BIO 107: Unit 3 - Ch 10 Muscular System
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Be sure to enable 'answer with term' in the Practice Test and Learn feature.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
How many fixed point of attachment (origin) does muscle have?
What have 1 fixed point of attachment (origin)?
How many moving point of attachment (insertion) does muscle have?
What have 1 moving point of attachment (insertion)?
What is the belly in the muscular system?
What is the central or body portion of the muscle?
What are actions in the muscular system?
What are movements produced by muscle contraction?
What are innervations in the muscular system?
What is the distribution of nerve(s) to muscle or muscle group?
What does the muscle term agonist (prime mover) means?
Which muscle terminology means:
Produces a particular movement
What does the muscle term antagonist means?
Which muscle terminology means:
Opposes movement of a particular agonist
What does the muscle term synergist means?
Which muscle terminology means:
A smaller muscle that assists a larger agonist by starting motion or to stabilize origin of agonist
What does the muscle term fixators means?
Which muscle terminology means:
Synergist that assists by preventing movement at another joint or by stabilizing the origin of a muscle
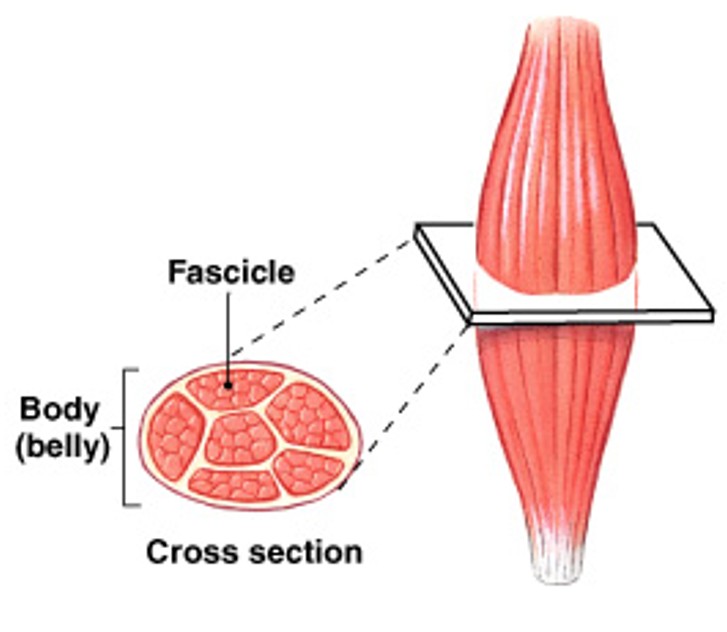
What are parallel muscles of fascicle organization?
Which pattern of fascicle organization is:
Fibers parallel to the long axis of muscle
The center or body of the muscle thickens when contracts
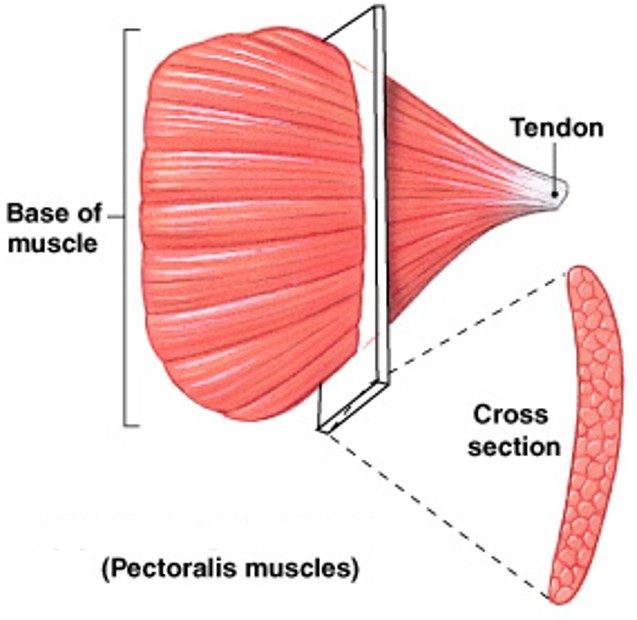
What are convergent muscles of fascicle organization?
Which pattern of fascicle organization is:
A broad area converges on attachment site
Muscle fibers pull in different directions, depending on stimulation
What are pennate muscles of fascicle organization?
