BWL
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
cost comparison calculation

Selection of investment alternatives
Total cost comparison (cost comparison per period) with the same capacity utilisation
Unit cost comparison (cost comparison per quantity produced) with different capacity utilization
Determination of the critical capacity utilisation/quantity for unforeseeable utilisation
armortization comparison calculation (years of use until the investment was worth it)

influence factors for investments
the current profit situation of the company
the order situation of the company
the economic environment
the level of capital market interest rates
tax aspects
Types of investment
New/Initial Investment: Initial equipment of a company with fixed and current assets.
Expansion Investment: Increase of existing assets by acquiring additional goods, e.g., purchasing more identical machines to expand capacity.
Replacement Investment: Replacement of goods that have been consumed in the production process, e.g., worn-out machines are replaced by new, identical machines, maintaining the same production capacity.
Rationalization Investment: Replacement of economically consumed goods with new, technically improved goods, e.g., old machines are replaced by new, faster, or more efficient machines, often resulting in job losses.
ROI comparison calculation

Annuity method formula
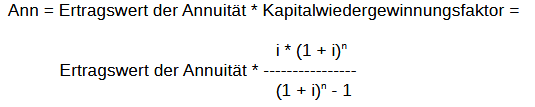
net present value method
cash inflows (Et )
outflows (At )
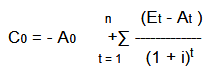
internal rate of return
C = value
p = interest rates
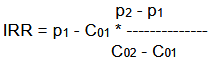
Explain the term effective interest rate.
The term "effective interest rate" refers to the true cost of borrowing money or the actual return on an investment. It takes into account not just the stated interest rate (the nominal rate), but also additional fees, the timing of payments, and compounding effects. This gives a more accurate picture of what you're really paying or earning.
creditworthiness
ability to conclude legally effective credit agreements. The
examination of creditworthiness includes the examination of legal capacity, legal capacity
and power of representation.
effective annual interest rate
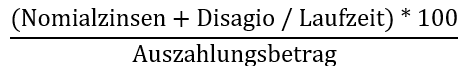
SKonto zu Jahreszinssatz (Näherung)

Skonto zu Jahreszinssatz (genau)

