3.2.3(.2) - Exchange: Active Transport
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
How does active transport work?
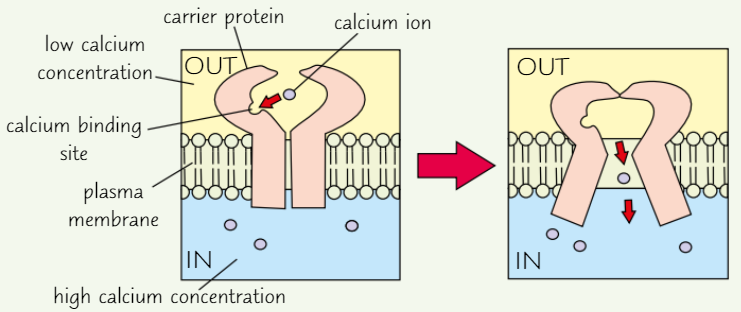
Molecule attaches to carrier protein
Protein changes shape → moves molecule across membrane
Molecule released on other side
Active transport involves ____ proteins
carrier
Differences between active transport and facilitated diffusion
Active transport usually moves solutes from low to high conc.
Facilitated diffusion always moves them from high to low conc.Active transport requires energy - facilitated diffusion doesn’t
How is ATP used in active transport?
ATP undergoes hydrolysis reaction, splitting into ADP + Pᵢ
→ releases energy so solutes can be transported
Active transport of calcium
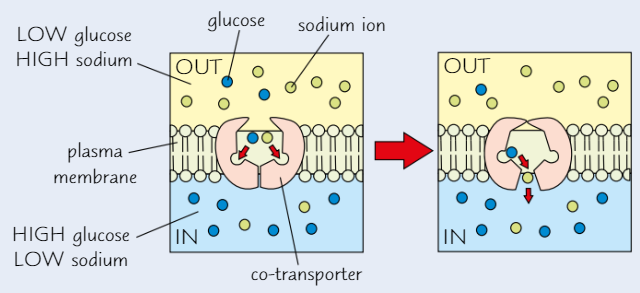
Co-transporters
Type of carrier protein
Bind two molecules a time
Conc. gradient of one of the molecules is used to move other molecule against its own conc. gradient
Diagram shows sodium ions moving into cell down conc. gradient
→ this moves glucose into cell, against its conc. gradient
How does speed of individual carrier proteins affect rate of active transport?
The faster they work, the faster the rate of active transport
How does number of carrier proteins affect rate of active transport?
More proteins = faster rate of active transport
How does rate of respiration affect rate of active transport?
If respiration is inhibited, won’t be any ATP → active transport can’t take place
Why is co-transport needed in the ileum?
In ileum, glucose conc. is too low for glucose to diffuse out of blood
→ glucose is absorbed from lumen of ileum by co-transport
Co-transport of glucose in ileum
Sodium ions are actively transported out of ileum epithelial cells, into blood, by Na-K pump
→ creates conc. gradient - now there’s higher conc. of Na⁺ in lumen of ileum than inside cell
Causes Na⁺ to diffuse from lumen of ileum into epithelial cell, down conc. gradient, via sodium-glucose co-transporter proteins
Co-transporter carries glucose into cell with sodium
→ glucose conc. inside cell increases
Glucose diffuses out of cell, into blood, down conc. gradient, through protein channel by facilitated diffusion