Which pattern of fascicle organization is:
Form an angle with the tendon
Do not move as far as parallel muscles
Contain more myofibrils than parallel muscles
Develop more tension than parallel muscles
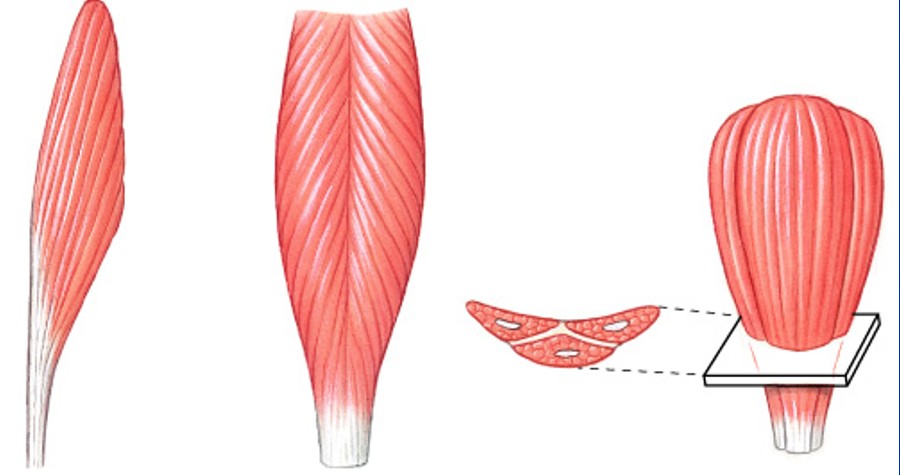
What are unipennate muscles?
Which type of pennate muscle have:
Fibers on 1 side of tendon
What are bipennate muscles?
Which type of pennate muscle have:
Fibers on both sides of tendon
What are multipennate muscles?
Which type of pennate muscle have:
Tendon branches within muscle
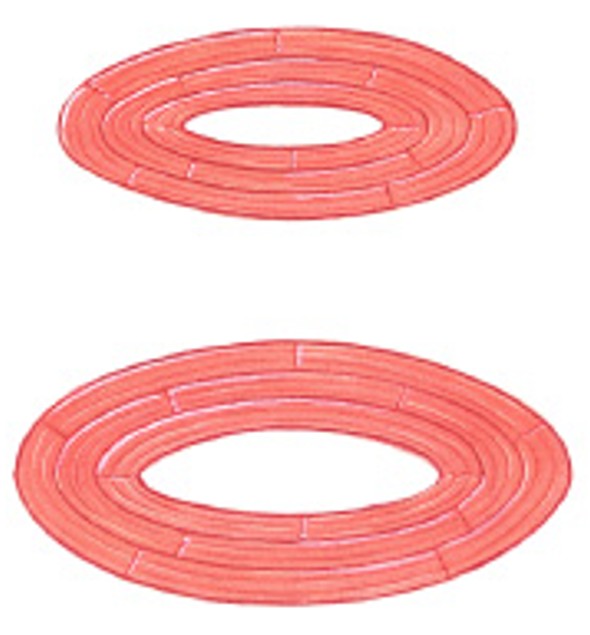
What are circular muscles of fascicle organization?