Berechnung Finanzierungserfolg bei Skonto

Marketing
Promoting and selling products by understanding customer needs, creating awareness, and driving sales in a competitive market.
Marketing Mix
Combination of elements used by companies to promote/sell products/services, often called the 4 Ps (Product, Price, Place, Promotion) and expanded to 7 Ps including People, Process, and Physical Evidence.
Product (in Marketing)
What is offered to the customer, including features, design, and quality.
Price (in Marketing)
The cost for the customer, based on costs, demand, and discounts.
Place (in Marketing)
Distribution channels, or where the product is sold.
Promotion (in Marketing)
Methods/strategies of promoting the product, such as advertising, sales promotion, and other activities.
People (in Marketing)
Employees, including their training, motivation, and empowerment.
Process (in Marketing)
Smooth/streamlined delivery to the customer, including ordering process and after-sales customer service.
Physical Evidence (in Marketing)
Tangible elements that support the brand/offerings, such as logo, branding, and design of stores.
Market Research
Gathering information about market situation through surveys, analyzing trends, studying competitor strategies, and finding target audiences.
Product Strategy
Developing/Improving product to meet customer needs and stand out, including product design, feature development, product testing, and gathering customer feedback.
Pricing Strategy
Determine pricing of offering by analyzing production costs, researching competitor pricing, assessing market demand, and setting competitive/ profitable price.
Promotion Strategy
Planning how to communicate/promote product to audience, including designing advertising campaigns, creating marketing materials, managing social media presence, and public relations (PR) efforts.
Distribution Strategy
Deciding how to make product available to customer, including selecting distribution channels, managing inventory, and ensuring efficient product delivery.
Marketing Controlling
Monitoring/Evaluating marketing activities to ensure effectiveness and alignment with company goals and to optimize marketing for better results.
types of market research
primary research
secondary research
quantitative research
qualitative research
market indicators
Market Potential: The maximum possible demand if every potential customer bought the product.
Market Volume: The actual amount of goods sold or consumed in the market during a given period.
Market Share: The percentage of total market sales a specific company or product holds.
Sales Volume: The real number of units a company sells over a specific time.
Sales Potential: The upper limit of sales a company could achieve if it captured all available demand.
SWOT
• Helps to understand a companies position in the market
1. Strengths: Advantages of product/company (strong brand reputation, skilled employees, innovative technology)
2. Weaknesses: Weakness of product/company (lack of resources, outdated technology, poor customer service)
3. Opertuntities: External factor good for company/product (growing market, changing trends, new partnership)
4. Threats: External factor bad for company/product (strong competition, economic downturn, regulations)
STP
Segmentation: Dividing the overall market into distinct groups based on common characteristics like demographics, behaviors, or interests.
Targeting: Selecting one or more of these segments to prioritize, usually those that are most promising or profitable.
Positioning: Crafting a unique value proposition and brand image that clearly differentiates a product or service in the minds of the chosen target segment.
Types of positioning
Market Leader: Holds the largest share and enjoys strong brand recognition.
Challenger: Actively competes against the leader by offering distinctive features or pricing.
Follower: Maintains a stable position by imitating leaders rather than aggressively challenging them.
Niche Player: Focuses on a specific segment with specialized offerings.
types of market segmentation
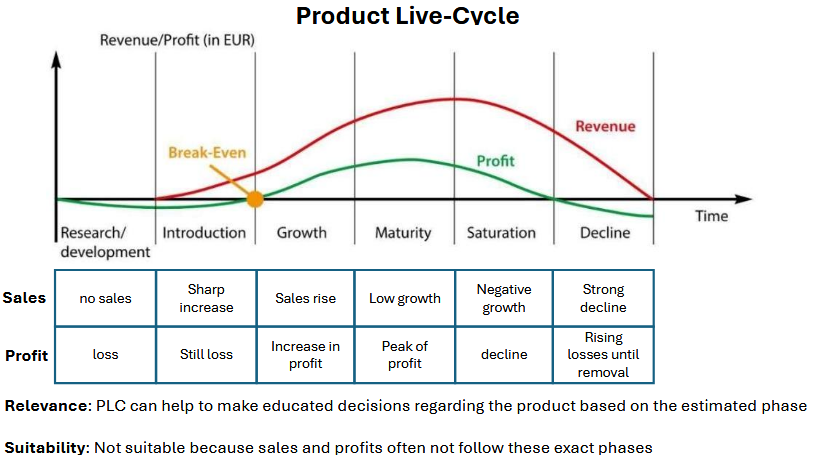
Product Lifecycle
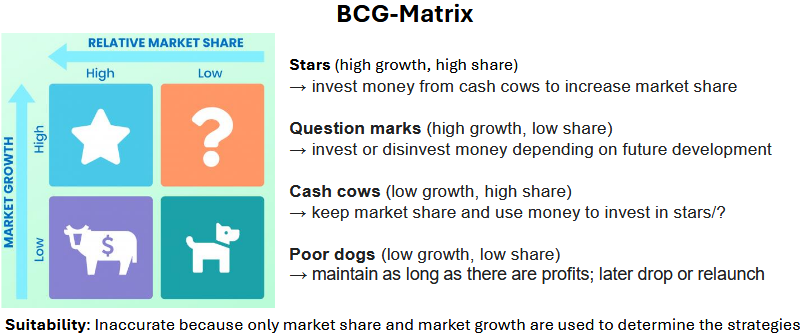
BCG matrix
Measures of product policy
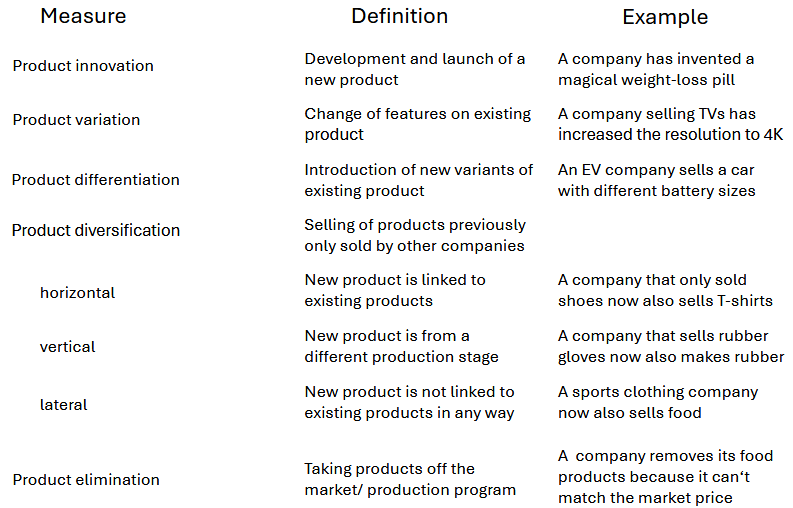
Advantages/Disadvantages of branding

