Chemistry Test 3: Chapter 22 Terms & Definitions
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
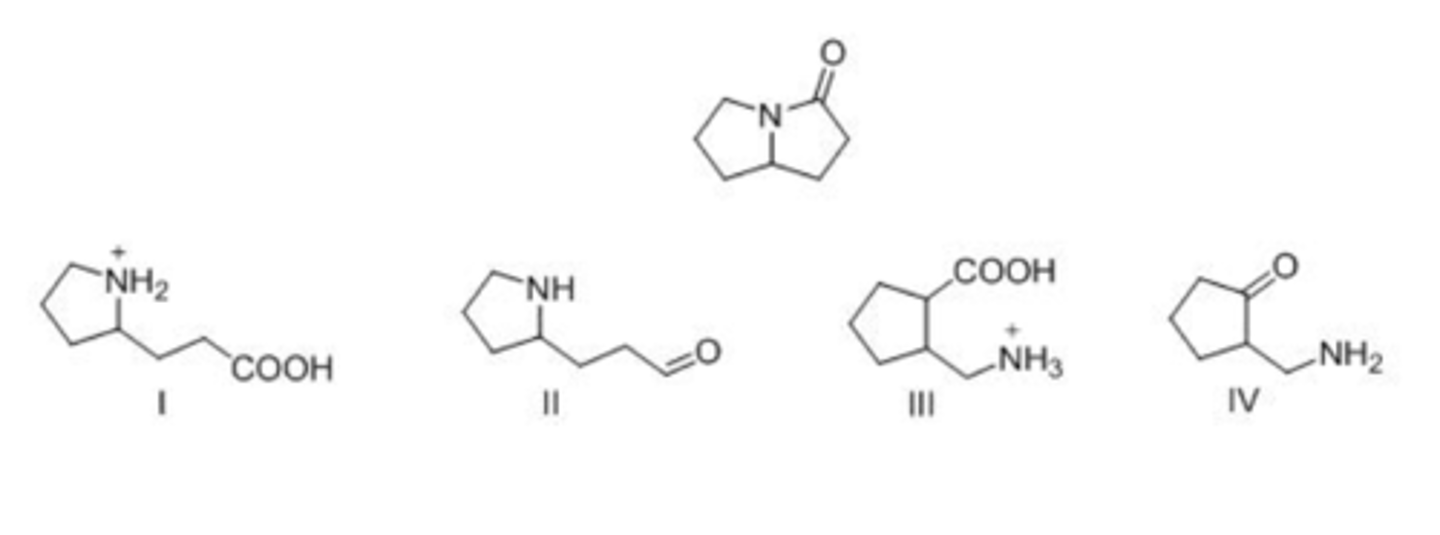
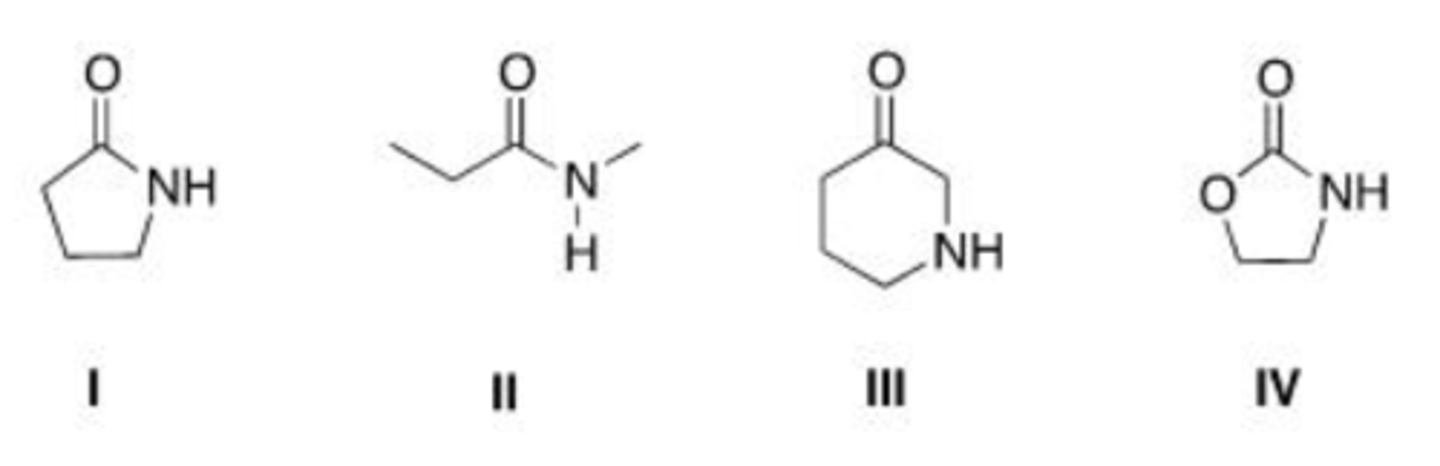
Which of the following is a lactam?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
A
Why is an amide less reactive to nucleophilic acyl substitution than an acid chloride?
A. Nitrogen is a better leaving group.
B. Chloride is a better leaving group.
C. Nitrogen donates more electron density into the carbonyl.
D. The amide anion is less basic.
C
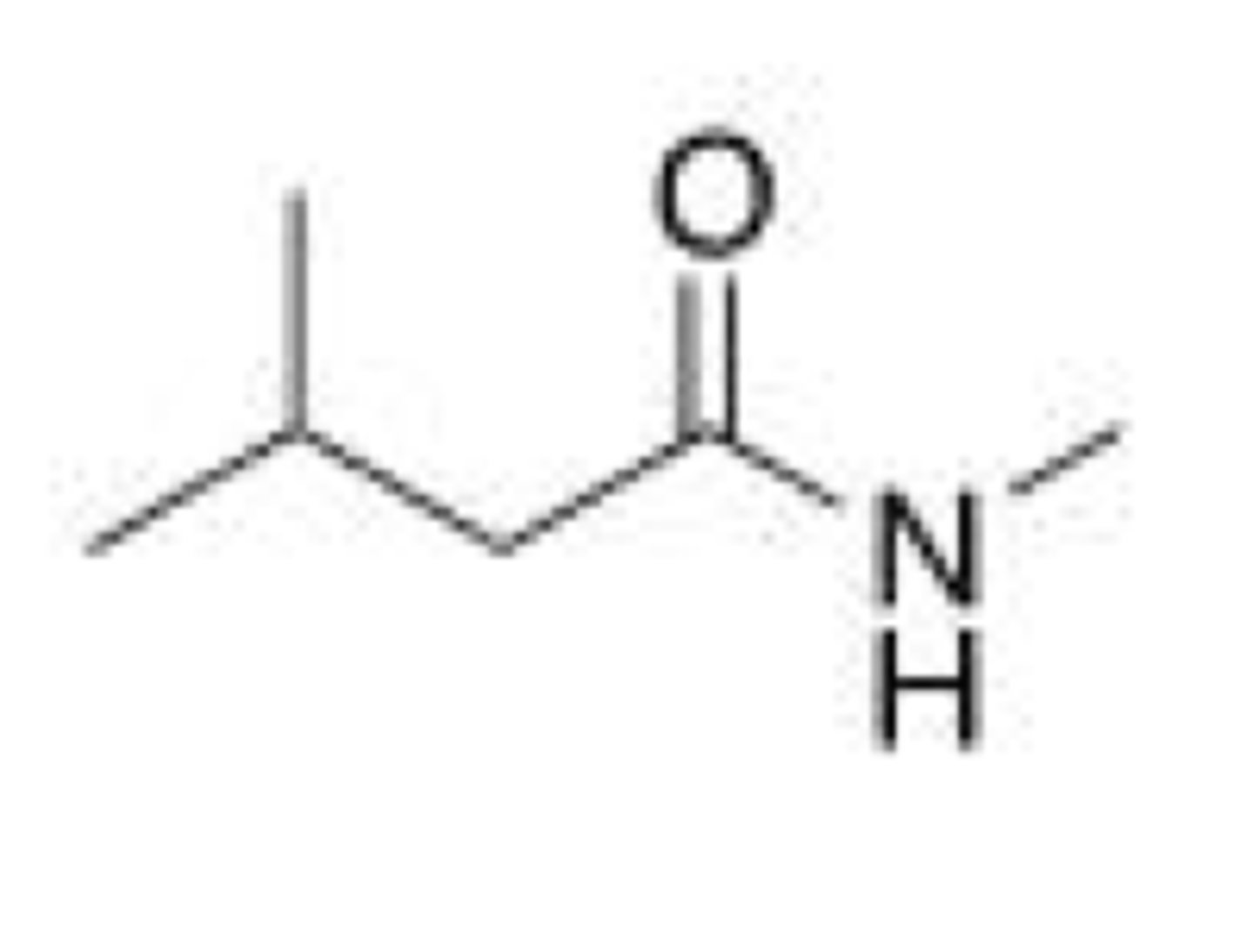
What is the IUPAC name for the following compound?