Which pattern of fascicle organization is:
Also called sphincters
Open and close to guard entrances of body

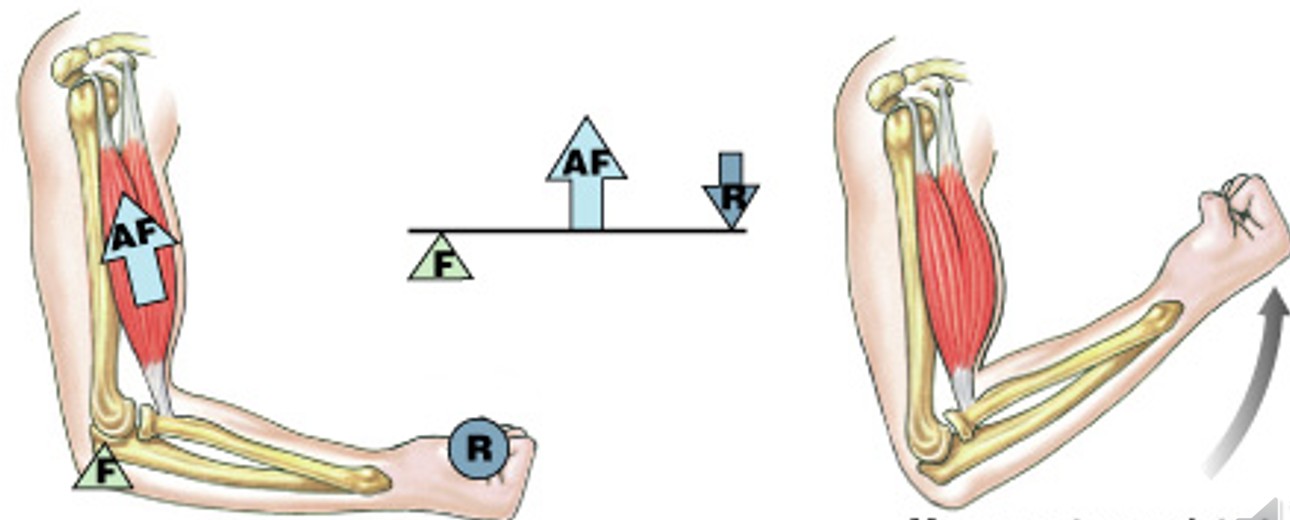
What are the functions of levers?
What are these functions of:
Mechanically, each bone is a lever (a rigid moving structure)
Each joint is a fulcrum (a fixed point), (F)
Muscles provide applied force (AF)
(AF) Required to overcome resistance (R)
What are first-class levers?
Which class of levers have:
Seesaw is an example
Center fulcrum between applied force and resistance
Force and resistance are balanced
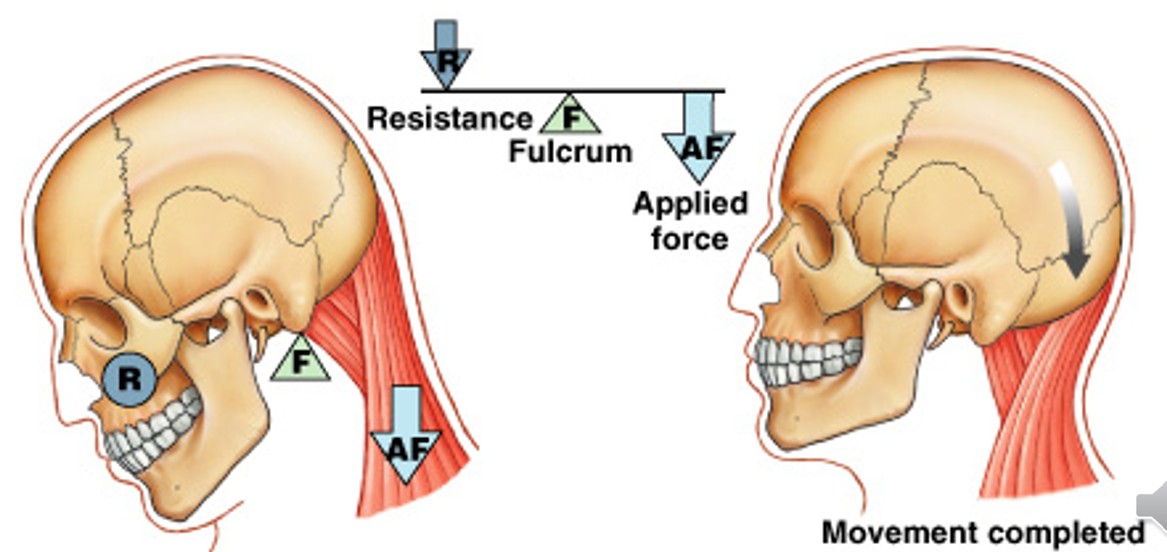
What are second-class levers?
Which class of levers have:
Wheelbarrow is an example
Center resistance between applied force and fulcrim
A small force moves a large weight

What are third-class levers?
Which class of levers have:
Most common levers in the body. Ex - shovel
Center applied force between resistance and fulcrum
Greater force moves smaller resistance
Maximizes speed and distance traveled