Ansoff matrix

Fixed Asset Intensity Definition
Measures a company's investment in fixed assets relative to its sales or revenue.
Current Asset Intensity Definition
Measures a company's investment in current assets relative to its sales or revenue.
Equity Ratio Definition
Indicates the proportion of equity used to finance a company's assets.
Debt Ratio Definition
Indicates the proportion of debt used to finance a company's assets.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio Definition
Compares a company's total debt to its total equity.
Coverage Ratio I Definition
Measures a company's ability to cover its interest expenses with its earnings.
Coverage Ratio II Definition
An alternative measure of a company's ability to cover its interest expenses.
Liquidity 1. Degree Definition
A measure of a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations (One-to-five = min. 20%).
Liquidity 2. Degree Definition
A stricter measure of a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations (One-to-one = min. 100%).
Fixed asset intensity

Current asset intensity
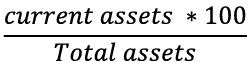
Equity ratio
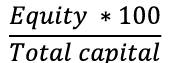
Debt ratio
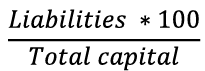
Debt-to-equity ratio
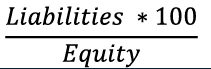
Coverage ratio 1
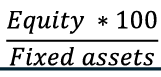
Coverage ratio 2
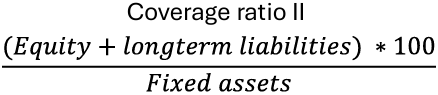
Liquidity 1. Degree

Liquidity 2. Degree
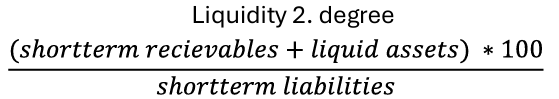
ROE
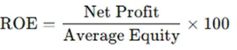
ROTC
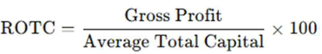
Gross Profit
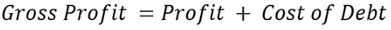
ROS
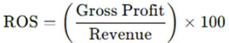
ROI
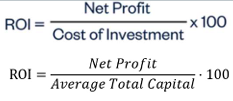
ROE (leverage)
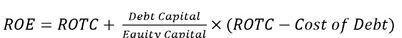
gross cashflow
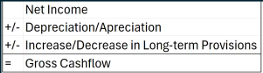
Cashflow-to-revenue ratio
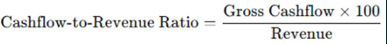
EBIT (short)

EBIT (long)

EBIT margin

Pricing Policies
Cost-oriented
Determining minimum price (based on cost accounting)
Short-term, variable cost should be covered
Long-term, total costs should be covered
Market-oriented
Prices based on competitors and customers
Goal is profit maximization
Competition-oriented
Competitors already have optimal prices so copy them
We have to be different in other ways to distinguish ourselfs
Demand-oriented
Based on demand for existing products on market
Focus on price elasticity
Differentiation strategy to create unique selling points
fixed price strategies
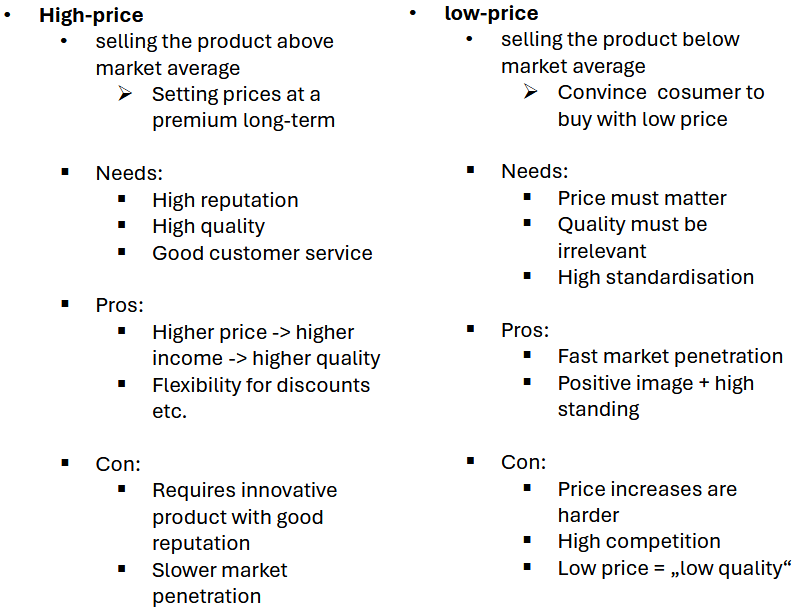
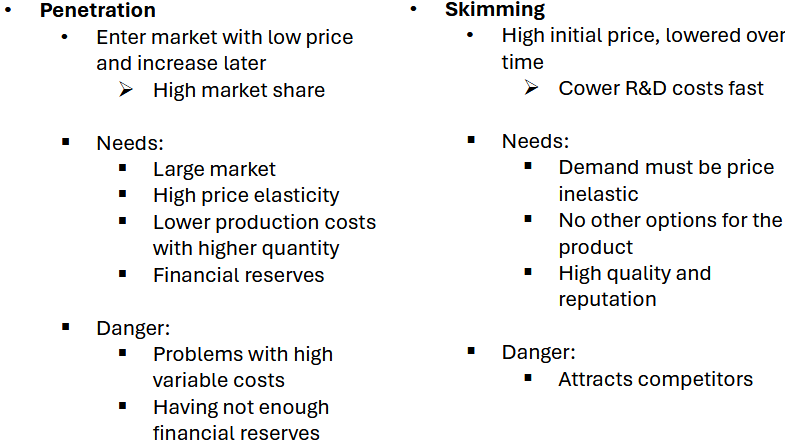
Price sequencing strategies
Price differentiation

