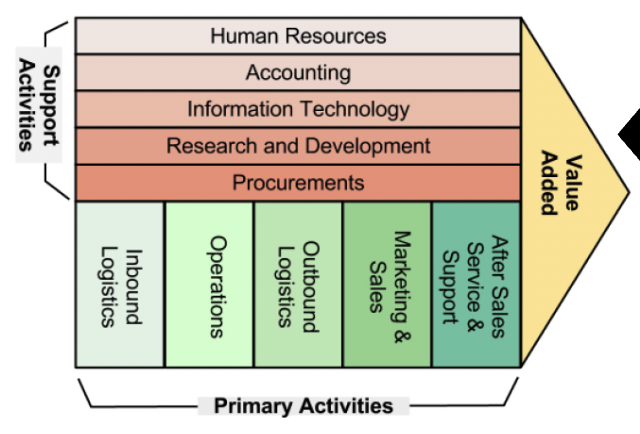
57
New cards
W9: What are the components of the Value Chain and key resources?
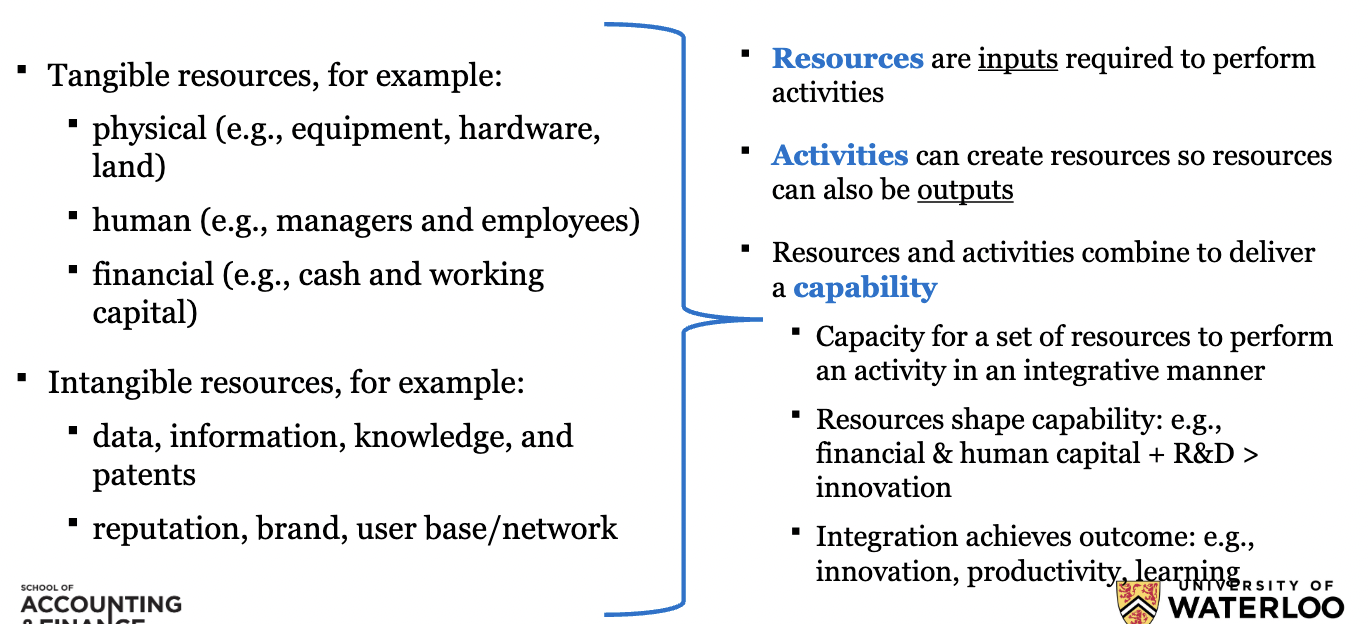
58
New cards
W11: What is the formula to formulating an effective prompt?

