Bootcamp.com - Integumentary System
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
what are the key components of the integumentary system?
skin, hair, nails, glands, and nerves
from superficial to deep, the three distinct layers are ______, ______, ______
epidermis (epi = above), dermis, and hypodermis
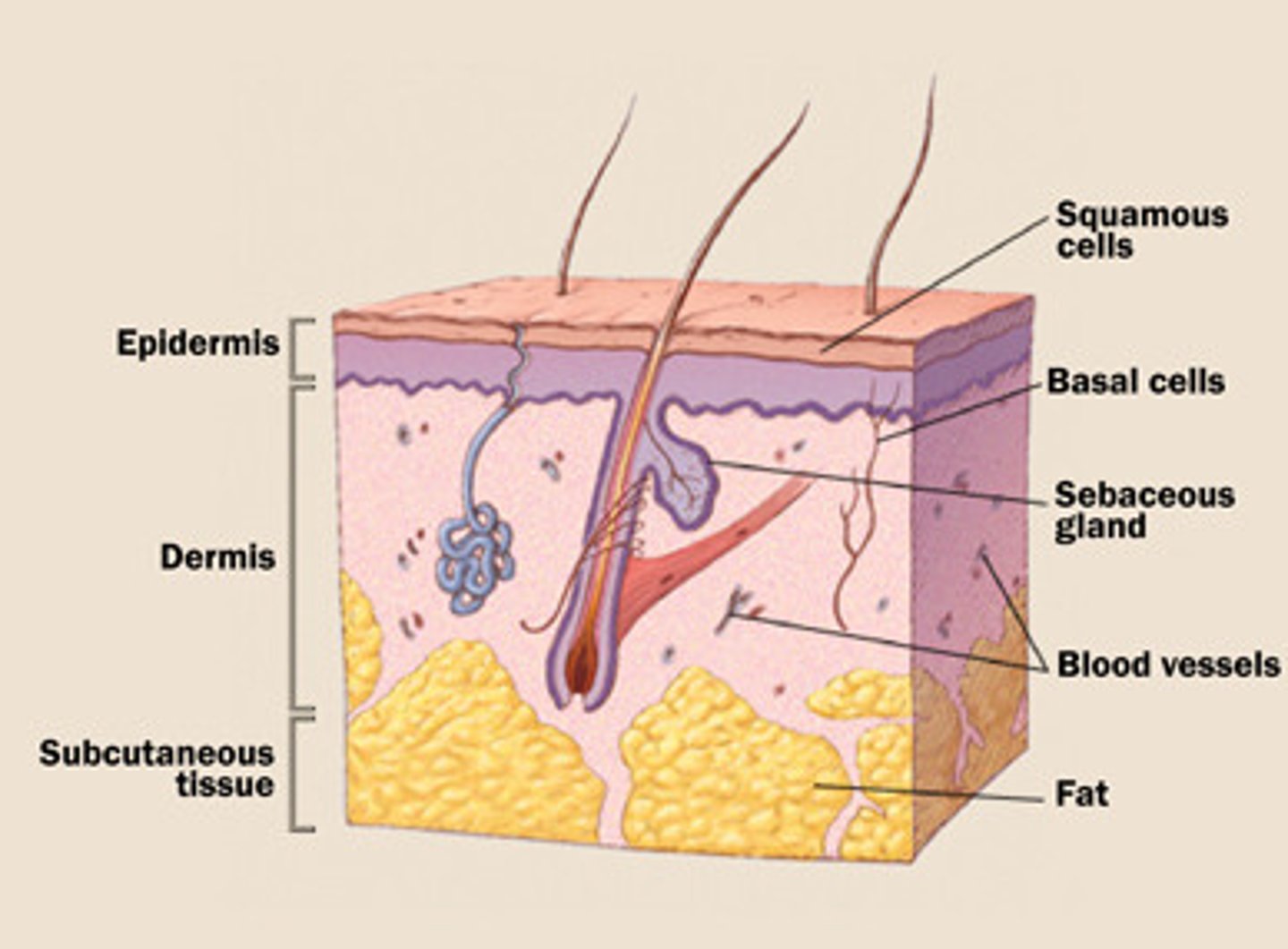
is the skin composed of the hypodermis?
no, the "skin" is only composed of the epidermis and dermis
the epidermis is the most _____ layer of the skin, and it is thin and avascular
superficial
does the epidermis contain blood vessels?
no, the epidermis is avascular, meaning it does not contain blood vessels!
