BAP 1165 Final Exam (Beef, Dairy, Small Ruminants)
1/514
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
515 Terms
Define Beef
meat from cattle/bovine
Cow
female bovid who has given birth
Heifer
female bovid who hasn't given birth
Bull
intact adult male bovid
calf
young immature bovid
steer
castrated male bovid
bovid
mammal of cattle family
Cull
select from large quantity and remove (unwanted)
Know cattle anatomy!
What has happened to the beef sale market?
The market peaked in 70's, steadily decreased, and is now leveling out
Cattle inventory is BLANK, but Beef production is BLANK
decreasing, increasing
Is beef consumption declining or increasing?
declining
Where does the United States rank in beef consumption?
first!
Is beef the most consumed protein in the world?
No
What is a cow/calf?
make the babies
What is a feeder operation?
feed the cattle from cow/calf operations
What is a stocker?
graze grass 3-4 months before the feedlot
what is backgrounding?
growing and feeding of calves from weaning until entry into a feedlot
What is a feedlot?
large facilities with lots of cattle, fed TMR
What is the difference between a seedstock and commercial operation?
Seedstock; purebred, specific breeds
Commercial; cross breeds with particular purpose
What is the average farm size?
50 cattle or less
Where are most operations located? What are the top 3 states?
grain belt, very dry arid places
- Texas, Oklahoma, Missouri
How does Missouri Rank in # of farms, # of beef cattle, and # of cow calf operations?
2nd in number of farms, 3rd in number of beef cattle, 3rd in cow calf operations
What parts are more tender and tougher?
Front=tougher