59
New cards
W11: What are the four steps in Prompt Priming
1. **Problem Formulation** - determining what to ask the AI (think first)
2. **Exploration** - using major AI (get creative)
3. **Critical Thinking** - weeding out poor AI context (fact check & edit)
4. **Reflection** - AI is here to add/improve, not replace (learn & improve)
60
New cards
W11: What is **Domain Specific** and its **importance**
* remixes the concept of LLMs by using smaller models that are trained on a subset of the larger data set along with proprietary first party data
* complex and unique language within certain industries that warrant a different approach
* Bloomberg is experimenting with internal corporate AI models
* complex and unique language within certain industries that warrant a different approach
* Bloomberg is experimenting with internal corporate AI models
61
New cards
W11: AI & Healthcare
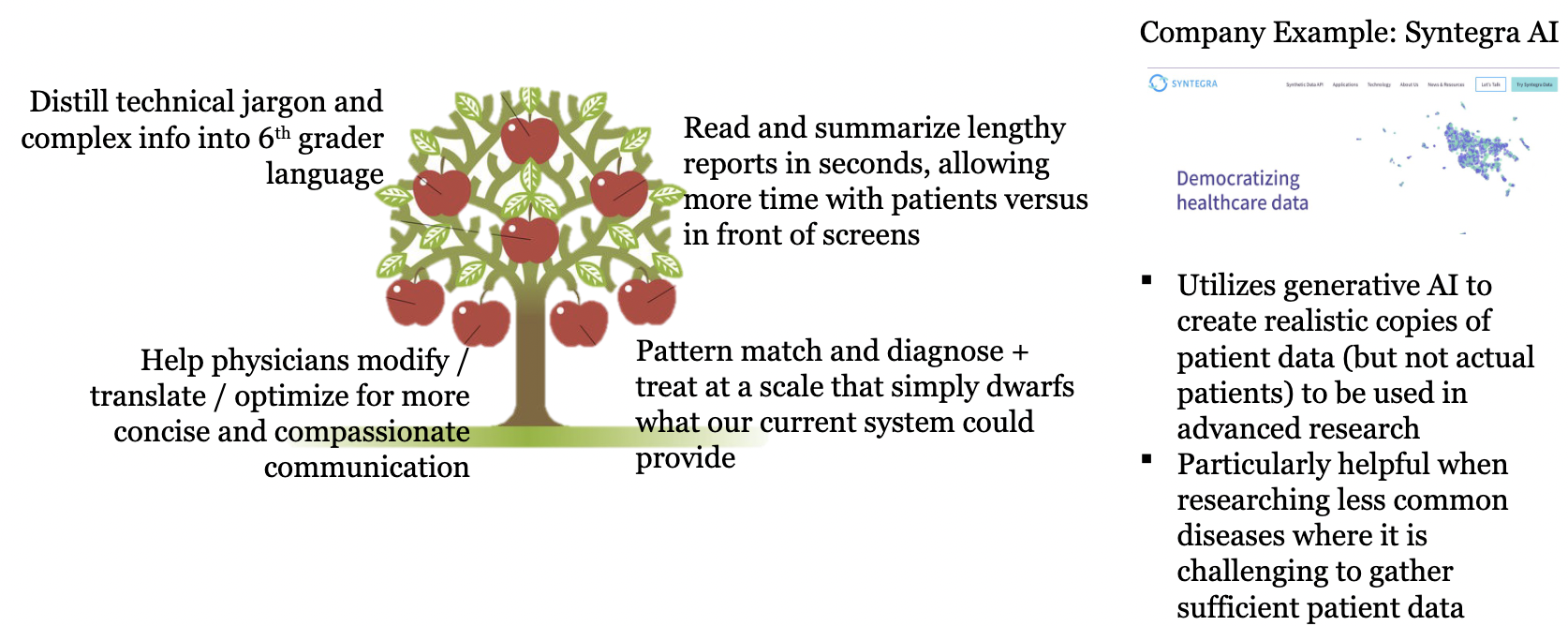
62
New cards
W11: AI & Product Development

63
New cards
W11: What are some issues that are arising as a result of Generative AI’s popularity

64
New cards
W11: What are some potential risks of AI?

65
New cards
W11: What needs to be considered when implementing AI in the **legal** field?

66
New cards
W11: What needs to be considered when implementing AI: **Organizational**

67
New cards
W11: What needs to be considered when implementing AI: **Societal**

68
New cards
W11: What needs to be considered when implementing AI: **Ethical**

69
New cards
W11: Define **Disruptive Technologies**
technologies that create market shocks and catalyze growth (aka disruptive innovation)
* based on the concept of giant killing market shocks that knock off and displace once-dominant (**incumbent**) firms, including their product and market alliances
* often powered by a shift from atoms to bits (software)
* based on the concept of giant killing market shocks that knock off and displace once-dominant (**incumbent**) firms, including their product and market alliances
* often powered by a shift from atoms to bits (software)
70
New cards
W11: What are characteristics of disruptive technology?