A. Methyl 3-methylbutanamide
B. 5-Methylhexanamide
C. N-Methyl 3-methylhexanamide
D. N-Methyl 3-methylbutanamide
D
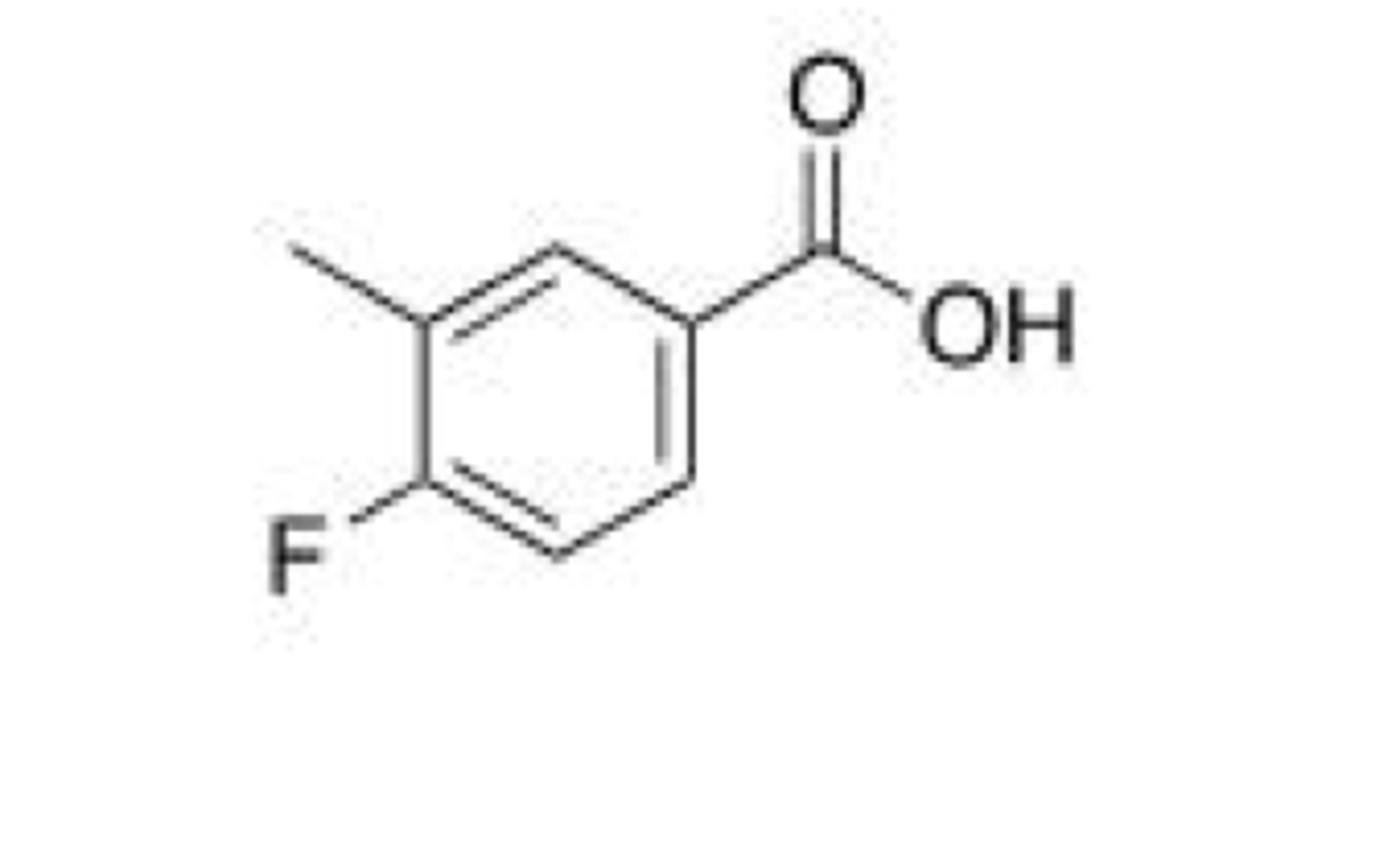
What is the IUPAC name for the following compound?
A. 4-Fluoro-3-methylbenzoate
B. 4-Fluoro-3-methylbenzoic acid
C. 3-Methyl-4-fluorobenzoic acid
D. 4-Fluoro-5-methylbenzoic acid
B
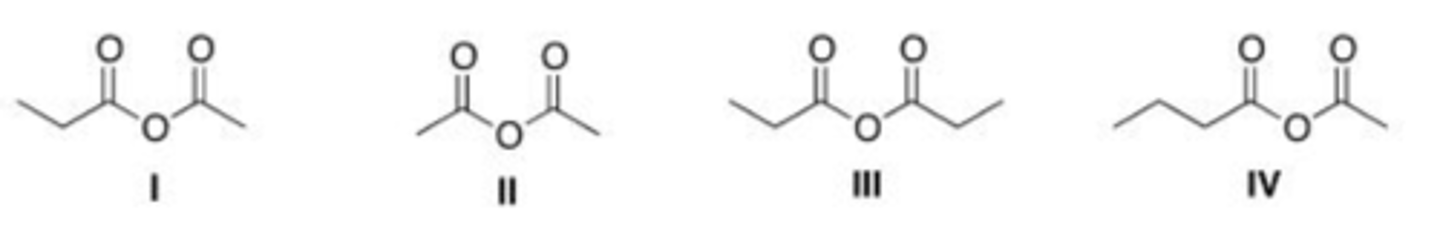
What is the structure for acetic propanoic anhydride?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
A
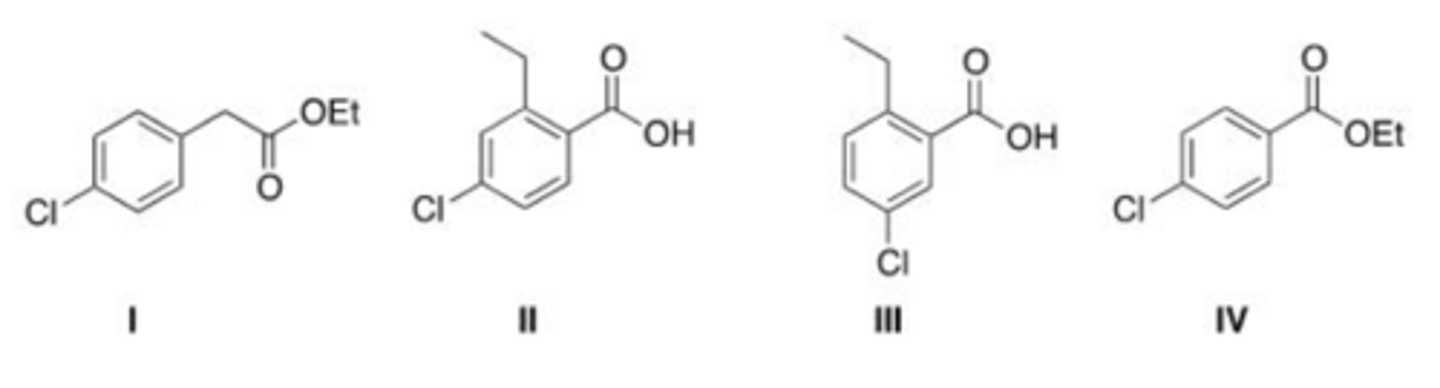
What is the structure for ethyl 4-chlorobenzoate?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
D
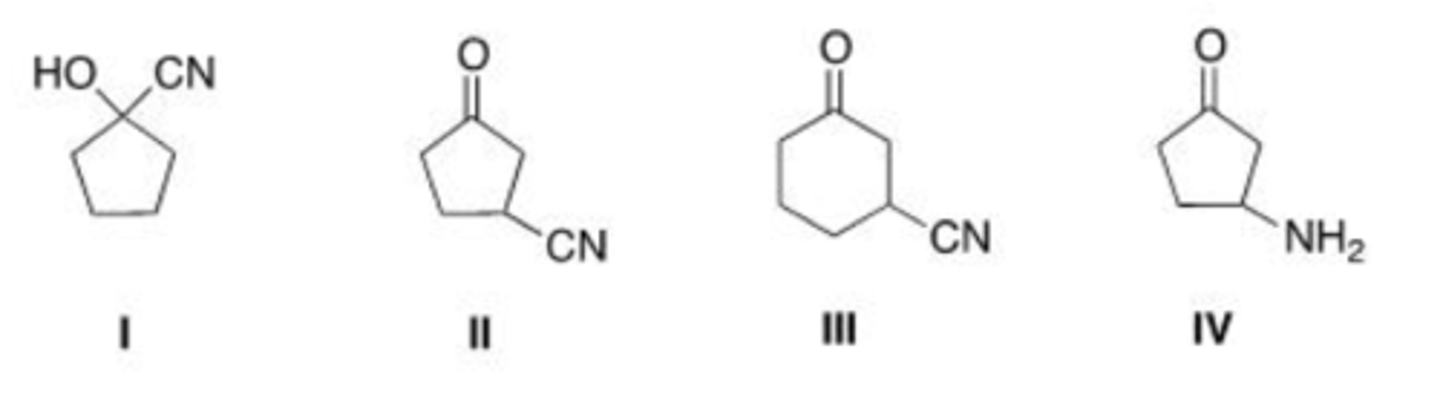
What is the structure for 3-cyanocyclopentanone?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
B
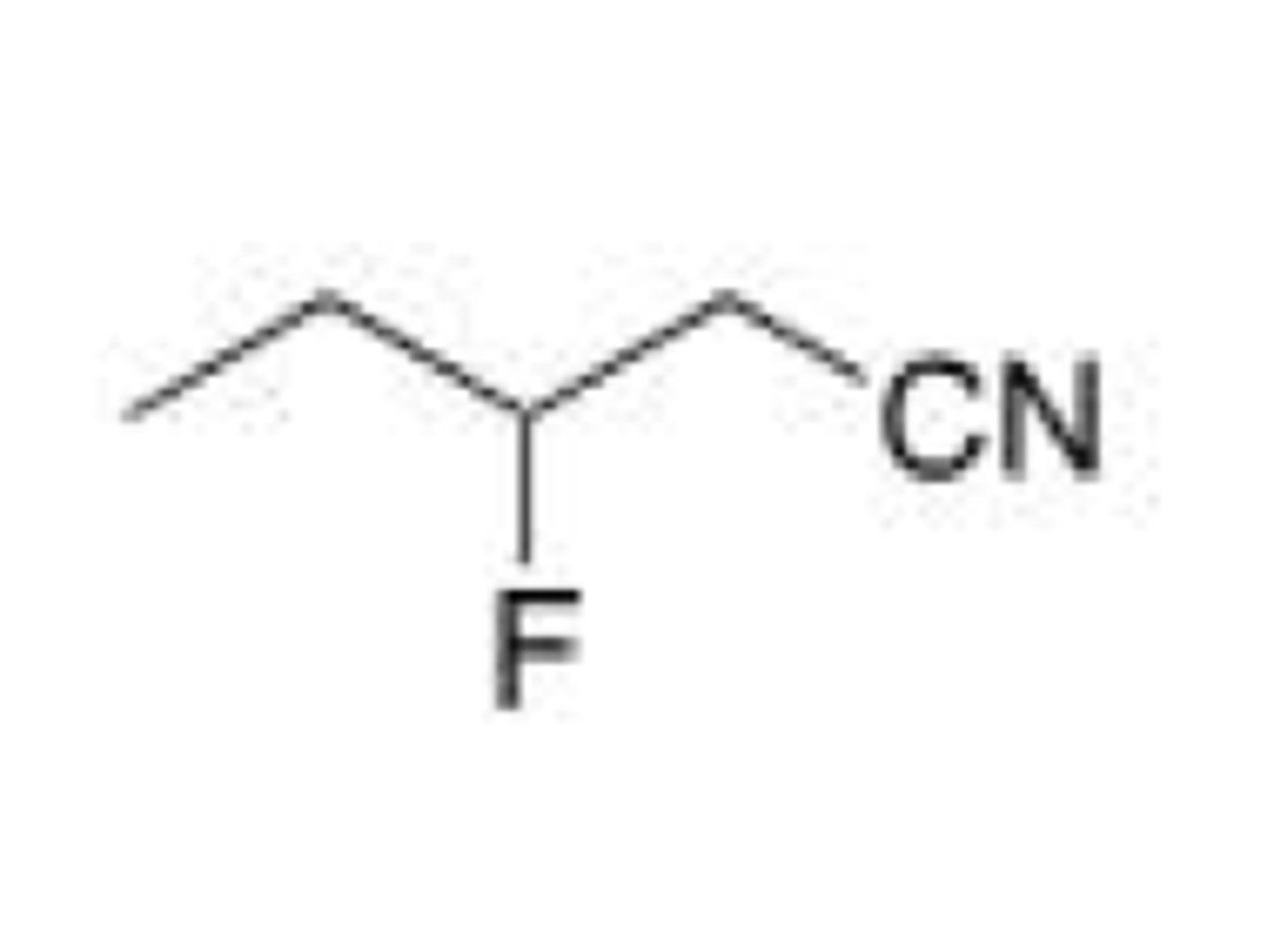
What is the IUPAC name for the following compound?
