L6: Personality & Individual Differences II
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1. Describe the features of the Dark and Light Triad. 2. Critically evaluate the concepts and measures relating to the Dark and Light Triad. 3. Explain how we can use a nomological network to validate and differentiate between Dark and Light Triad traits. 4. Explain the predictive validity of the Dark and Light Triad traits.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
history of the term Dark Triad
emerged abt 20y ago
personality psychologists Paulhus and Williams (2002) wanted to explore personality traits that are maladaptive but subclinical (within normal range of functioning)
The Dark Triad
refers to a constellation of three socially undesirable personality traits
narcissism
machiavellianism
psychopathy
Furnham, Richards, & Paulhus (2013): clinical vs subclinical
narcissism and psychopathy are established clinical disorders
but support for a subclinical definition bc these traits also found in normal populations
studied prev amongst clinical pops, e.g. committed crime
three traits already been identified
The Myth of Narcissus
Narcissus was a young man known for his beauty, but also for his mean and cold-hearted demeanour. many fell in love w him bc of his beauty, and he would always cruelly reject them
Nemesis decided to punish Narcissus for his cruelty and lured him to a still pool of water
as Narcissus leaned over the water to drink, he saw his own reflection for the first time and was captivated by the beautiful image he saw
Narcissus became obsessed with his reflection and could not pull himself away
he wasted away beside the pool, unable to eat or drink and eventually died
narcissism (Ames, Rose, & Anderson, 2006)
a grandiose, yet fragile, sense of self, as well as a preoccupation with success and demands for admiration
the narcissistic personality
an excessively self-centred perspective and a strong sense of entitlement, and preoccupation with success
require excessive admiration and believe that they are special, leading them to insist on associating only with high-status people
at root of inflated egos are feelings of inferiority, and so are envious of others, and will diminish others’ success or accomplishments
origin of term narcissism
myth of narcissus
origin of term machiavellian
niccolo machiavelli
Niccolo Machiavelli
italian diplomat, philospher, and writer
lived during Renaissance (1469-1527)
wrote the book “The Prince” which discusses the strategies and tactics rulers and leaders should employ to maintain power and achieve their political goals
famously argued that it is sometimes needed for rulers to be ruthless, cunning, and willing to use any means, even morally questionable ones, to achieve and maintain political authority
Niccolo Machiavelli quote
never attempt to win by force what can be won by deception
machiavellianism (Wilson et al., 1996(
a personality trait that refers to a strategy of social conduct that involves manipulating others for personal gain, often against the other’s self-interest
Machiavellian personality
master manipulators who use a range of deliberate manipulation techniques (e.g. flattery) for personal gain
engage in a plethora of unethical and counterproductive behaviours including lying, theft, and sabotage
possess a cynical view of human nature and demonstrate very little concern for the welfare of others above their own wellbeing
psychopathy (Ames, Rose, & Anderson, 2006)
a drive to engage in impulsive or antisocial behaviour without empathy, anxiety, or remorse
psychopathic personality
impulsivity and thrill-seeking; may engage in risky behaviours without consideration for consequences
callousness and a consistent lack of empathy
lack of emotional bonds and do not experience feelings of guilt or remorse for their behaviour
measuring the DT traits
two commonly used questionnaires that measure all three traits within gen pop
The Dirty Dozen
The Short Dark Triad
The Dirty Dozen
(Jonason and Webster, 2020)
questionnaire measuring all 3 DTs for gen pop
12 items
4 for each dimension

The Short Dark Triad
(Jones & Paulus, 2014)
27 items
9 for each dimension