the _____ protects us from dehydration, UV radiation, and pathogens
epidermis
the epidermis receives oxygen and nutrients from the blood supply of the ______
dermis (papillary dermis is also an acceptable answer)
the epidermis is composed of ______ cells, which are flattened, disk-shaped cells arranged into multiple layers
stratified squamous
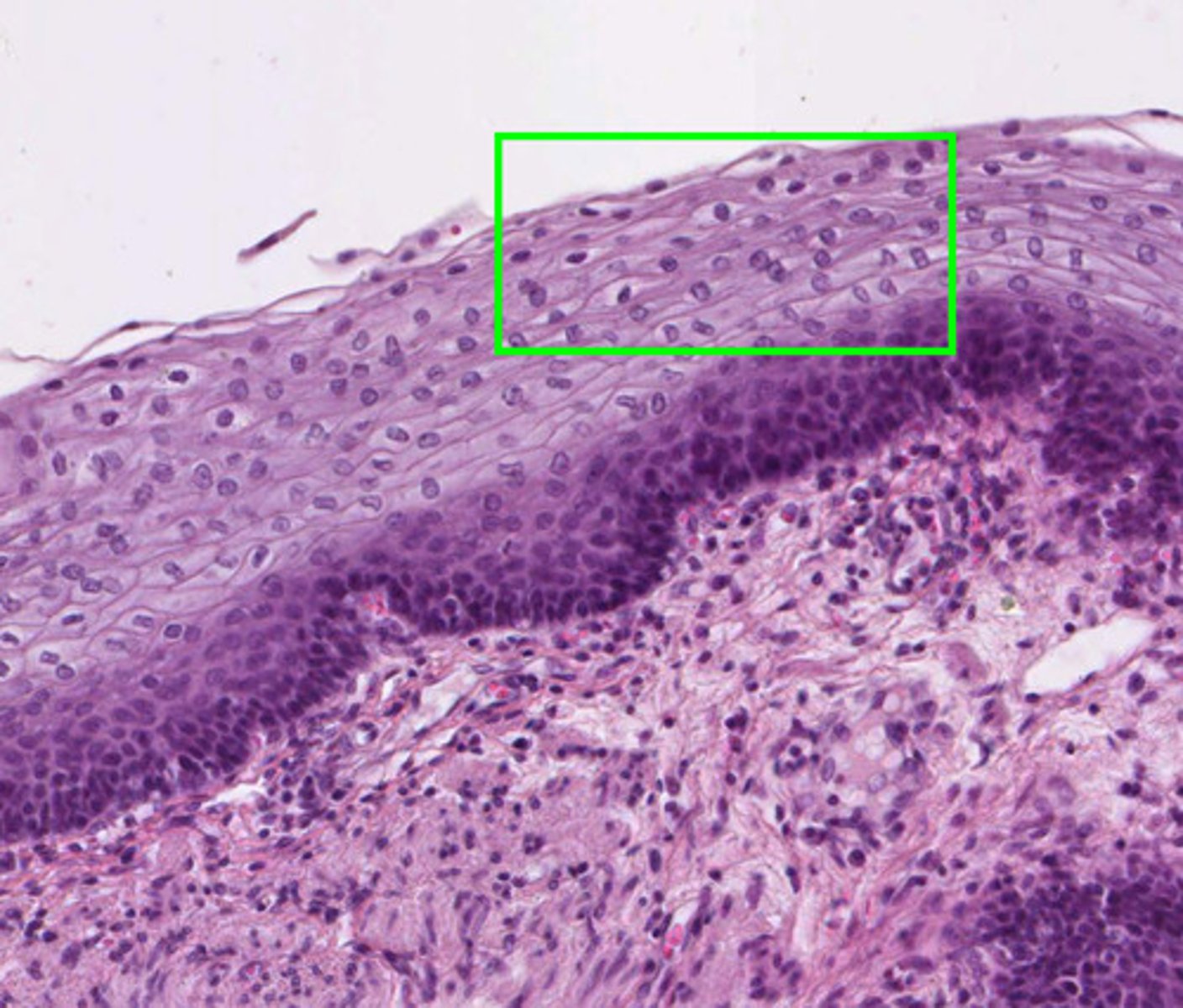
the epidermis has 4 to 5 layers, which are mostly ______