71
New cards
W11: Define **Sustaining Innovation**
occurs when a company creates a better performing product to sell for higher profits to its existing customers
* leveraged by already successful companies in their industries
* motivation is profit: better products, pursue even higher profit margins
* not a successful in isolation
* better performance and lower cost
* leveraged by already successful companies in their industries
* motivation is profit: better products, pursue even higher profit margins
* not a successful in isolation
* better performance and lower cost
72
New cards
W11: When does disruptive innovation **occur**?
when a company with fewer resources (and often a lower performing product) move upmarket to challenge the incumbent’s core business
73
New cards
W11: Define **low end disruption**
company uses a low cost business model to enter at the bottom of an existing market and claim a segment, causing the incumbent to retreat upmarket to make higher margins
* form of asymmetric motivation
* form of asymmetric motivation

74
New cards
W11: Define **new market disruption**
company creates and claims a new segment in an existing market by catering to an undeserved or neglected customer base, slowly improving in quality until incumbent businesses are obsolete (out of date)

75
New cards
W11: How is **not** all innovation disruptive
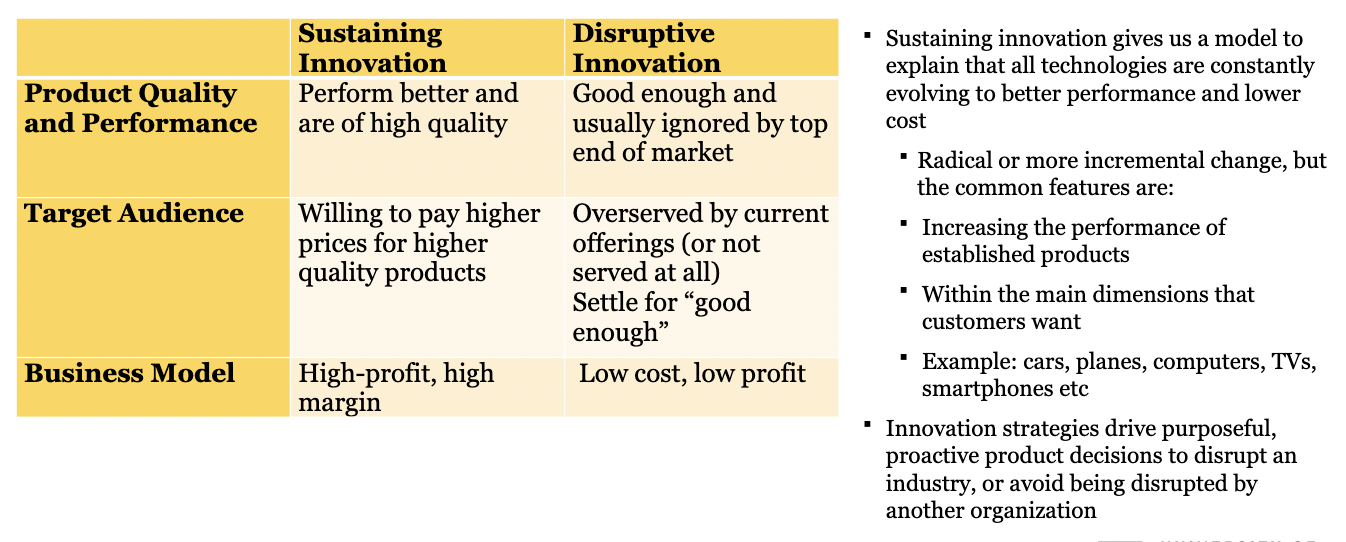
76
New cards
W11: What is a disruptor’s strategy to creating a low-end disruption?

