L4 - Viewing the image intensifier image and image intensifier problems
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
what is the size of the output phosphor in II
2.5-5cm
what is matched with the output
CCD
what does the output phosphor do
converts into electrons to light which directs it to CCD
how is the light from the output phosphor directed to the CCD
fiber optics
what does the CCD optics do
converts light into an electronic signal
the light is porportion ot the ___
radiaiton
1 fiber optic tube = x pixel
1
name steps from the xray source to operating console
xray source > patient > II > CCD > ADC > computer > electrons > DAC > operating console
why should the II be placed close to the patient
to maximize distance between xray source and patient
what happens to the electric signal from the CCD
signal is sent to the ADC and switched to digital signal
What is the photosensitive layer on the CCD
crystalline silicone
what happens when electrons hit the crystalline silicon
creates an electrical charge
what are the main characteristics of CCD
good spatial resolution, high DQE, high SNR
why do CCD have good DQE
no lateral spread of light with the fibre optic coupling, good signlaing caught. Lower patient dose
What are CCD not affected by
changes in magnetic fields
what are the problems in II
vignetting, image lag, pincushion/s distortion, veilinng glare, and image magnification
What is vignetting
decrease in brightness in the periphery of images
why does vignetting happens
the periphery is unfocused and not bright, shape of the input phosphor
what is image lag
persistance of an image before while the II is being moved. system cannot resolve the image as fast as the equipment is moving annd creates a blurred image
what is iamge bloom
intense brightness on the monitor because of the CR being moved thus there is no anatomy between II and xray tube
what are the 2 types of shape distortion
pincushion and s-distortion
what is pincushion
a type of shape disortion caused by the image from the curved input phosphor doesnt match with the output phosphor. worse in edges
what is S-distortion
Caused by the changing in magnetic fileds causing the trajectory of the electrons to move in an S pattern
what is veiling glare
light being reflected from the window of the output phosphor. this reduces iamge contrast. happens when moving from thick tissue to thin
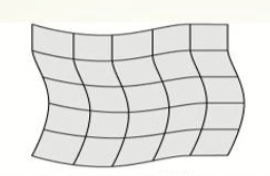
what type of distortion is this
S distortion
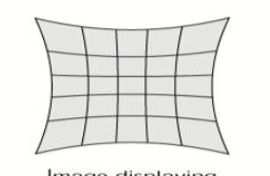
what type of distortion is this
pincushion
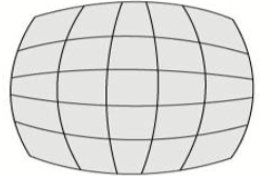
what type of distortion is this
barrel