Human Anatomy: Cardiovascular, Lymphatic, Urinary Systems
1/527
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
528 Terms
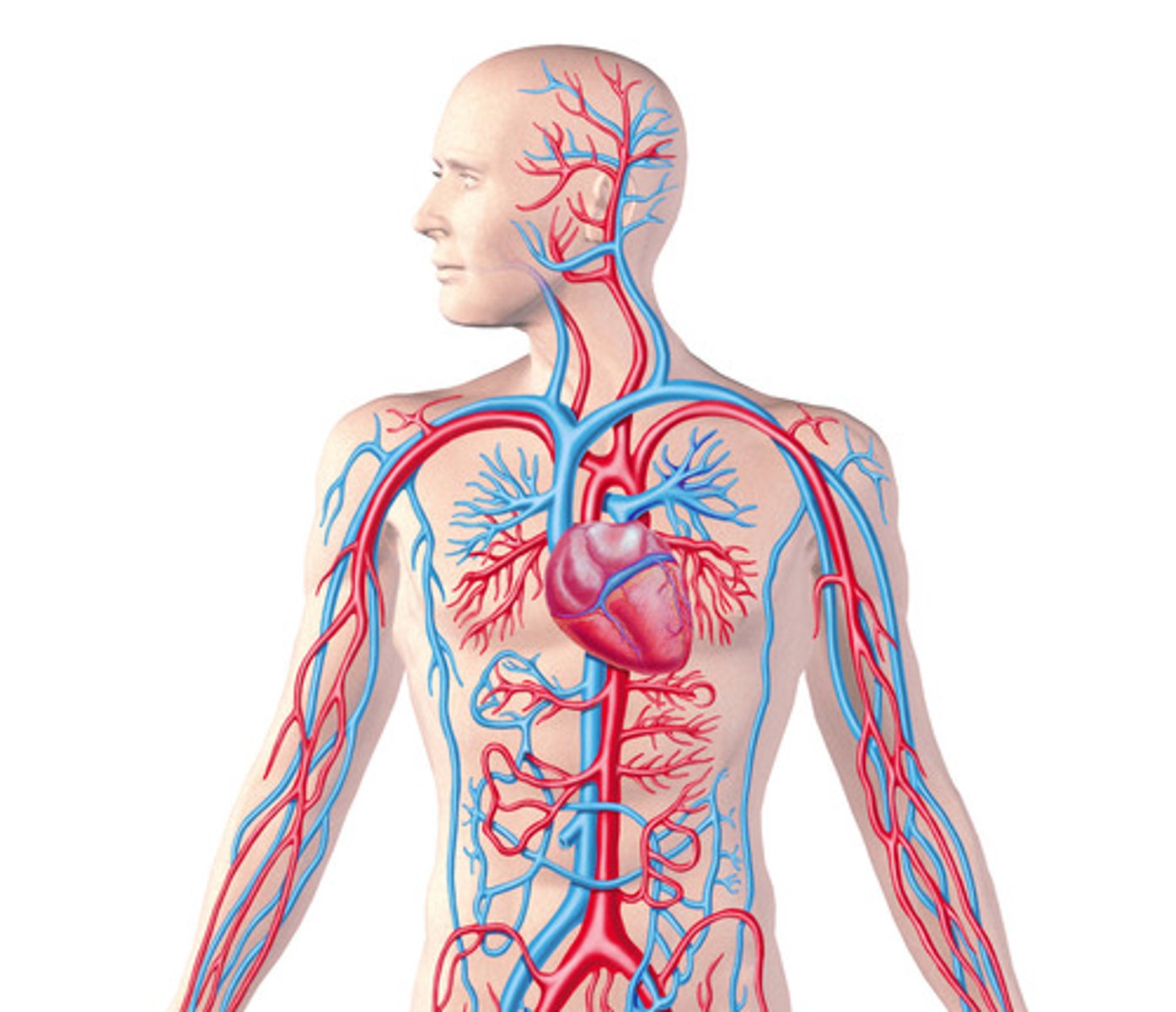
Cardiovascular System
System responsible for blood circulation in the body.
Heart Contractions
Rate and force adjust to tissue metabolic needs.
Mediastinum
Central thoracic cavity housing the heart and other organs.
Heart Anatomy
Cone-shaped, size of a closed fist.
Base of Heart
Positioned posteriorly and superiorly.