77
New cards
W11: What is a disruptor’s strategy to creating a new market disruption?

78
New cards
W11: Why do Incumbent firms fail?
*** last one: “startups amass expertise quickly. big firms forced to play catch-up. few ever close the gap with new* __*leaders*__

79
New cards
W11: What should you do if a potential disruptor is spotted?

80
New cards
W11: What is the big bang disruption

81
New cards
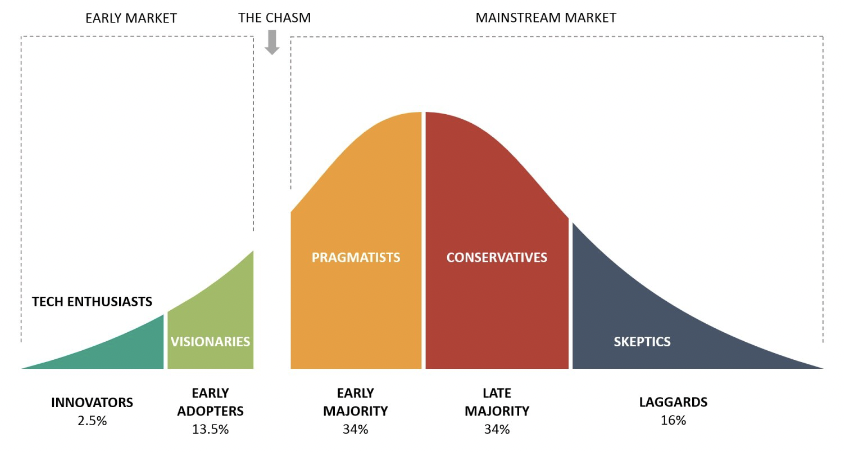
W11: Describe the Traditional Technology Adoption Curve
* new technology is adopted slowly in stages by a series of customer types
1. starts with a small group of innovators
2. moves to early adopters
3. then moves to cross the ‘chasm’ to early majority and then the late majority
4. and eventually picks up the laggards
1. starts with a small group of innovators
2. moves to early adopters
3. then moves to cross the ‘chasm’ to early majority and then the late majority
4. and eventually picks up the laggards
82
New cards
W11: Describe the differences between the Trad. Tech Adoption Curve and Big Bang Disruption
\
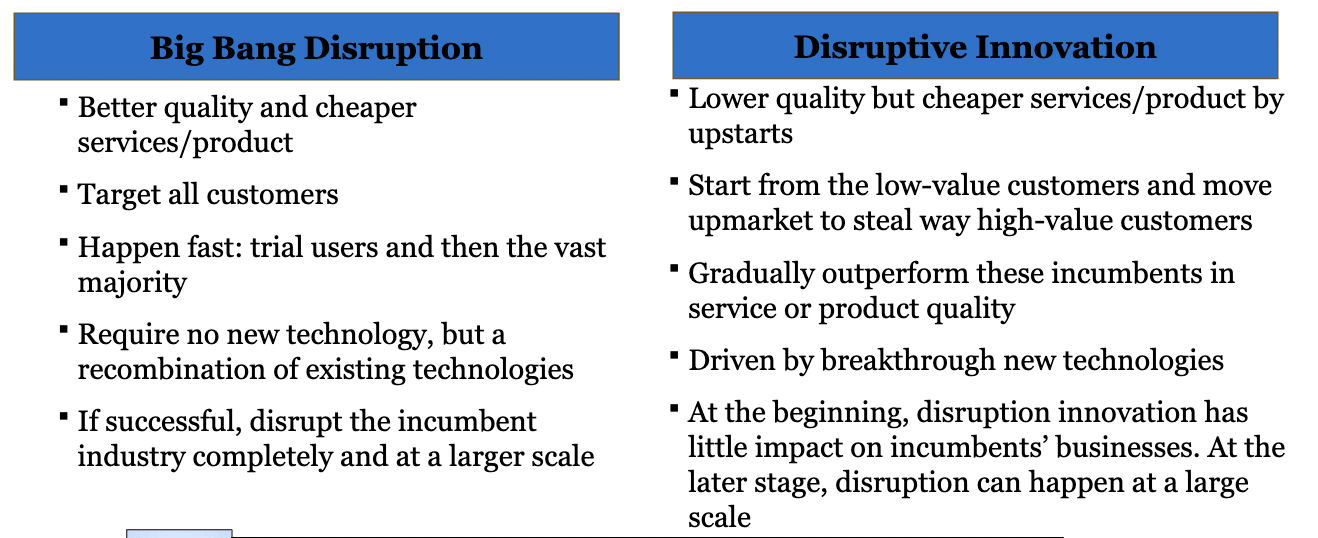
83
New cards
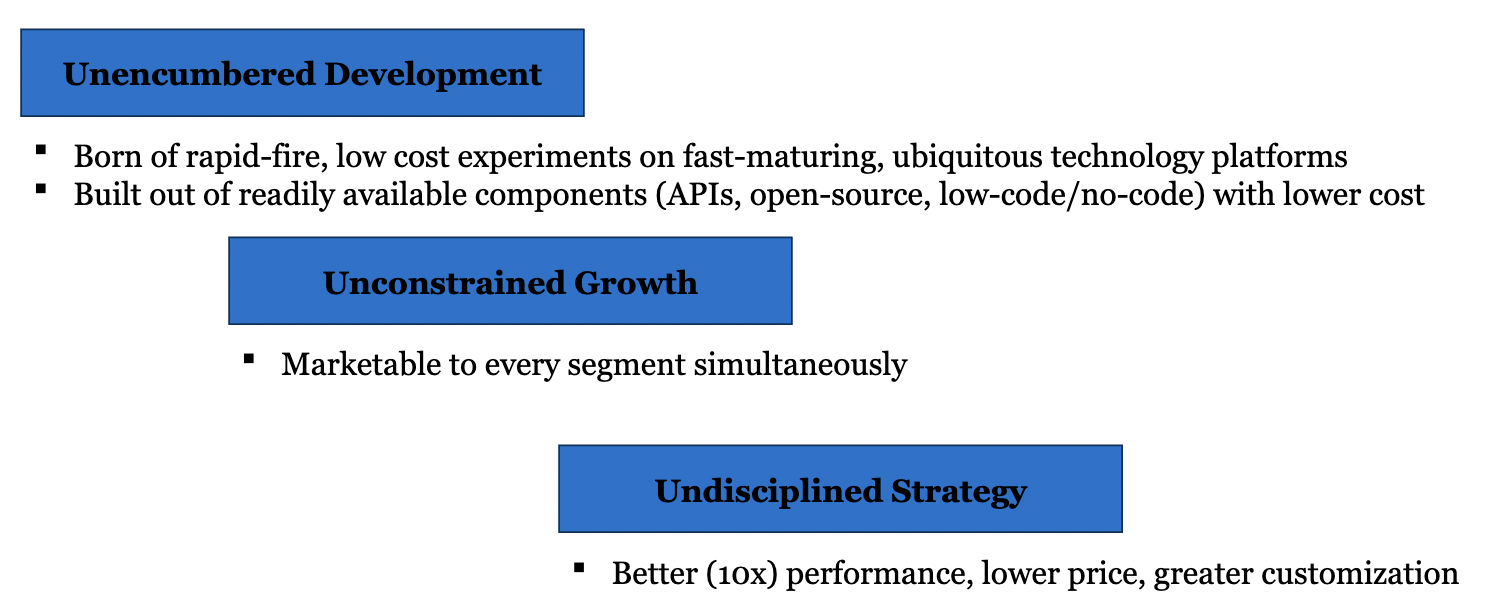
W11: What are **three characteristics** of Big Bang Disruption
* e.g., Spotify
