BIOL101: Ch. 12 - Biotechnology and DNA Technology
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Cloning
Making an exact genetic copy of an organism that already exists
First, collect an oocyte from a female and remove the nucleus and DNA. Next, extract chromosomes from the organism you want to copy and insert them into the empty egg. Lastly, implant the egg into a surrogate mother and allow to grow.
Explain how an organism would be cloned.
Collect an oocyte from a female and remove the nucleus and DNA
What is the first step for an organism to be cloned?
Extra chromosomes from the organism you want to copy and insert them into the empty egg
What is the second step on how an organism can be cloned?
Implant the egg into a surrogate mother and allow to grow
What is the third step on how an organism can be cloned?
Plasmid
Is a small DNA molecule that is physically separate from, and can replicate independently of, chromosomal DNA within a cell
Bacteria uses plasmids to pass genetic information to each other
How do bacteria usually use plasmids? (Simple answer)
This is where bacteria forms a tunnel called a pilus and plasmid DNA can pass through the tunnel. Plasmids can carry very useful genes that gives cells an advantage.
How exactly do bacteria use plasmids?
This is how bacteria become resistant to antibodies
What is the advantage of plasmids delivering info to bacteria?
The gene of interest is spliced out of the human cell and into the bacterial host. The bacteria now has the recipe to make the protein. Bacteria copies fast to create an army of cells who can rapidly produce the protein.
Explain how a human gene is loaded into a bacterial cell.
Because bacteria are simple, grow rapidly, genetically easy to manipulate with plasmids
Why put the gene into bacteria and not into any other creature?
Plants are genetically modified through the process of putting the plasmid into a bacterium which will infect plants. This plasmid might have a gene of interest that we want to insert into our plant’s genome. We can use this to insert a gene that would be helpful for the plant.
Explain how plants are genetically modified
Yes
Are plasmids used again for plants’ genetic modification?
Pest Resistant, Herbicide Tolerant, Disease Resistant, Cold Tolerant
What are the pros for genetically modified foods?
Targets pests, Concerns of safety, Concerns for spread, Ethically wrong, Exercise carefulness when dealing with genes that are modified
What are the cons for genetically modified foods?
To separate biomolecules for analysis or for purification
What is the purpose of DNA gel electrophoresis?
From negative charge on the phosphate groups of the DNA molecule
What drives the movement of molecules in an electrophoresis gel?
When the molecules move through the gel, they’re going to be separated on the basis of size
How are the molecules within distinct bands on a gel different?
Smaller molecules and they go farther
What moves through the gel more quickly? Do they go farther?
Larger molecules and they don’t go far
What moves through the gel slowly? Do they go far?
same
Things that are the _____ size are gonna move the same distance in DNA gel electrophoresis
Polymerase Chain Reaction
What does PCR stand for?
DNA polymerase, Taq polymerase, lots of copies of primers, lots of deoxyribonucleotides that need to be dNTPs
What components must be added to a PCR mixture?
The 3 repeated steps in PCR are Steps 2-4 (Denaturation, Primer annealing, and extension)
What are the three repeated steps in PCR?
Create reaction mixture, we need to separate the 2 strands by using high heat
What is Step 1 of PCR? Explain it
Denaturation; We’re going to heat and denature, separate the two strands
What is Step 2 of PCR? Explain it
Primer Annealing; We’re going to reduce the temperature to about 55 or 60 degrees Celsius and we’re going to allow our primers to anneal
What is Step 3 of PCR? Explain it.
Extension; We’re going to raise the temp. To about 72 degrees which is the optimal temp. for Taq polymerase and the DNA polymerase will extend here, starting at the 3’ end of the primer and extend out
What is Step 4 of PCR? Explain it.
Non-coding regions of the DNA that contain different numbers of repeats in different individuals
What is a short tandem repeat?
Short Tandem Repeat
What is a region of DNA that is not coding for any particular protein?
Different individuals may have different numbers of repeats of this STR so we can take advantage of these differences in identifying whether or not a particular biological sample, perhaps blood, is from the same individual or related individuals
How can be tandem repeats be used to differentiate between DNA samples from different individuals?