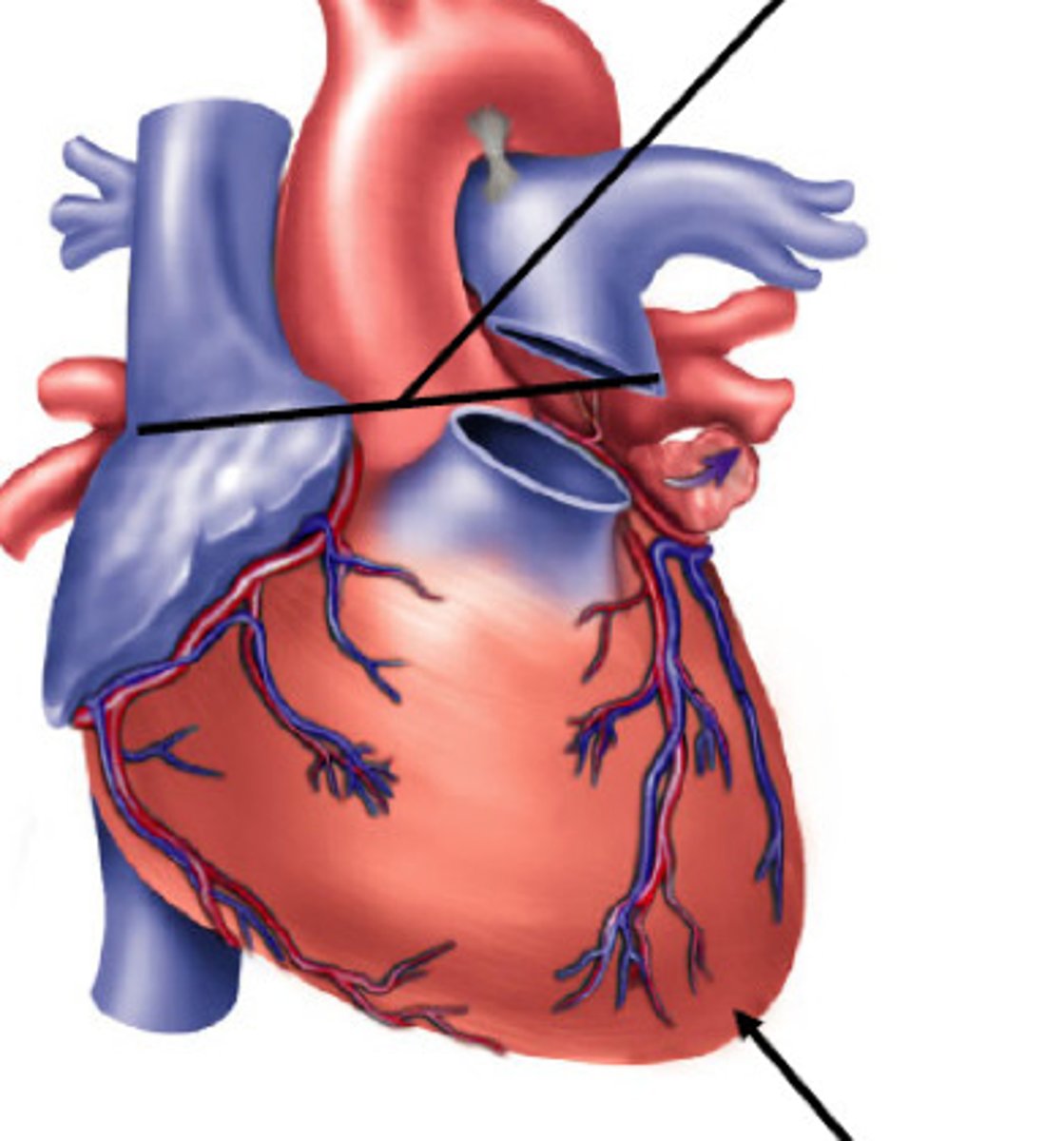
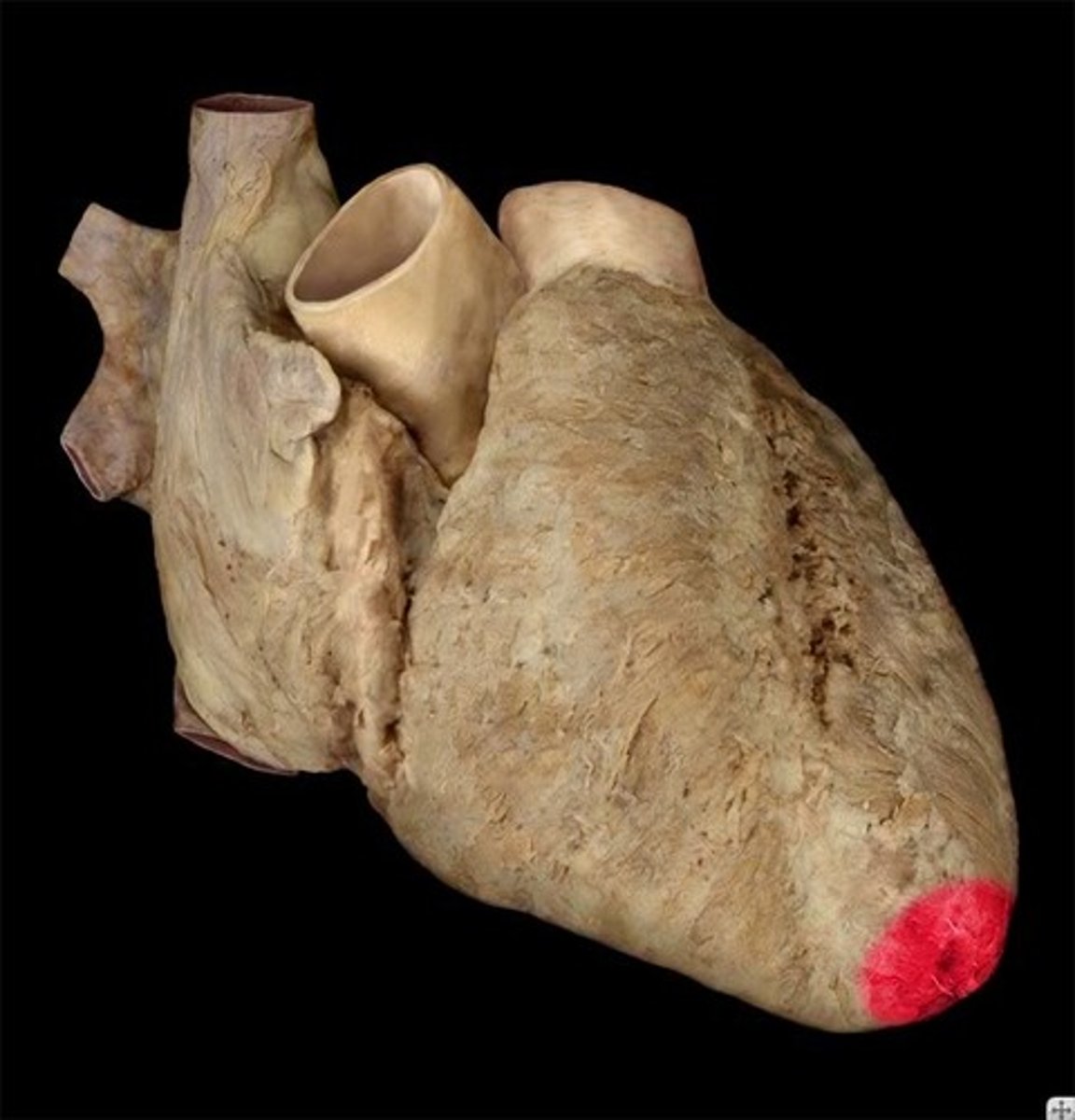
Apex of Heart
Pointed lower part, positioned anteriorly and inferiorly.
Pulmonary Circulation
Right heart pumps blood to lungs for gas exchange.
Systemic Circulation
Left heart pumps oxygenated blood to body tissues.
Fibrous Pericardium
Outer layer preventing heart overdistension.
Serous Pericardium
Inner layer, consists of parietal and visceral parts.
Parietal Pericardium
Lines the fibrous pericardium.
Visceral Pericardium
Covers the heart surface, also called epicardium.
Pericardial Cavity
Space between visceral and parietal pericardia.
Pericardial Fluid
Serous fluid reducing friction during heart movement.
Heart Wall Layers
Composed of epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium.
Epicardium
Superficial layer of the heart wall.
Myocardium
Muscular middle layer responsible for heart contractions.
Endocardium
Inner layer lining the heart chambers.
One-Way Blood Flow
Valves ensure unidirectional blood movement.
Generating Blood Pressure
Heart contractions create pressure for blood movement.
MYOCARDIUM
Thick, muscular middle layer of the heart.
ENDOCARDIUM
Inner layer of heart, smooth for blood flow.
PECTINATE MUSCLES
Muscular ridges in auricles and right atrium.
CRISTA TERMINALIS
Ridge separating smooth atrial wall from pectinate.
TRABECULAE CARNEAE
Muscular ridges in ventricular walls aiding ejection.
CORONARY SULCUS
Groove separating atria from ventricles externally.
ANTERIOR INTERVENTRICULAR SULCUS
Groove on anterior surface between ventricles.
POSTERIOR INTERVENTRICULAR SULCUS
Groove on posterior surface between ventricles.
AURICLES
Flaplike extensions of atria seen anteriorly.
VENA CAVA
Carries blood from body to right atrium.
INFERIOR VENA CAVA
Carries blood from lower body to right atrium.
CORONARY SINUS
Drains blood from heart walls into right atrium.