keratinocytes
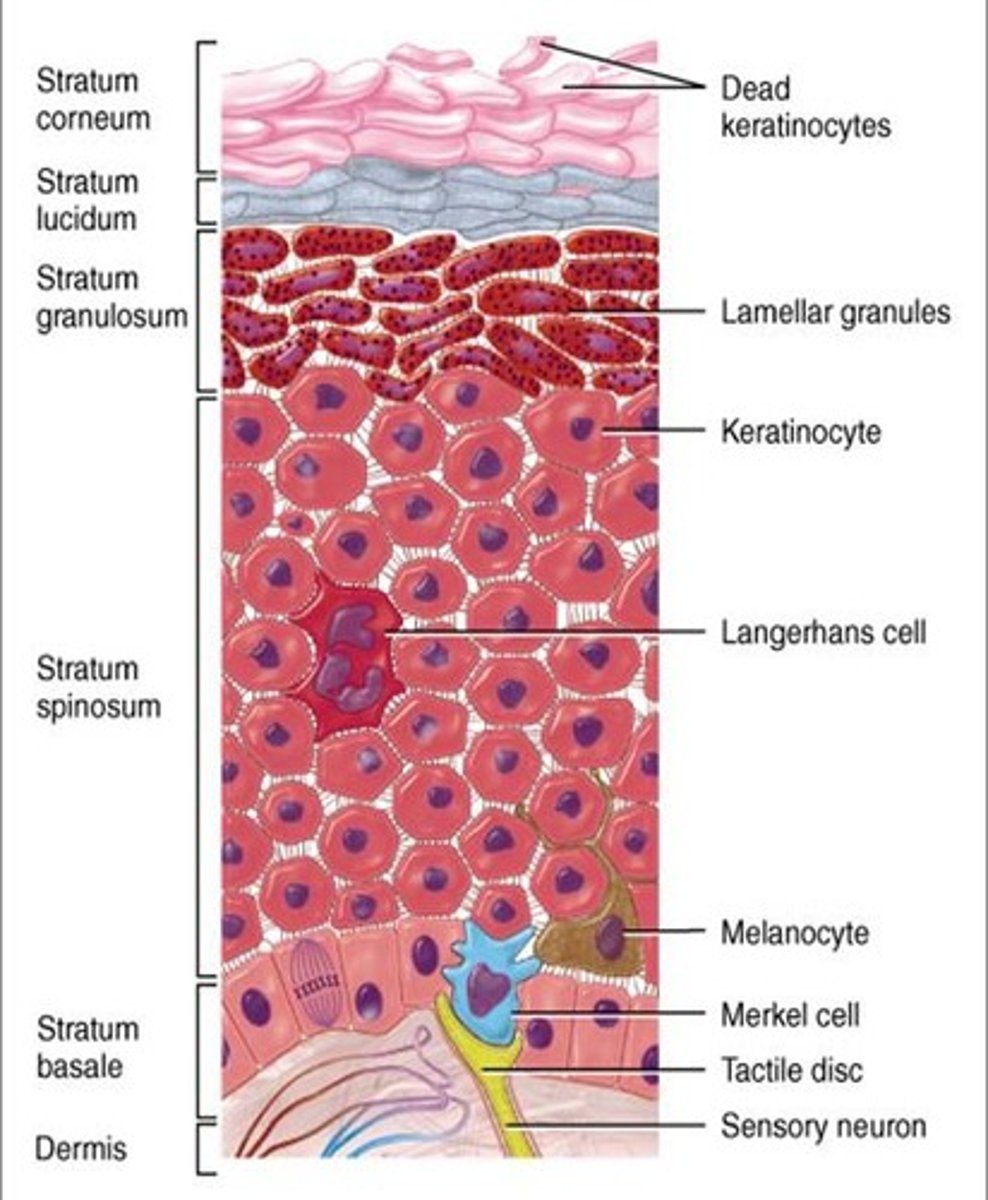
as keratinocytes divide and differentiate, they migrate from the ______ to more ______ layers
deeper; superficial