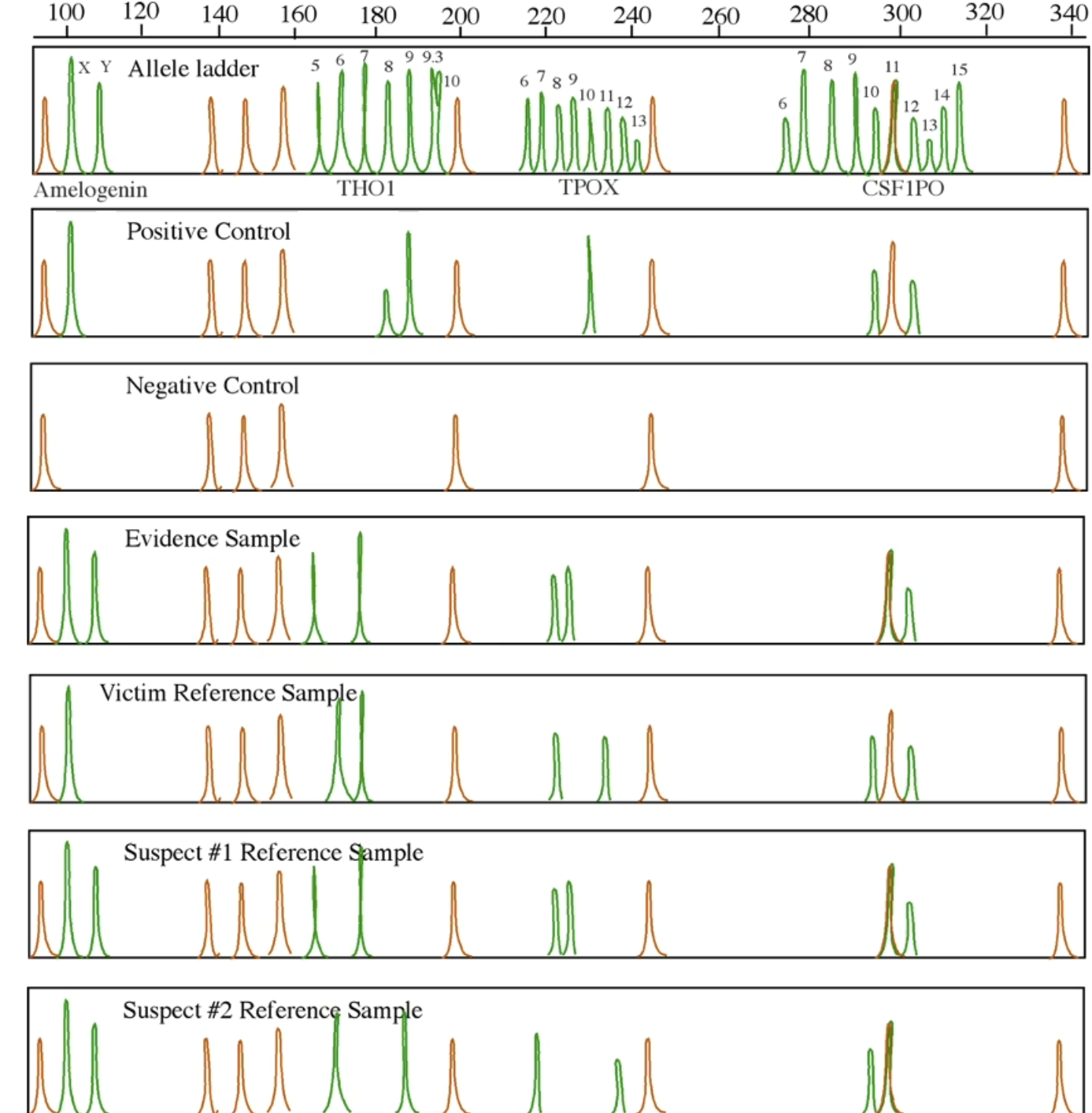
Suspect #1
Which suspect’s DNA is consistent with the evidence?
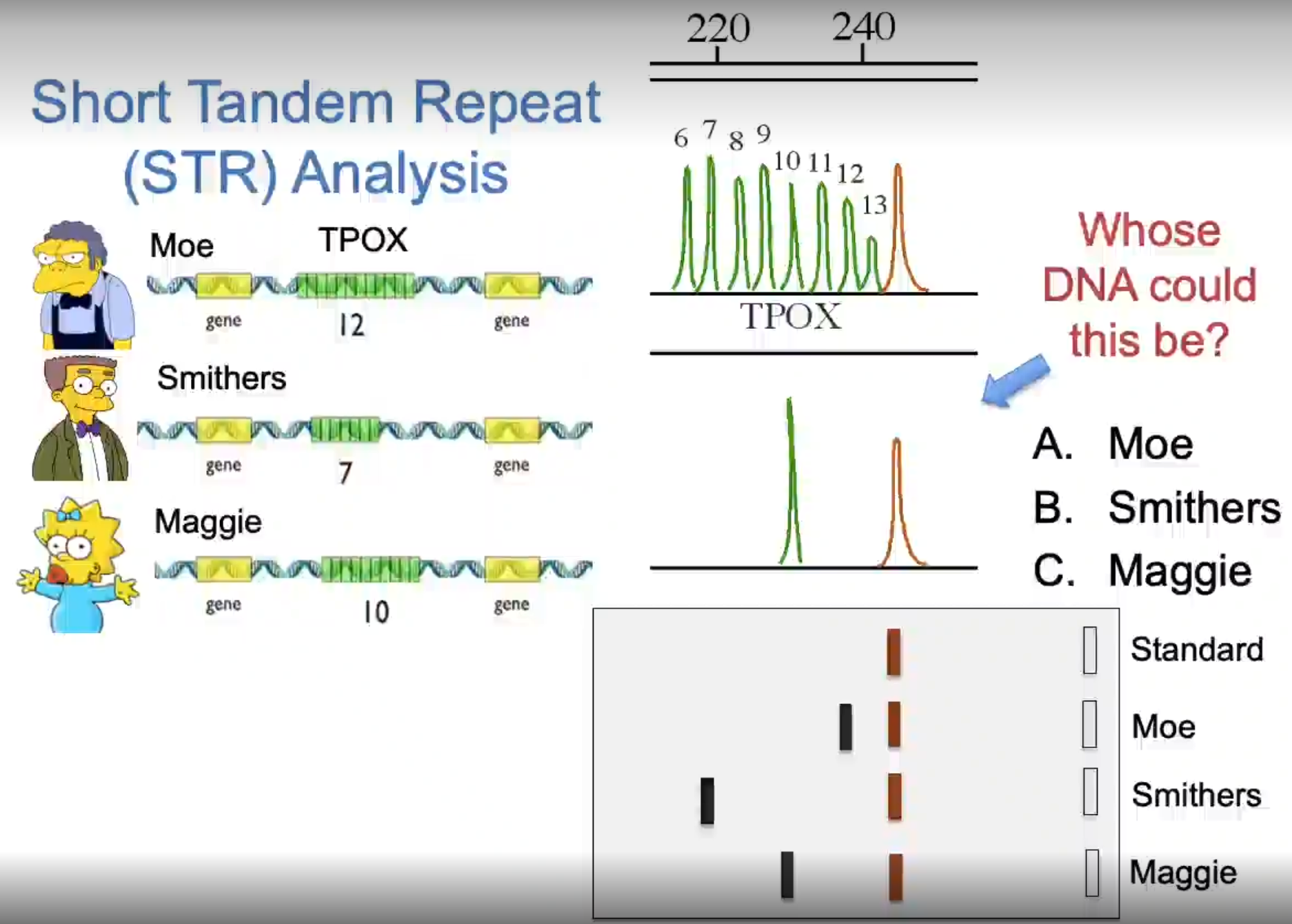
Maggie
Whose DNA could this be? Moe, Smithers, or Maggie
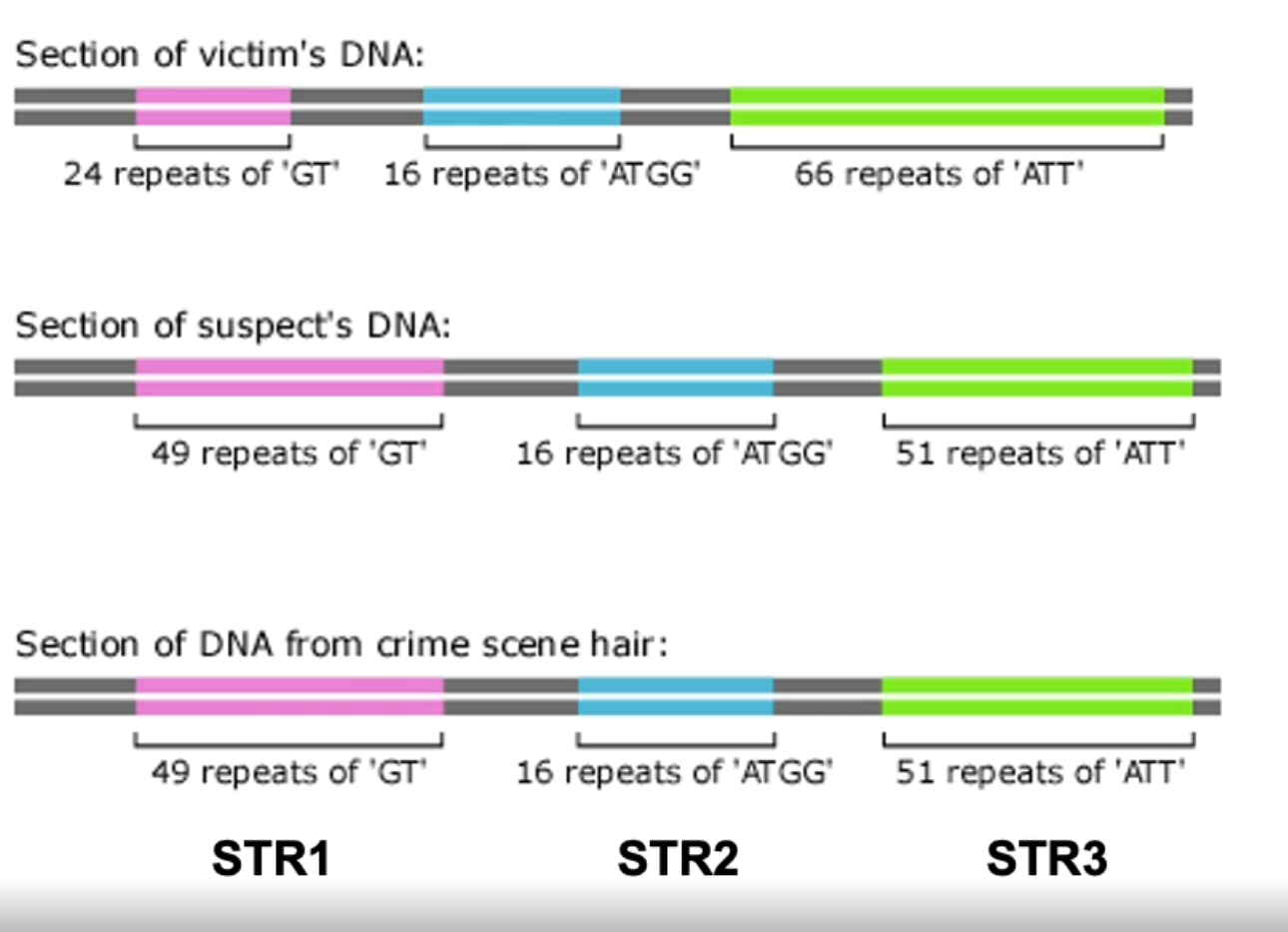
Suspect’s
Is this the suspect’s or victim’s hair?
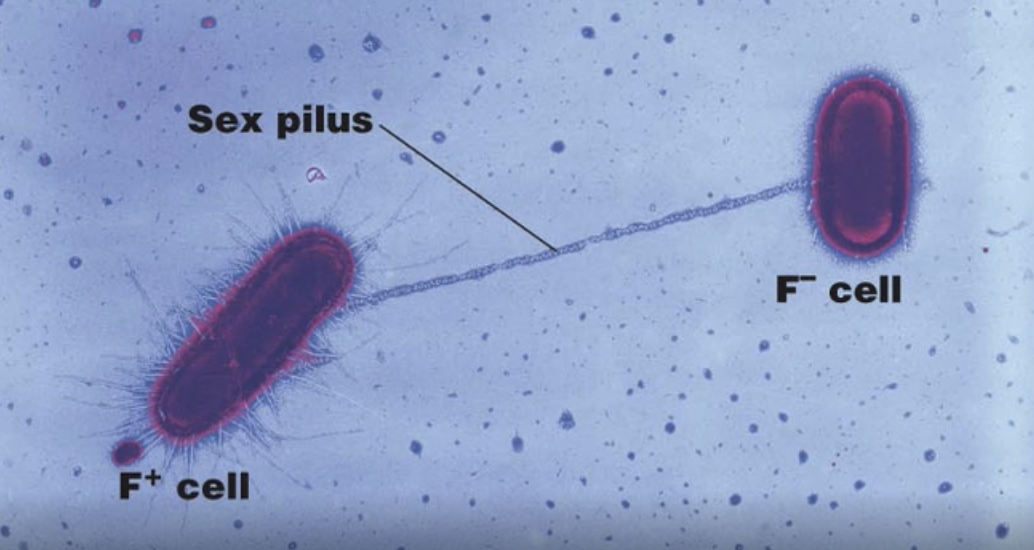
Bacteria using plasmids to pass genetic info to each other
What is this diagram showing?
Genetic Engineering
Manipulates an organism’s DNA directly using biotechnology to change it’s characteristics as well as involving adding, removing, or changing specific genes to create the desired trait(s)
E.coli
You can clone one specific gene using inside a host cell. The host cell is usually:
Yes
Once the bacteria have the gene and the correct amino acids, can they build the protein?
Human insulin
Name 1 human medication that is made by recombinant DNA technology?
Taq Polymerase
Name the special type of heat resistant DNA polymerase used in PCR reactions:
True
The length of tandem repeats varies from person to person, true or false?
Size
Gel electrophoresis separates the tandem repeats on the basis of what?
13
What is the minimum number of STR loci analyzed in forensic analysis?
False
It is likely that two individuals share the same STR pattern, true or false?
Bone marrow and umbilical cord blood
Name two non-embryonic sources of stem cells?
Stem cells that have the ability to turn into any cell or tissue of the body
What is a totipotent stem cell?
Zygote
Where are totipotent stem cells found?
Bone marrow
Name an adult stem cell that is commonly transplanted?