topic 6 waves
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
When do waves move at a faster speed?
in denser materials
What causes refraction?
A change in density of a medium.
How are sound waves produced by us when we speak?
When our vocal cords vibrate we produce sound waves.
What are transverse waves?
The oscillations of a transverse wave are perpendicular to the direction in which the waves transfer energy.
What property of sound waves remains the same when it enters a different medium?
frequency
What can happen to a wave when it reaches a boundary?
Reflected
Absorbed
Transmitted
What does wavelength of a wave measure?
The distance from a point on one wave to the equivalent point on the advacent wave.
What are longitudinal waves?
The oscillations of a longitudinal wave are parallel to the direction in which the waves transfer energy.
What are mechanical waves?
Mechanical waves causes oscilations of particles in a solid, liquid or gas and must have a medium.
What is the speed of electromagnetic waves?
About 300,000,000 m/s.
What are electromagnetic waves?
Transvervse waves that transfer energy from the source of the waves to an absorber. They do not require a medium to travel through.
What are some examples of transverse waves?
Ripples on the surface of water
Seismic S waves
Electromagnetic waves
What is the period of waves?
The amount of time it takes for a complete wave to occur.
What does speed measure in waves?
The distamce a wave travells per second.
What properties of sound waves change when entering a different medium?
Wavelength and speed.
Do sound waves move quicker or slower in a denser medium?
Quicker.
Why does the amplitude of a wave decrease as it enters a new substance?
BC the substance abosrbs some of the wave's energy when it enters it.
What is reflection?
Reflection occurs when a wave hits boundary between two media but the wave stays in the original medium.
What is the formula for wave speed?
wave speed, v = frequency, f * wavelength, λ
What is the speed of sound in air?
330m/s.
What is diffuse reflection?
Diffuse reflection occurs when waves hit a distored, uneven surface.
What is specular reflection?
Reflection from a smooth, flat surface.
What is the angle of incidence?
The angle between the incident light ray and the normal.
What range of sounds can the human ear detect
From 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
What is the angle of reflection?
The angle between the normal and reflect ray.
What are ultrasound waves?
Ultrasound waves have a frequency higher than the upper limit of hearing for humans.
What happens to ultrasound when it meets a boundary between two different media?
It gets partially reflected.
What are the uses of ultrasound?
Medical imaging
Industrial imaging
Echo sounding - distance to seabed
What are the uses of echo sounding?
Echo is used to detect objects in deep water and to measure water depth below a ship.
How does echo sounding work?
The pulses from the transmitter are reflected at the sea bed directly below the ship.
The time taken by each wave to travel to the sea bed and back is measure.
This can be used to calculate the depth of the sea bed below the ship.
What are P-waves?
Longitudinal waves that can travel through liquids and solids
What is an incident ray?
An incoming ray of light that gets reflected,.
What type of waves are S-waves?
Transverse seismic waves that cannot travel through liquids
Whatr type of waves are produced by earthquakes?
Seismic waves.
What media can P-waves travel through?
Solids and liquids.
What media can S-waves travel through?
Through solids but not liquids.
What is an S-wave/P-wave shadow zone?
An area of the Earth's waves where S-waves or P-waves are not detected following an earthquake.
Why do S-wave shadow zones form?
As a waves approach the Earth's liquid outer core, they are absorbed, creating an absence of these waves beyond a certain angle from the earthquake.
Where are P-wavss refracted?
At the boundary between the mantle and outer core when they enter the core and leave the core.
Why do P-wave shadow zones form?
Because the second refraction is further around, the waves can't reach the shadow zone.
What factors affect whether a wave will get reflected, absorbed or transmitted?
The wavelength of the wave and the properties of the materials.
What is the angle of incidence always equal to?
The angle of reflection or emergence
When do you get a real image?
When light rays actually meet at a point.
What is principal focus?
The point where the parallel set of incident rays meet after refraction.
What is the amplitude of a wave?
The maximum displacement of a point of a wave from its rest position.
When do you get a virtual image?
If light rays come from the same point but don't meet.
What is a focal point?
The point where parallel light rays bends inward and meet on the other side of the lens
What is white light?
White light is a mixture of all the colours of the spectrum.
What is focal length?
The distance from the lens to the principle focus.
How do colour filters work?
By absorbing certain wavelengths and transmitting other wavelengths.
What is principal axis?
A line through the middle of a lens.
What is the peak of a wave?
The highest point of a wave above the rest position.
What do pigments do?
Absorb light of specific wavelengths and strongly reflect other wavelengths.