back=tender
How much of the animal becomes product?
60%
List products other than meat that come from beef cattle
Leather, tallow, bone marrow
Species
group of organisms of similar individuals capable of exchanging genes
Define Breed
subgroup of organisms within a species having distinct appearance; usually developed by deliberate selection
Bos Tarus (Taurine)
look like cattle we usually see; live in dry climates
Bos Indicus
fatty hump, floppy ear, humid climate
What species of cattle are noted for their heat tolerance and resistance to certain parasites and diseases?
Bos Indicus; akf-milk and meat production, #1 breed in AUS
What are the two types of cattle?
British and continental
British cattle
-originated from Ireland, Scotland, and England
-smaller, mature faster
-known for calving ease and fertility
-higher quality grades, lower carcass yields
Continental Cattle(exotic)
-continental European regions
-larger mature size, low fat
-higher carcass yields, lower quality carcass
-have more calving difficulties
What breeds are considered triple purpose?
Simmental, Gelbvieh
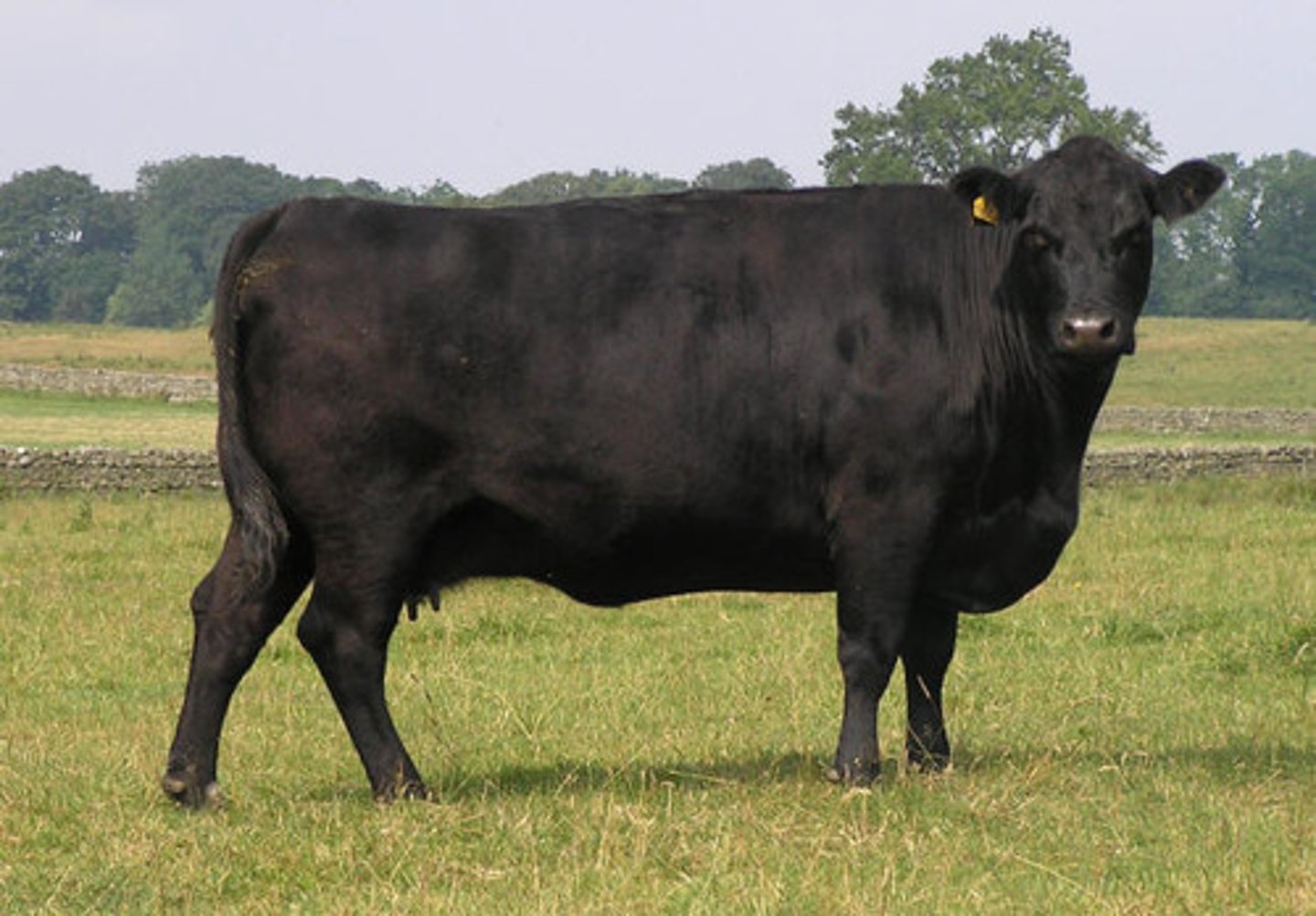
Aberdeen Angus
-British; org in Scotland
-Black color
-Most common US breed

What is CAB?
certified angus beef; quality assurance
-!0 characteristics
What are the characteristics of CAB?
-modest or higher marbling
-medium or fine marbling texture
-harvested at 30 mo or younger
-10-16 sq in ribeye area
-1,100 lb hot carcass weight
-less than 1" fat thickness
-Superior muscling
-practically free of capillary ruptures
-no dark cutters
-no neck hump exceeding 2"
How much influence does a cow need to be registered angus?
