Chemistry - 11 Polymers
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Natural polymers [3]:
- polynucleotides (DNA)
- polypeptides (proteins)
- carbohydrates
Polysaccharide
carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides
Amino acid structure
a carboxyl group, amine group, and R group
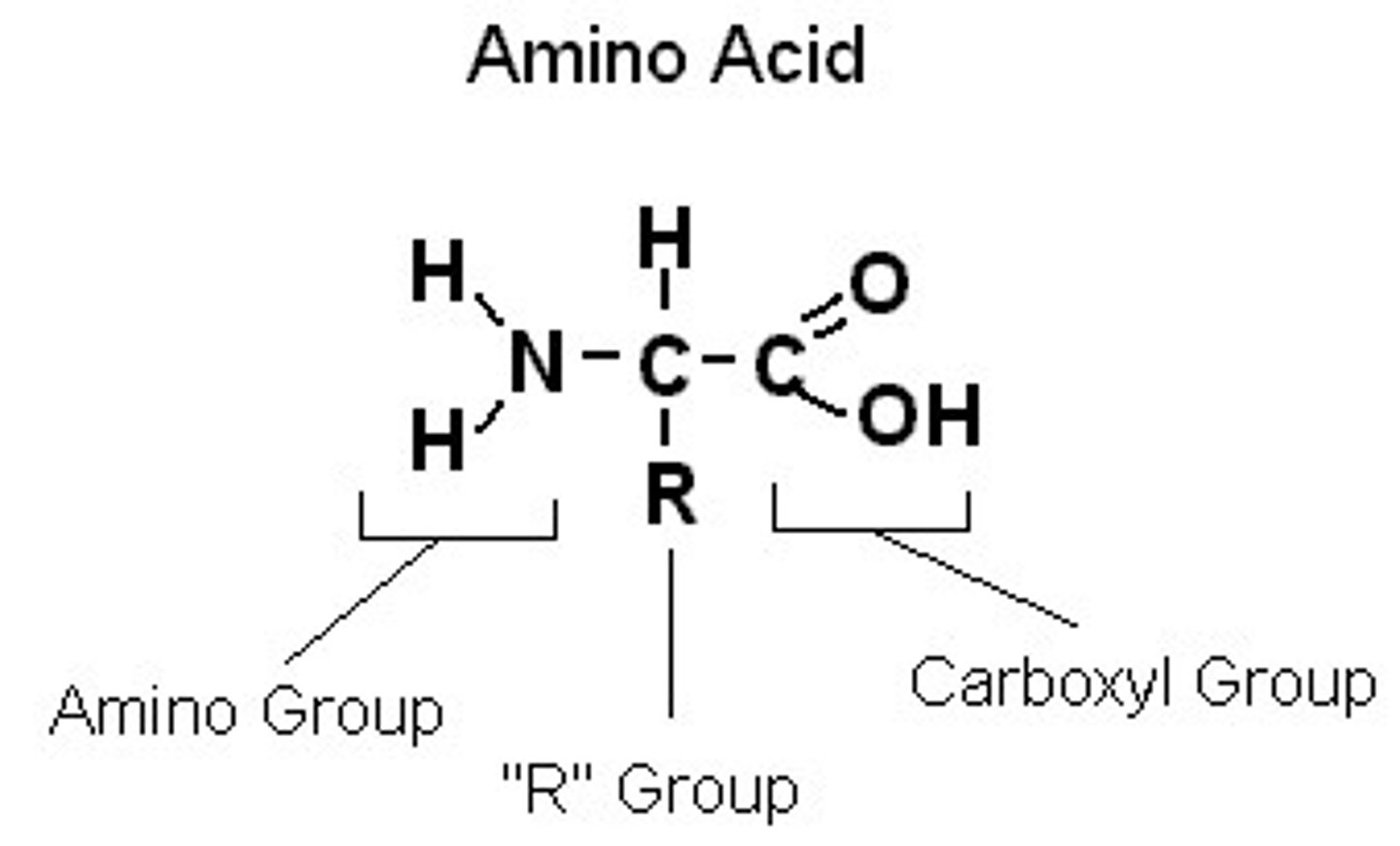
R group
a functional group that defines a particular amino acid and gives it special properties
How do amino acids join?
condensation polymerisation
Dipeptide
two amino acids bonded together
Functional group of polypeptides
peptide linkage
Peptide linkage
bond between amino acids in a protein
Polypeptides are ... while polyamides are ...
natural, synthetic
Basic group in an amino acid
amine group
Acidic group in an amino acid
carboxyl group
Starch
storage polysaccharide consisting entirely of glucose.