A. 2-fluorobutanonitrile
B. 2-fluoropentanonitrile
C. 3-fluoropentanonitrile
D. 2-fluorobutylcyanide
C
What is the first step in the general mechanism for nucleophilic acyl substitution?
A. Protonation of the carbonyl
B. Removal of an a-proton
C. Addition of the nucleophile to the carbonyl
D. Loss of the leaving group
C
Why doesn't nucleophilic acyl substitution stop at the tetrahedral intermediate?
A. The nucleophile is too basic.
B. Reforming the carbonyl is energetically favorable.
C. The leaving group is unstable and wants to be negatively charged.
D. There is no tetrahedral intermediate.
B
Will the following reaction occur?
A. Yes
B. No
B
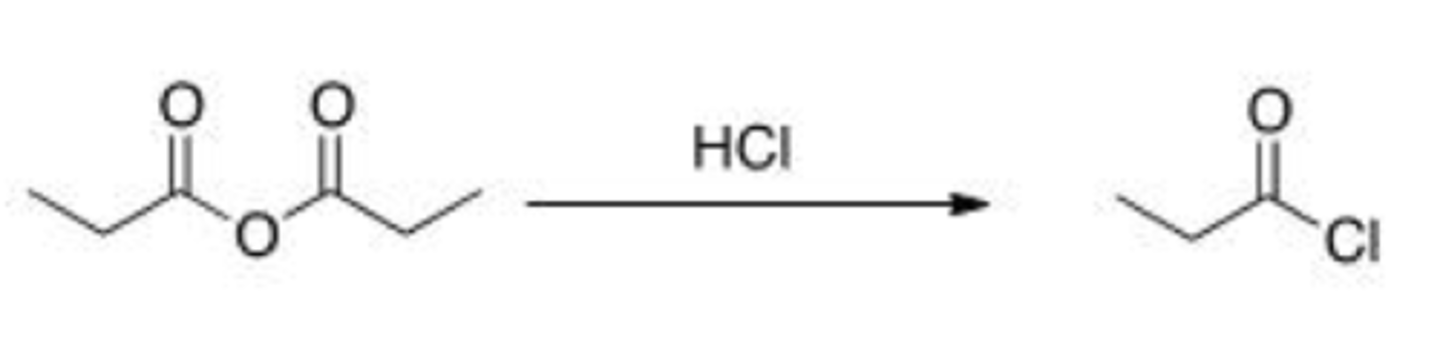
Will the following reaction occur?
A. Yes
B. No
A
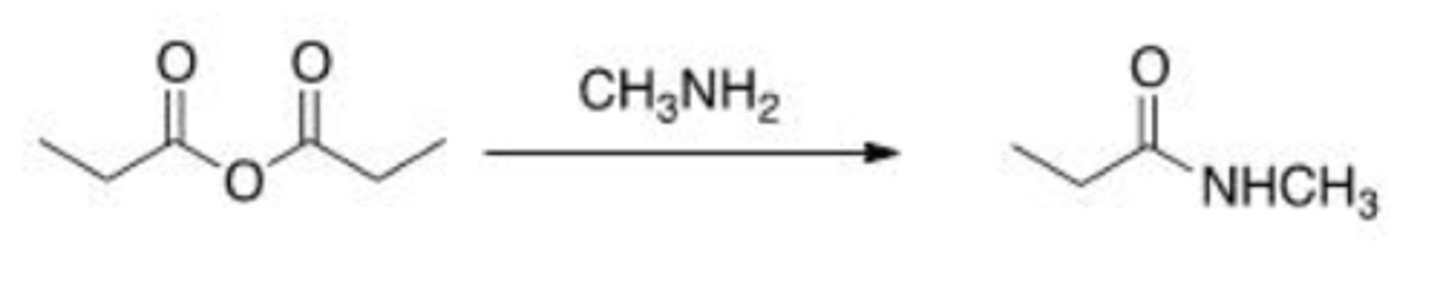
Will the following reaction occur?
A. Yes
B. No
B
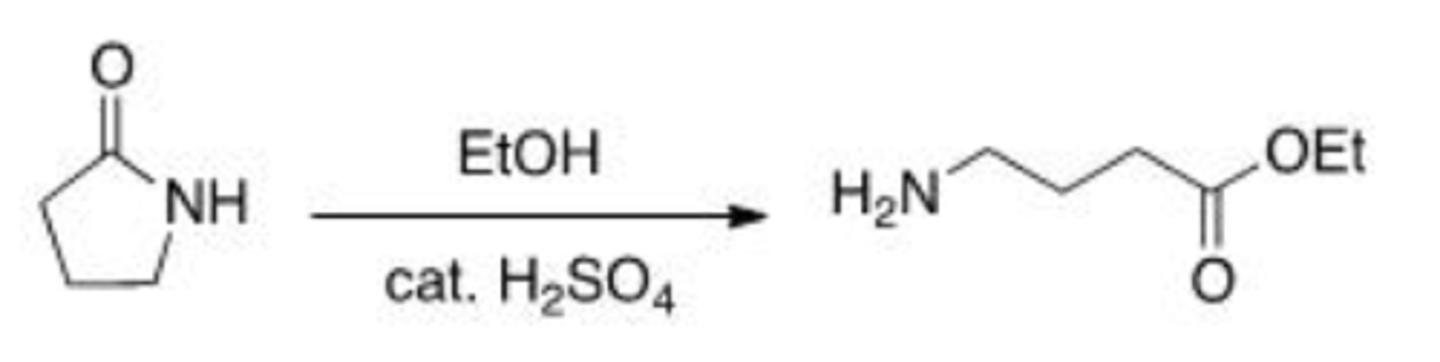
Why is pyridine included in the reaction of an acid chloride and an amine or alcohol?