when keratinocytes migrate, they expel their ______ and produce additional ______
nuclei; keratin
eventually, fully differentiated keratinocytes are shed during ______
epidermal turnover
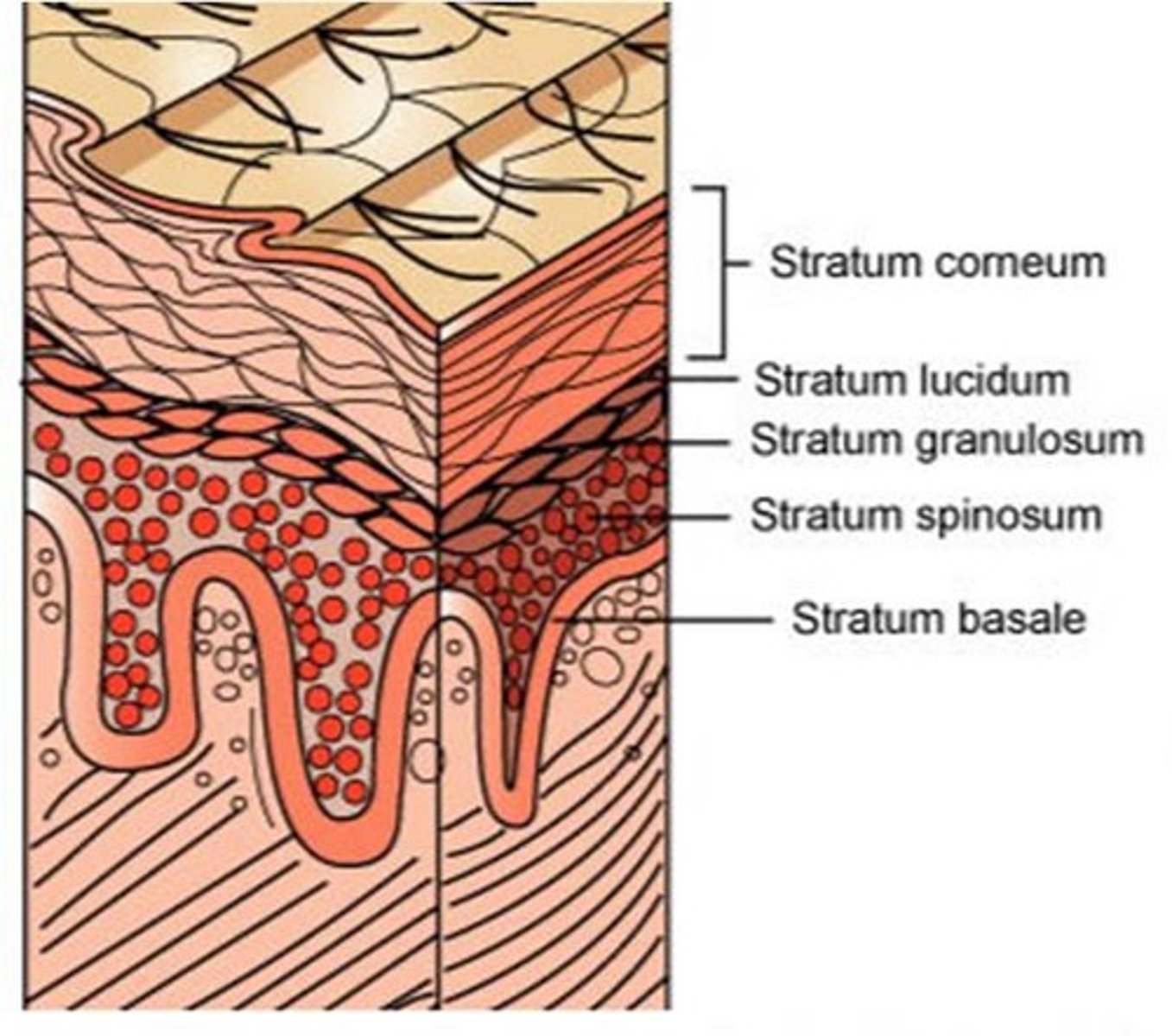