Cellulose
polysaccharide consisting of glucose monomers
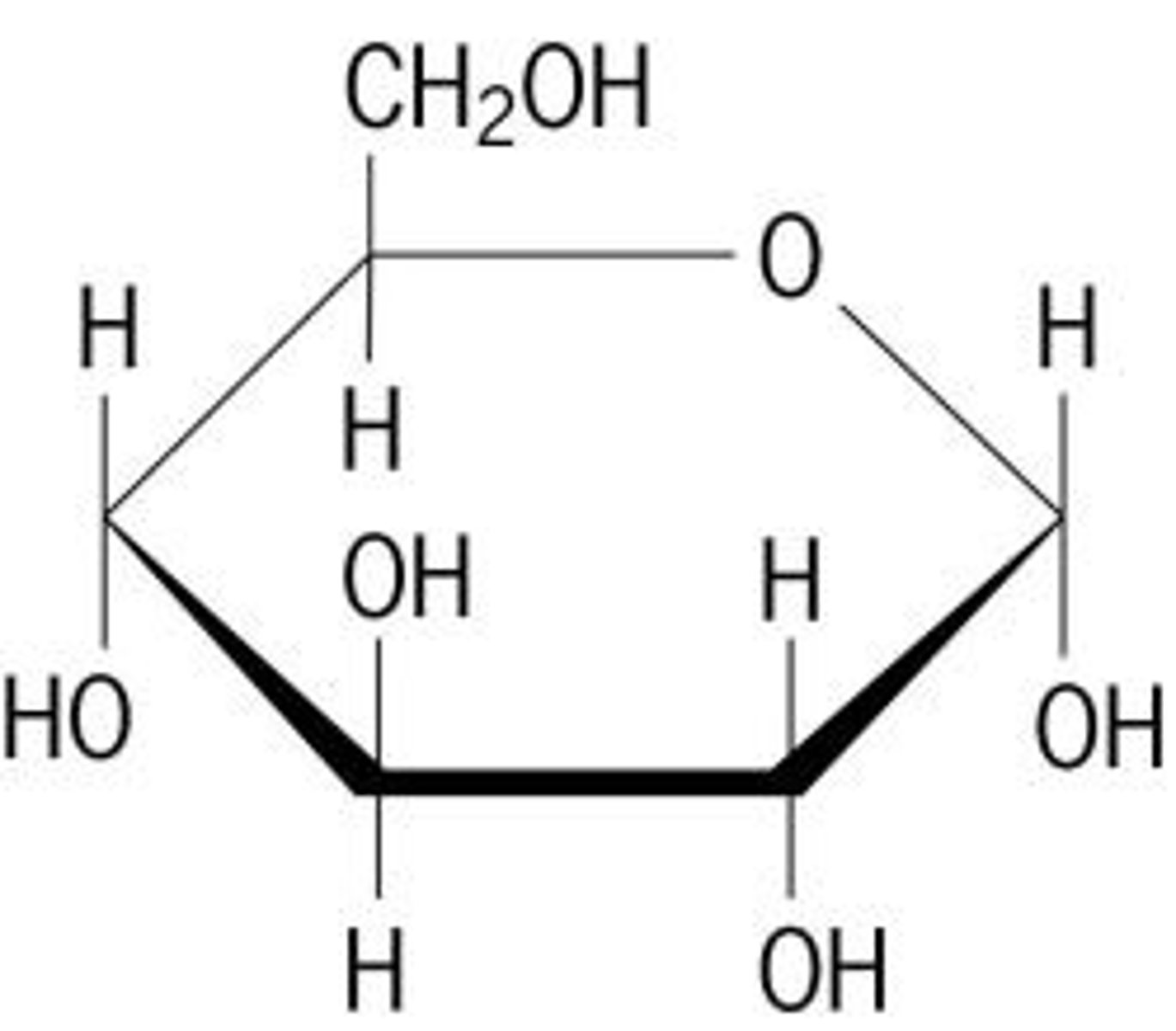
Glucose structure
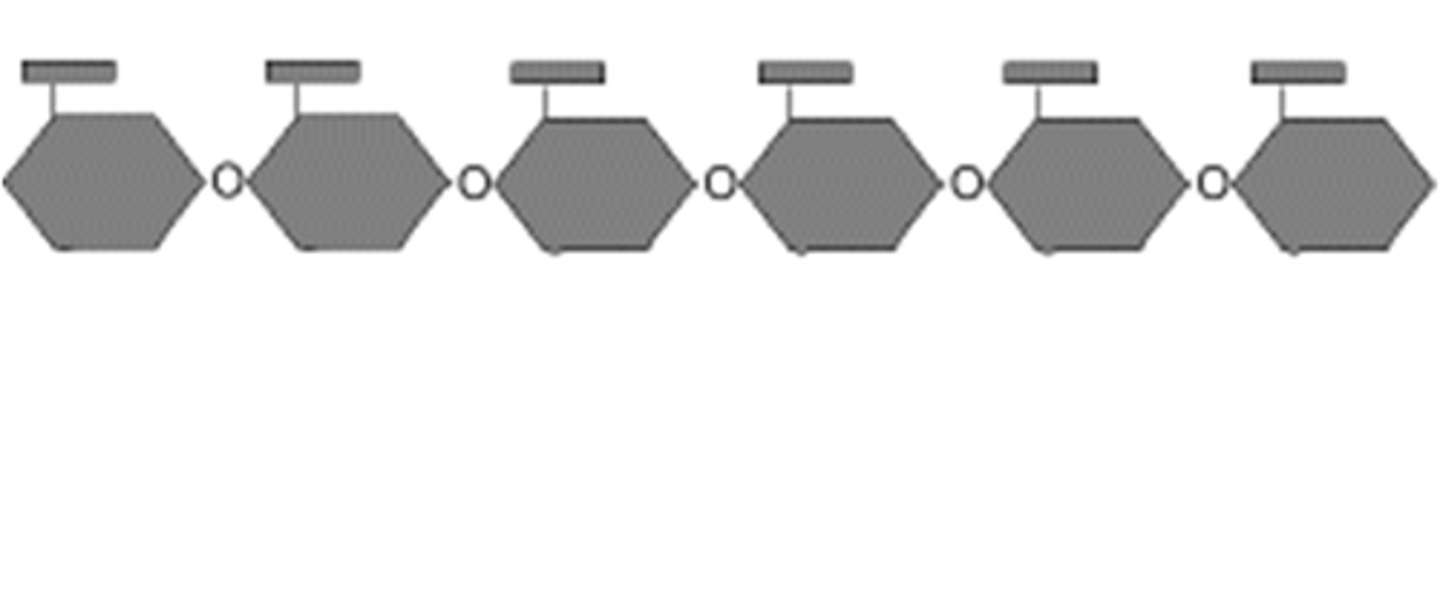
Starch structure
