Work, Energy, and Chemical Reactions
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to work, energy, chemical reactions, and pH.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Work
The application of force over a distance, measured in Joules.
Kinetic Energy (KE)
The energy of an object in motion.
Potential Energy (PE)
Stored energy in an object due to its position or state, such as gravitational potential energy.
Conservation of Energy
The principle stating that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
Acidic Solution
A solution with a low pH, characterized by a high concentration of hydrogen ions (H+).
Neutral Solution
A solution with a pH of 7, having equal concentrations of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-).
Basic Solution
A solution with a high pH, characterized by a low concentration of hydrogen ions (H+).
Chemical Reaction
A process in which reactants are transformed into products through breaking and forming chemical bonds.
Law of Conservation of Mass
The principle stating that the mass of reactants must equal the mass of products in a chemical reaction.
Types of Energy
thermal energy and mechanical energy
what is energy measured on
joules (kgm²/s²)
three types of thermal energy transfer
conduction, convection and radiation
Conduction
direct contact; e.g. sunlight hitting the ground surface
Convection
thermal energy transfer in fluids or gases
Radiation
thermal energy transfer to empty space
work formula
W=FxD. (work=force)
Potential energy formula
p.e.= mgh (mass x gravitational force x height)
Kinetic Energy formula
K.E= 1/2mv² (v= velocity)
Mechanical wave types
transverse waves and longitudinal waves
Transverse Wave
particles move perpendicular to the flow of energy
shorter wavelength higher the amplitude
lower the frequency higher the wave length
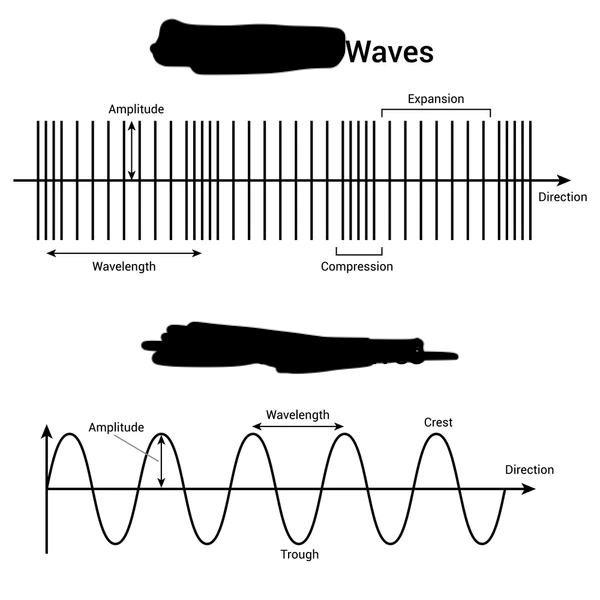
Longitudinal Waves
particles move parallel to the flow of energy
many trough = lose waves
many crest= tight waves
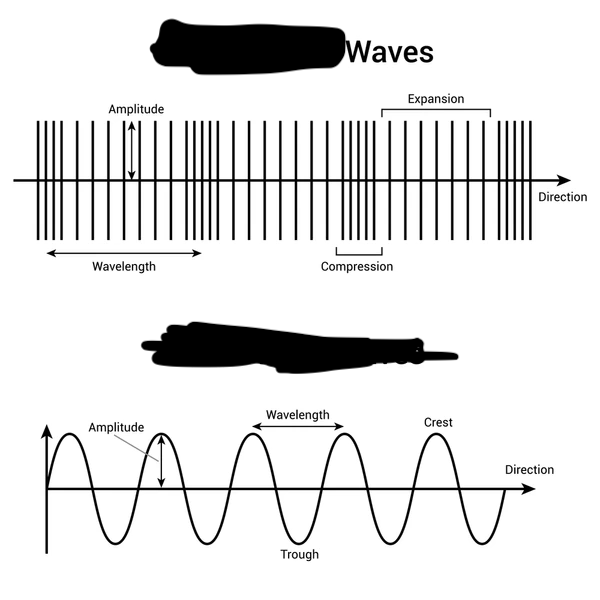
frequency of wave formula
frequency= n/t (# of waves/time)
speed of the wave formula
speed of the wave= wavelength x frequency
Physical property
properties that can be exhibited with out changing properties
Chemical property
any change in identity of new substance
Density (P)
a physical property where how much mass a substance has for space it occupies
Density formula
D=M/V (density= mass/volume)
pH (C)
a chemical property where it describes basicality and acidity of fluid
(← 7 → lower acidic higher basic)
If object only have mechanical energy, and the object is going upward..
Kinetic Energy is present from the start and potential energy would be up at the air
If object only have mechanical energy, and the object is going downward..
Potential Energy is converted (starting point) to Kinetic energy (present when hit ground)