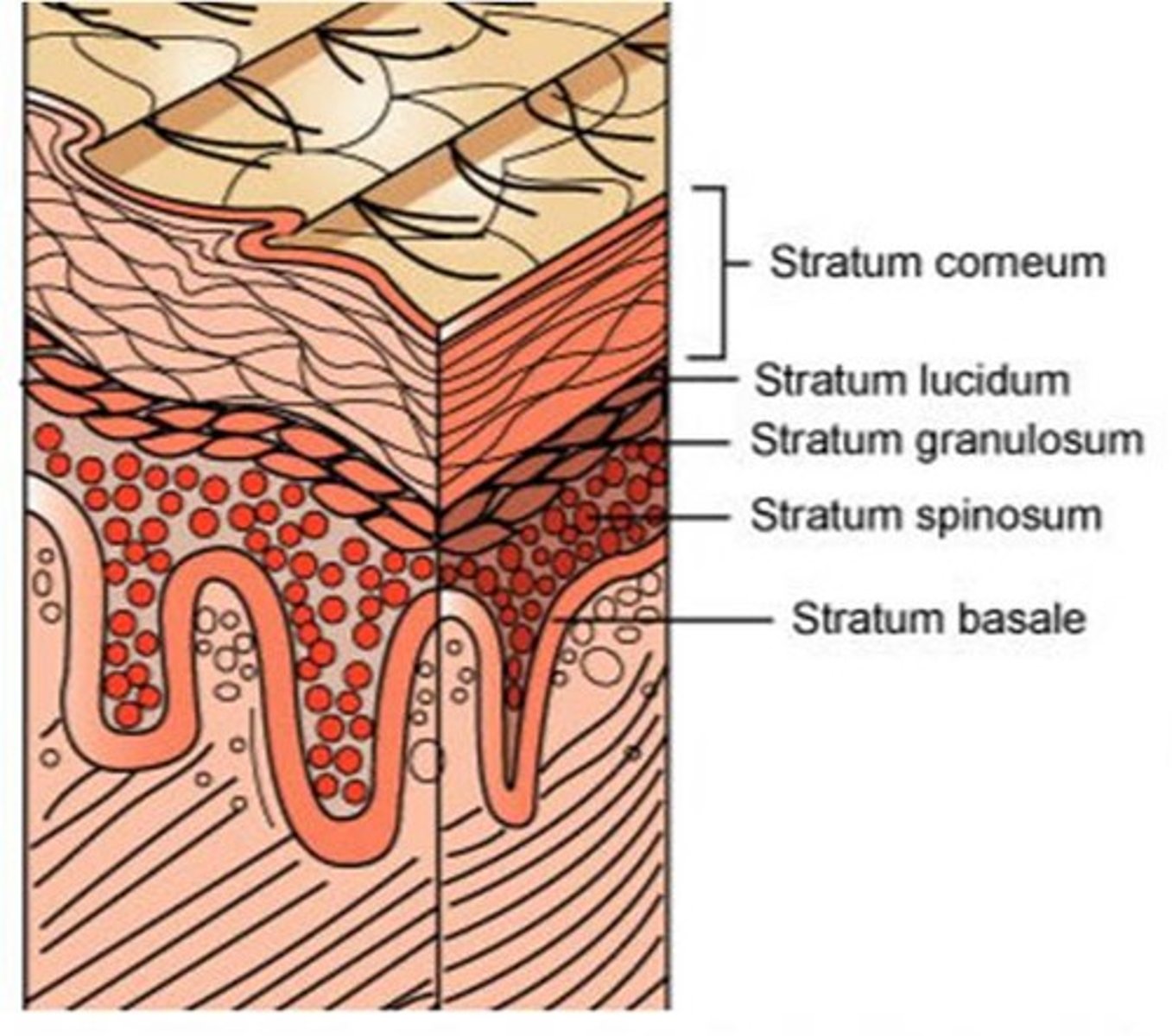
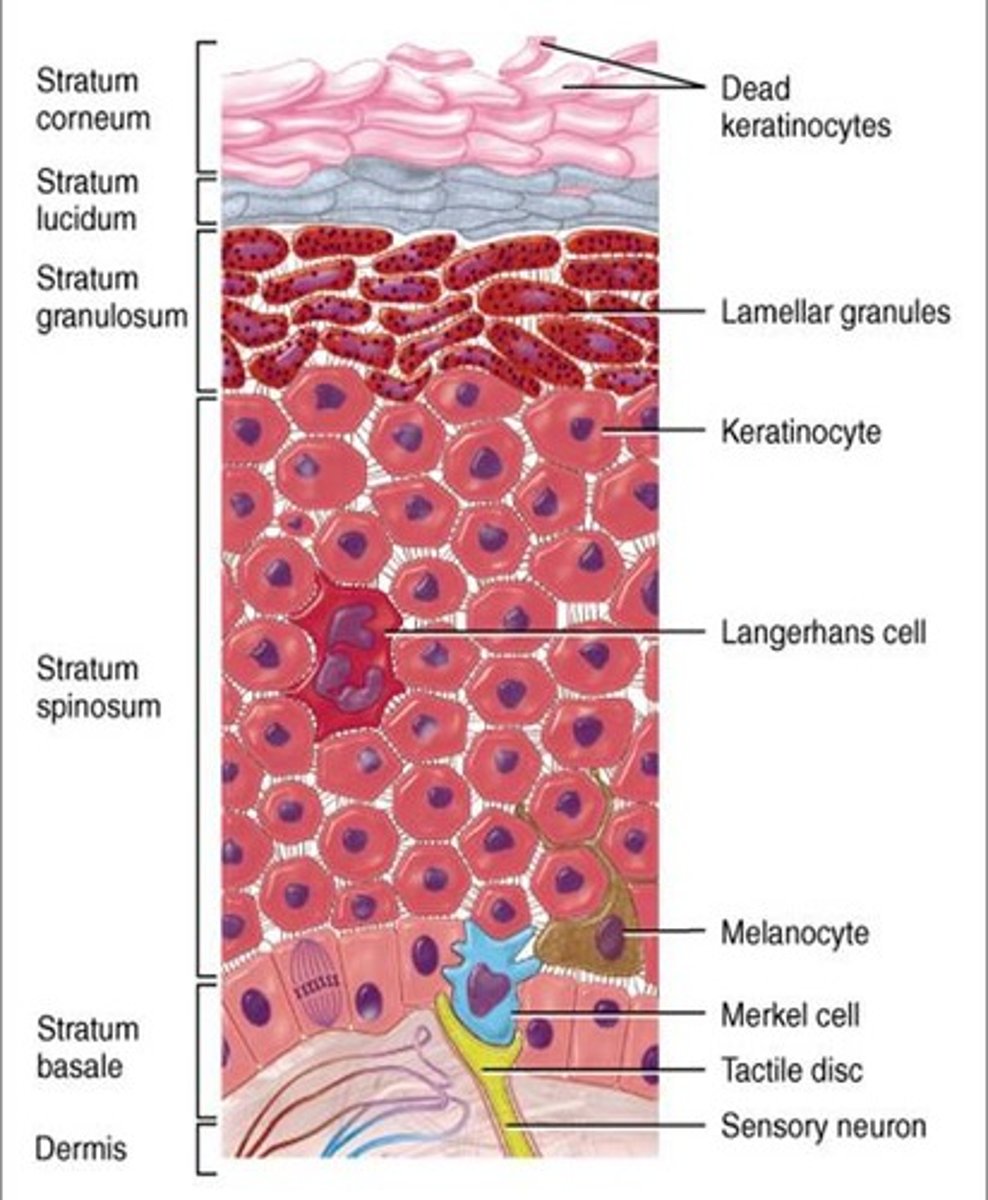
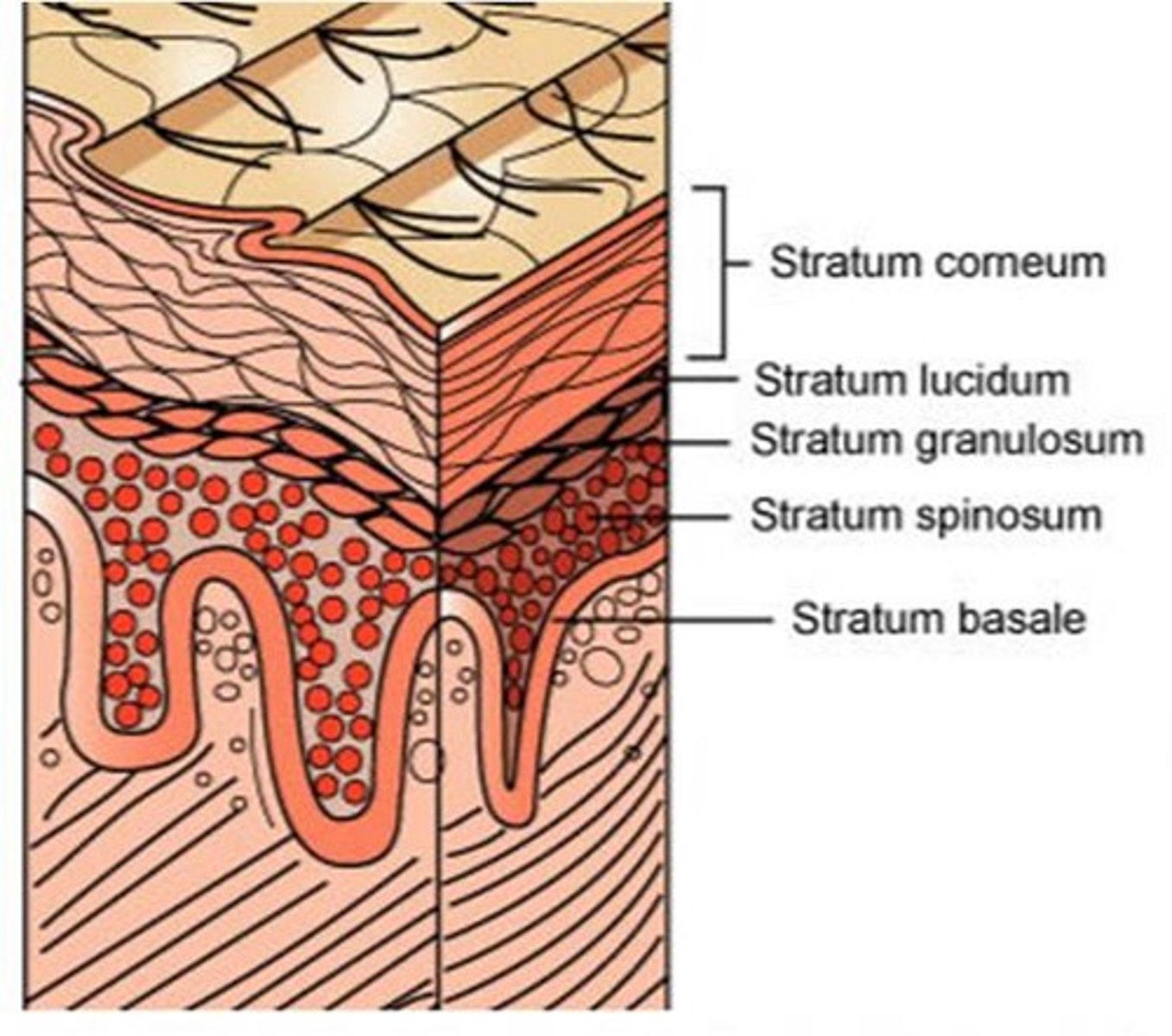
the 5 layers of the epidermis from superficial to deep are ______
1. stratum Corneum
2. stratum Lucidum
