Unit 2.2: The Endocrine System
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
pineal gland
produces melatonin, targets many organs, and functions as a biological clock
pituitary gland hormones
produces FSH/LH, ADH, growth hormone, oxytocin, and prolactin,
thyroid gland
produces thyroxin, targets the liver, and controls metabolic rate
pituitary gland target organs
ovaries, kidneys, uterus, breast tissue and many other organs
pituitary gland function
menstrual cycle, osmoregulation, growth and division, birth contractions, and milk production
adrenal glands
produces adrenaline and cortisol, targets many organs, controls fight or flight and anti-stress
pancreas
produces insulin/glucagon, targets the liver, and controls blood sugar levels
ovaries
produces estrogen/progesterone, targets the uterus, and controls menstrual cycle
testes
produces testosterone, targets many organs, and produces male characteristics
blood sugar regulation
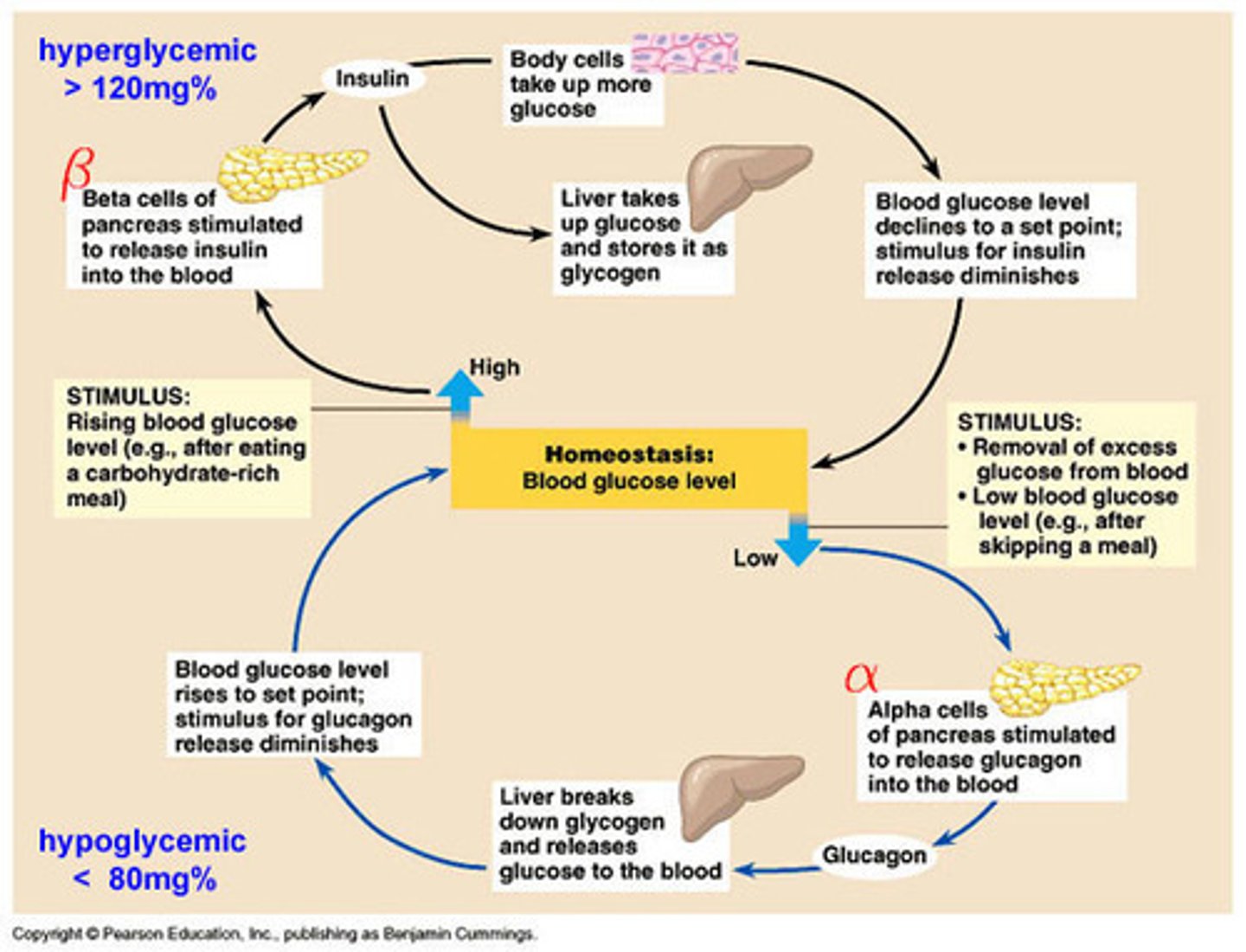
type 1 diabetes
"juvenile onset", autoimmune or genetic cause, non-functional pancreas, no insulin produced, cannot be prevented or reveresed
diabetes symptoms
thirst, frequent urination, blurry vision