A. Pyridine will deprotonate the amine or alcohol, making it a better nucleophile.
B. Pyridine will neutralize the acid by-product of the reaction.
C. Pyridine will protonate the carbonyl of the acid chloride, making it more reactive.
D. Pyridine will absorb the heat of the reaction.
B
What is the product of the following reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
C
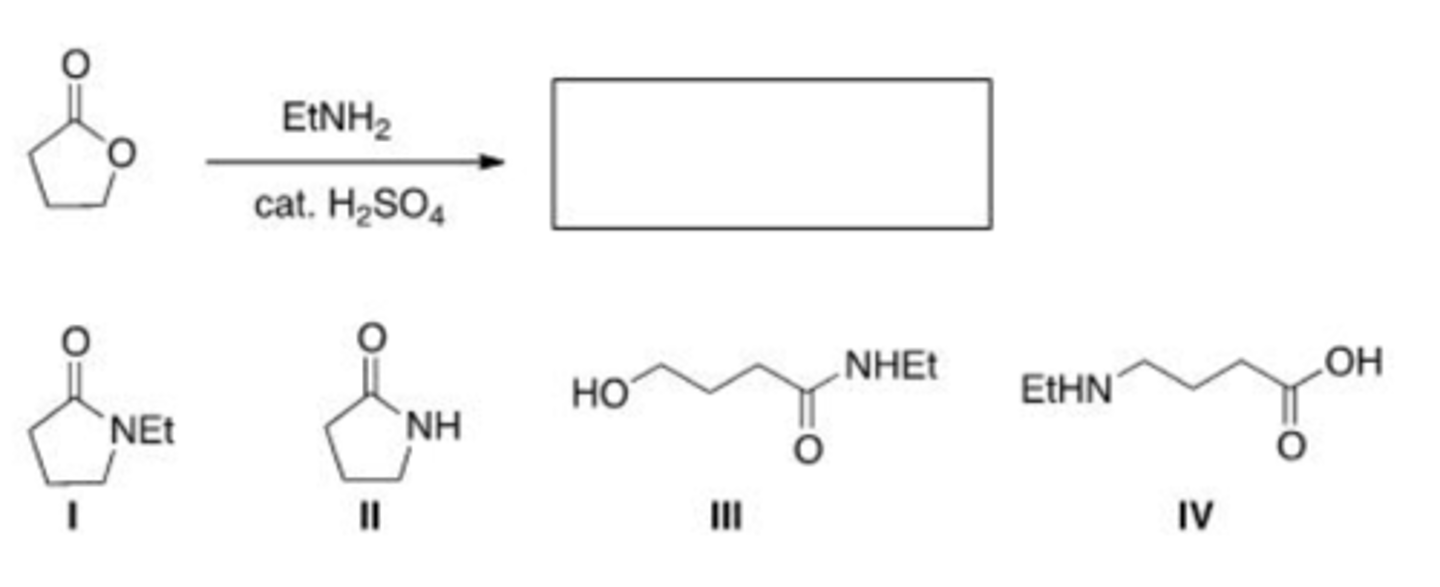
What is the product of the following reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
B
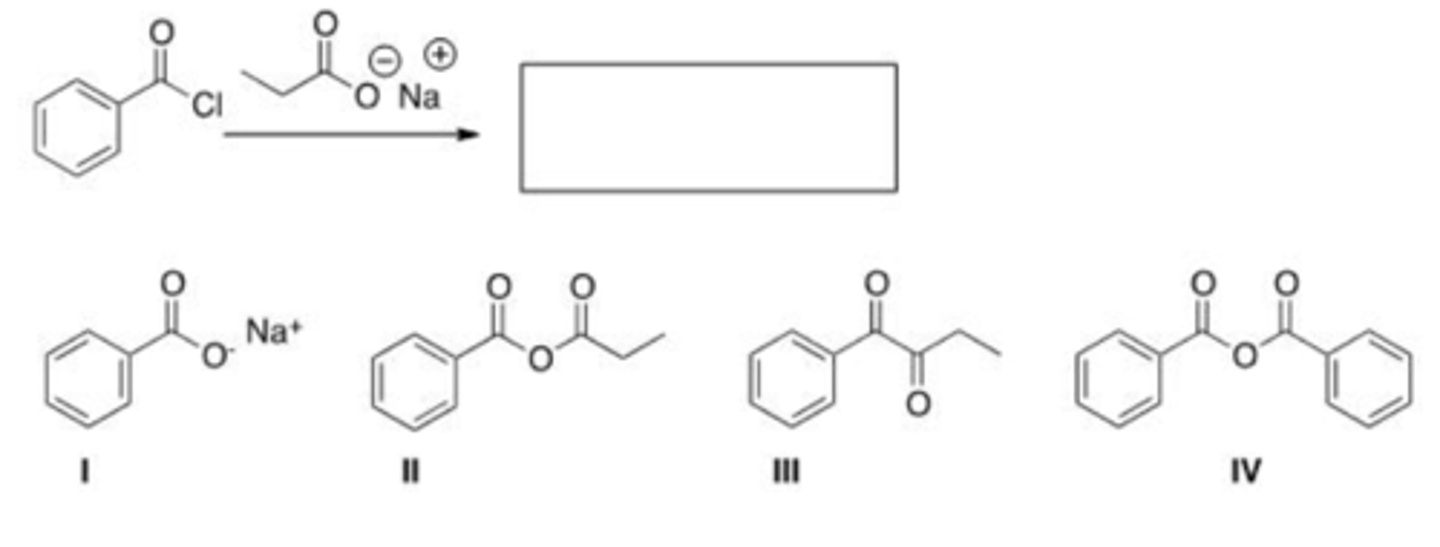
How can you convert a carboxylic acid into an ester?
A. Heat with an alcohol and catalytic acid.
B. Deprotonate with a base and react with an alcohol.
C. Deprotonate with a base and react with an alkyl halide.
D. Both (a) heat with an alcohol and catalytic acid and (c) deprotonate with a base and react with an alkyl halide.
E. Both (a) heat with an alcohol and catalytic acid and (b) deprotonate with a base and react with an alcohol.
D
How can you convert a carboxylic acid into an acid chloride?
A. Heat with hydrochloric acid.
B. React with thionyl chloride (SOCl2).
C. React with sodium chloride.
D. React with Cl2 and FeCl3.
B
What is the product of the following reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
C
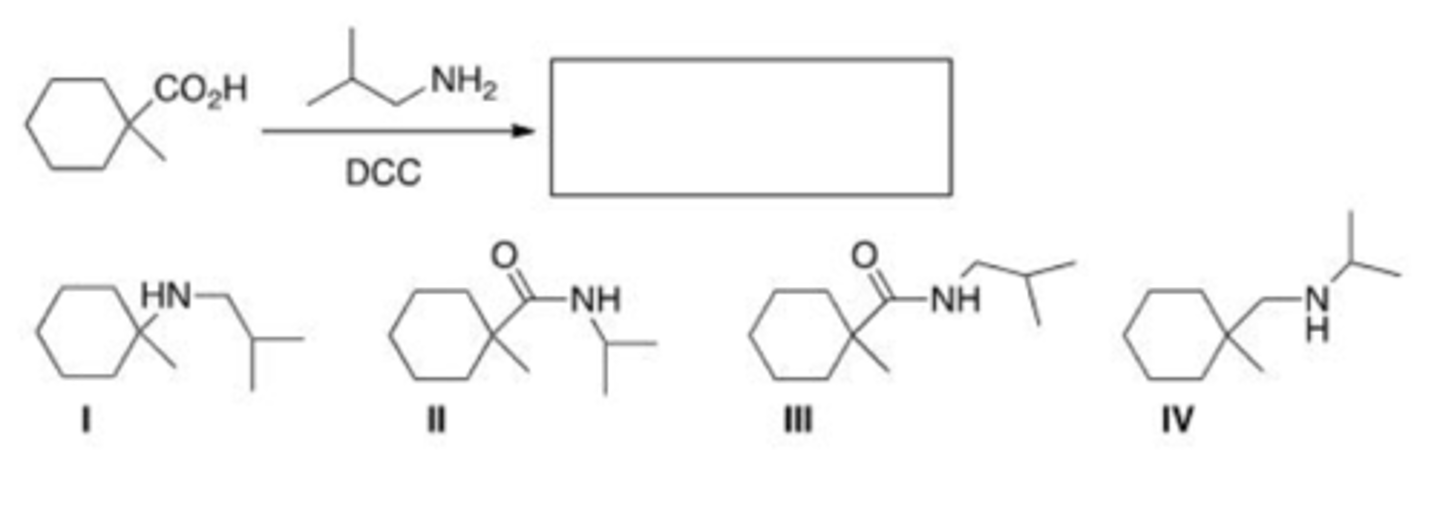
What is the direct product of the base-promoted hydrolysis of an ester?
A. A nitrile
B. A carboxylic acid
C. An amide
D. A carboxylic acid salt
D
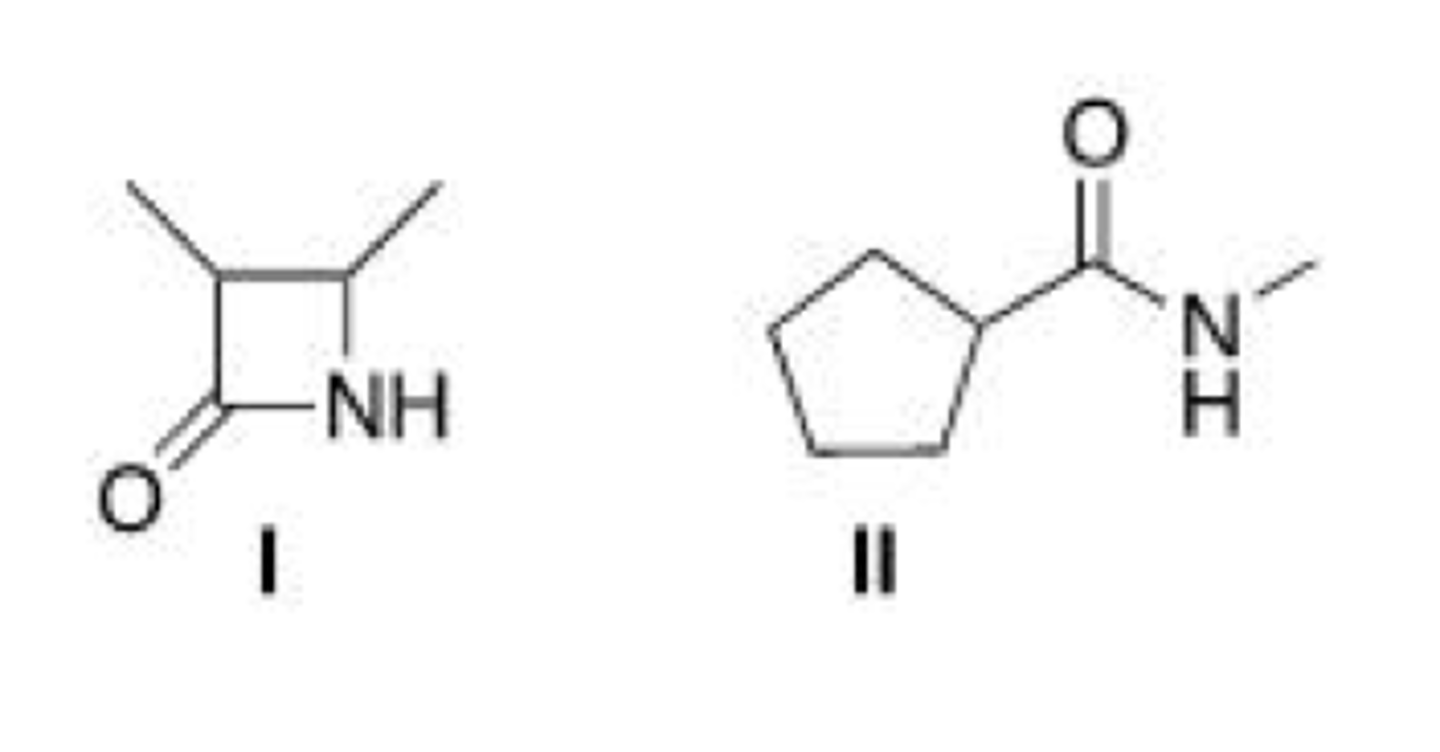
Which of the following two amides will react more readily with a nucleophile? Why?