51% and black hide
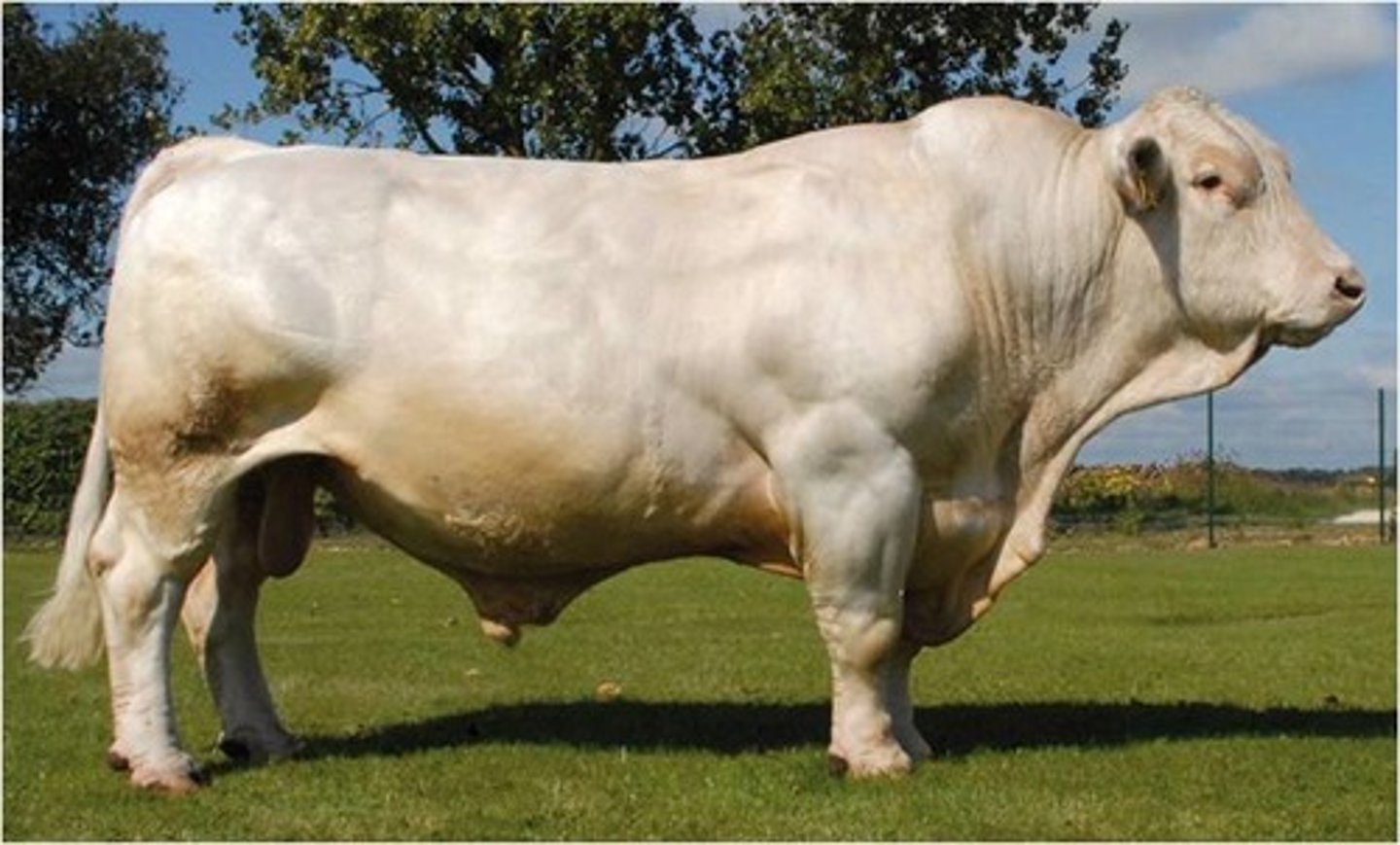
Charolais
-Continental Breed; org in France
-Medium to large frame
-White Color, Pink Muzzle

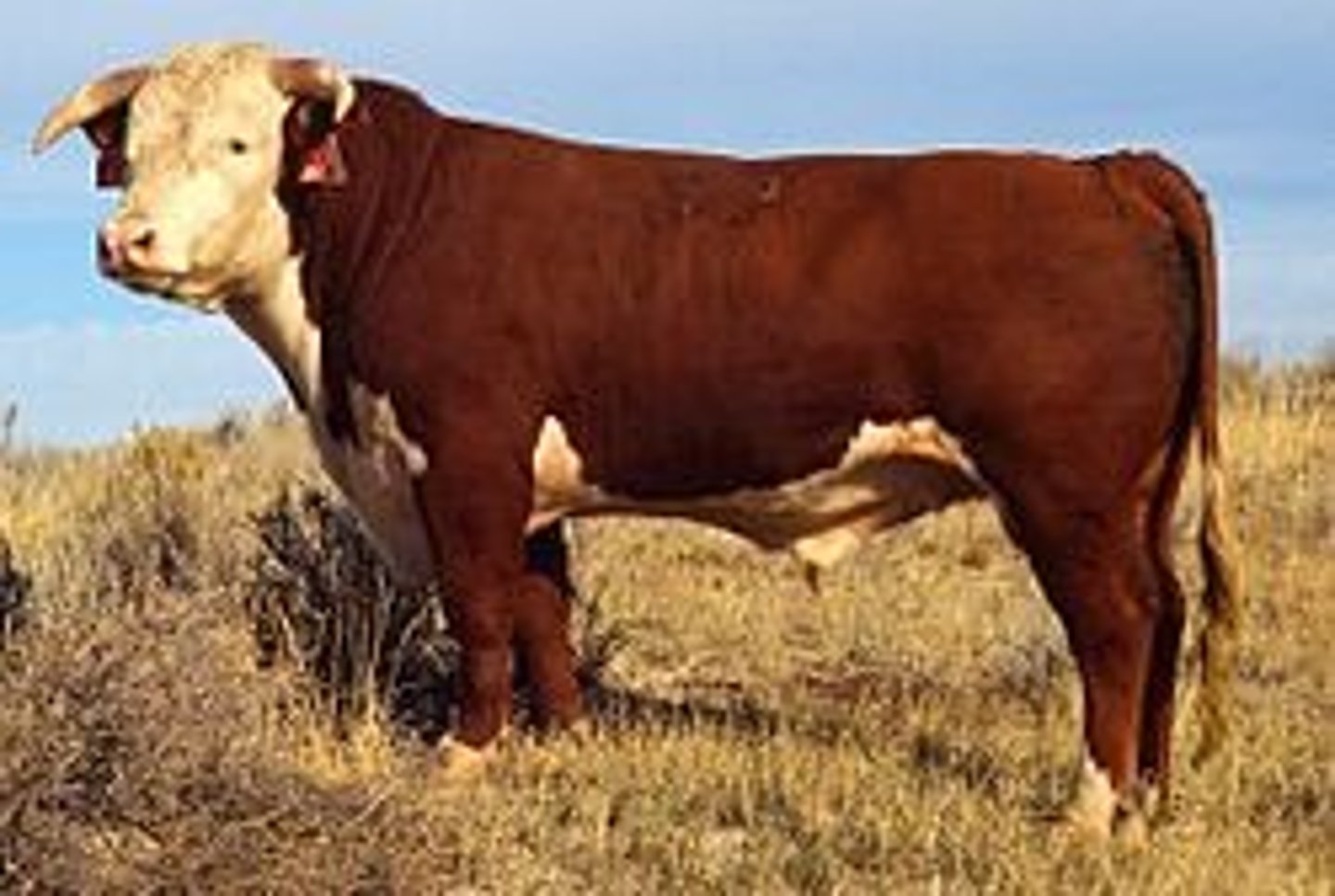
Hereford
-British Breed
-Red with white face
-Known for longevity

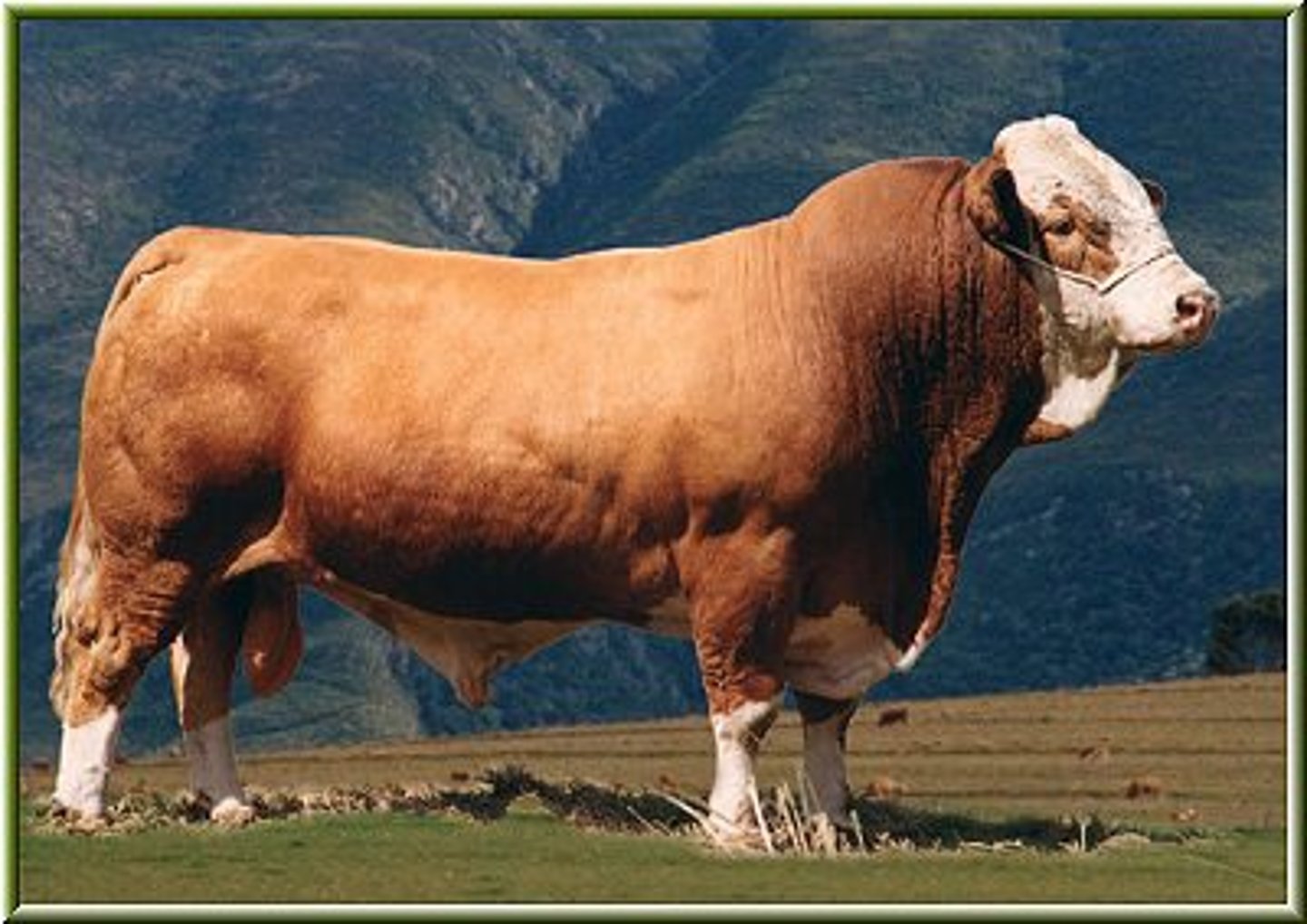
Simmental
-Continental Breed
-Used for milk, meat, and draft animals
-Traditionally a red color

Red Angus
-British Breed
-Same origin as black angus
-Red angus established in 1954

Texas longhorn
-Eat grass, plants, and weeds
-US beef founded on longhorns
-Lean
-Known for longevity and docility

Gelbvieh
-Continental Breed; "yellow cattle" in germen
-Came to US in 1970
-Triple purpose breed
-Reddish gold, rust, black color
-Fine hair med to large body

Limousin
-Contiental Breed; central and SW France
-Sturdiness, health, adaptibility
-Work and meat; lean carcass
-Golden Red

Highland
-British Breed; Scottish highlands
-Meat; Milk high in fat
-Horns help with foraging

Shorthorn
-British Breed
-Dual Purpose
-Oldest Breed
-Can be red, white, known for roan

What does the term "cattle are converters" mean?
-they can convert low-quality food like forages into nutrient dense foods
-utilize low quality land
What is a by-product?
leftover foods from processes that cattle can eat; generally cheap
Are cow calf operations a large or small land investment? Why?
Large; they require land and less facility needs
What are forms of pasture and range management?
mow land, fertilize, rotate cattle
Why is herd health important for management?
Healthy cows live longer
Why managing reproduction important?
You need to make sound genetic decisions to produce healthy cattle
How can you asses profitability of a herd?
Know annual cattle cost, compare market prices with your break even price, know calf crop percentage weaned
What weight should calves be at weaning? When should their target be?
Half of weight at weaning, target at 7 months
What is the average gestation length of cattle?
280 days
What are pros of utilizing all year breeding?