* buying and downloading mp3s vs unlimited streaming for a monthly subscription
* apple was even put on the defensive here and responded with Apple Music
* buying and downloading mp3s vs unlimited streaming for a monthly subscription
* apple was even put on the defensive here and responded with Apple Music
84
New cards
W11: What are the **defining** characteristics of Big Bang Disruption
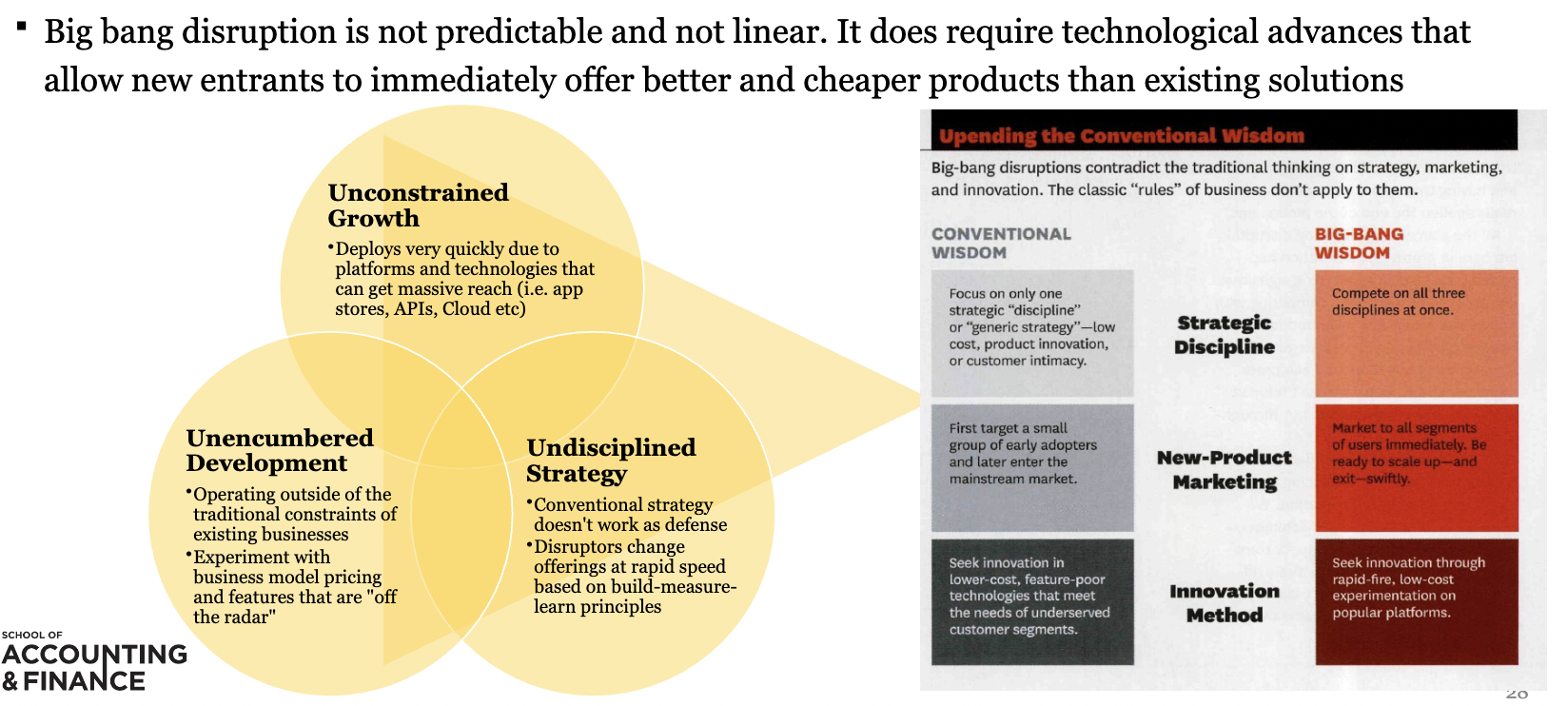
85
New cards
W12: How does Disney integrate technology into usual manual experiences?
The MagicBand which is part of their MyMagic+ system. It can be used:
* for park and attraction admission
* for keyless entry to your hotel room
* to pay for rides
* to locate you to deliver restaurant meals
* for park and attraction admission
* for keyless entry to your hotel room
* to pay for rides
* to locate you to deliver restaurant meals
86
New cards
W12: What costs does Disney incur for each MagicBand user?
87
New cards
W12: What costs does Disney incur for each user of the MagicMobile app?
\
88
New cards
W12: What are the financial benefits when software (app) replaces hardware (band)?
89
New cards
W12: What is an **Internet of Things (IoT) device**?
any computing device with the ability to transfer data over a network
90
New cards
W12: How is IoT important for CPAs and CFAs?