all the same way up
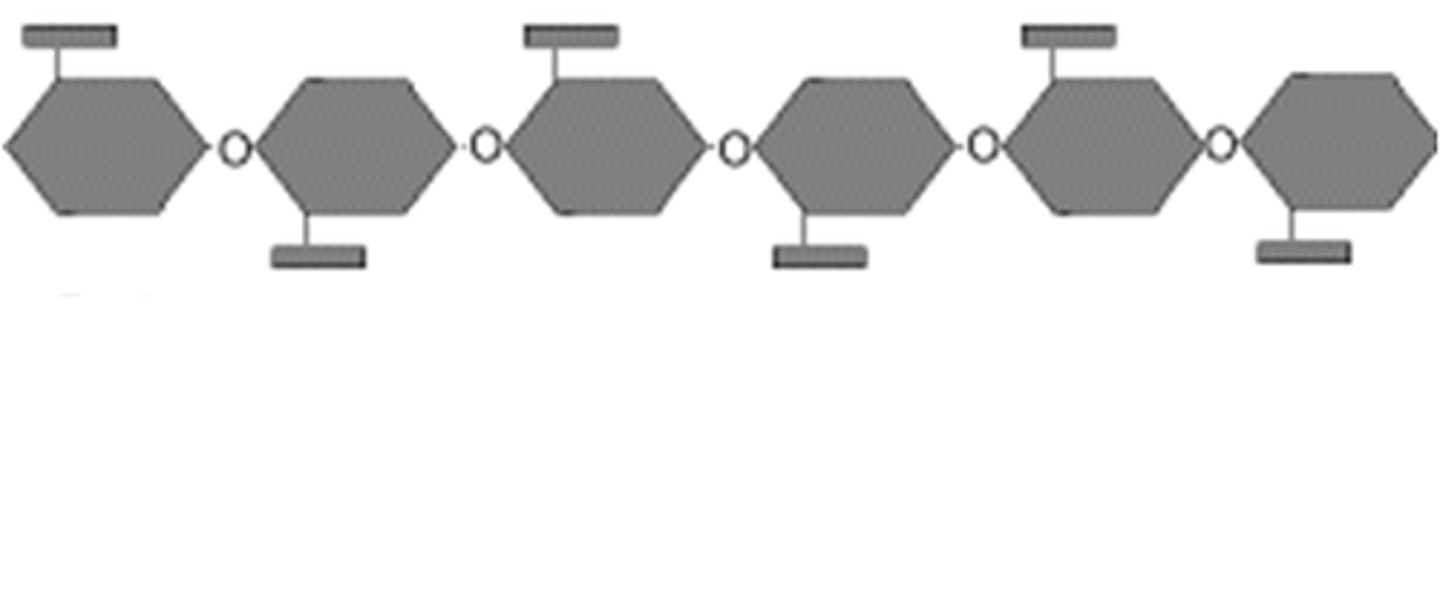
Cellulose structure
alternating ways up
Polypeptide general word equation
variety of amino acid monomers → protein polymers + water
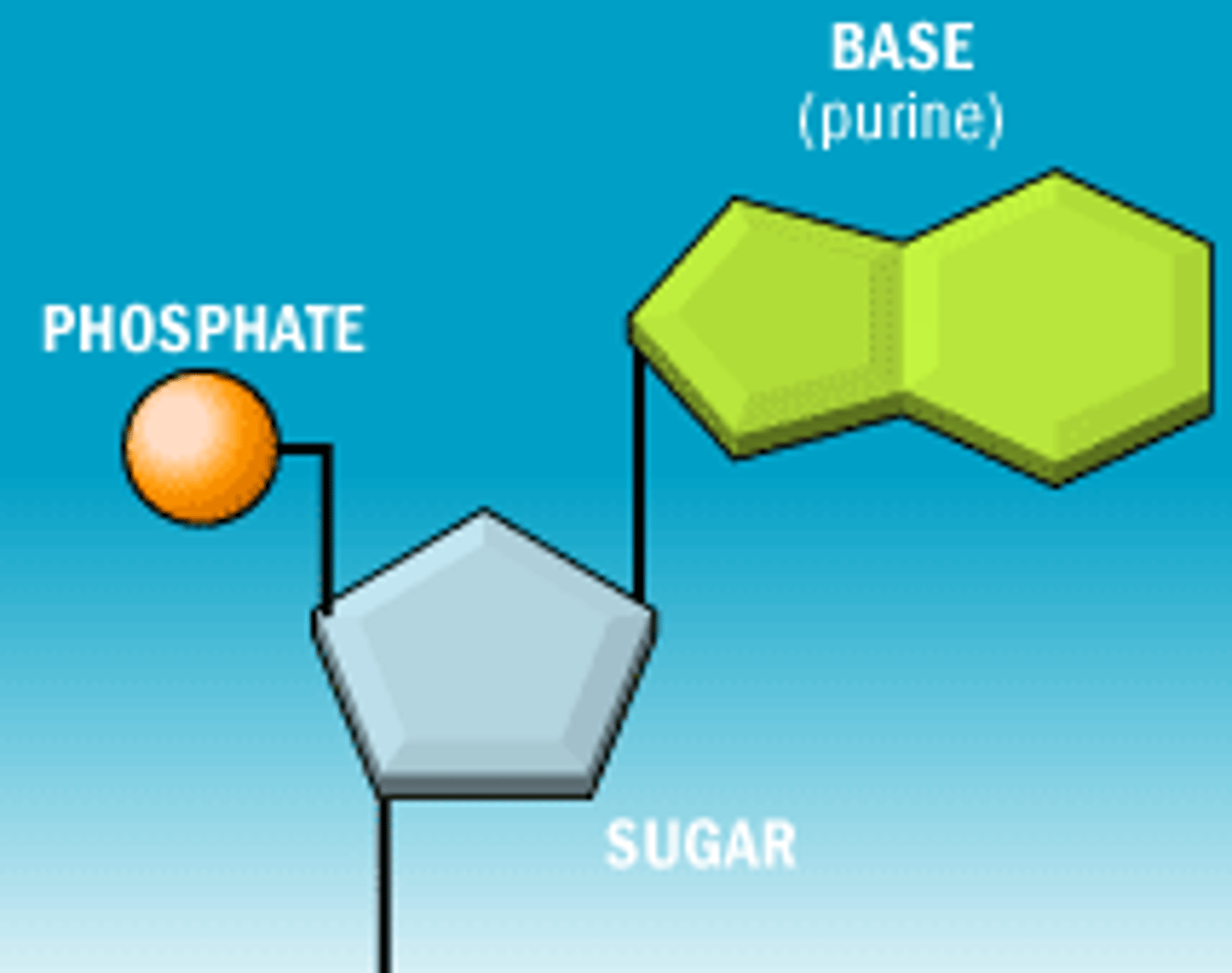
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids
Components of a nucleotide [3]:
- pentose sugar
