East Asia
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
how fashion did the land from east to west ride
in a step like fashion to the Tibetan plateau
what were the two main rivers
Yellow River
Yangtze River
what was grown by the yellow river? yangtze?
yellow = cooler region = good for millet
yangtze - warmer region = good for rice
what was land like around the yellow river? Yangtze?
yellow - vast floodplain with constant flooding
yangtze - marshy
was the Yellow or Yangtze river more agricultural productive
yellow
what were the Legendary origins of ag in East Asia
Shennong the divine farmer associated with the invention of agriculture
taught his people how farming techniques
invented the plough
understood medicine and pharmacology
created musical instruments
what were two cultures associated with the origins of ag in East Asia
Peiligang
A mixed economy of hunting, fishing, and agriculture, with early cultivation of millet
Sedentary villages with both round and square semi-subterranean houses
differential grave goods between males and females
Cishan
Focused heavily on millet cultivation and storage
Known for abundant, deep storage pits
pottery was more utilitarian and lacked painted designs.
One of the earliest cultures in China to make pottery
pelligang
what was iconic of Jiahu burials
unique and rich grave goods
bone flutes
tortoise shells

what was the northern limit of wild rice
Valley of Yangzi River
was wild rice associated with a warming or cooling period
warming period
what were three cultures showing rice cultivation
Hemudu - wild rice cultivation
Shangshan - clay vessels with rice temper
Kuaguqiao - small quantities of domesticated rice
what type of sites showed the best development from wild to domesticated rice
cave sites
examples of cave sites with development of domesticated rice
Yuchanyang
Diatotonghuan
Xianrendong
why were cave sites better for showing the development from wild to domesticated rice
the stable, often drier, conditions within caves provide superior preservation of both macrobotanical remains (like grains and spikelet bases) and phytoliths
what were two Neolithic cultures
Yangshao Culture
Dawenkou culture
describe the Yangshao period
distinctive painted pottery
represents a crucial stage in the development of early Chinese civilization
conomy was primarily based on millet agriculture
what were sites found in the Yangshao culture
Banpo
Xishuipo
what was the Xishuipo site in the Yangshao period know for
Puyang Shaman
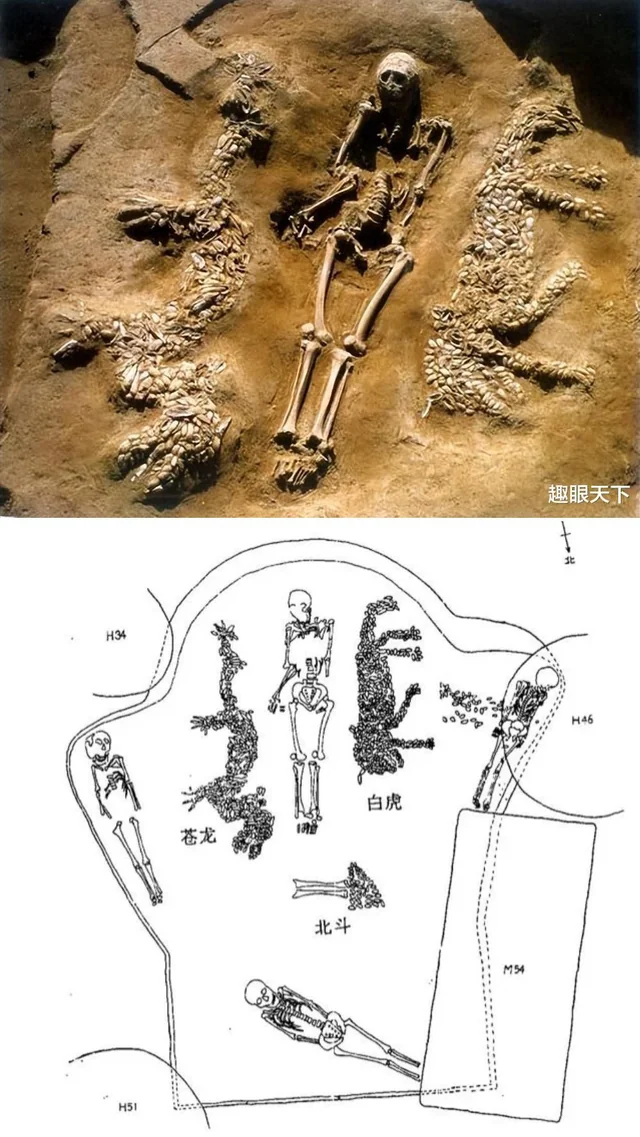
describe the Puyang Shaman
tomb with shaman in the middle and clamshell inlaid images on either side accompanied by 3 young children
image: one of the oldest known depictions of a dragon
image: big cat (tiger or lion)
where was the Hongshan Culture
Mongolia
what was significant about the Hongshan Culture
Jade work
monumental architecture
likely female ancestor worship
what were the 4 types of burials of the Hongshan Culture
Large, central grave = elites
Large stone-coffin graves
Regular stone coffins
