BIO 201L Midterm Exam Review Flashcards
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards based on lecture notes for the BIO 201L midterm exam.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Anatomical Position
A standardized reference point for describing the body; standing upright, facing forward, arms at sides, palms facing forward.
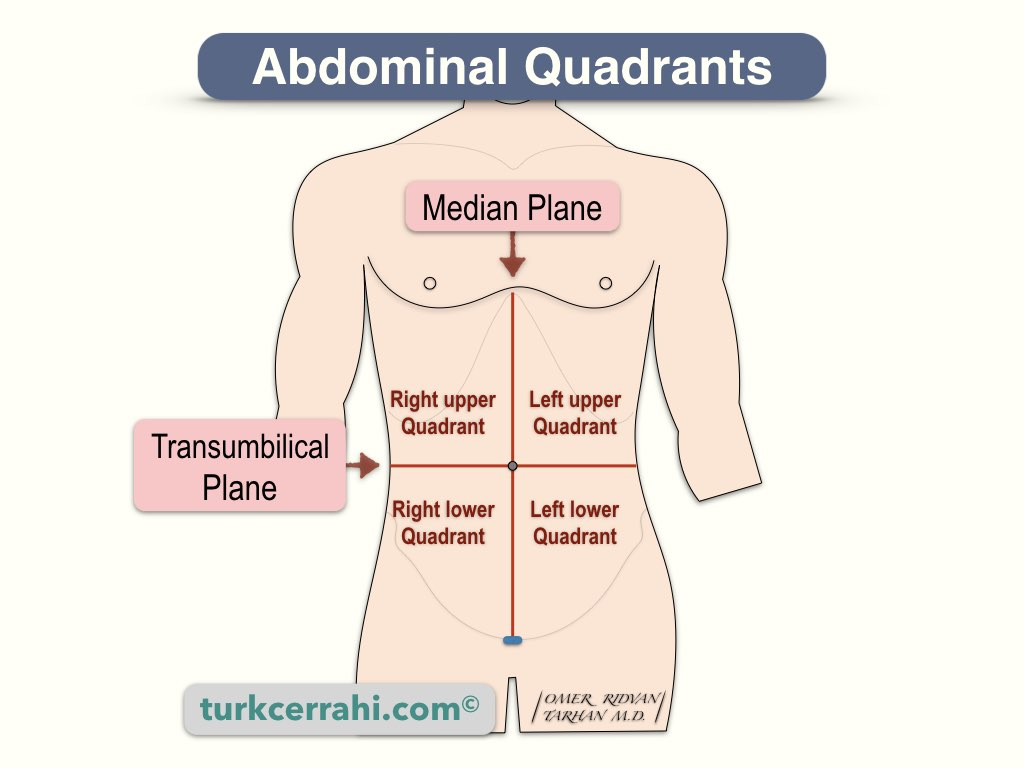
Abdominopelvic Quadrants
Four divisions of the abdominopelvic cavity: right upper, left upper, right lower, and left lower.
Abdominopelvic Regions
Nine divisions of the abdominopelvic cavity: right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypochondriac, right lumbar, umbilical, left lumbar, right iliac, hypogastric, left iliac.
Pleura
The serous membrane lining the thoracic cavity and surrounding the lungs.
Pericardium
The double-layered membrane enclosing the heart.
Peritoneum
The serous membrane lining the abdominal cavity and covering the abdominal organs.
Cytoplasm
The material or protoplasm within a living cell, excluding the nucleus.
Extracellular Fluid
Fluid outside the cells.
Intracellular Fluid
Fluid inside the cells.
Neoplasm
A new and abnormal growth of tissue in some part of the body, especially as a characteristic of cancer.
Cell Wall
A rigid layer lying outside the plasma membrane of the cells of plants, fungi, and bacteria. (Note: Animal cells do not have a cell wall.)
Cytosol
The aqueous part of the cytoplasm within which various particles and organelles are suspended.
Mitochondrion
An organelle in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
A network of tubular membranes within the cytoplasm of the cell, studded with ribosomes.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
A network of tubular membranes within the cytoplasm of the cell, lacking ribosomes.
Golgi Complex
An organelle that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other organelles.
Nucleolus
A structure in the nucleus where ribosomes are synthesized.
Cytoskeleton
A network of protein filaments that supports and shapes the cell.
Ribosomes
Organelles that synthesize proteins.
Hydrophobic
Tending to repel or fail to mix with water.
Hydrophilic
Tending to dissolve in, mix with, or be wetted by water.
Plasma Membrane
The membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment.
Phospholipid Bilayer
A two-layered arrangement of phosphate and lipid molecules that form a cell membrane, the lipid layers forming a barrier to the passage of ions and molecules into and out of the cell.
Proteoglycans
A molecule consisting of a core protein attached to glycosaminoglycans (GAGs).
Glycoproteins
Proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains (glycans) covalently attached to polypeptide side-chains.
Glycocalyx
A carbohydrate-rich coating outside the cell.
Diffusion
The net passive movement of particles (atoms, ions or molecules) from a region in which they are in higher concentration to regions of lower concentration.
Osmosis
A process by which molecules of a solvent tend to pass through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated solution into a more concentrated one.
Selective Permeability
A property of cellular membranes that allows only certain molecules to enter or exit the cell.
Aquaporins
Channel proteins that facilitate the passage of water.
Filtration
A process that separates solids from fluids by passing the fluid through a porous barrier.