type 2 diabetes
"adult onset", insulin resistance obesity or aging, partially functional pancreas, some insulin produced, can be prevented or reversed
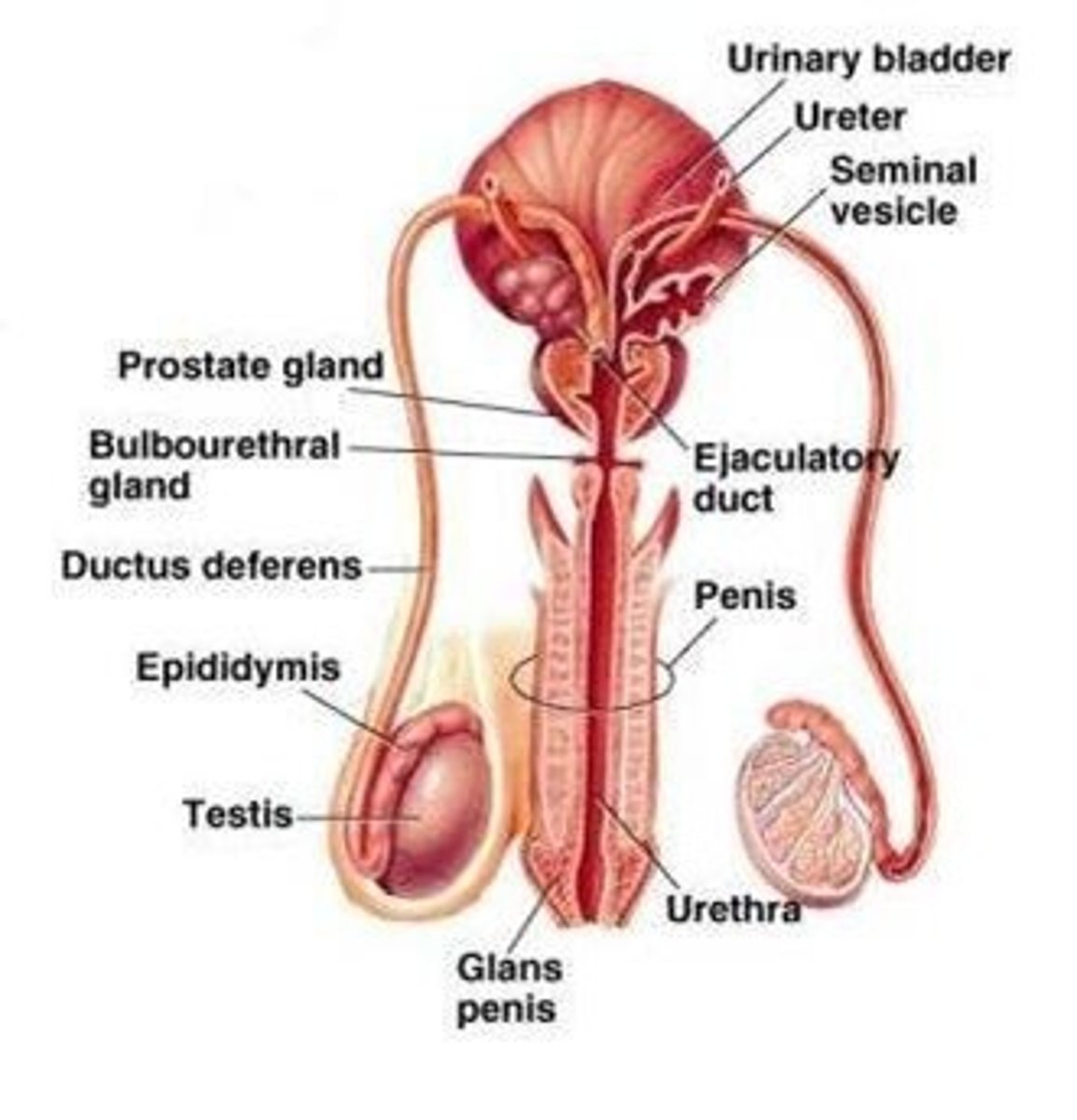
Male Reproductive System
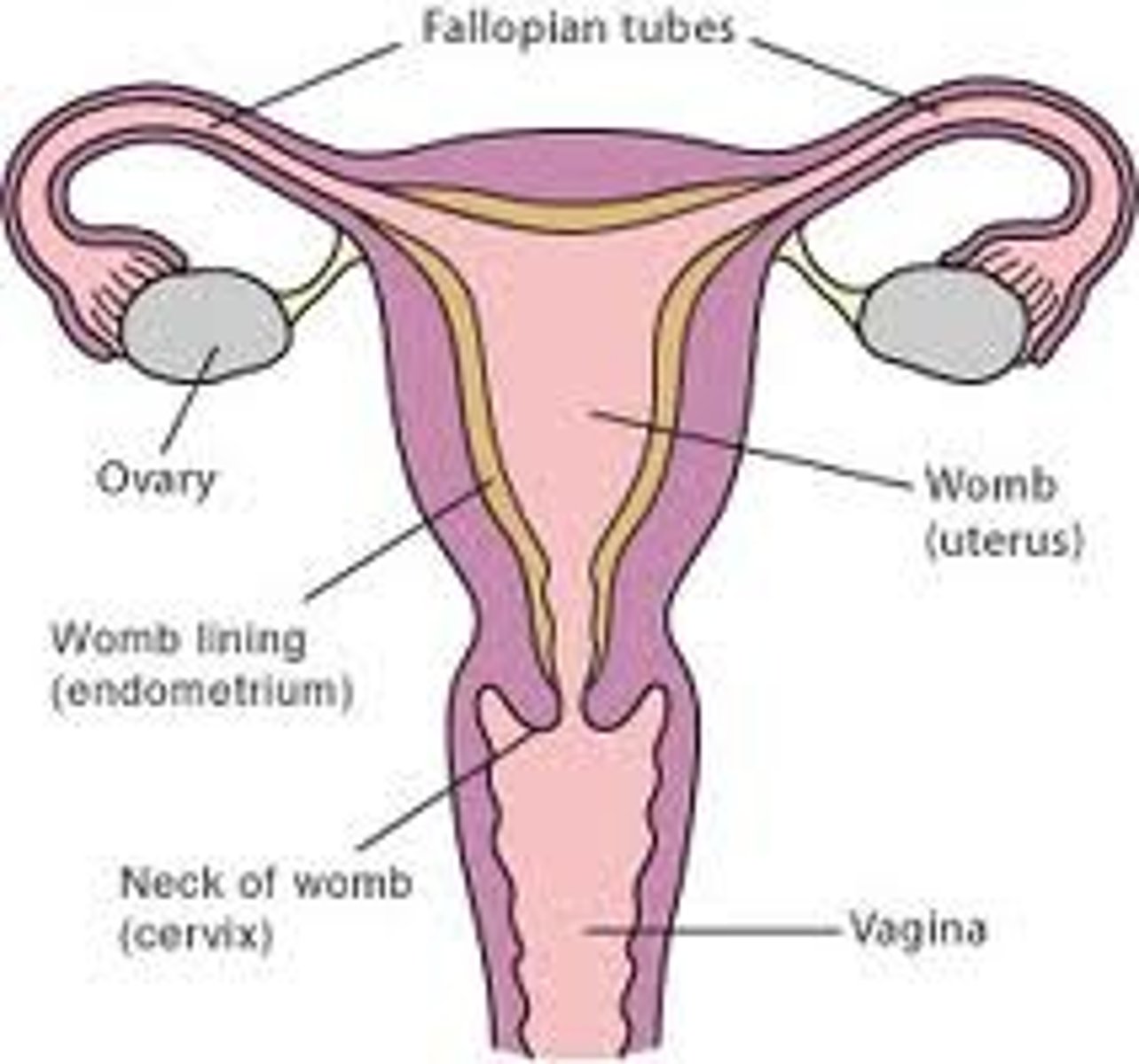
Female Reproductive System
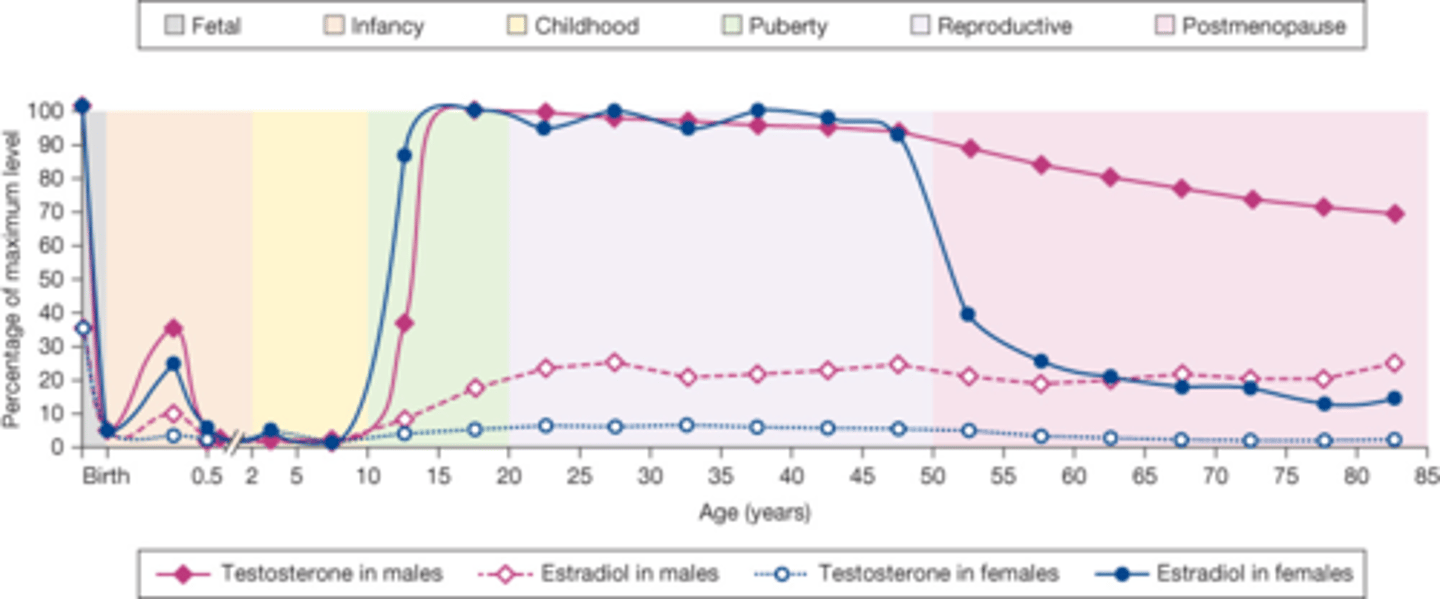
Sex hormone levels throughout life
Esterogen
refers to a steroid hormone that is important in the reproductive deveopment in females
Estrogen is produced by
the growing grafian follicle
Estrogen is secreted by
ovaries prior to ovulation: also produced by the placenta during pregnancy
Estrogen secretion is regulated by
FSH
Estrogen is involved in the formation and maintenance of
secondary sex characteristics also important in bone resorption
Estrogen is involved in the enlargement of
the uterus and breasts during pregnancy
Progesterone refers to a
steroid hormone that prepares the uterus for pregnancy
Progesterone is produced by the
corpus luteum
Progesterone is secreted by
the ovaries after the ovulation: also produced by the placenta during pregnancy
Progesterone secretion is regulated by
LH
Progesterone is involved in the formation and maintenance of