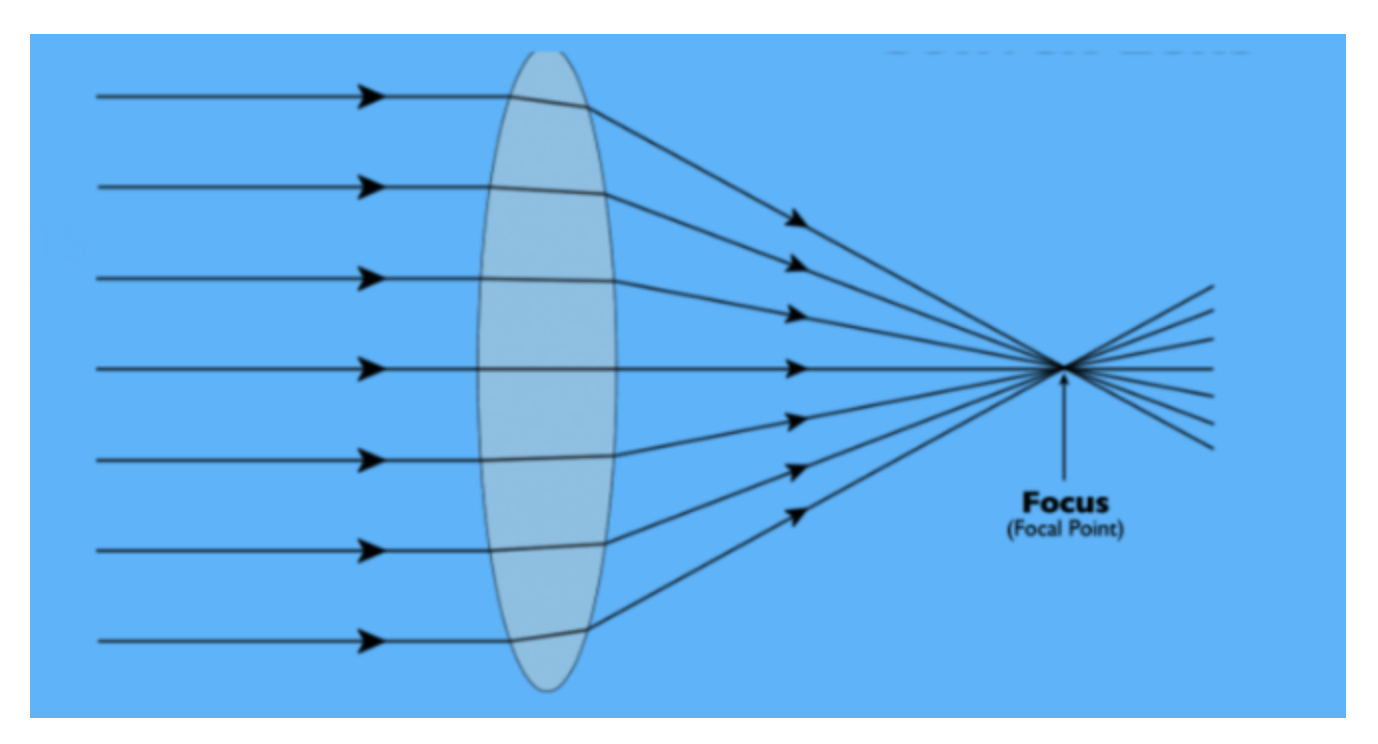
What type of lens is this?
convex
What do white surfaces do?
Reflect light of any wavelength.
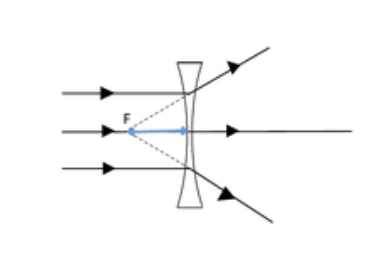
concave
What is an opaque object?
Light cannot pass through the object as it absorbs or reflects all light that reaches it.
How do you make a lens more powerful?
By making it more curved
By using a material that refracts light more
Are mechanical waves transverse or longitudinal?
Mechanical waves can be transverse and longitudinal.
What can happen to light at an opaque surface?
Reflected, scattered or absorbed.
What do you have to comment on in an image?
Virtual or real
Upright
Size
What do transparent objects do?
Transmit all the incident rays that enters the object.
How can you tell if an image is real?
If the rays actually pass through the image.
What do translucent objects do?
Let some light pass through the, but the light is scattered or refracted.
What is a convex lens?
A convex lens makes parallel rays converge to a focus.
What do concave lenses do?
make parallel rays diverge
What will an object at 2F make?
A real, inverted image the same size as the object.
What will an object between F and 2F make?
A real, inverted image bigger than the object.
What will an object at F make?
A virtual image, bigger than the object, on the same side of the lens.
What type of image do concave lenses always produce?
Virtual images
Right way up
Smaller than the object.
What is refraction?
Refraction of waves is the change of direction in which they are travelling when they cross a boundary between one medium and another medium.
What is a normal line?
a line 90 deg to the normal
What direction do waves bend towards when they slow down?
the normal
What is a laser?
A concentrated source of light.
What direction to waves bend when they speed up?
Away from the normal.
Why do x-rays have better resolution than ultrasound?
Because they have smaller wavelength than sound waves.
When do waves not change direction?
If they enter or leave a medium at right angles to the surface (along the normal).
What is a wave front?
An imaginary line that conntects the same points in a wave.
what are em waves
transverse waves that transfer energy from the source of the waves to an absorber
What is the formula for the period of a wave?