small burials without artifacts
what gave a clear hierarchical order in the Hongshan Culture
the four types of burials
what were depicted in the jade statues of the Hongshan
humans
animals
pig dragons
what is significant of the Liangzhu culture
Earliest Known Large-Scale Water Management System
evidence of stratification
Pinnacle of Prehistoric Jade Culture
what type of jade artifacts were found in the Lianghzu culture
Bi (left)
Cong (right)
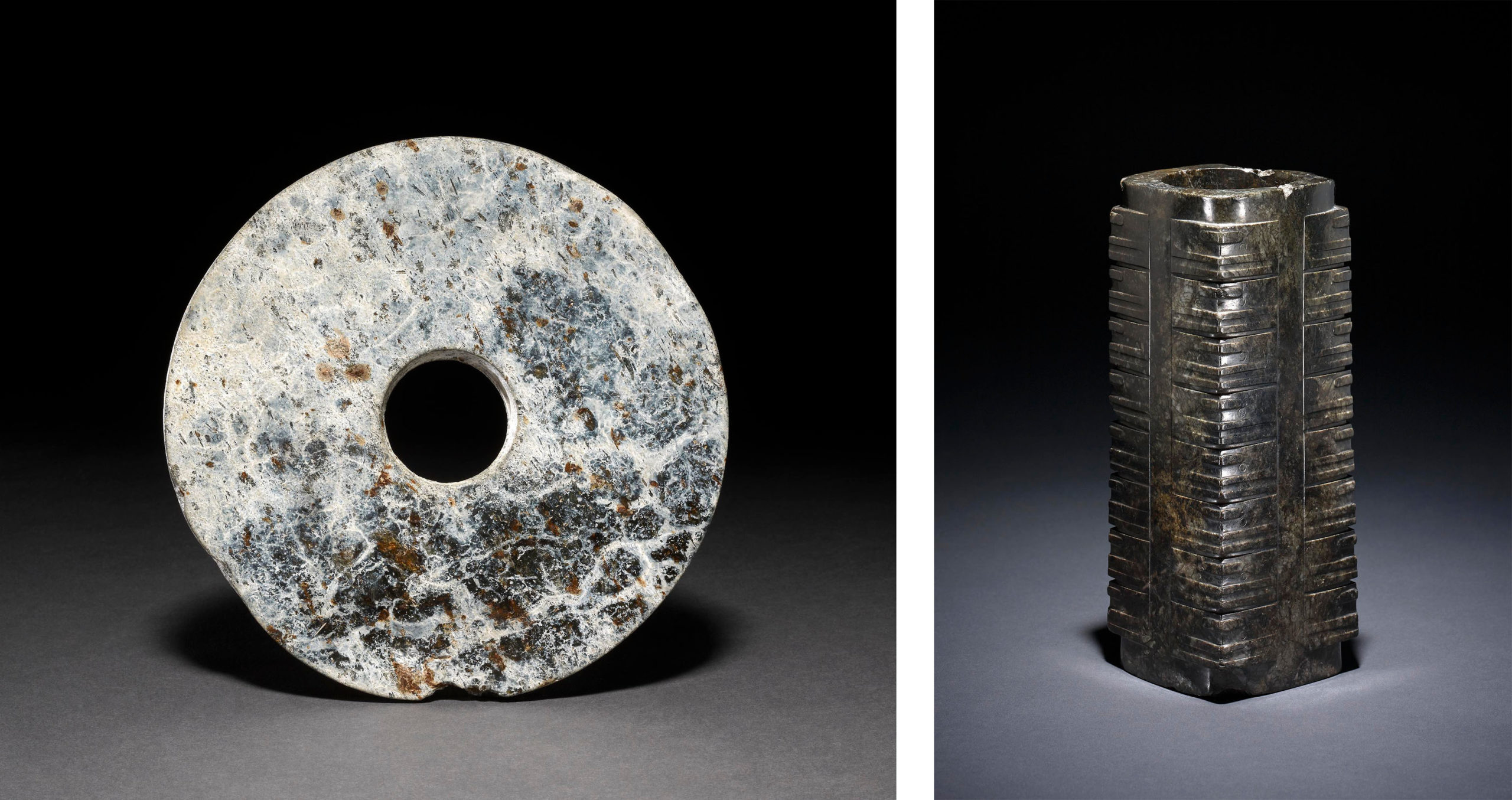

what culture sees jade production intensify
Liangzhu culture
what is the only prehistoric culture to use sapphires
Liangzhu
what was jade seen as an embodiment of
life spirits and breath spirits
what kind of ceramic vessels did Tianluoshan culture have
fu (rectangle cooking pot)
what was significant of the Tianluoshan
exceptionally well-preserved evidence of early rice cultivation
waterlogged and anaerobic conditions of the site preserved organic artifacts
what culture in East Asia was waterlogged
Tianluoshan
Longshan translates to
dragon Mountain
was there evidence of conflict at Longshan
YES
what was characteristic of Longshan
Distinctive Black Pottery
highly stratified
hang tu defenses
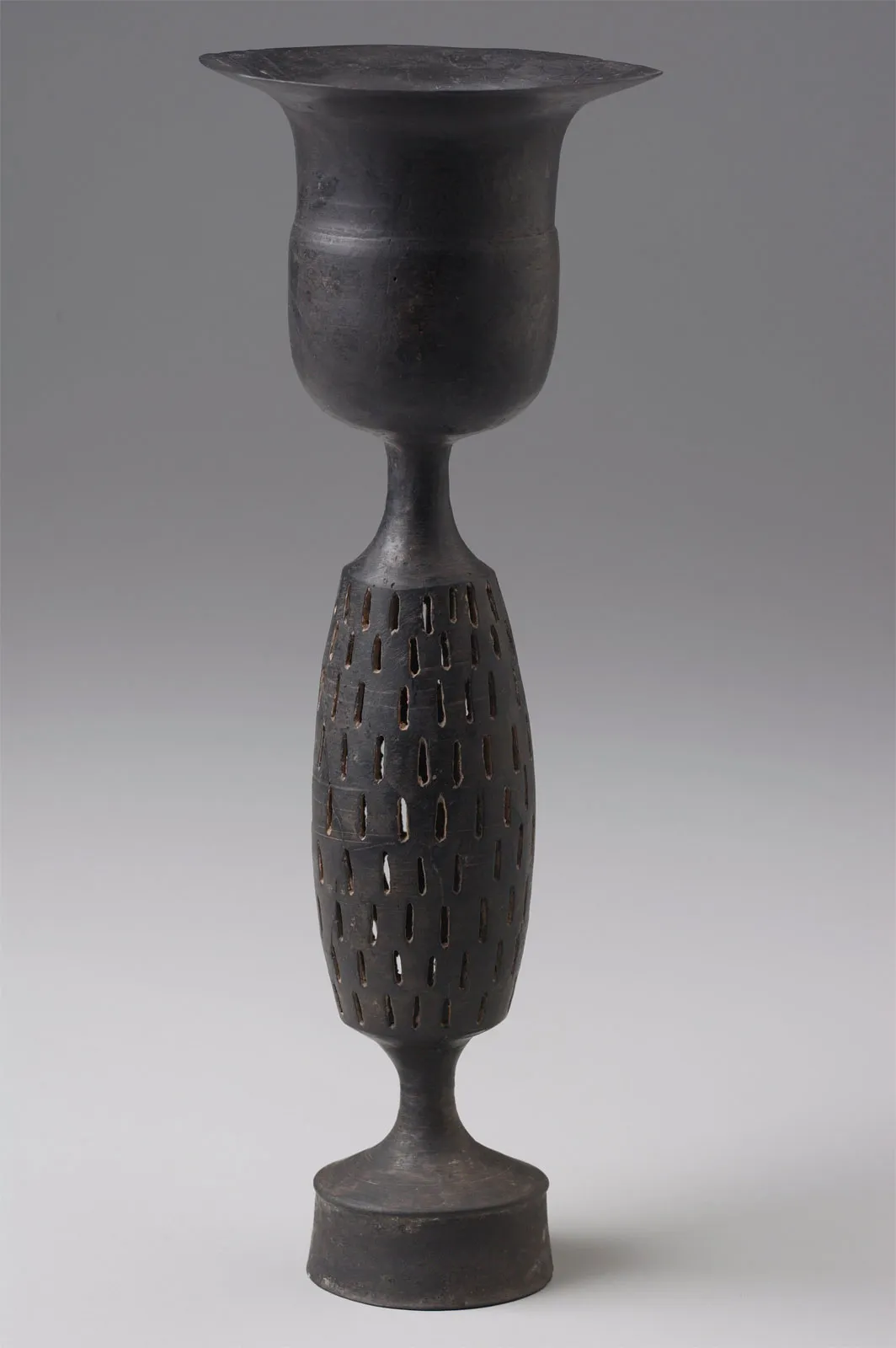

what was evidence of conflict in Longshan culture
hang tu - fortifications made of rammed earth between wooden slats
what was characteristic of the Taosi cemetery
extreme social stratification
large tombs for the elite
medium-sized tombs for lower elites/bureaucrats
small, bare graves for commoners