A. I, because it is less hindered
B. II, because it is less hindered
C. I, because it is more strained
D. II, because it is more strained
C
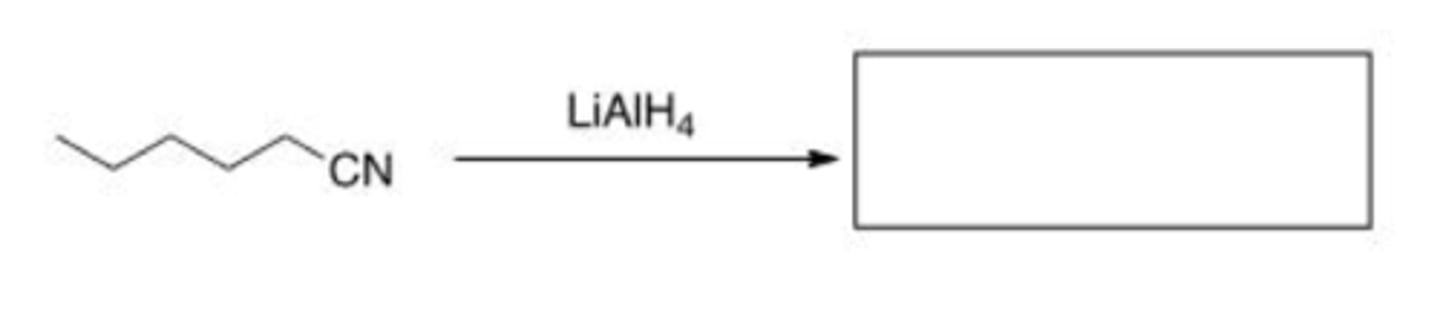
What is the product of the following reaction?
A. Hexanoic acid
B. 1-Hexanamide
C. Hexanal
D. 1-Hexanamine
D
What is the product of the following reaction (after acidic work-up)?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
B
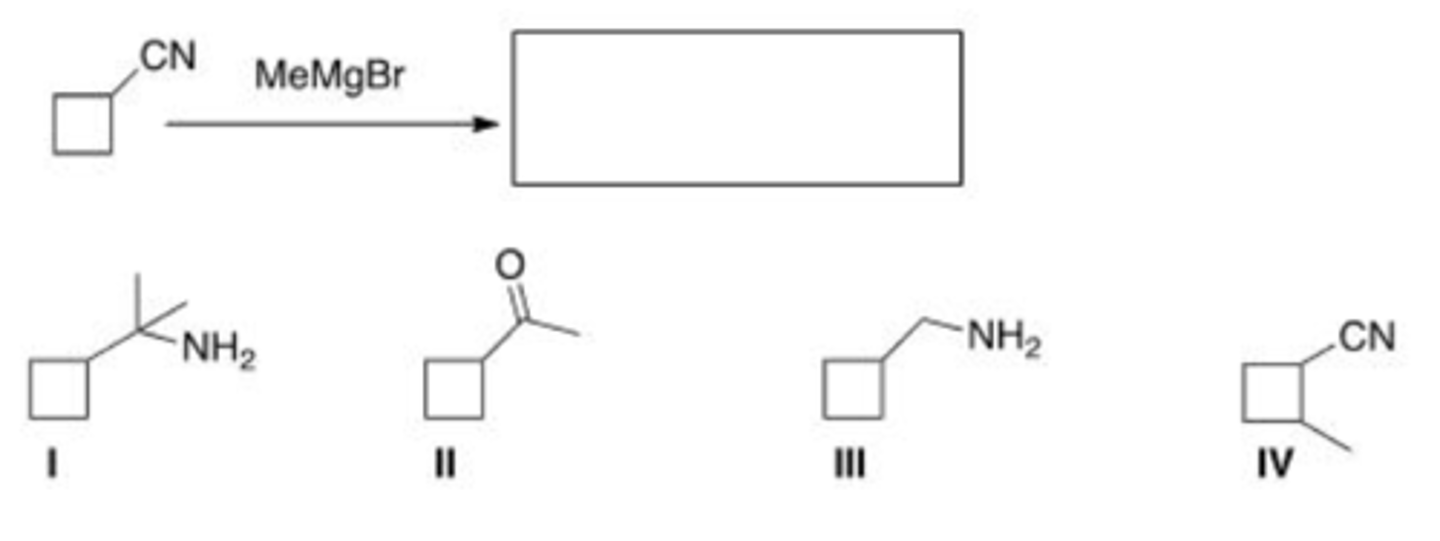
What reagent would you use for the following transformation?
A. LiAlH4
B. DIBAL-H
C. NaBH4
D. H2, Pd/C
B

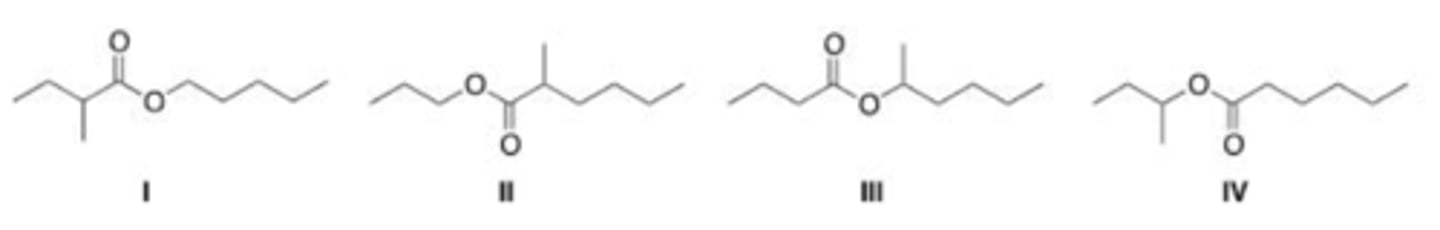
What is the structure for the compound whose IUPAC name is pentyl 2-methylbutanoate?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
A
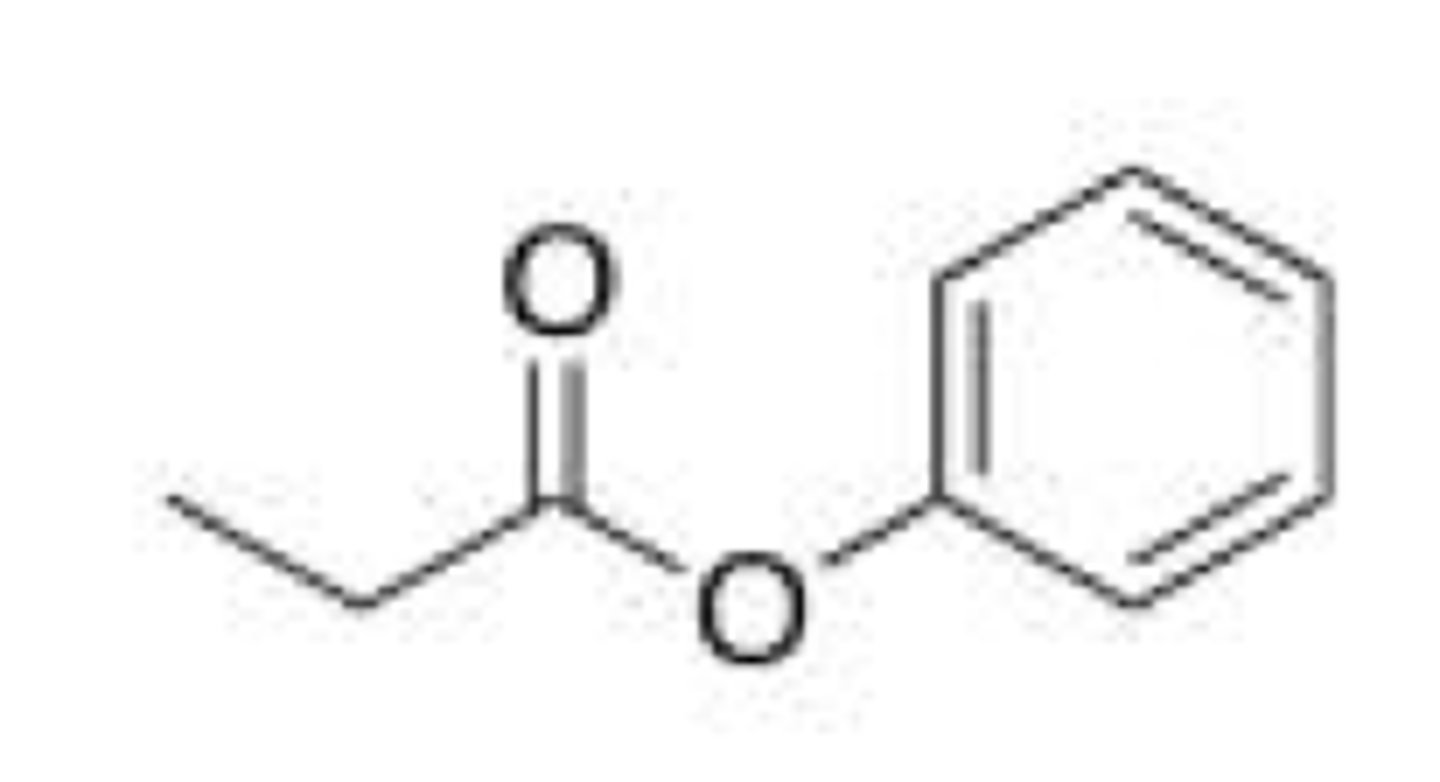
What is the IUPAC name for the following compound?