3. stratum Granulosum
4. stratum Spinosum
5. stratum Basale
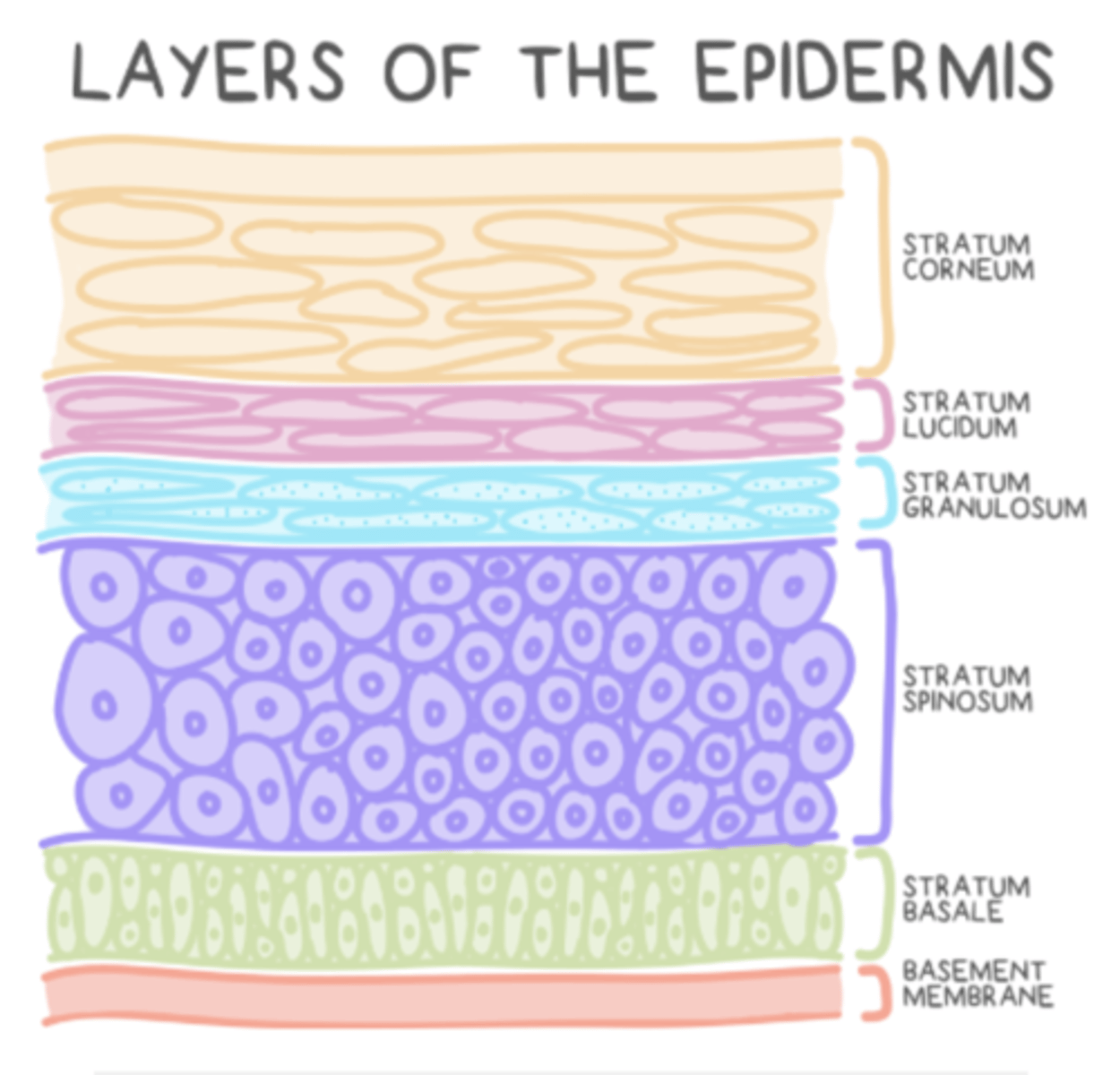
what are some mnemonics to remember the order of the 5 layers of the epidermis from superficial to deep?
