Unit 7
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
What is macroeconomics?
A branch of economics concerned with the behaviour and performance of an economy as a whole
What are government macroeconomic objectives?
Quantifiable targets that the government wishes to achieve through the implementation of macroeconomic policy
What are the four main objectives for the macroeconomy?
Balance of payments equilibrium
Economic growth at trend rate
Employment
Price stability
What are the other 5 important objectives?
Fiscal balance
Living standards
Income and wealth equality
Productivity
Social indicators
What is GDP?
The total value of goods and services produced within an economy over a given period of time
What is aggregate demand?
The value of the demand for all the goods produced in the UK economy
What is aggregate demand made up of?
AD = C + I + G + N
What are the influences on consumption?
Interest rate
Rate of direct taxation (IT)
Incomes
Consumer confidence
What are the influences on investment?
Interest rates
Rates of direct taxation (Corp Taxes)
Income levels
Profit expectations
What are the influences on government spending?
Economic activity
Market failure
What are the influences on government net exports?
Income abroad
Income at home
Domestic price level
Exchange rates
What is the exchange rate?
The value of one currency in terms of another currency
What is appreciation?
When one currency increases in value against another so can buy more of that currency.
What happens to the price of UK exports following an exchange rate appreciation?
Price of UK exports rises as pound is worth more.
What happens to the price of imports following an exchange rate appreciation?
Price of imports coming into the UK falls as the pound is worth more
What is depreciation?
When one currency decreases in value against another so can buy less of that currency
What is a balanced budget?
When government spending = taxation receipts.
What is a budget deficit (fiscal deficit)?
When government spending exceeds taxation receipts.
What is a budget surplus (fiscal surplus)?
When government spending is less than taxation receipts
What is national debt?
The accumulation of previous borrowing that has not been paid back
Who lends the government money?
Banks/building societies, pension funds, investors
What are the 5 main objectives of the UK taxation system?
Fund Government spending
Managing the economy as a whole
Redistribution of income
Correcting market failure
Repay national debt
What are direct taxes?
Taxes directly levied on an individual or firm
What are indirect taxes?
Taxes on consumption
What are tax thresholds?
The level of income that has to be reached before tax is paid or before the tax payer moves into a higher rate of taxation
What’s hypothecation?
The principle that taxes are raised for a specific purpose. Taxes should be linked to the benefits taxpayers receive.
What is progressive taxation?
When the proportion of a person’s income paid in taxes increases as incomes increases
What is proportional taxation?
The same proportion of a tax payer’s income is taken regardless of the income earned
What is regressive taxation?
The proportion of a person’s income paid in taxes decreases as incomes increase
What are the benefits of income tax?
Direct taxes can be progressive
Can improve distribution of income
Simple to pay
Revenue can be forecast
What are the problems with income tax?
Can only be changed in the budget
Disincentive effects on work
What are the benefits of VAT and indirect taxes?
Influence spending patterns
Correcting externalities (internalising)
Can be changed easily
People have a choice whether to buy products
What are the problems of VAT and indirect taxes?
Regressive distributional effects
Can trigger cost-push inflation
Many people are unaware of how much indirect tax they pay
What are the benefits of corporation tax?
Profitable firms contribute to the economy
What are the problems of corporation tax?
If too high can be a disincentive for FDI
Large MNC’s have avoided paying it
What are the benefits of wealth taxes?
Equitable – those with more wealth should contribute more to society
What are the problems with wealth taxes?
Danger of taxing twice
Wealthy people may not have much income
What is an interest rate?
The cost of borrowing and the reward for saving. It is a percentage charge on the capital sum.
What is a real interest rate?
The nominal interest rate minus the rate of inflation
What is the Annual Equivalent Rate (AER)?
The interest rate on savings with annual compound interest added on.
Why are there different rates of interest?
Risk
Amount
Time
Expectations of future interest rates and inflation
Security
What is economic growth?
An increase in the economic activity of an economy over a period of time
What is GDP?
The value of all goods and services (output) produced within an economy over a given period of time.
What is real GDP?
The country’s output measured in constant prices with inflation accounted for
What is demand-led growth?
When an increase in aggregate demand is due to consumer-led spending or government spending
What is the economic cycle?
The regular fluctuations in economic activity over time. The stages to the cycle consist of boom, recession, slump/depression and recovery.
What happens in a boom?
GDP rises faster than the trend rate of growth. The economy may be producing beyond full capacity.
What happens in a recession?
Economic activity slows down
What happens in a slump/depression?
There’s negative economic growth where the economy is producing at below is the previous peak level of output.
What happens in a recovery?
Economic activity begins to increase and output begins to rise at a faster pace
What is supply led growth?
When increases in aggregate supply are due to the costs of production falling.
What are the benefits of economic growth?
Welfare increases
Employment increases
Living standards increase
Less poverty
What are the costs of economic growth?
Well-being
Other objectives
Relative incomes
Sustainability
Externalities
What is employment? Why is it important?
The employment of labour in the economy. It’s important as people rely on wages for most of their income.
What is full employment?
When the economy uses all of its workforce - those who want a job have one
What is the labour force/workforce?
People of working age who are willing and able to work
What is unemployment?
When workers who are able and willing to work are unable to find employment at current wages.
What is the unemployment rate?
The number of people willing and able to work but unable to secure employment expressed as a percentage of the workforce.
What is the formula for the unemployment rate?
Unemployment Rate = (Number of Unemployed / Labour Force) x 100
What is the claimant count?
A measure of unemployment according to the number of people claiming unemployment-related benefits
What are the 4 main types of unemployment?
Structural, cyclical, frictional, seasonal
What is structural unemployment?