A. Propionyl phenol
B. Phenyl propanoate
C. Phenol propanoate
D. Phenyl acetate
B
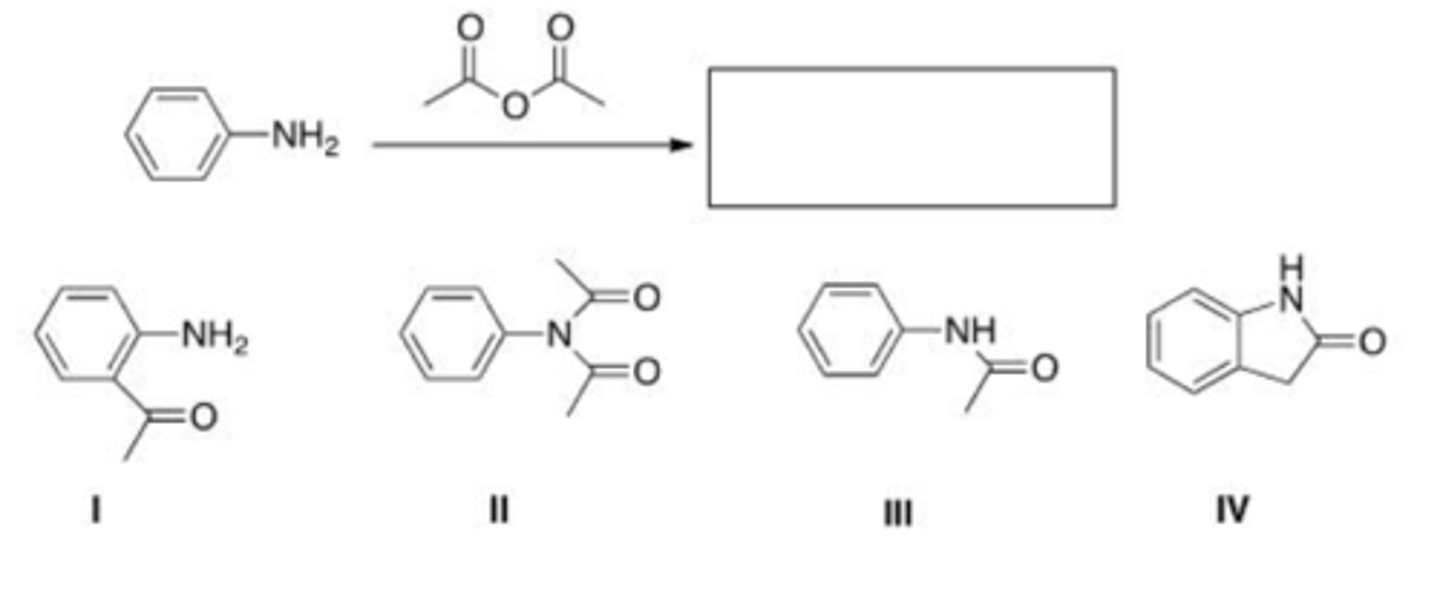
What is the product of the following reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
C
What is the product of the following reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
A
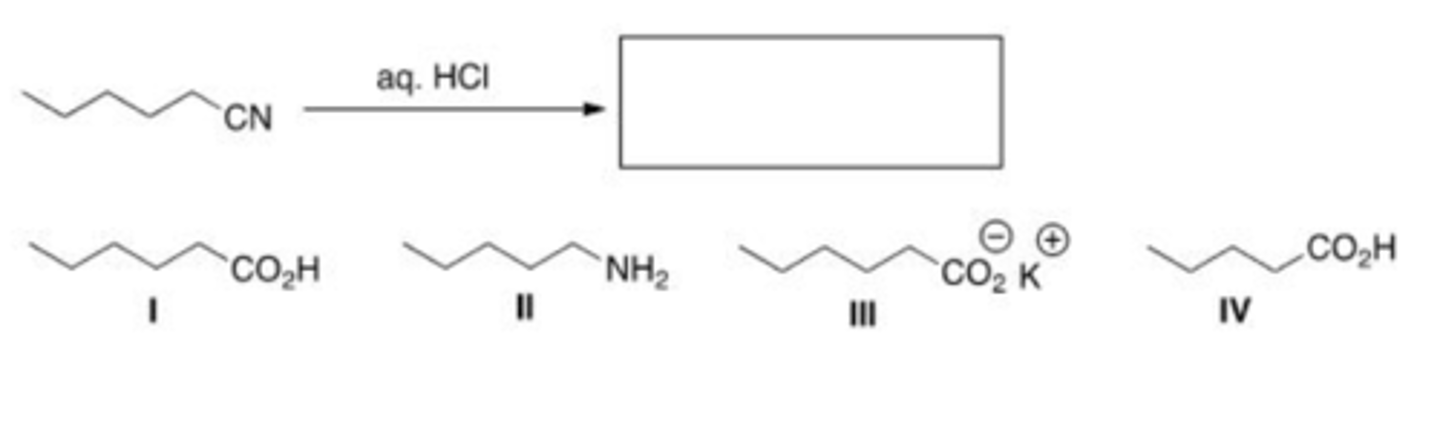
What is the product of the following reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
A
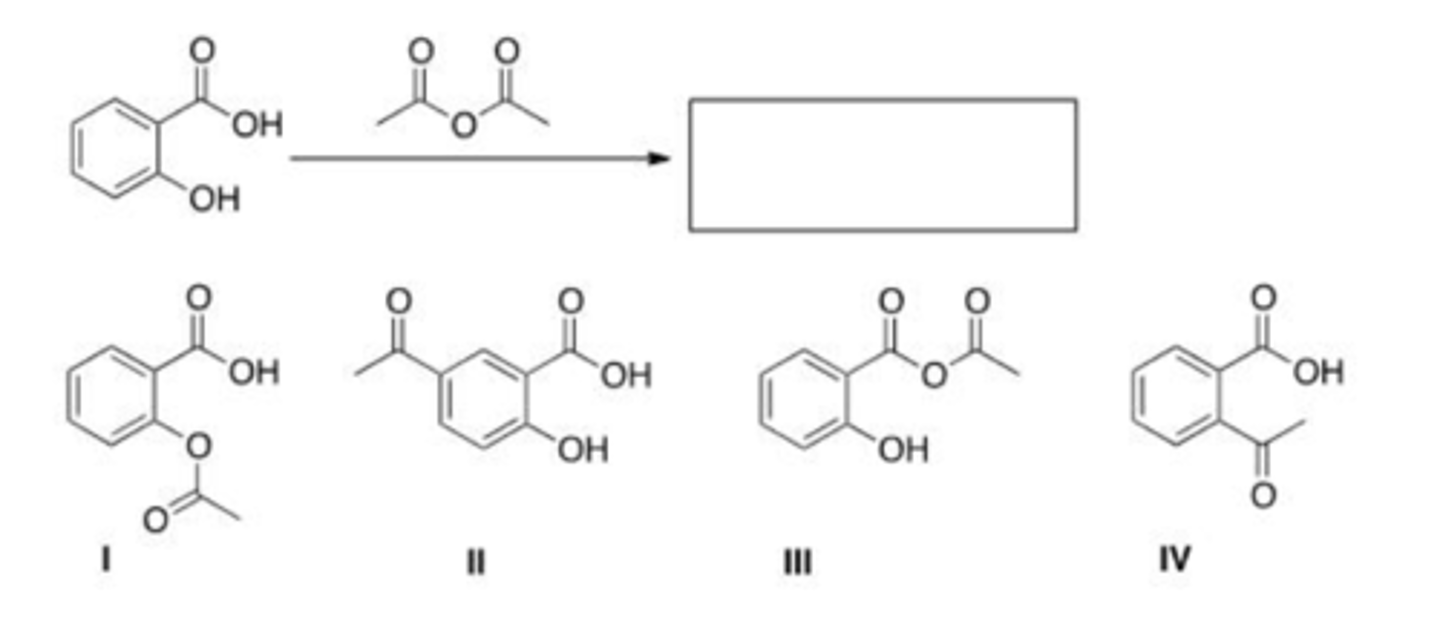
What is the product of the following reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
