Anatomy of Joints: Types, Movements, Injuries, and Disorders
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is a joint?
point of contact between two or more bones, cartilage and bone, or teeth and bone.
How can joints be classified structurally?
based on the presence of a joint cavity and the type of connective tissue involved.
What are the three structural classifications of joints?
Fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial.
What are fibrous joints?
held together by dense connective tissue, have no joint cavity, and permit little to no movement.
Give an example of a fibrous joint and its type.
Suture (e.g., lambdoid suture) is a type of fibrous joint.

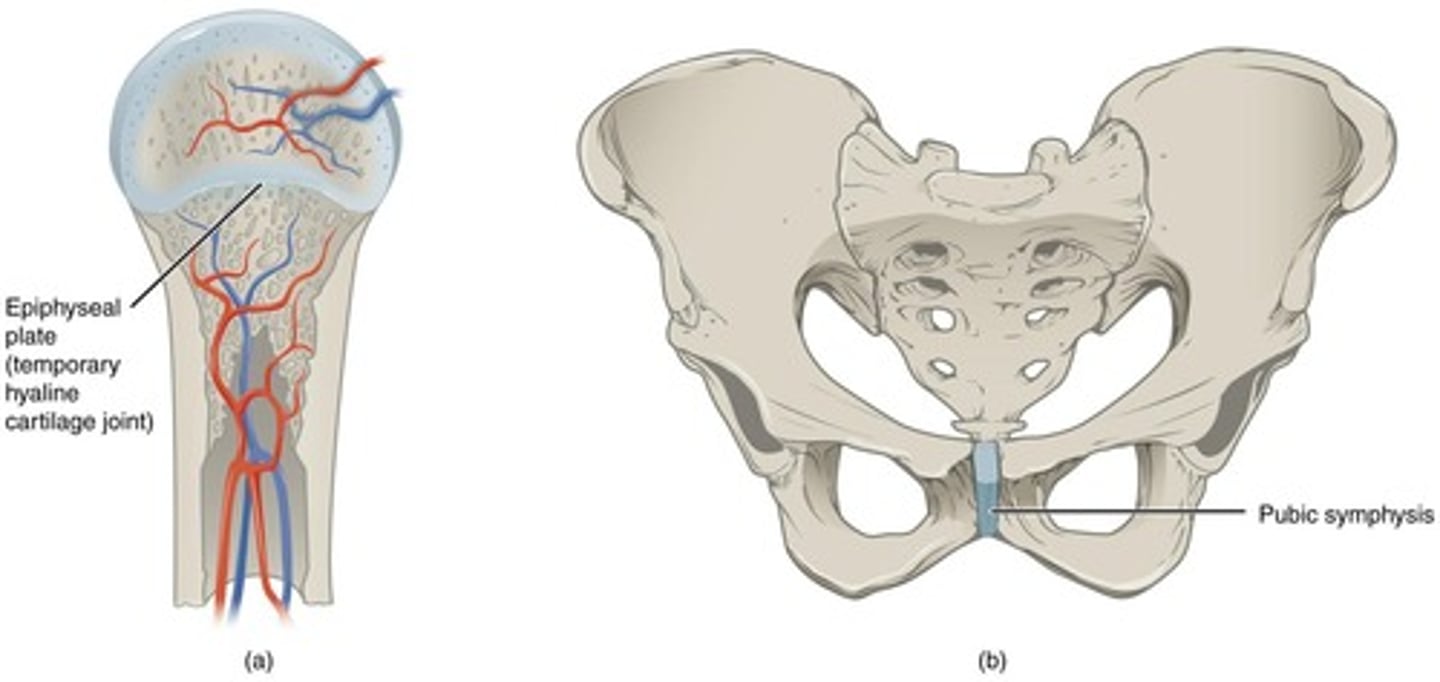
What are cartilaginous joints?
held together by cartilage, lack a joint cavity, and allow very limited movement.
What are the two main types of cartilaginous joints?
Synchondroses and symphyses.
What is a synchondrosis?
type of cartilaginous joint where connecting material is hyaline cartilage, allowing no movement after growth.
What is a symphysis?
type of cartilaginous joint connected by fibrocartilage, allowing some movement.
What are synovial joints?
held together by a complex joint cavity, allowing for a large range of movement.