When the industrial structure changes the types of jobs needed and, thus, the skills required
What is cyclical unemployment?
When the economic cycle may be in recession so there’s less demand for goods and services so workers are laid off
What are the problems for the economy that are caused by unemployment?
Wasted resources
Budget deficit
Regional problems
Excluded workers (the Hysteresis effect)
What are the problems for the individual that are caused by unemployment?
Social problems
Lower living standards
Cost to taxpayers
What is price stability?
When the general level of prices is kept constant or grows at an acceptably low rate over time without volatility
What is inflation?
The sustained rise in the general price level over time (the rate figure is positive).
What is the rate of inflation?
The sustained rise in the general price level over a period of time expressed as the percentage increase in the price level.
What is deflation?
A sustained fall in the general price level over time (the rate figure is negative)
What is disinflation?
Falling rates of inflation. This means that the general price level is increasing at a slower rate.
How is inflation measured?
The CPI (consumer prices index) is published by the ONS monthly
What is demand-pull inflation?
Inflation that arises from increases in aggregate demand
What is cost-push inflation?
Arises when the costs of production increase, leading to higher prices goods and services
What happens in a wage-price spiral?
If prices rise, the cost of living rises so wages rise. Then the cost of production rises so prices rise
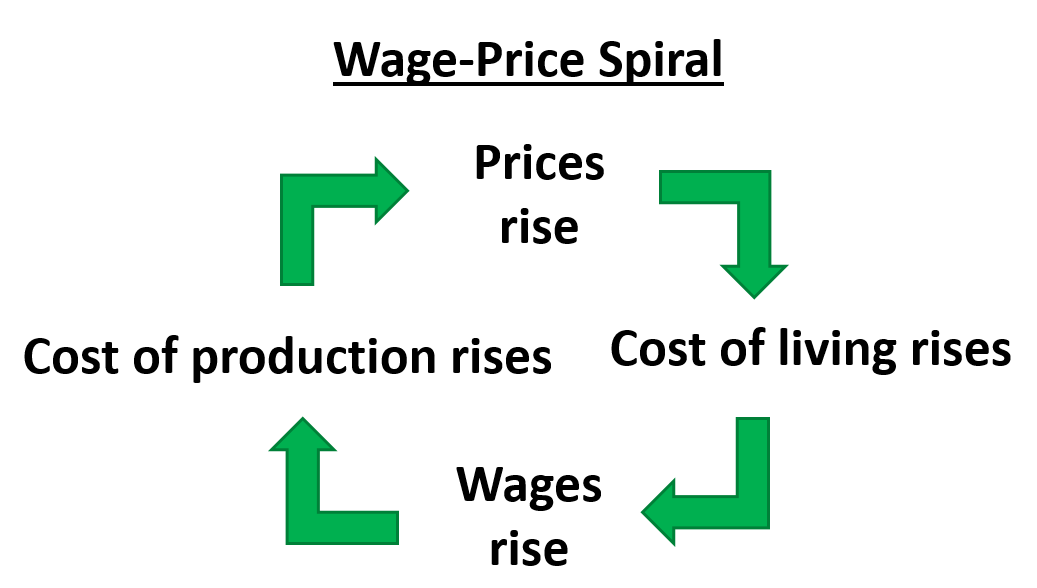
What are examples of cost-push inflation?
Higher wages
Imported inflation
Higher taxes
What are examples of demand-pull inflation?
Lower interest rates
Rising real wages and incomes
Depreciation of exchange rate
What are the costs of inflation to the economy?
Income redistribution problems
Business and consumer confidence decreases
Can affect Bank of England’s credibility as there’s a symmetric target
What are the costs of inflation to an individual?
Income redistribution problems
Real wages are worth less
Fiscal drag (higher wages lead to higher tax brackets)
What are the benefits of inflation to an economy?
Depreciates the real value of debt
Incentives to producers and consumers
What are the benefits of inflation to an individual?
Real value of debt falls
What is the balance of payments?
Records the money flows into and out of a country over time. Record of the financial transactions of one country with the rest of the world
What is the current account?
The balance of payments which measures the inflow and outflow of goods, services, investment incomes and transfer payments
What is the balance of trade?
The difference in value between a country's imports and exports.
How is a deficit on the current account paid for?
By raising money on the financial account
What is a current account deficit?
When a country sends more money abroad than it receives. Outflows > Inflows
What is a current account surplus?
When a country sends less money abroad than it receives from abroad. Outflows < Inflows.
What is a cyclical deficit?
A deficit caused by high rates of economic growth when the economy is in a boom
What is a structural deficit?
A deficit throughout the economic cycle caused by a lack of international competitiveness.
What are the reasons why a current account deficit is a problem?
Financed through the financial account
Shows lack of competitiveness
Too many imports may lead to decreased domestic demand and unemployment
What are the reasons why a current account deficit is not a problem?
A small deficit as a percentage of GDP means it’s not important
Imports of capital good
Only short term so may cure itself
What is income?
A flow of money to a factor of production.
What is the distribution of income?
Describes how income is shared out between the factors of production, households or between regions
What is the gini-coefficient?
A measure of inequality that condenses the income/wealth distribution for a country into a number between 0 and 1
What are the reasons as to why inequality of income is not a problem?
Incentives
Revenue product of labour
Trickle-down effect
What are the challenges as to why inequality of income is a problem?
Inequality of opportunity
Cause social problems
Living wage
What is absolute poverty?
A condition characterised by severe deprivation of basic human needs
What is relative poverty?
When a household’s financial resources fall below the average income level
What is wealth?
A stock of assets owned by an individual or organisation
What does the welfare state do?
Provides benefit payments
Provides vital social services
How is the welfare state funded?
Through tax revenue and NI contributions