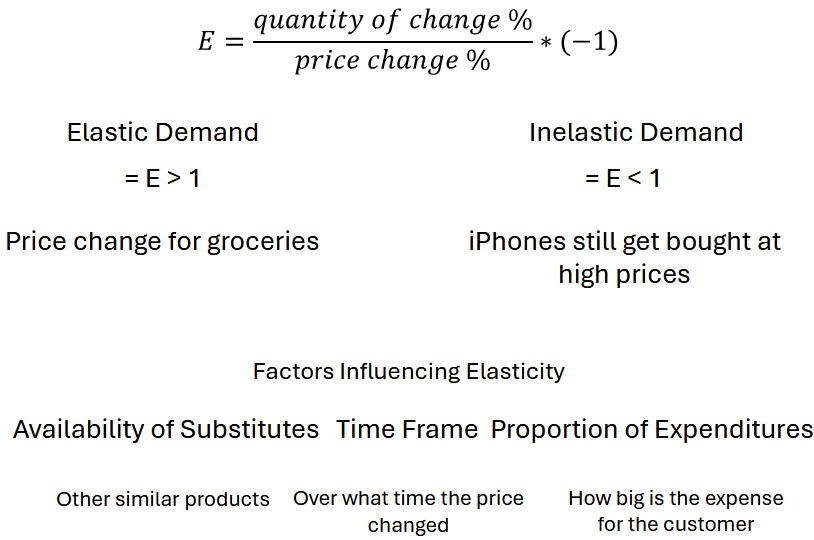
Price elasticity
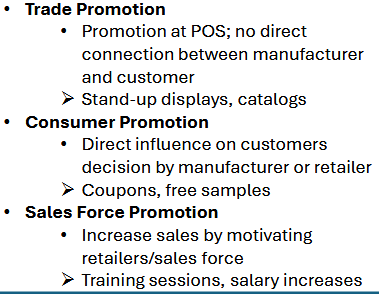
Promotion types
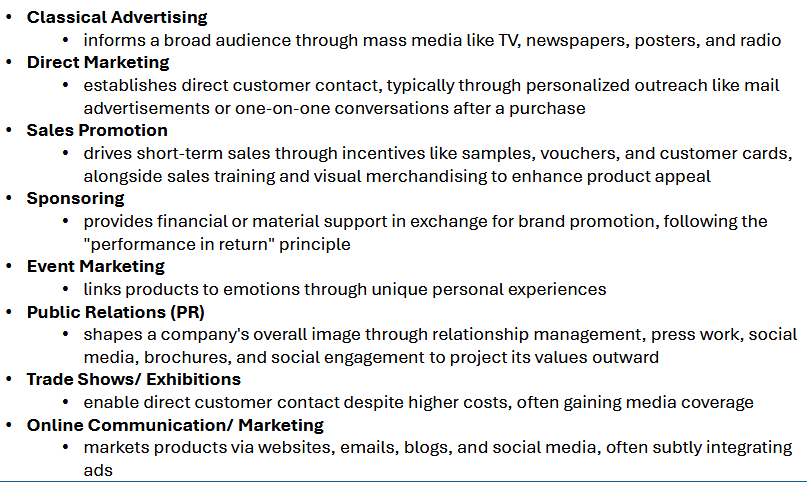
difference between sales promotion and classical advertising