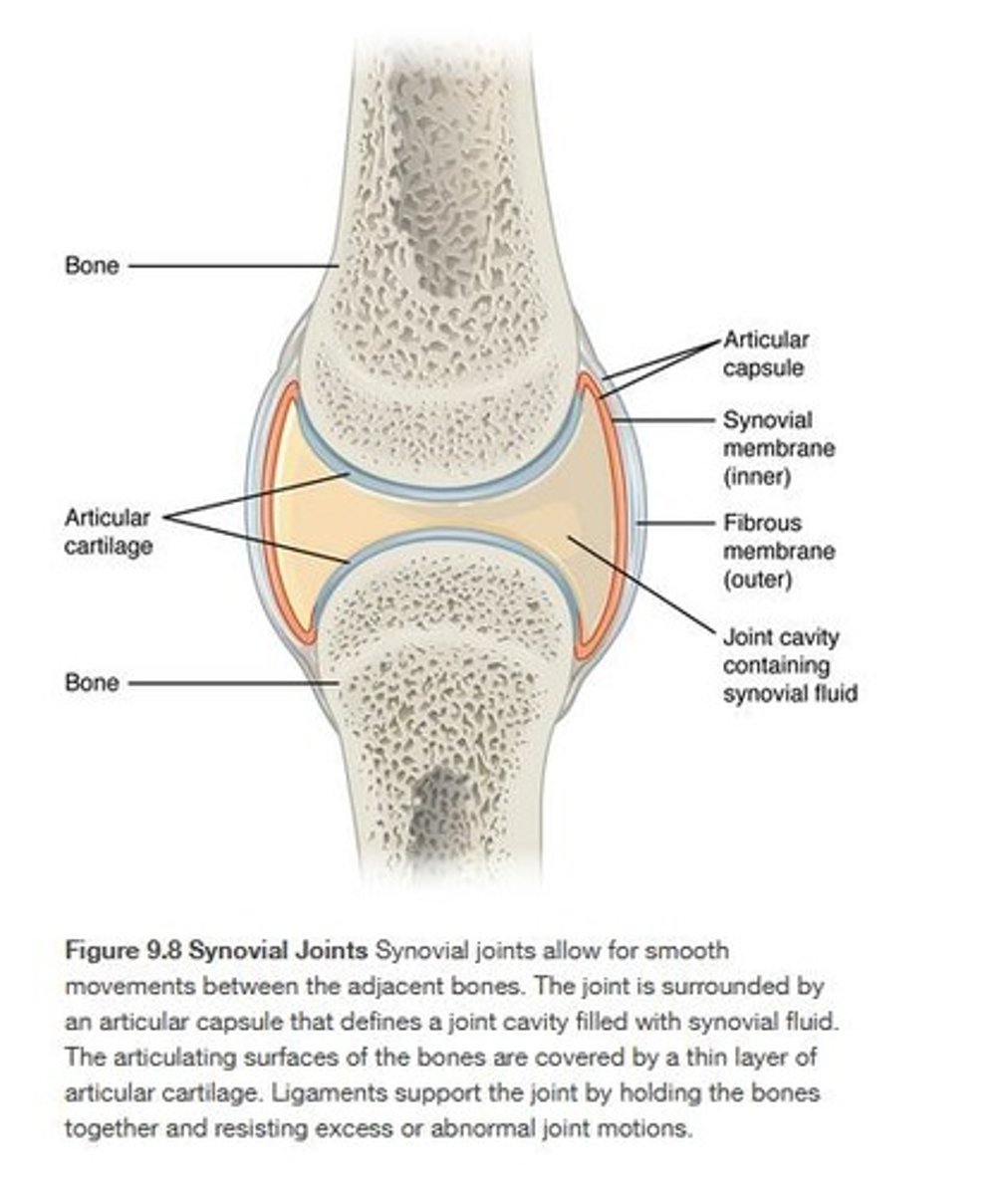
What structures are found in a synovial joint?
Articular cartilage, articular capsule, synovial fluid, and ligaments.

What is the function of synovial fluid?
lubricates the joint, reduces friction, absorbs shock, and removes waste.
What are the three functional classifications of joints?
Synarthroses (no movement), amphiarthroses (little movement), and diarthroses (freely movable).
What is an example of a synarthrosis joint?
Suture or gomphosis.
What is an example of an amphiarthrosis joint?
Pubic symphysis or intervertebral discs.
What is an example of a diarthrosis joint?
Hip, knee, shoulder, elbow, or TMJ.