Microvilli
Microscopic cellular membrane protrusions that increase the surface area for secretion, excretion, absorption, etc.
Cilia
Hair-like structures on the surface of cells that beat in a coordinated manner.
Isotonic Solution
A solution having the same osmotic pressure as some other solution, especially one in a cell or a body fluid.
Hypertonic Solution
A solution with a higher concentration of solutes than another solution.
Hypotonic Solution
A solution with a lower concentration of solutes than another solution.
Normal Saline
A solution of sodium chloride (NaCl) in water, typically at a concentration of 0.9%.
Epithelial Tissue
A sheet of cells that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity.
Connective Tissue
Tissue that supports, connects, or separates different types of tissues and organs in the body.
Extracellular Matrix
A collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells.
Basement Membrane
A thin, delicate membrane of protein fibers and glycosaminoglycans separating an epithelium from underlying tissue.
Simple Epithelium
A single layer of epithelial cells.
Stratified Epithelium
Multiple layers of epithelial cells.
Squamous Epithelium
Epithelial cells that are wider than their height (flat and scale-like).
Cuboidal Epithelium
Epithelial cells whose height and width are approximately equal (cube-shaped).
Columnar Epithelium
Epithelial cells that are taller than they are wide (column-shaped).
Keratinized Epithelium
Epithelium containing keratin, a protein that makes the tissue tough and waterproof.
Goblet Cells
Columnar epithelial cell found in the respiratory and intestinal tracts, which secretes the main component of mucus.
Hyaline Cartilage
Translucent bluish-white cartilage consisting of cells embedded in an apparently homogeneous matrix, present in joints and respiratory passages, and forming most of the fetal skeleton.
Elastic Cartilage
Cartilage with abundant elastic fibers; more flexible than hyaline cartilage.
Fibrocartilage
Cartilage containing strong collagen fibers; found in intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, and menisci of knee.
Eccrine/Merocrine Glands
Major sweat glands of the human body, found in virtually all skin, produce sweat.
Apocrine Glands
Sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete a thicker sweat, that produce odor when come in contact with bacteria on the skin.
Holocrine Glands
Gland whose secretion consists of disintegrated cells.
Sebaceous Glands
Glands that secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, to lubricate and waterproof the skin and hair of mammals.
Ceruminous Glands
Specialized sudoriferous (sweat) glands that are located subcutaneously in the external auditory canal, produce cerumen.
Integumentary System
The organ system which protects the body from various kinds of damage, such as loss of water or abrasion from outside.
Epidermis
The outer, avascular layer of the skin.
Dermis
The layer of skin between the epidermis and subcutaneous tissues, consisting of connective tissue and elastic fibers.
Hypodermis
The lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates, directly above the periosteum of bone.
Melanocytes
A mature melanin-forming cell, typically in the skin.
Hemoglobin
A protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
Bilirubin
An orange-yellow pigment formed in the liver by the breakdown of hemoglobin and excreted in bile.
Malignant Melanoma
A type of skin cancer that develops from melanocytes.
Mucous Membrane
An epithelial tissue that secretes mucus and lines many body cavities and tubular organs including the gut and respiratory passages.
Chondrocytes
A cell which has secreted the matrix of cartilage and become embedded in it.
Osteocytes
A bone cell, formed when an osteoblast becomes embedded in the matrix it has secreted.
Axial Skeleton
The part of the skeleton that consists of the bones of the head and trunk of the body.
Appendicular Skeleton
The portion of the skeleton of vertebrates consisting of the bones that support the appendages.
Frontal Bone
The bone that forms the front part of the skull and the upper part of the eye sockets.
Parietal Bone
A bone forming the central side and upper back part of each side of the skull.
Temporal Bone
A bone forming part of the side of the skull on each side and enclosing the middle and inner ear.
Occipital Bone
The bone that forms the back of the skull.
Sphenoid Bone
A butterfly-shaped bone at the base of the skull.
Ethmoid Bone
A square bone at the root of the nose, forming part of the cranium and having many perforations through which the olfactory nerve passes.
Sutures (Skull)
Fibrous joints that connect the bones of the skull.
Cervical Vertebrae
The vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull.
Thoracic Vertebrae
The 12 vertebrae that articulate with the ribs.
Lumbar Vertebrae
The five vertebrae forming the lower part of the back.
Sacrum
A triangular bone in the lower back formed from fused vertebrae and situated between the hip bones.
Coccyx
A small, triangular bone at the base of the spinal column, formed from fused vertebrae.
Sternum
The breastbone.
Clavicle
The collarbone.
Scapula
The shoulder blade.
Humerus
The bone of the upper arm.
Ulna
The inner and longer of the two bones of the human forearm.
Radius
The outer and slightly shorter of the two bones of the human forearm.
Carpals
The eight small bones forming the wrist.
Metacarpals
The five bones forming the palm of the hand.
Phalanges (Hand)
The bones of the fingers.
Pelvis
The bony structure formed by the hip bones, sacrum, and coccyx.
Femur
The bone of the thigh.
Patella
The kneecap.
Tibia
The larger and stronger of the two lower leg bones.
Fibula
The smaller of the two lower leg bones.
Tarsals
The seven bones forming the ankle.
Metatarsals
The five bones forming the arch of the foot.
Phalanges (Foot)
The bones of the toes.
Collagenous Fibers
A type of protein fiber found in connective tissue, providing strength and support.