Sales promotion pros/cons

sales promotion types
AIDA advertising model

online marketing tools

key terms for advertising campaigns

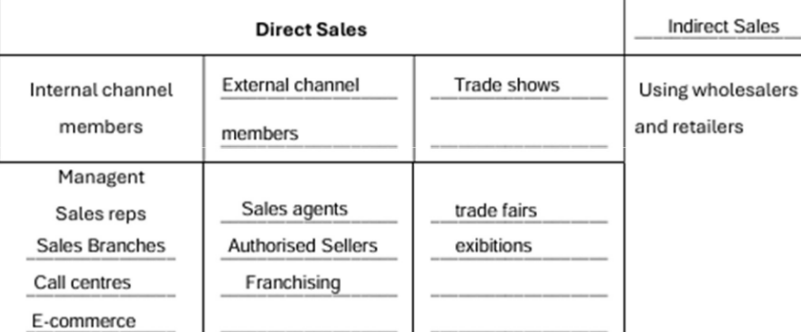
types of distibution
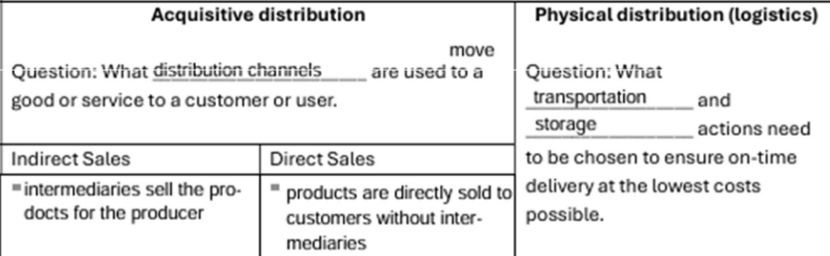
distribution channels
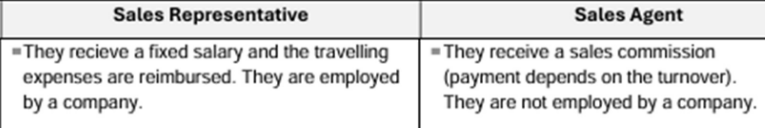
sales representative vs sales agent
Definition Rückstellungen
Rückstellungen sind Schulden (Verbindlichkeiten), die zum Zeitpunkt ihrer Entstehung dem Grunde nach bekannt sind, deren Höhe und/oder Fälligkeit jedoch noch ungewiss ist
Rückstellungen müssen für folgendes gebildet werden:
ungewisse Verbindlichkeiten (z. B. für Pensionsverpflichtungen, für erwartete Steuernachzahlungen, Prozesskosten, Garantieverpflichtungen, Provisionsverpflichtungen),
drohende Verluste aus schwebenden Geschäften (z. B. erheblicher Preisrückgang bereits gekaufter, jedoch noch nicht gelieferter Rohstoffe),
unterlassene Instandhaltungsaufwendungen, die im folgenden Geschäftsjahr innerhalb von drei Monaten nachgeholt werden,
Abraumbeseitigung, die im folgenden Geschäftsjahr nachgeholt wird,
Gewährleistungen ohne rechtliche Verpflichtungen (Kulanzgewährleistungen)
Buchungen zu Rückstellungen

Auflösung von Rückstellungen (Buchungen)

Definition kalkulatorische Kosten
Kosten, denen stehen entweder keine Aufwendungen oder Aufwendungen in anderer Höhe gegenüber. Diese Kosten stellen kalkulatorische Kosten dar.
Arten kalkulatiorische Kosten