criticisms of Dark Triad measures
social desirability bias
short measure lose nuance in each construct
cultural assumptions
criticisms of Dark Triad measures: social desirability bias
for self report measure, but esp for socially dark traits
ppl high in traits more likely to lie, manipulate, or ‘fake good’, so asking to self rate may lack reliability
some items v blatant e.g. i manipulate others to get my way
criticisms of Dark Triad measures: short measures lose nuance in each construct
convenient but do not capture complexity of each trait
argue measure ‘dark vibe’ rather than specific traits well
when reflect back at all diff characteristics, elements missed
esp in narcissism bc insecure, inferiority aspect to it as well
short and/or combined measures not good at measuring each strait specifically
criticisms of Dark Triad measures: cultural assumptions
WEIRD
many scales developed in Western samples
items may not capture how manipulation or narcissism is expressed in other cultures
DT + gender: study: procedure
Muris et al (2017)
meta analyses to explore gender differences in three DT traits
50 studies, 65 samples, 25,930 Ps
dummy coded gender (0=f, 1=m) and computed effect sizes (r.) for the relationship between gender and each DT trait
positive r = higher in men
DT + gender: study: results
psychopathy (r+ = .29)
narcissism (r+ = .15)
machiavellianism (r+ = .16)
+. means higher in MEN
DT + gender: study: conclusion
men generally display higher levels of all the DT traits relative to women
stronger effects found for psychopathy- medium-sized effect (0.29)- than narcissism (0.15) and machiavellianism (0.16)- small-sized effects
DT + age: study: procedure
(Klimstra et al., 2020)
combined multiple cross-sectional datasets
N = 4,292 Ps
various ages
completed Dirty Dozen Scale and measures of agreeableness
DT + age: study: findings
all show a rise during adolescence
after early 20sish, traits seem to decrease. suggesting adult ageing is associated with lower levels of these dark tendencies
suggests evidence for the maturity principle
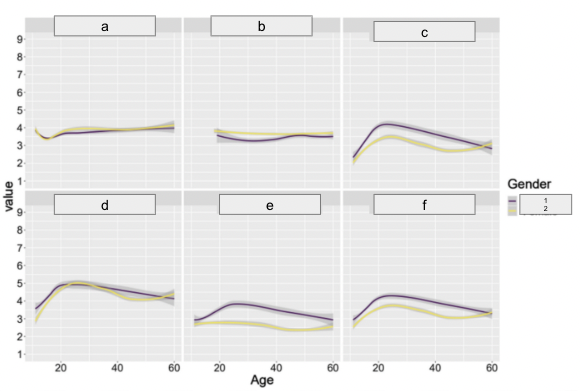
label 1,2,a,b,c,d,e,f
Male
Female
BFI Agreeableness
NEO Agreeableness
Machiavellianism
Narcissism
Psychopathy
Total Dark Triad
maturity principle
as people age, traits that are socially useful and acceptable tend to go up, on average
DT + course: procedure
(Vedel & Thomsen, 2017)
the Big Five and the Dark Triad traits were measured in sample of newly enrolled students (N = 487) from diff academic majors:
psychology, econ/business, law, pol sci
mean scores on DT traits compared across academic courses
DT + course: findings
no difference on psychopathy scores between courses
psych students scored lower on Machiavellianism than students on all other corses
psych students scored lower on narcissism than students studying econ/business
is narcissism increasing?
Twenge et al., (2008): examined how narcissism scores changed over time in college students
found since 1982, narcissism scores increased signficantly
NPI scores 30% higher in most recent cohort (2006) compared to first cohort (1980)
increase found particularly among women
long and established study, but recently called into question
why might we be seeing a rise in narcissism?
research shows relationship between social media use and narcissism in young adults
other research attributes it to changes in parenting styles
social media x narcissism
Reed et al (2018)
higher amounts of visual social media use associated with higher levels of narcissism
specifically, Ps who posted large quantities of photos and selfies showed a 25% increase in narcissism
hwvr, rls only found for visual forms as opposed to non visual forms of social media
parenting styles x narcissism
Brummelman et al (2015)
565 7-12y/os and parents over 2 years
measured 1. child self esteem, 2. child narcissism, 3. parental warmth, 4. parental overvaluation
parental overvaluation predicted child narcissism, but not self esteem
parental warmth predicted self-esteem, but not narcissism
parental overvaluation
parents believing their child to be more special and more entitled than others
what behaviours can we predict with DT traits?