- phosphoric acid
- organic base (variable)
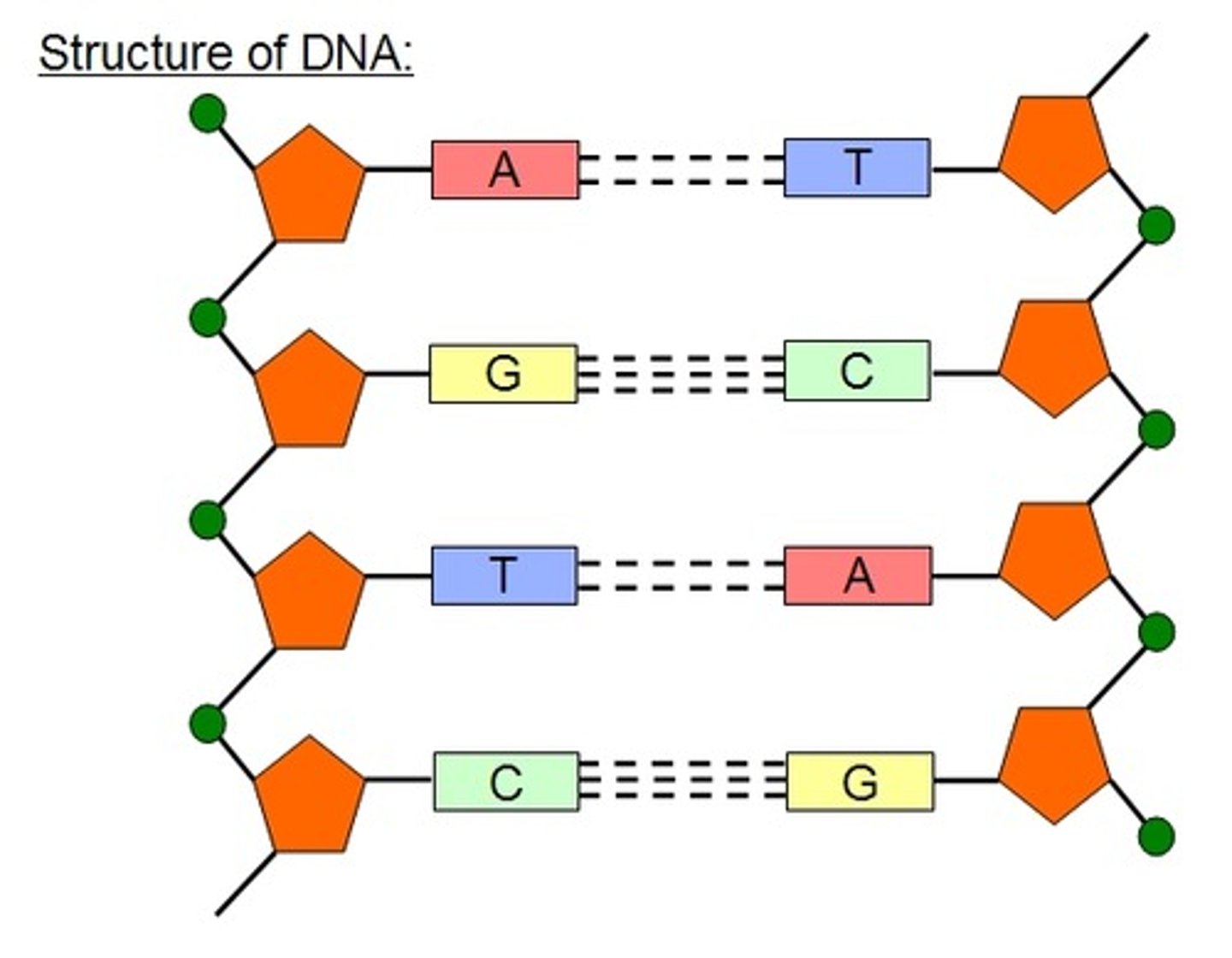
Bases in DNA [4]:
- adenine
- thymine
- cytosine
- guanine
A combines with...
