2 - Basic concepts of Probability
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
types of variables
endogenous
exogenous
depending on the problem a variable can change from endogenous to exogenous & vice versa
variable
something whose value can change either quantitatively or qualitatively
endogenous variable
dependent variable that moves passively or as a result of changes in another variable
exogenous variable
explanatory variable that moves actively or is the cause of changes in other variables
consumption function
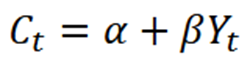
Ct - endogenous
Yt - exogenous
alpha & beta - constants
consider demand curve
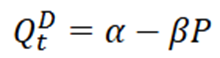
price determines quantity demanded, hence:
Qdt - endogenous
P - exogenous
inverse demand curve
arguably quantity demanded can determine price as well, meaning:
Qdt - exogenous
P - endogenous

random errors

systematic behaviour is likely to be affected by random errors
these errors occur randomly and can only be known after the fact
introduces randomness to the behaviour of endogenous variable, making it no longer perfectly predictable
consumption function with random errors
consumption is now random and not perfectly predictable because of random errors
Ct is determined by both the systematic part and random errors
consumption function with random errors graphed
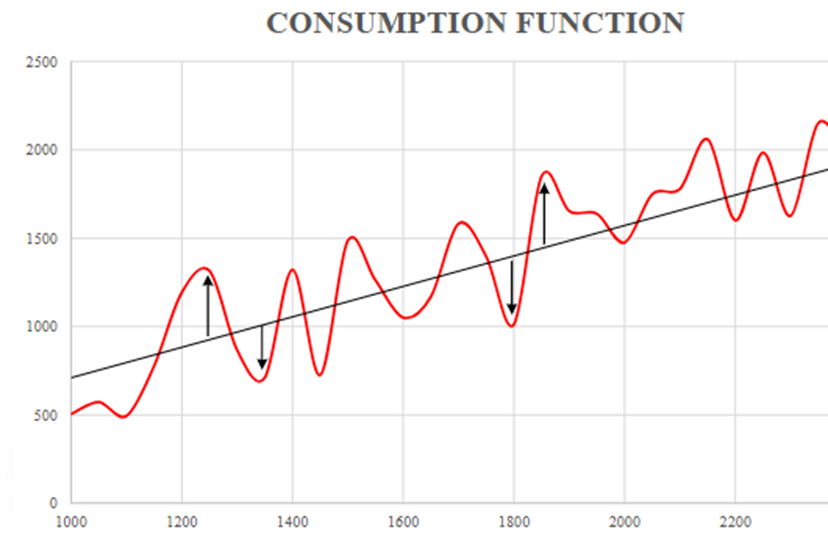
red line - actual consumption
black line - predicted consumption
gaps - prediction errors/randomness
distribution of variables
variables follow a kind of distribution
distribution - described possible values a variable can take and the corresponding likelihood
values can be
numerical
non-numerical - i.e. head/tail of coin
discrete - specific, distinct values
discrete, numerical - outcome from rolling a die
discrete, non-numerical - outcome from flipping a coin
continuous - number of possible values is infinite
continuous, numerical - possible temperature of Cardiff
distribution
distributions are formed by the number of observations
summarises information about the variable:
probability/frequency - likelihood of observing
mean
volatility (variance)
probability
likelihood of observing a value or event based on the number of possible outcomes