91
New cards
W12: How do businesses benefit from the use of IoTs?
* increase productivity
* automate process
* optimize value chain
* improve customer experience
* create new business models
* automate process
* optimize value chain
* improve customer experience
* create new business models
92
New cards
W12: Explain the IoT **device** risks and mitigation strategies
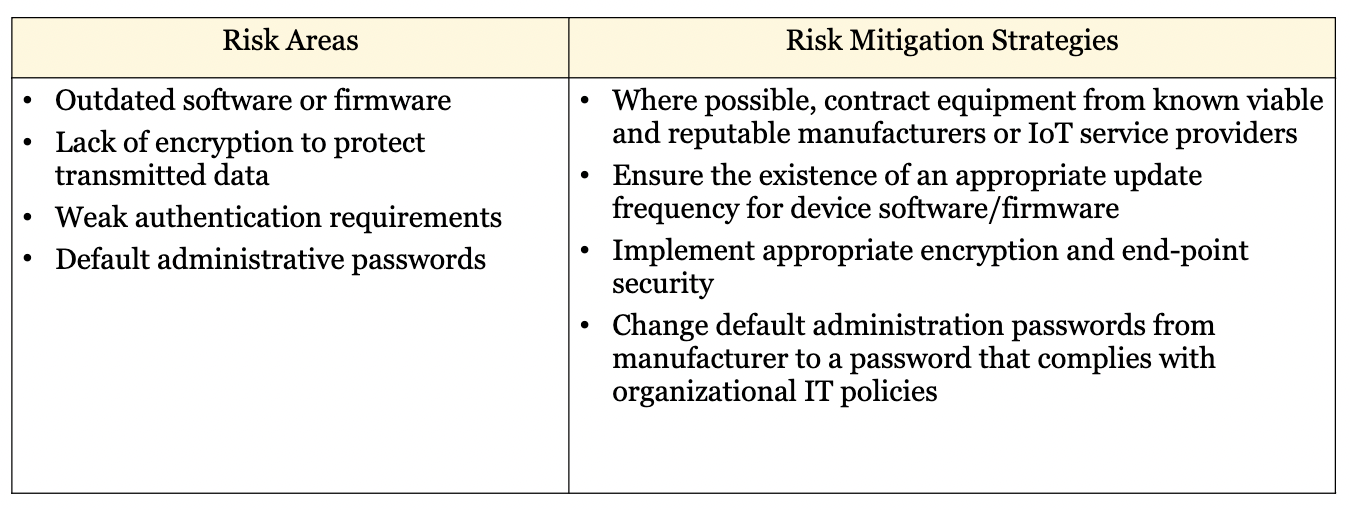
93
New cards
W12: Explain the IoT **data storage** risks and mitigation strategies
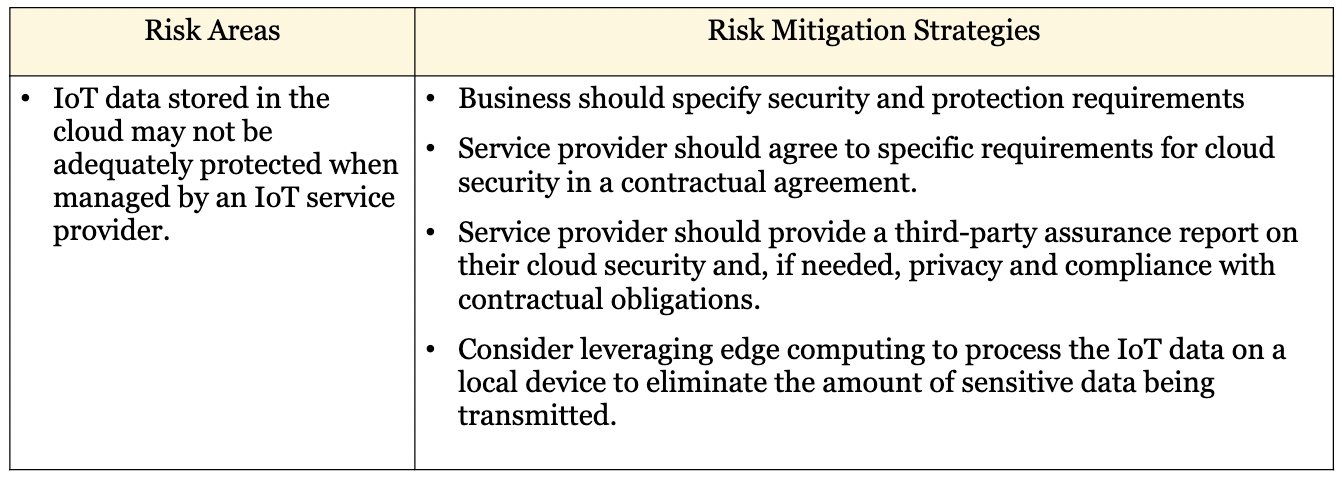
94
New cards
W12: Explain the IoT data breach risks and mitigation strategies