1/f
all types of EM waves travel at [...] through a vacuum
all types of EM waves travel at the same velocity through a vacuum
how is the EM wave spectrum grouped
wavelength and frequency
order of wavelength and frequency strength along the spectrum
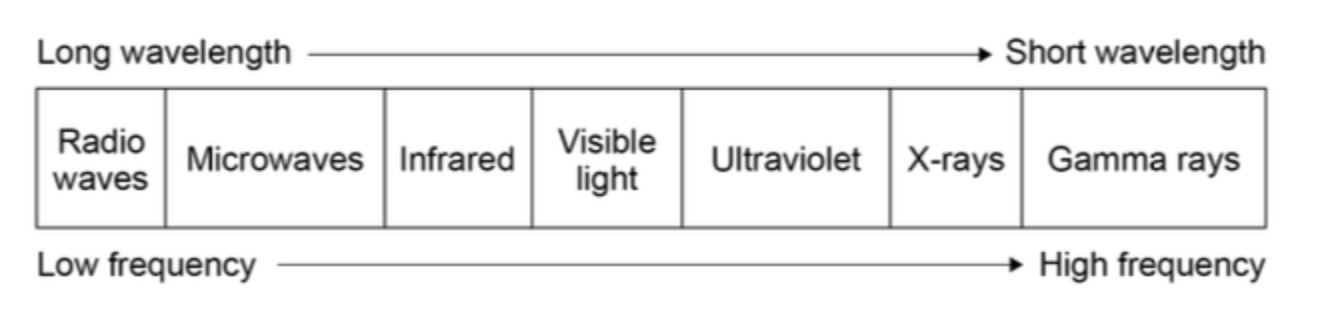
EM wave spectrum order
radio
micro
infrared
visible light
UV
x ray
gamma
What is frequency in waves?
The number of waves that pass a point per second.
What is the trough of a wave?
The lowest point below the rest position of a wave.
RQP 10: Investigate how the amount of infared radiation absorbed or radiated by a surface depends on the nature of that surface
1) use leslie's cube with 4 different surfaced sides and place a infrared detector towards each of the surfaces
2) measure the amount of infrared emitted from each surface whilst making sure it is the same distance from the infrared detector
RESULTS - high to low - matte black, shiny black, white, shiny metallic
b) 1)place 2 different (matte black + shiny metallic) metal plates on each side of an infrared heater
2) attatch a drawing pin to each plate using vaseline and measure time taken for drawing pin to fall off
>due to metal plate absorbing heat, ^temp, melts vaseline
RESULTS - time is less for matte black BC it absorbs more infrared
how can radio waves be produced
by oscillations in electrical circuits
what do radio waves create when they are absorbed
alternating current with same frequency as radio wave itself
Changes in [...] can result in electromagnetic waves being generated or absorbed over a wide frequency range.
Gamma rays originate from changes in [...]
Changes in atoms and the nuclei of atoms can result in electromagnetic waves being generated or absorbed over a wide frequency range.
Gamma rays originate from changes in the nucleus of an atom.
The effects of UV, xrays and gamma waves on body tissue depend on [...]
The effects of UV, xrays and gamma waves on body tissue depend on type of radiation and dose
What is a reflected ray?
A ray that is thrown back from a surface.
consequences of UV radiation exposure
causes skin to age prematurely > increase risk of skin cancer
why are xrays and gamma rays dangerous
ionising radiation - causes mutation of genes and cancer
Practical applications of EM waves and reasons:
• radio waves – [...] - [...]
radio waves – television and radio - travel long distances
how can ultrasound be used to find out if a substance has a genuine core (e.g. Gold bars)
Ultrasound is partially reflected when it crosses the boundary
between two different materials.In a solid gold bar, the first reflection would occur when ultrasound enters the bar.
Then there would be a second reflection when the ultrasound hits/reaches the other side of the bar.
So if the bar was solid gold there would be two reflections in total.
If the bar has a fake core, there would be a third reflection when the ultrasound enters the fake substance.
There would also be a fourth reflection when the ultrasound leaves the fakes substance.
So if the bar had a fake core then there would be four reflections.
The speed of a sound wave will be different in gold than it is in the fake substance
What are some examples of longitudinal waves?
Sound waves
Seismic P waves
Ultrasound
RQP 9: Investigate the reflection of light by different types of surfaces and the refraction of light by different substances
Set up a ray box to produce a narrow ray of light (switch it off when not used to prevent excess heat)
Get piece of paper and draw a straight line down the centre, and a normal to it aswell
Place a glass block/other material against the first line so the normal is near the centre of the block
Turn off lights in the room
Use ray box to direct light ray to hit the glass block on the normal
Measure the angle of reflection and the angle of transmission (when you change the direction from which the light ray is coming from) using a protractor
Change the material from glass to another one
The angle of reflection will stay the same but the angle of refraction will be different
microwaves – [...] - [...]
satellite communications,
cooking food - water molecules in food absorb microwave energy,
passes through atmosphere without reflection/refraction
infrared – [...] - [...]
electrical heaters, cooking food, infrared cameras - easily absorbed by surfaces