-Use same bull both seasons
-Gives heifers flexibility
-Spreads out marketing risks
What are cons of all year breeding?
-More labor
-More pasture management
When does spring calving take place?
Feb-April
Who should calve first? Why?
Heifers
-allows heifers more attention and assistance
-gives bigger window to breed back
What are advantages of spring breeding?
increasing temperatures, growth of grass
What are disadvantages of spring breeding?
rain, snow, and mud
When does fall calving take place?
Late August-October
What are advantages of fall calving?
-weaning calves marketed in spring
-better breeding weather
Disadvantages of fall breeding
-heat stress
-have to get calves through winter
What is fescue toxicity?
-Endophyte causes reaction
-restricts blood vessels and causes less lactation, decrease in consumption, and gestation problems
What are the stages of parturition?
-Prep; get calves into position
-Delivery; 2-4 hours, look for progress or dystocia
-Clean up; pass placenta in 8-12 hours
What is the calf mortality loss?
3-5%; 44 % had difficult births; 63% lost in the first day
What is the Matigan Squeeze Technique?
Tie rope around ribcage area and pull to stimulate birth
What are causes of calf loss?
Small calves, large calves born to heifers, scours, pneumonia
What is a cotyledonary placenta?
has cotyledonary attachments
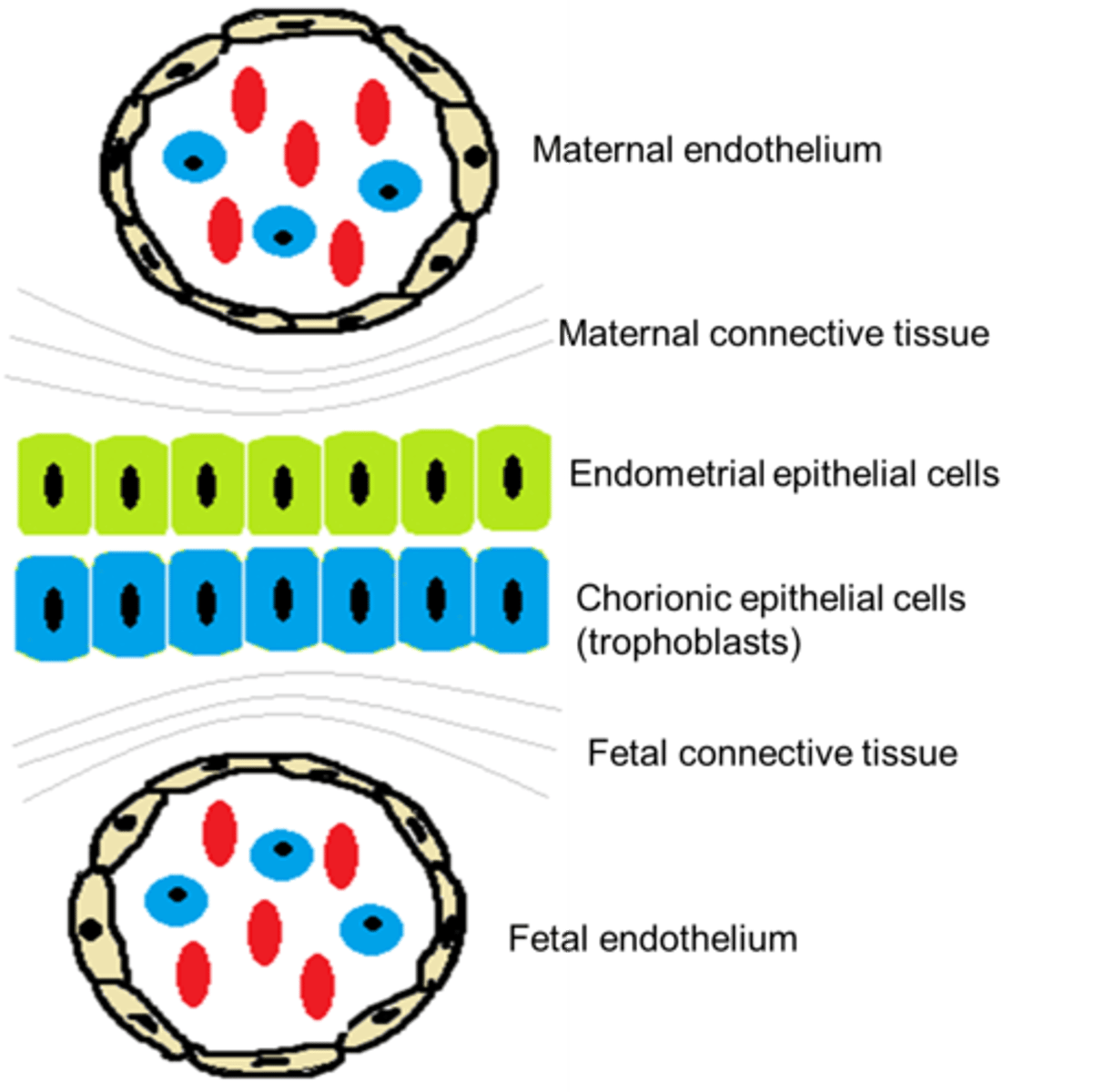
What is the epitheliochorial placenta?