D
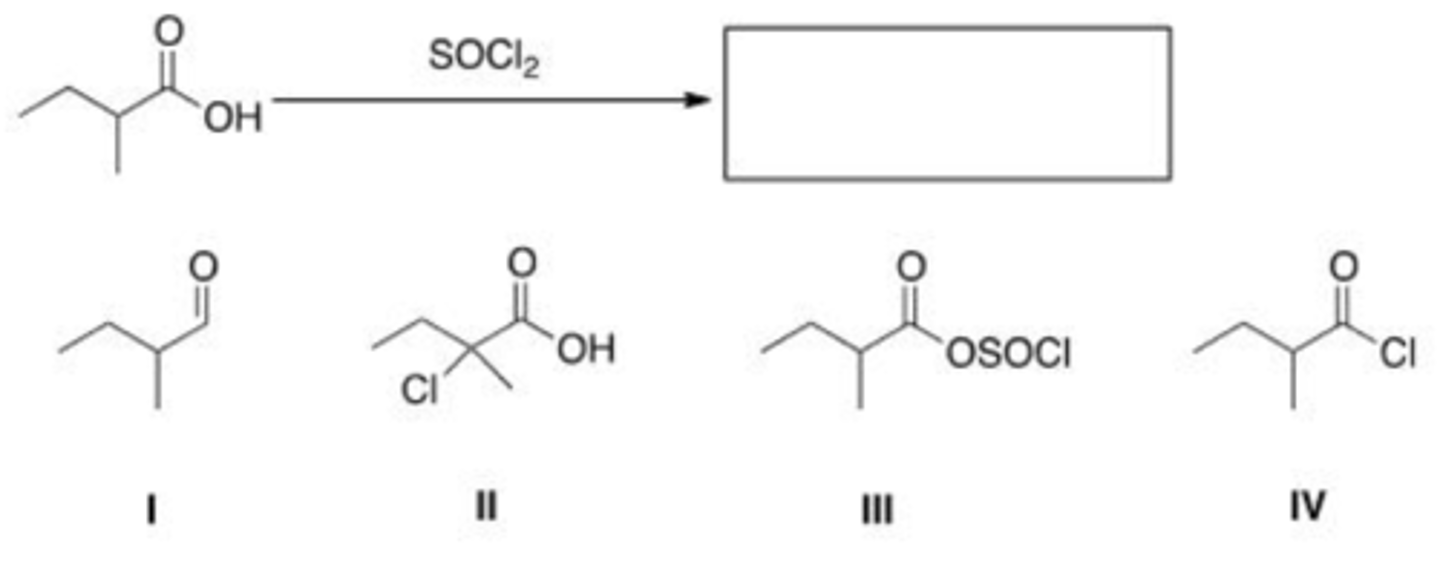
What is the product of the following reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
B
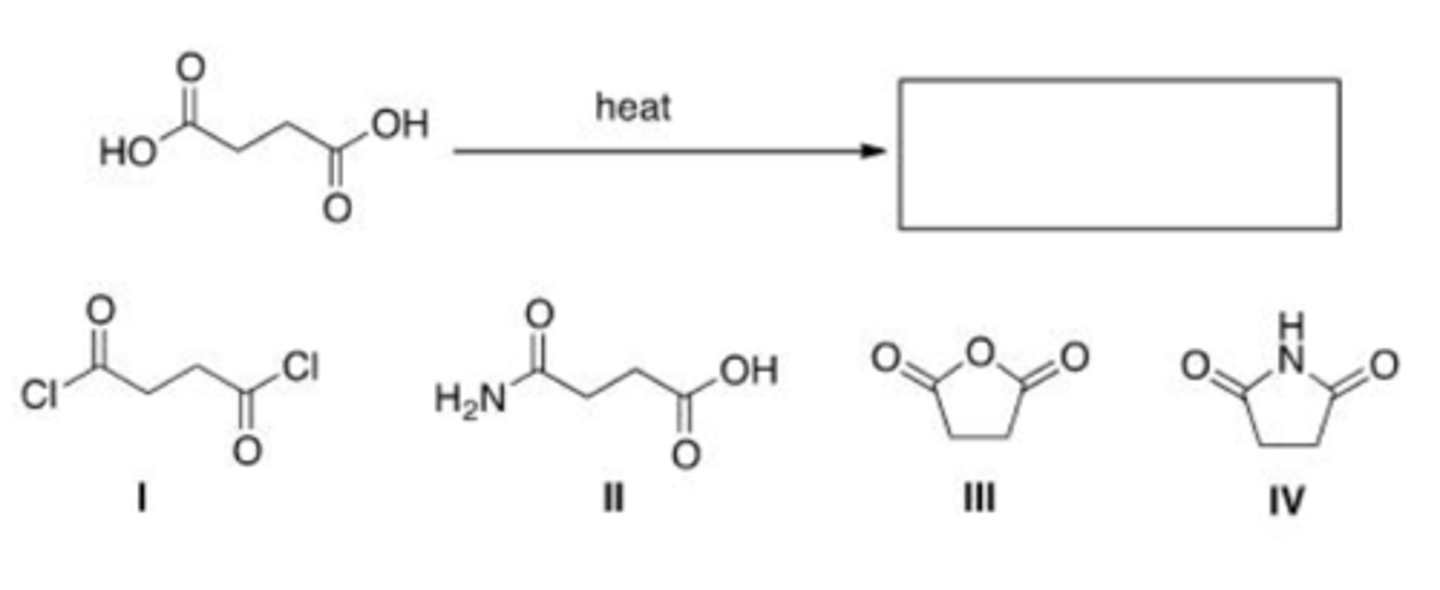
What is the product of the following reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
D
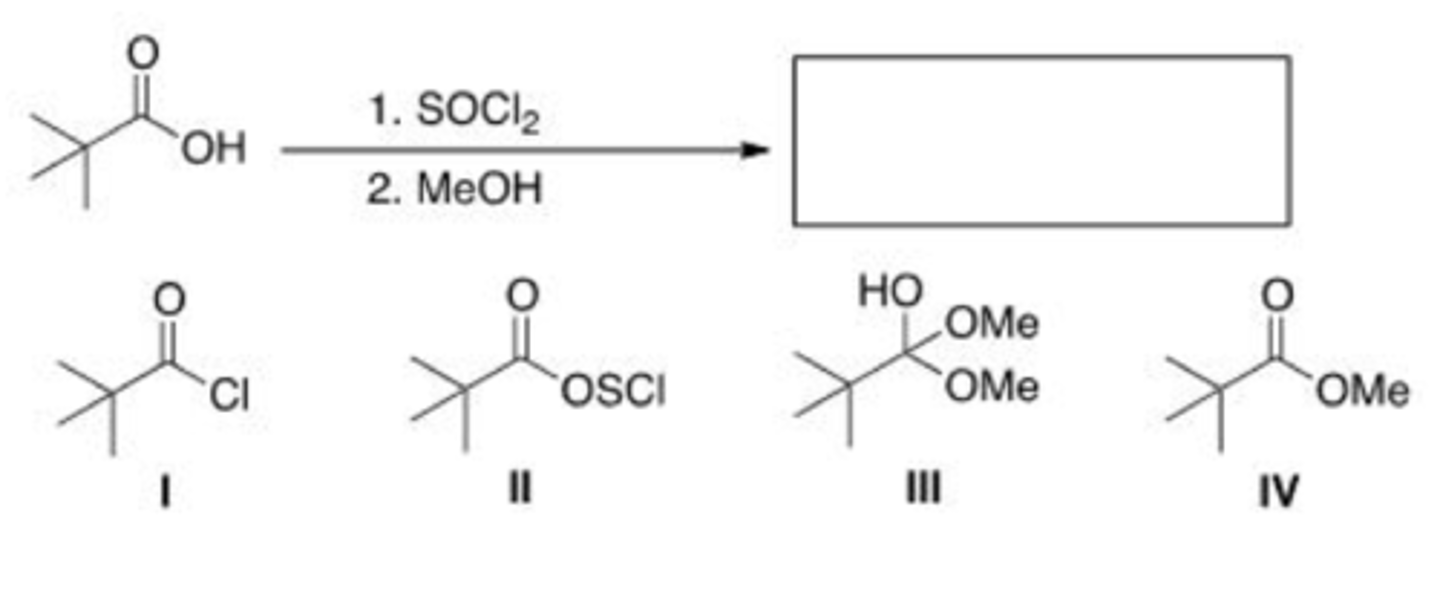
What is the missing reagent in the reaction below?
A. Acetic acid
B. NaOMe
C. SOCl2
D. Pyridine
C
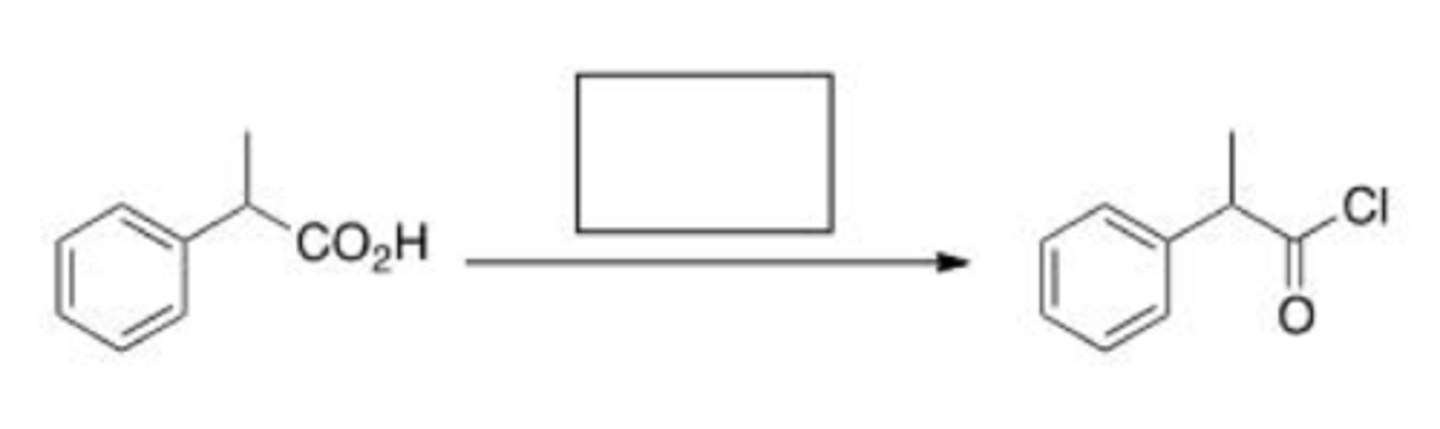
Which of the following reaction conditions can be used to synthesize an ester (RCOOR')?
