CLASSIFICATION BASED ON CATALYTIC REACTION
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Enzymes are grouped into six major classes on the basis of the
types of reactions they catalyze.
1. Oxidoreductase
2. Transferase
3. Hydrolase
4. Lyase
5. Isomerase
6. Ligase
It is an enzyme that catalyzes an oxidation-reduction reaction.
Oxidoreductase
Oxidation of a substrate
Oxidases
Reduction of a substrate
Reductases
Introduction of double bond (oxidation) by formal
removal of two H atoms from a substrate, the H
being accepted by a coenzyme
Dehydrogenases
It is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one
molecule to another.
Transferase
Transfer of an amino group between substrates
Transaminases
Transfer of a phosphate group between substrates
Kinases
It is an enzyme that catalyzes a hydrolysis reaction in which the addition of a
water molecule to a bond causes the bond to break.
Hydrolase
Hydrolysis of ester linkages in lipids
Lipases
Hydrolysis of amide linkages in proteins
Proteases
Hydrolysis of sugar-phosphate ester bonds in
nucleic acids
Nucleases
Hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds in carbohydrates
Carbohydrases
Hydrolysis of phosphate-ester bonds
Phosphatases
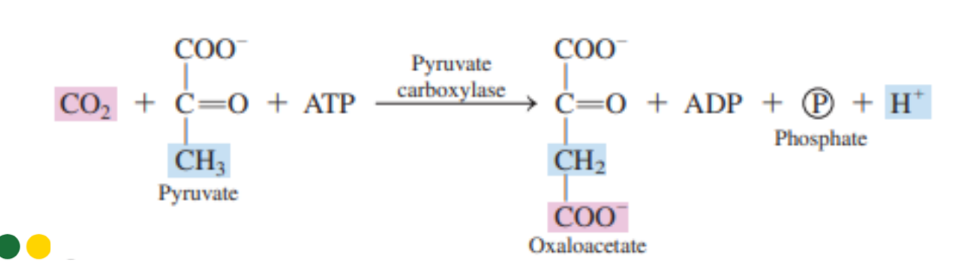
It is an enzyme that catalyzes the addition of a group to a double bond or the removal of a
group to form a double bond in a manner that does not involve hydrolysis or oxidation.
Lyase
Removal of H2O from a substrate
Dehydratases
Removal of CO2 from a substrate
Decarboxylases
Removal of NH3 from a substrate
Deaminases
Addition of H2O to a substrate
Hydratases
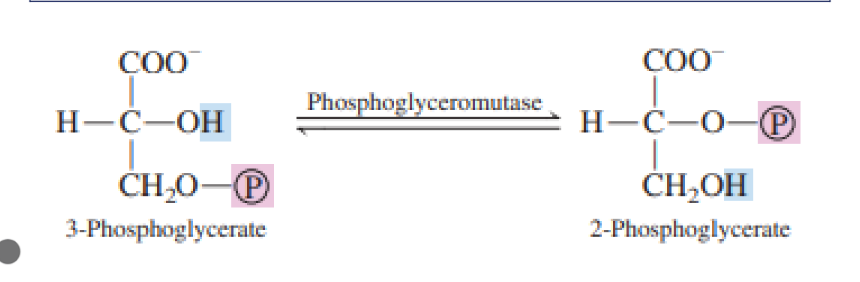
It is an enzyme that catalyzes the isomerization (rearrangement of atoms) of
a substrate in a reaction, converting it into a molecule isomeric with itself.
Isomerase
Conversion of D isomer to L isomer, or vice
versa
Racemases
Transfer of a functional group from one position
to another in the same molecule
Mutases
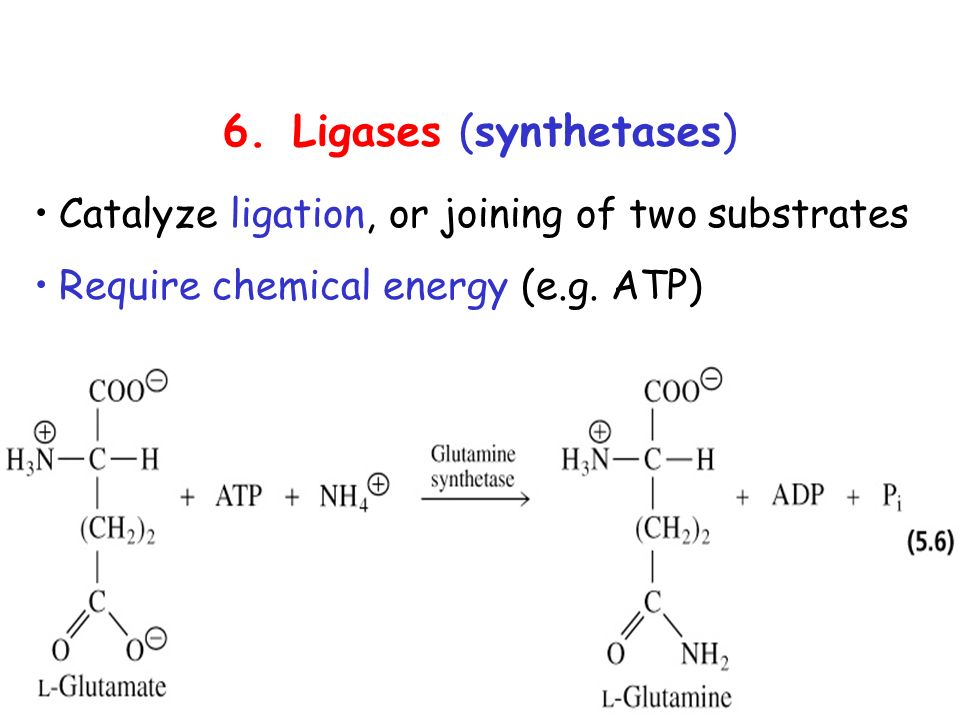
It is an enzyme that catalyzes the bonding together of two molecules into one
with the participation of ATP.
Ligase
Formation of new bond between two substrates,
with participation of ATP
Synthetases
Formation of new bond between a substrate and
CO2, with participation of ATP
Carboxylases