What is a sprain?
an injury to ligaments caused by a joint being forced beyond its normal range of motion.
What is a strain?
injury to tendons caused by overstretching or tearing muscle/tendon fibers.
What is bursitis?
inflammation of the bursae, which are fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints.
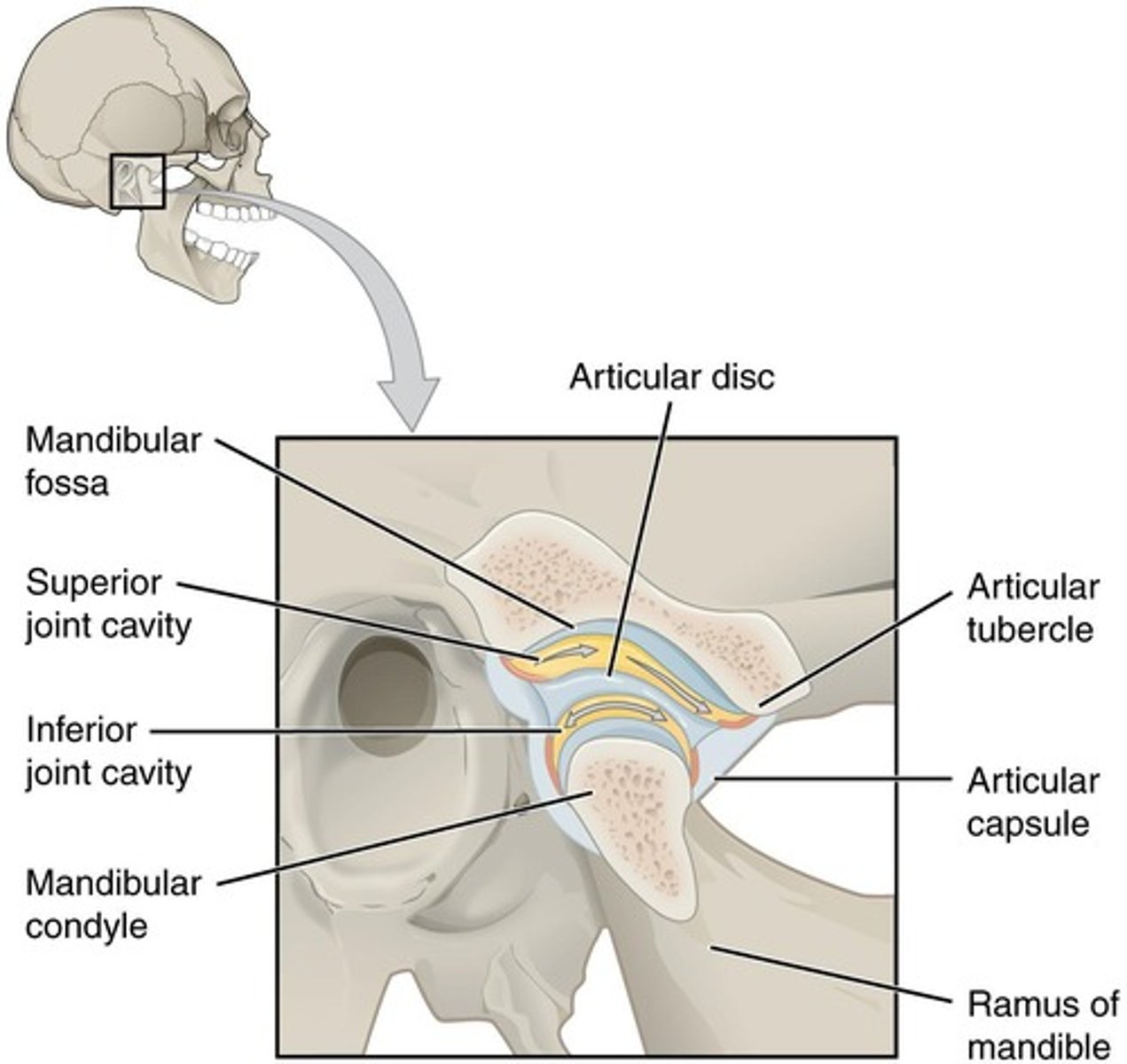
What causes TMJD (Temporomandibular Joint Disorder)?
night-time bruxism, excessive gum-chewing, stress, or physical trauma.