T
C combines with...
G
Between C and G, there are...
3 hydrogen bonds
Between A and T, there are...
2 hydrogen bonds
DNA structure
double helix
Monomer
small chemical unit that makes up a polymer
Polymer
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
Polymer of alkene
poly(alkene)
Addition polymerisation
combination of a large number of monomers to form a single chain
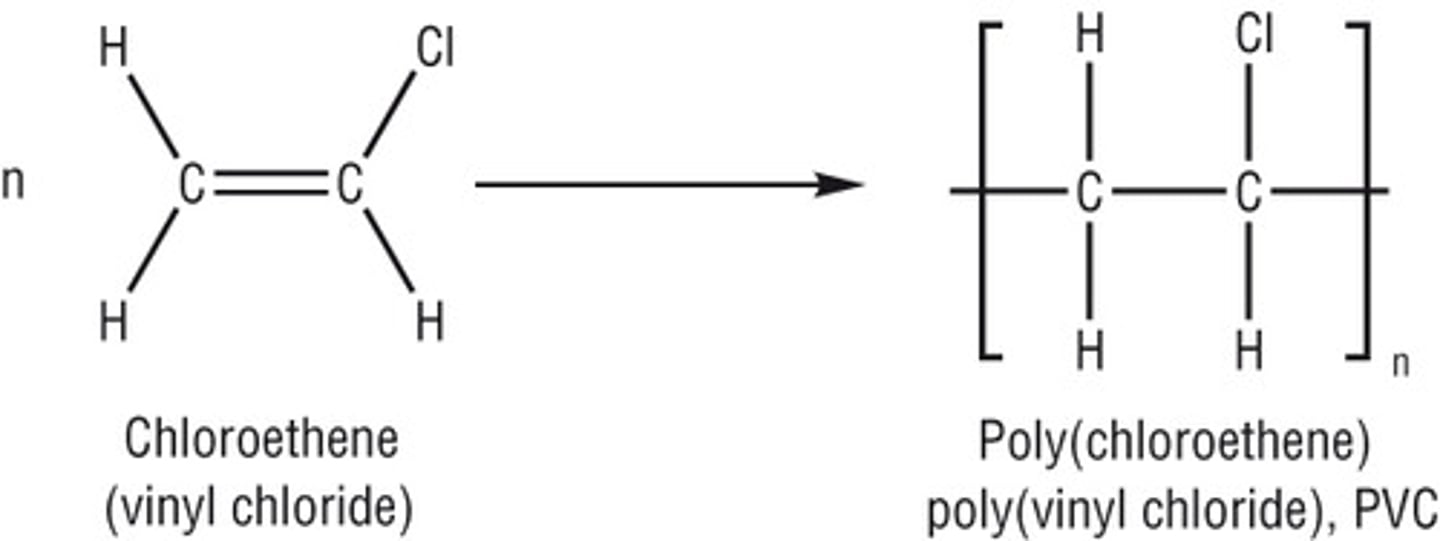
Why are polyalkenes unreactive?
as they are saturated and contain only single covalent bonds
How does addition polymerisation work?