have a greater distance between maternal and fetus blood, prevents antibody transfer
What do you do post birth for cattle?
give colostrum, weigh, tag, and castrate
Why is it important to make sure the calf has colostrum within the first 24 hours? Explain the timeline
-When calves are born, they have an absorption window
-The older they get the less IgB they're able to absorb
-If they aren't given the colostrum within 24 hours, they're unable to get passive immunity and will get sick and die
What are in immunoglobins?
fat soluable vitamins, vit B-12, iron. absorbed through passive immunity transfer
What is passive transfer?
temporary protection from the dam, must be digested in the first 24 hours. can be provided through plasma transfer
what is active immunity?
acquired from exposure to the infection or vaccine
Why is it important for the milk to pass through the rumen into the abomasum?
to avoid fermination
How can you prevent illness in calves?
-Provide clean environment
-Dip umbilical chord
Give the when, why, how of castration
-When; sooner the better
-Why; without the testosterone less muscle mass -->more tender product due to fat utilization
-How; surgical or bloodless with band/clamp
What is chemical castration?
-inject testes to kill them (not long term)
-use hormones; pervents development of testes
The BLANK the calf is at castration the BLANK weight they lose in the days following the procedure
older, more
What are forms of identification?
-Ear tag
-Branding
give the when, why, and how of dehorning
-When; earlier the better
-Why; safety for farmers and other animals
-How; caustic paste, hot knife, hot iron
What are consumer concerns with polling?
-Pain management
-getting naturally polled animals
Which vaccinations are given to cattle at the certain ages?
-60-90 days; 7-way
-2-4 weeks; 7 way, IBR, BVD, BRSV, PI3
-Weaning; IBR, BVD, BRSV, PI3, brucellosis for heifers
Why do we give vaccinations before weaning?
Stress causes a compromised immune system
What do clostridial diseases effect?
-Are bacteria
-Affect muscle, liver, intestine
What are some common clostridial diseases?
Black leg and malignant edema (fluid on leg)
Define joint ill.
infection through bacteria that settles in the joints
What is Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)?
Highly Contaigious
Acute inflammation of the upper respiratory tract due to Bovine Herpes Virus 1 (BHV-1)
What are some signs of IBR?
Snotty nose, reduced energy
What is the cure for IBR?
there is no cure, the virus is never fully removed and lies dormant in brain nerves
What are symptoms of Bovine Viral Diarrhea (BVD)?
Diarrhea, fever, pneumonia. Can cause reduced fertility and abortions
How is BVD spread?
Contact of infected animals, can spread in utero
How does BVD have and economic impact?
-Easily spreads
-Detrimental to reproduction
-Uncurable, cattle usually culled
What is Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus (BRSV)?
Respiratory disease that effects the lower tract
-Leads to weak immune system --> pneumonia
How does BRSV spread?
respiratory aerosols or direct contact
How is BRSV identified and treated?
Requires lab test; often identified by cough, discharge, eye gunk, fever