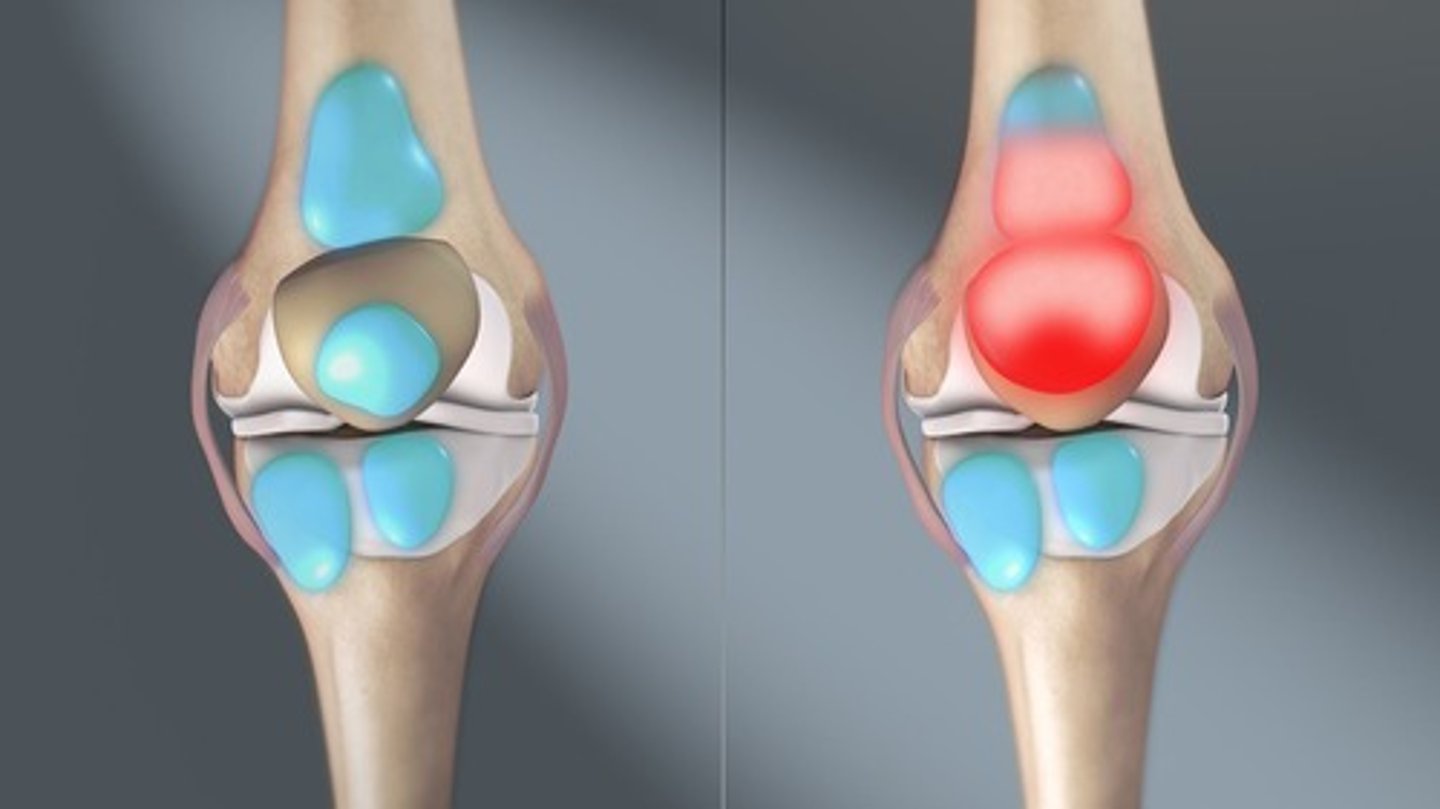
What is osteoarthritis?
condition where articular cartilage breaks down, leading to joint pain.
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the synovial membrane.
What is gout?
disorder characterized by the deposition of uric acid crystals in joints, causing pain.
What factors affect the range of motion at synovial joints?
Structure and shape of bones, strength of ligaments, muscle arrangement, soft part contact, hormones, and disuse.
What are bursae and tendon sheaths?
Bursae are sac-like structures filled with synovial fluid that cushion movement, while tendon sheaths are tube-like bursae that wrap around tendons.
What is the structure of a synovial joint's articular capsule?
a fibrous membrane made of dense irregular tissue and a synovial membrane made of areolar tissue.