CME-260: Chapter 4
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Solid Solution
An atomic-scale mixture of two or more elements forming a single crystalline phase.
Solvent
The major component in a solid solution (host material)
Solute
The minor component that dissolves into the solvent
Substitutional Solid Solution
A solid solution in which solute atoms replace solvent atoms at normal lattice sites
Interstitial Solid Solution
A solid solution in which small solute atoms occupy interstitial (void) spaces between solvent atoms
Random Solid Solution
A solid solution where solute atoms are randomly distributed among lattice sites
Ordered Solid Solution
A solid solution in which solute atoms occupy specific lattice positions in a repeating pattern
Hume-Rothery Rules
Conditions favoring substitutional solid solution formation:
<15% atomic radius difference
Same crystal structure
Similar electronegativity
Same valence
Nonstoichiometric Compound
A compound in which variations in ionic charge cause deviations from ideal chemical ratios
Point Defect
Zero-dimensional imperfection at a single lattice point
Vacancy
A missing atom at a lattice site
Interstitialcy
An atom located at an interstitial site (between normal lattice positions)
Frenkel Defect
A vacancy-interstitial pair where an ion leaves its normal site and occupies an interstitial site
Schottky Defect
A pair of oppositely charged ion vacancies in an ionic crystal to maintain charge
Linear Defect
One-dimensional lattice imperfection along a line of atoms
Dislocation
A linear defect responsible for plastic deformation in crystalline materials
Edge Dislocation
A dislocation formed by an extra half-plane of atoms
Burgers vector is perpendicular to the dislocation line
Screw Dislocation
A dislocation characterized by a spiral stacking of crystal planes.
Burgers vector is parallel to the dislocation line.
Mixed Dislocation
A dislocation that has both edge and screw character.
Burgers Vector
The displacement vector needed to close a stepwise loop around a dislocation.
Planar Defect
Two-dimensional disorder in crystal structure.
Grain
A single crystal region within a polycrystalline material.
Grain Boundary
The interface between two adjacent grains of different orientations.
Twin Boundary
A special grain boundary where the crystal structures on either side are mirror images
Tilt Boundary
A low-angle grain boundary formed by a periodic array of edge dislocations.
Grain-Boundary Dislocation (GBD)
Dislocations that exist along high-angle grain boundaries.
Grain-Size Number (G)
A measure of grain size defined by:
where N is number of grains per square inch at 100x magnification
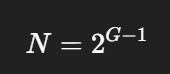
Hirth-Pound Model
A model describing crystal surfaces as containing atomic ledges and kinks rather than smooth planes
Noncrystalline Solid
A solid lacking long-range atomic order (amorphous)
Amorphous Metal
A metallic glass formed by rapid cooling that prevents crystallization.
Amorphous Semiconductor
A semiconductor material lacking long-range order
Short-Range Order
Local atomic arrangement resembling crystalline bonding.
Medium-Range Order
Atomic ordering extending beyond nearest neighbors but not fully periodic.
Long-Range Order
Regular, repeating atomic pattern throughout the material (crystallinity)
Random Network Theory
Theory describing amorphous solids as continuous random atomic networks
Zachariasen Model
Model of oxide glass structure describing a random network of connected polyhedra.
Bernal Model
Model of amorphous metals representing atoms as irregularly connected polyhedra