(2025 Edition) Barron’s AP Human Geography Terms - Unit 6
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
[THESE ARE THE EXACT DEFINITIONS FROM THE TEXTBOOK UNLESS IN PARENTHESIS] Remember, when defining: Can I define these terms in my OWN WORDS? Can I give an example(s) for each term (if possible)? If you cannot, ask your tutor, teacher, or resources for help.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
The downtown or lucleus of a city where retail stores, offices, and cultural activities are concentrated; building densities are usually quite high; and transportation systems converge.
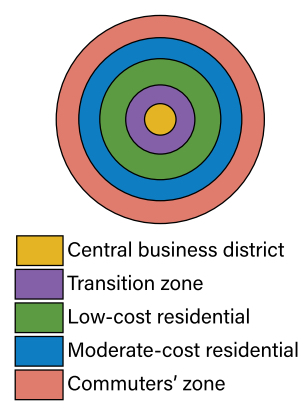
CONCENTRIC ZONE MODEL / BURGESS MODEL
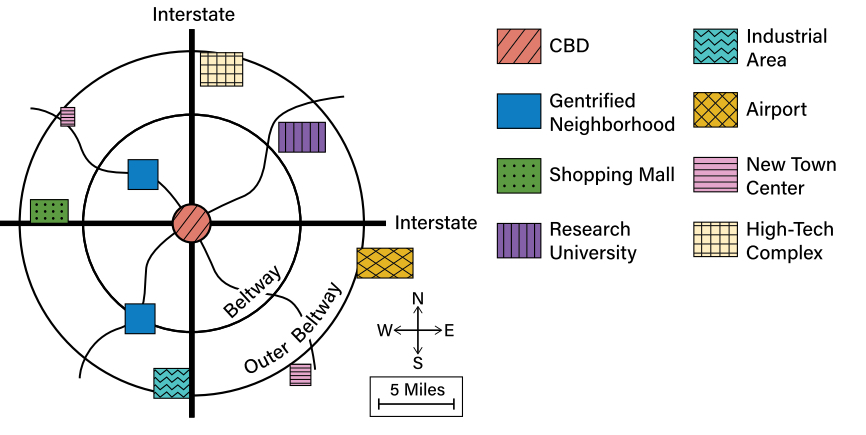
(Developed by Chauncey Harris) A circular-city model that characterizes the role of the automobile in the postindustrial era.
Those parts of large urban areas that lose significant portions of their populations as a result of change in industry or migration to suburbs. Because of these changes, the inner city loses its tax base and becomes a center of poverty.
Cities in Muslim countries that owe their structure to their religious beliefs. Islamic cities contain mosques at their center and walls guarding their perimeter. Open-air markets, courtyards surrounded by high walls, and dead-end streets, which limit foot traffic in residential neighborhoods, also characterize Islamic cities.
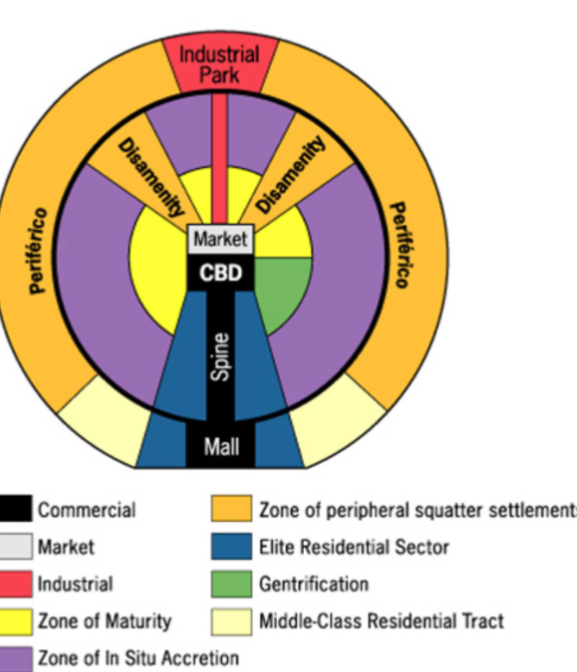
LATIN AMERICAN CITIES / GRIFFIN-FORD MODEL
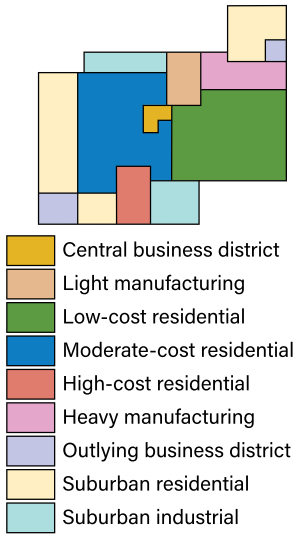
MULTIPLE-NUCLEI MODEL / HARRIS AND ULLMAN MODEL
A reaction in archi-rectural design to the feeling of sterile alienation that many people get from modern architecture. Postmodernism uses older, historical styles and a sense of lightheartedness and eclecticism. Buildings combine pleasant-looking forms and playful colors to convey new ideas and to create spaces that are more people-friendly than their modernist predecessors.
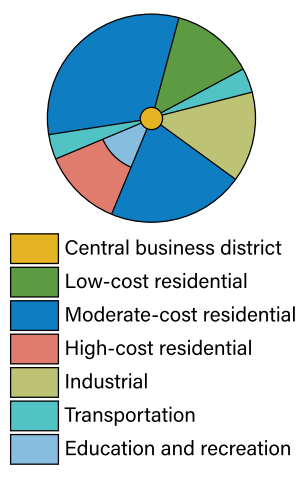
SECTOR MODEL / HOYT’S MODEL
Residential developments characterized by extreme poverty that usually exist on land just outside of cities that is neither owned nor rented by its occupants.
Residential communities, located outside of city centers, that are usually relatively homogeneous in terms of population.
The process occurring in some urban areas experiencing inner-city decay that usually involves the construction of new shopping dis-tricts, entertainment venues, and cultural attractions to entice young urban professionals back into the cities, where nightlife and culture are more accessible.