95
New cards
W12: Explain the IoT network risks and mitigation strategies
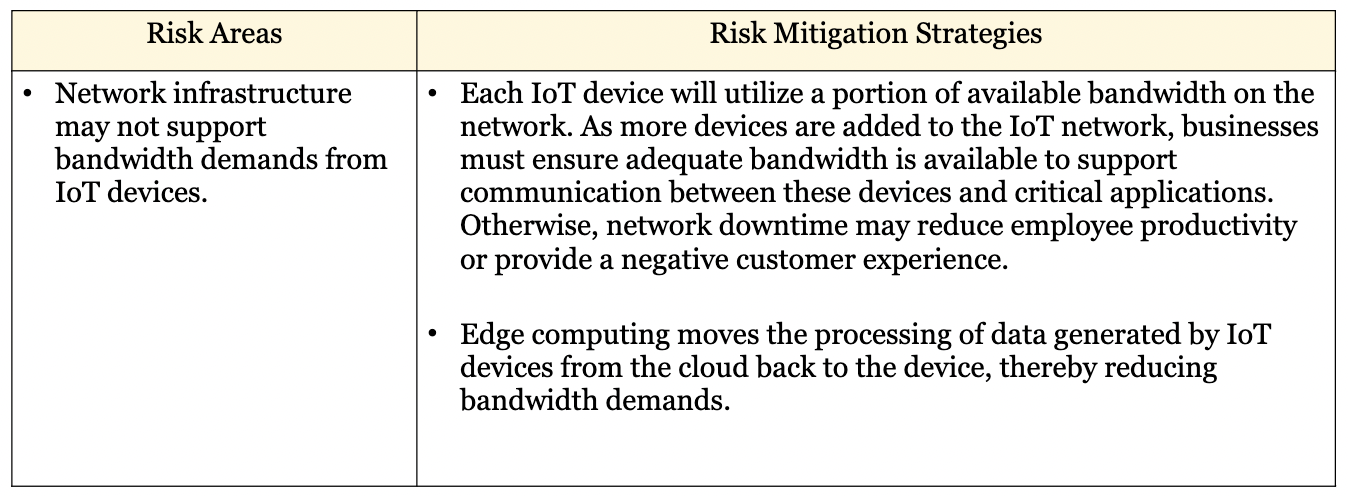
96
New cards
W12: Explain the IoT employee risks and mitigation strategies