what style of coffin were the elite buried in at the Taosi cemetery
boat shaped coffins
what was Man Bac
early farming site in Vietnam
what were four main food sources in Man Bac
forest uplands - gathering
grasslands - pigs, otters, cows…
mangrove shore of a river - fishing
rice - not reliable food source
what kinds of burials were found at Man Bac
two unique burials for immigrant farmers and native hunter-gatherers:
how did immigrant farmer and native hunter-gatherer burials differ in Man Bac
farmers
diet based on domesticated plants and animal
Grave goods found in specific burials may reflect emerging social hierarchies and community organization
hunter-gatherer
Often buried in a flexed (foetal) position
Grave goods generally reflect a simpler material culture,
diet heavily reliant on marine or wild resources.
What was significant of Ban Non Wat
oldest known remains of a domestic chicken
grave goods like bronze tools and exotic shell and marble jewelry = extensive trade networks
hierarchical society
what site had the oldest known remains of a domestic chicken
Ban Non Wat
what is sericulture
silk production
what was the mythological origins of sericulture
Confucius claims the wife of Yellow Emperor invented sericulture while having tea
what was the 4 step process of sericulture
selectively breeding flightless moths with their 500 eggs
once hatched fed a careful diet until they spin cocoons
cocoons were heated to kill the pupa then immersed in water so the filaments unwind
spun into threads