PULMONARY VEINS
Carry oxygenated blood from lungs to left atrium.
PULMONARY TRUNK
Carries deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lungs.
AORTA
Carries oxygenated blood from left ventricle to body.
GREAT CARDIAC VEIN
Drains blood from left side of heart.
SMALL CARDIAC VEIN
Drains blood from right margin of heart.
LEFT MARGINAL ARTERY
Supplies blood to lateral wall of left ventricle.
CIRCUMFLEX ARTERY
Supplies blood to posterior wall of the heart.
SYSTOLE
Phase when heart muscle contracts, reducing blood flow.
CORONARY CIRCULATION
Blood vessels supplying heart tissue with blood.
HEART CHAMBERS
Four chambers: two atria and two ventricles.
THIN-WALLED ATRIA
Form anterior parts of the heart.
THICK-WALLED VENTRICLES
Form anterior and inferior parts of the heart.
Diastole
Phase when heart muscle relaxes.
Right Coronary Artery
Supplies blood to right heart regions.
Right Marginal Artery
Branches from right coronary artery, supplies right ventricle.
Posterior Interventricular Artery
Supplies blood to heart's inferior and posterior parts.
Coronary and Systemic Circulation
Oxygen delivery process to heart and muscles.
Oxygen Release
O₂ is delivered to surrounding cells during blood flow.
Resting State O₂ Release
Coronary arteries release about 70% O₂ at rest.
Exercise O₂ Release
Skeletal muscles increase O₂ release to about 70%.
Anastomoses
Direct connections between arteries for blood supply.
Atrioventricular Valves
Ensure blood flows from atria to ventricles.
Tricuspid Valve
AV valve between right atrium and ventricle.
Bicuspid Valve
AV valve between left atrium and ventricle.
Papillary Muscles
Muscles that attach to AV valve cusps.
Chordae Tendineae
Connective tissue strings attaching papillary muscles to valves.
Interatrial Septum
Separates the right and left atria.
Fossa Ovalis
Depression on interatrial septum, former foramen ovale.
Foramen Ovale
Opening between right and left atria in fetus.
Coronary Sinus
Receives blood from the heart itself.
Superior Vena Cava
Receives blood from the upper body.
Inferior Vena Cava
Receives blood from the lower body.
Left Ventricle Thickness
Thicker wall for stronger systemic blood pumping.
Atrioventricular Canal
Pathway between atria and ventricles for blood flow.
Semilunar Valves
Valves between ventricles and great arteries.
Aortic Semilunar Valve
Valve allowing blood from left ventricle to aorta.
Pulmonary Semilunar Valve
Valve allowing blood from right ventricle to pulmonary trunk.
Interventricular Septum
Muscular wall separating left and right ventricles.
Superior Vena Cava
Vein delivering blood from upper body to right atrium.
Inferior Vena Cava
Vein delivering blood from lower body to right atrium.
Tricuspid Valve
Valve preventing backflow into right atrium during contraction.
Bicuspid Valve
Valve preventing backflow into left atrium during contraction.
Pulmonary Arteries
Carry deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs.
Pulmonary Veins
Return oxygenated blood from lungs to left atrium.
Foramen Ovale
Fetal opening allowing blood flow between atria.
Tunica Intima
Inner layer of blood vessel walls.
Blood Flow Route
Pathway of blood circulation through heart chambers.
Right Ventricle
Chamber pumping blood to lungs via pulmonary trunk.
Left Ventricle
Chamber pumping blood to body via aorta.
Cusps
Pocket-like structures in heart valves preventing backflow.
Blood Pressure
Force exerted by circulating blood on vessel walls.
Valve Closure Mechanism
Pressure changes cause valves to open and close.
Oxygenation of Blood
Process of blood picking up oxygen in lungs.
Carbon Dioxide Release
Process of blood releasing CO₂ in lungs.
Endothelium
Thin layer lining blood vessels internally.
Basement Membrane
Supportive layer beneath the endothelium.
Lamina Propria
Thin connective tissue layer in blood vessels.
Blood Vessels
Hollow tubes conducting blood throughout the body.
Internal Elastic Membrane
Fenestrated elastic fiber layer in arteries.
Tunica Media
Middle layer of blood vessels with smooth muscle.
Arteries
Vessels carrying blood away from the heart.
Capillaries
Smallest blood vessels for nutrient exchange.
Veins
Vessels returning blood to the heart.
Vasoconstriction
Smooth muscle contraction reducing vessel diameter.
Vasodilation
Smooth muscle relaxation increasing vessel diameter.
External Elastic Membrane
Layer separating tunica media from tunica adventitia.
Tunica Adventitia
Outer layer of blood vessels, connective tissue.
Elastic Arteries
Largest arteries, first to receive heart blood.