health
performance or behaviour at work or school
pro-environmental behaviours
sexual behaviours
criminal behaviours
citizenship
criticisms of the DT
debate about whether the DT traits are independent traits (uniqueness hypothesis) or represent a single construct (unification hypothesis)
three traits not enough to capture the dark side of human nature
unification hypothesis
traits show strong, positive intercorrelations and have been found to load onto the same factor in factor analysis
uniqueness hypothesis
the three traits have different patterns of associations with other traits and outcome variables
three traits are not enough to capture the dark side of human nature
recently, proposed that the trait “subclinical sadism” should be included to form a Dark Tetrad
subclinical sadism
defined as proneness to feel pleasant emotions while hurting others or watching others in pain
The Light Triad (Kaufman et al., 2019)
qualities that embody a loving and beneficent orientation towards others (“everyday saints”)
kantianism
humanism
faith in humanity
Kantianism
treating people as ends unto themselves (not mere means)
treat people like they matter as humans, not just as tools to get what you want
humanism
valuing the dignity and worth of each individual
every person has value and deserves respect
faith in humanity
believing in the fundamental goodness of humans
believing that most people are basically good
features of Kantianism
authentic
prefer honest over charm
truly interested in others
features of humanism
admire others
applauds the success of others
values all people and cultures
features of faith in humanity
trusts people
quick to forgive
looks for the best in others
what was the LT scale guided by
the question: “what would an everyday loving and beneficent orientation toward others look like that is in direct contrast to the everyday antagonistic orientation of those scoring high on dark traits?”
The Light Triad Scale (Kaufman et al., 2019)
12 items
4 each dimension
scale developed by brainstorming items relating to the conceptual opposite of each of the DT, but also items related to forgiveness, trust, honestly, caring, and acceptance
three factors also emerged from the factor analysis: faith in humanity, humanism, kantianism
issues with the LT scale
social desirability bias
relatively new scale, not much evidence to support its cross-cultural validity
tests primarily been on western cultures (UK, USA)
behaviours we can predict using LT traits
health
performance or behaviour at work or school
pro environmental behaviours
sexual behaviours
criminal behaviours
citizenship
Nomological Network of the Dark and Light Triads
the network of traits, qualities, and outcomes that you would expect to be associated with a trait to demonstrate that it is a valid construct
function of the nomological network
establish a measure has construct validity
construct validity
extent to which the measure behaves in a way consistent with our hypotheses and represents how well scores on the instrument are indicative of the construct
to assess the nomological network, you can:
correlate the measure with measures that you expect to be highly correlate (convergent validity)
correlate the measure with measures that you expect would not be correlated (discriminate validity)
explore whether the traits correlate or predict outcomes in line with expected hypotheses (predictive validity)
Kaufman et al (2019): design
cross sectional, online survey
Kaufman et al (2019): Ps + what
nomological network of dark and light triad
N = 1518 adults
Kaufman et al (2019): variables measured
light triad (light triad scale)
dark triad (short dark triad)
big five personality factors (BFI)
measures of well-being (life satisfaction, authenticity, self-esteem)
measures of moral and social behaviour (empathy, compassion, selfishness, aggression)
Big Five personality factors
agreeableness
openness
conscientiousness
extraversion
neuroticism
measured on BFI
Kaufman et al (2019): aim
explore the nomological networks of light vs dark triad traits
Kaufman et al (2019): calculations
a light vs dark triad balance score by subtracting each person’s score on the dark triad from their score on the light triad
Kaufman et al (2019): results
light triad total x dark triad total = -0.48**
**p < 0.01, *p < 0.05
mean balance score of entire sample was 1.3, suggesting average person is tipped towards the light triad more
extreme dark traits rarer than extreme light traits
DT correlations with other measures
positive with selfishness
positive with self-enhancement values
negative with life satisfaction
negative with compassion, empathy
negative with belief that others are good
negative with belief that one’s own self is good
LT correlations with other measures
positive with acceptance of others
positive with compassion, empathy
positive with life satisfaction
positive with positive enthusiasm
positive with belief that others are good
positive with belief that one’s own self is good