the C=C double bond is 'broken' so that either end can bond to another carbon
Advantages of polyester fibres [2]:
- hard-wearing
- less wrinkling
Advantages of nylon fibres [3]:
- lightweight
- less wrinkling
- non-absorbent (dries quickly)
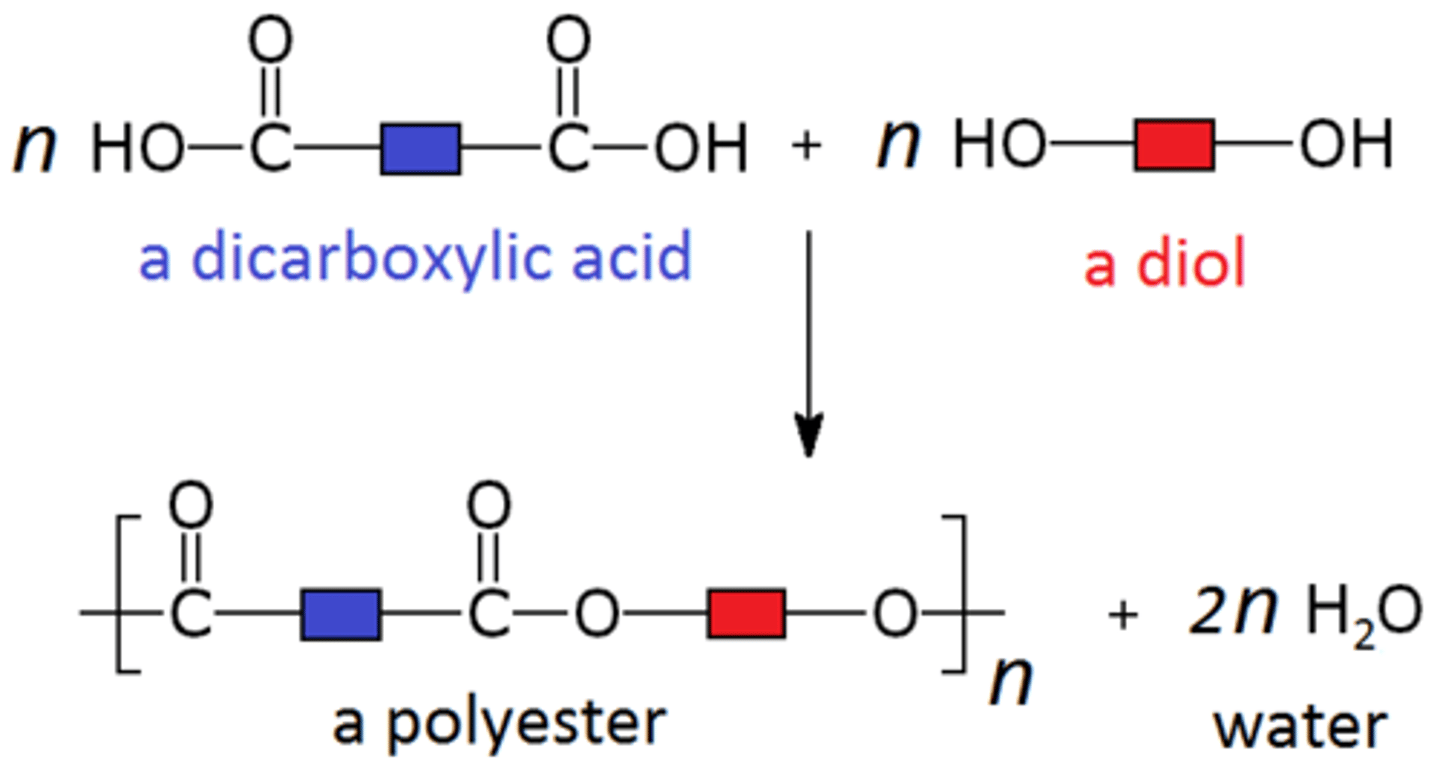
What are the products of condensation polymerisation?
condensation polymer + small molecule (H₂O or HCl)
Two types of condensation polymerisation [2]:
- between two different monomers with different functional groups on both ends (xAx + yBy)
- between the same monomer with two different functional groups on either side of each (xAy + xAy)
Diol
an alcohol containing two -OH groups (e.g. butane diol)
Dicarboxylic acid
a carboxylic acid containing two -COOH groups (e.g. butane dioic acid)
Carbon backbone
the chain or ring upon which the remainder of the molecule is built
Polyesters are made with... [2]
- a diol
- a dicarboxylic acid
Diol + dicarboxylic acid
condensation polymer + water
Amine group
NH₂
Amino acid
monomer of protein
What does the dicarboxylic acid give to the water molecule in condensation polymerisation?
-OH
What does the diol give to the water molecule in condensation polymerisation?
-H
Addition polymers are ... while polyesters are ...
non-biodegradable, biodegradable