A. RCOCl + R'NH2 + pyridine
B. RCOOH + R'OH + H+
C. RCOOH + R'OH + OH-
D. RCONH2 + R'OH
B
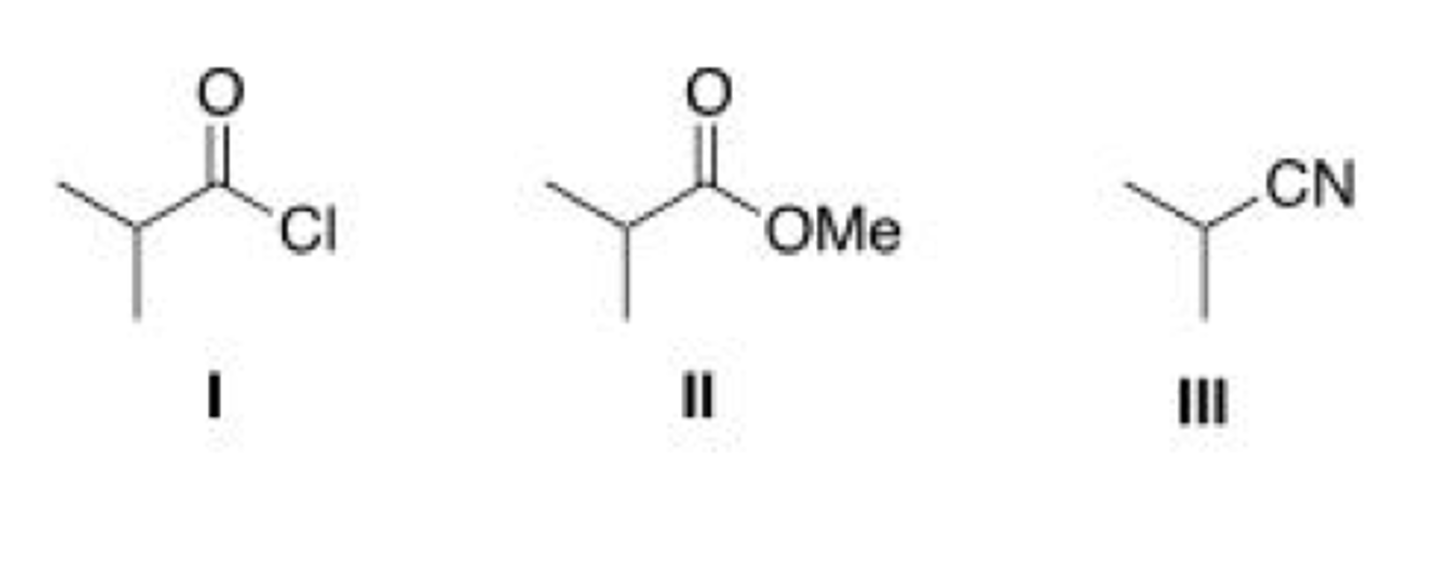
Rank the following compounds in order of increasing reactivity in nucleophilic acyl substitution.
III > II > I
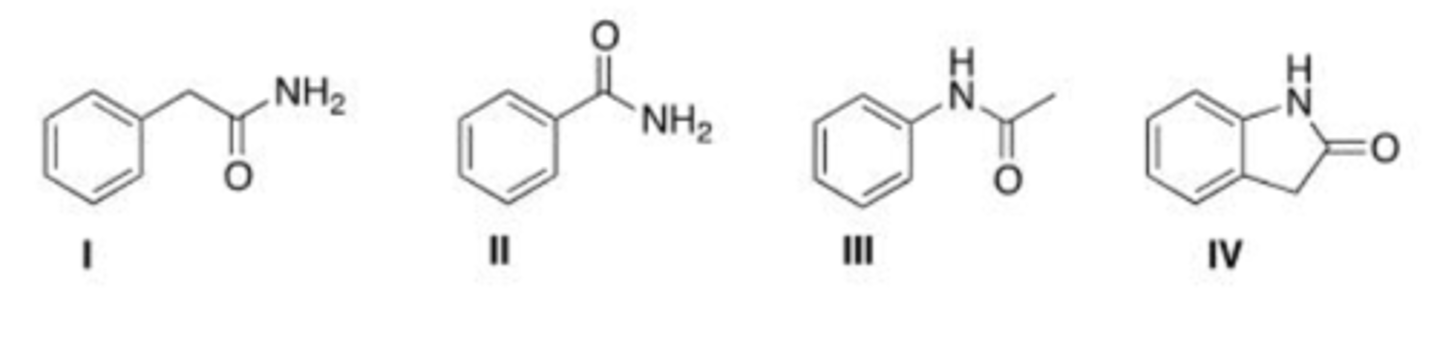
Draw the structure of N-phenyl acetamide.
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
C
Which of the following substrates cannot be used as an immediate precursor to synthesize an ester?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
B
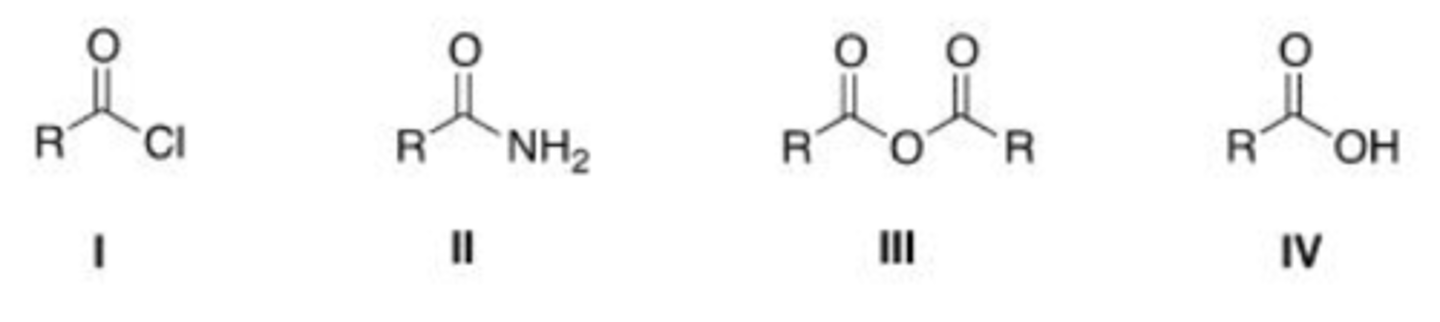
From the list below, pick the compound that does not react with acetyl chloride.
A. Isopropyl alcohol
B. Benzoic acid
C. Ammonia
D. Triethyl amine
D
Which of the following statements about amides is true?
A. Amides react with methyl alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst to form an ester.
B. Amides are hydrolyzed in acid or base to form carboxylic acids or carboxylate anions.
C. Amides react with thionyl chloride to form the acid chloride.
D. Amides do not react under any conditions. They are inert compounds.
B
n-Butanenitrile will undergo all of the following listed reactions except one. Which reaction listed is not true for n-butanenitrile?
A. n-Butane nitrile will react with ethylmagnesium bromide to form an alcohol.
B. n-Butanenitrile with be reduced to butyl amine in the presence of LiAlH4 with an aqueous work-up.
C. n-Butanenitrile is hydrolyzed in the presence of acid to form butanoic acid.
D. n-Butanenitrile is reduced with DIBAL-H to form n-butanal.
A
An unknown compound has a sharp, medium peak at 2250 cm-1. The unknown compound is probably
A. an alkane.
B. an aldehyde.
C. an alkene.
D. a nitrile.
D
All of the following contain sp2 hybridized atoms in their functional group except
A. a carboxylic acid.
B. a nitrile.
C. an aldehyde.
D. an anhydride.
B
What is the product formed by hydrolysis of the following lactone with acid?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
B
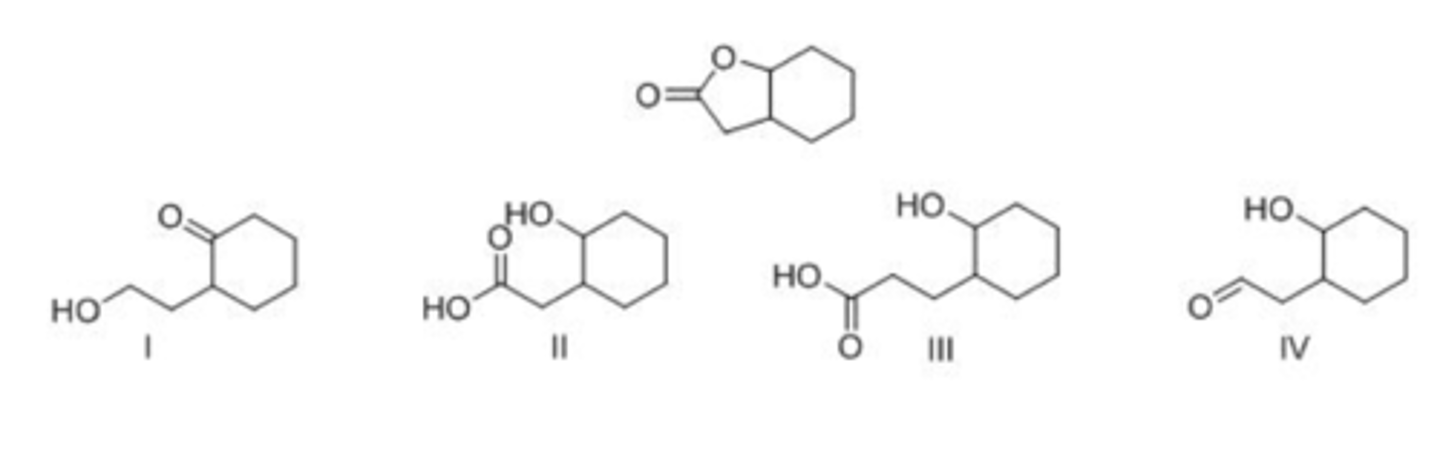
What is the product formed by hydrolysis of the following lactone with acid?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
A