Gliederung Rechnungswesen
Buchführung/Finanzbuchhaltung
Dokumentation aller Geschäftsfälle, Rechenschaftslegung (Erstellung
des Jahresabschlusses)
unternehmensbezogen
Rechnungskreis I (RK I)
Kosten- und Leistungsrechnung/KLR
Überwachung der Wirtschaftlichkeit, Ermittlung des Betriebsergebnisses, Ermittlung der Selbstkosten
betriebsbezogen
Rechnungskreis II (RK II)
Statistik
Aufbereitung und Auswertung der Zahlen der Buchführung und der Kosten- und Leistungsrechnung, Vergleichsrechnungen
Planung
Erstellung von Teilplänen (Investitionsplan, Beschaffungsplan, Absatz- und Finanzplan)
Aufbau Ergebnistabelle
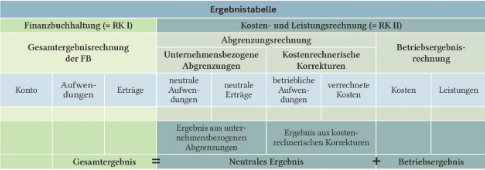
Kriterien für neutrale Erträge/Aufwände
betriebsfremd
periodenfremd
außerordentlich
Maschinenstundensatz

Herstellungskosten des Umsatz
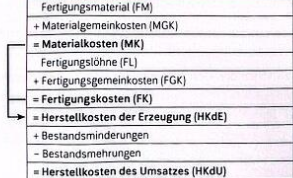
Zuschlagssätze

Hilfskostenstellen vs. allgemeine Kostenstellen
Hilfskostenstellen
Geben ihre Leistungen nur an Fertigungshauptkostenstellen ab
allgemeine Kostenstellen
Stellen ihre Leistungen allen anderen Stellen zur Verfügung
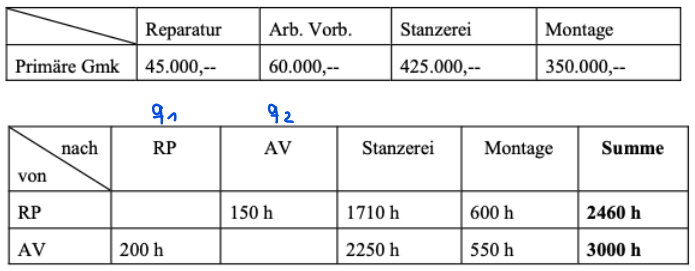
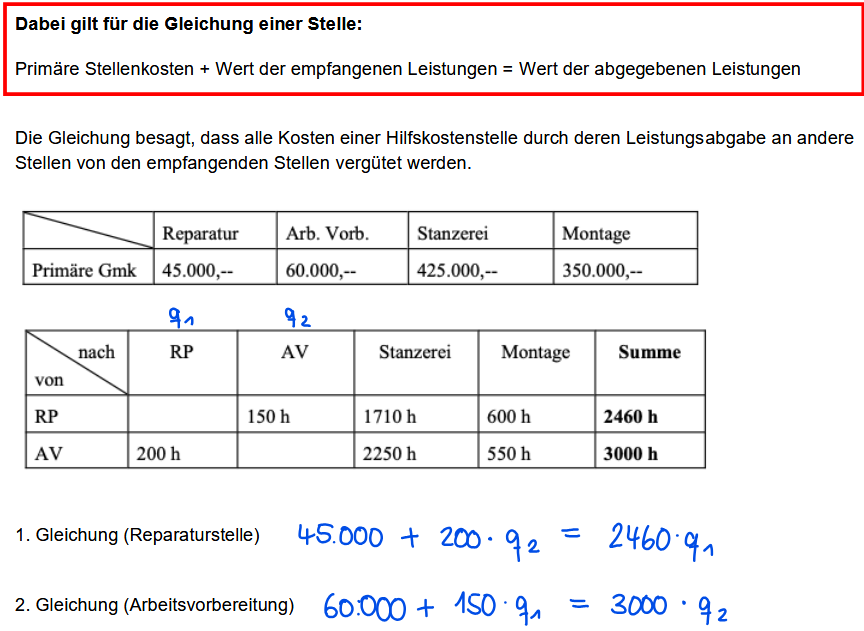
Wechselseitiger Leistungsaustausch
Gleichung aufstellen
Gleichung nach q und q2 auflösen
Gesamte Gemeinkosten berechnen:
Primäre Gemeinkosten
+ Leistungsmenge Hilfsstellen * Verrechnungspreis
= Gesamte Gemeinkosten
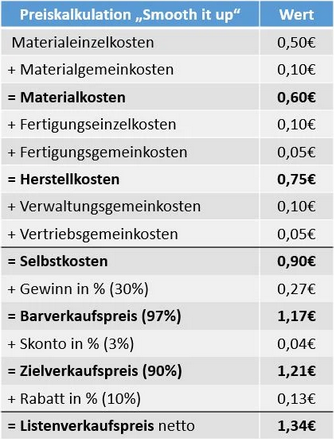
Listenverkaufspreis