the endometrium and uterus
Progesterone is involved in
the reduction of contractiliy of the uterus and stimulates the growth of mammary gland
Testosterone improves
the primary sex organs
Testosterone functions in
improving semen, semen production, achieving maturity of the penis and testicles
Pituitary tumor symptoms
enlargement of face, jaw, hands, and feet, weight gain, fatigue, low sperm count, blurry vision
Pituitary tumor treatment
A combination of medical therapy surgery and radiotherapy
Pituitary tumor effects of treatment
hypopituitarism, which would require permanent multiple hormone replacement therapy
Pituitary tumor prognosis
20% chance of remission after surgery to remove tumor. Will likely need hormone replacement for the rest of their life
Addison's disease (adrenal insufficiency) Symptoms
Weight loss, fatigue, irritability and depression
Addison's disease (adrenal insufficiency) treatment
Emergency medial treatment for adrenal crisis, followed by long-term medications such as corticosteroids
Addison's disease (adrenal insufficiency) effects of treatment
Sleep problems, changes in menstrual cycle, acne, dizziness, nausea
Addison's disease (adrenal insufficiency)
should recover and be able to lead a relatively normal life, although will need to take medications indefinitely
Grave's disease (hyperthyroidism) Symptoms
Anxiety, mild fever, compression in chest, heart palpitations and tachycardia
Grave's disease (hyperthyroidism) Treatment
Radioactive iodine therapy, anti-thyroid medications, and surgeries
Grave's disease (hyperthyroidism) Prognosis
Symptoms can likely be managed with the right medications, but surgery to remove part of thyroid gland could be an option
Myasthenia gravis (due to thymic hyperlasia) Symptoms
Hoarseness of voice, nasal regurgitation of liquids, difficulty chewing, swallowing, and speaking
Myasthenia gravis (due to thymic hyperlasia) Treatment
Medication such as cholinesterase inhibitors, corticosteroids, or immunosuppressants; possible surgery
Myasthenia gravis (due to thymic hyperlasia) Effects of Treatment
Diarrhea, nausea, excessive salivation
Myasthenia gravis (due to thymic hyperlasia) Prognosis
There is no cure for Myasthenia gravis, though treatments can help some of the symptoms
Hypocalcemia (hypoparahyroidism) symptoms
Muscle rigidity and cramps, tremors and twitching, abnormal movements of hands and feet
Hypocalcemia (hypoparahyroidism) treatment
calcium and vitamin D supplements, PTH injection
Hypocalcemia (hypoparahyroidism) effects of treatment
hypercalcemia, osteosarcomas
Hypocalcemia (hypoparahyroidism) prognosis
Will likely be able to lead a normal life with treatments
Pineal and pituitary gland issues (damage from traumatic brain injury) symptoms
difficulty sleeping at night, weight gain, dry skin
Pineal and pituitary gland issues (damage from traumatic brain injury) treatment
hyperthyoidism, headache, dizziness, nausea, drowiness
Pineal and pituitary gland issues (damage from traumatic brain injury) prognosis
Traumatic brain injuries can cause lifelong damage to structures, but it is possible the brain will recover over time
Hypopituitarism symptoms
delayed development of teeth, below average height, above average weight
Hypopituitarism treatment
growth hormone replacement therapy
Hypopituitarism effect of treatment
Allergic reactions, joint pain, headaches
Hypopituitarism prognosis
After years of treatment, if is likely that the patient will grow to rach their full adult height