97
New cards
W12: What is **Blockchain**?
* a digital system of record that is a decentralized, distributed ledger system where the transactions or ownership are recorded and verified across many computers in a network (peer-to-peer nature of blockchain)
* the transactions/associated data are bundled into digital blocks and are linked using cryptography, forming a chain
* highly resistant to modification (immutable -inchangable)
* the transactions/associated data are bundled into digital blocks and are linked using cryptography, forming a chain
* highly resistant to modification (immutable -inchangable)
98
New cards
W12: Describe how blockchain works
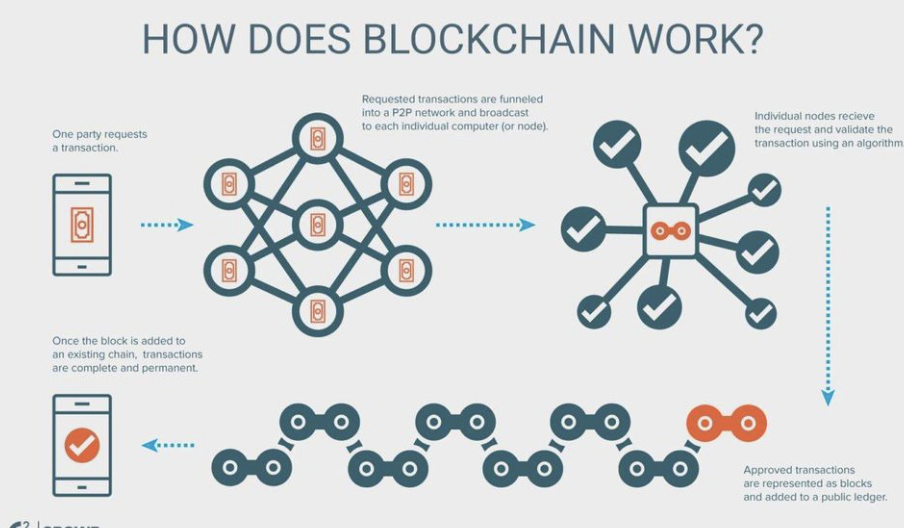
99
New cards
W12: Define **Cryptocurrency**
a digital asset where a secure form of mathematics (cryptography) is used to handle transactions, control the creation of additional units and verify the transfer of assets
100
New cards
W12: Define **Bitcoin**
an open source, decentralized payment system that operates in a peer-to-peer environment without a bank or a central authority