Come Lets Get Some Beers/Come Lets Go Sun Bathing
stratum Corneum
stratum Lucidum
stratum Granulosum
stratum Spinosum
stratum Basale
the stratum corneum is composed of dead, fully differentiated keratinocytes known as ______
corneocytes
corneocytes are flattened cells of ______
keratin
the stratum _____ provides protection against infection, dehydration, and physical harm
corneum
the stratum ______ has dead keratinocytes like the stratum corneum; however the keratinocytes are not fully differentiated into ______
lucidum; corneocytes
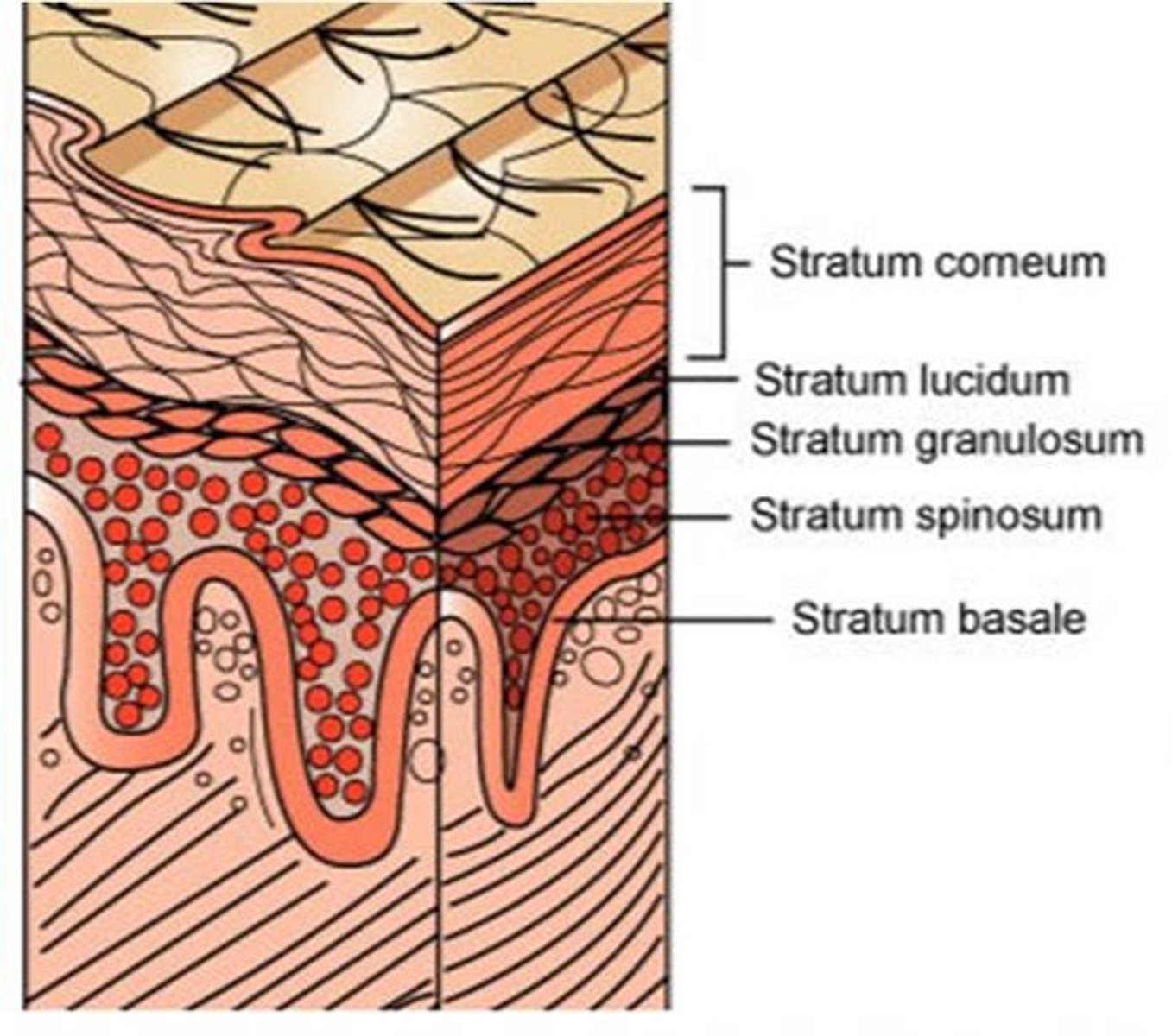
the stratum lucidum is only present in the _____ and the _____
palms of the hand; soles of the feet
the stratum granulosum is mostly ______ that migrated from the stratum ______
keratinocytes; spinosum
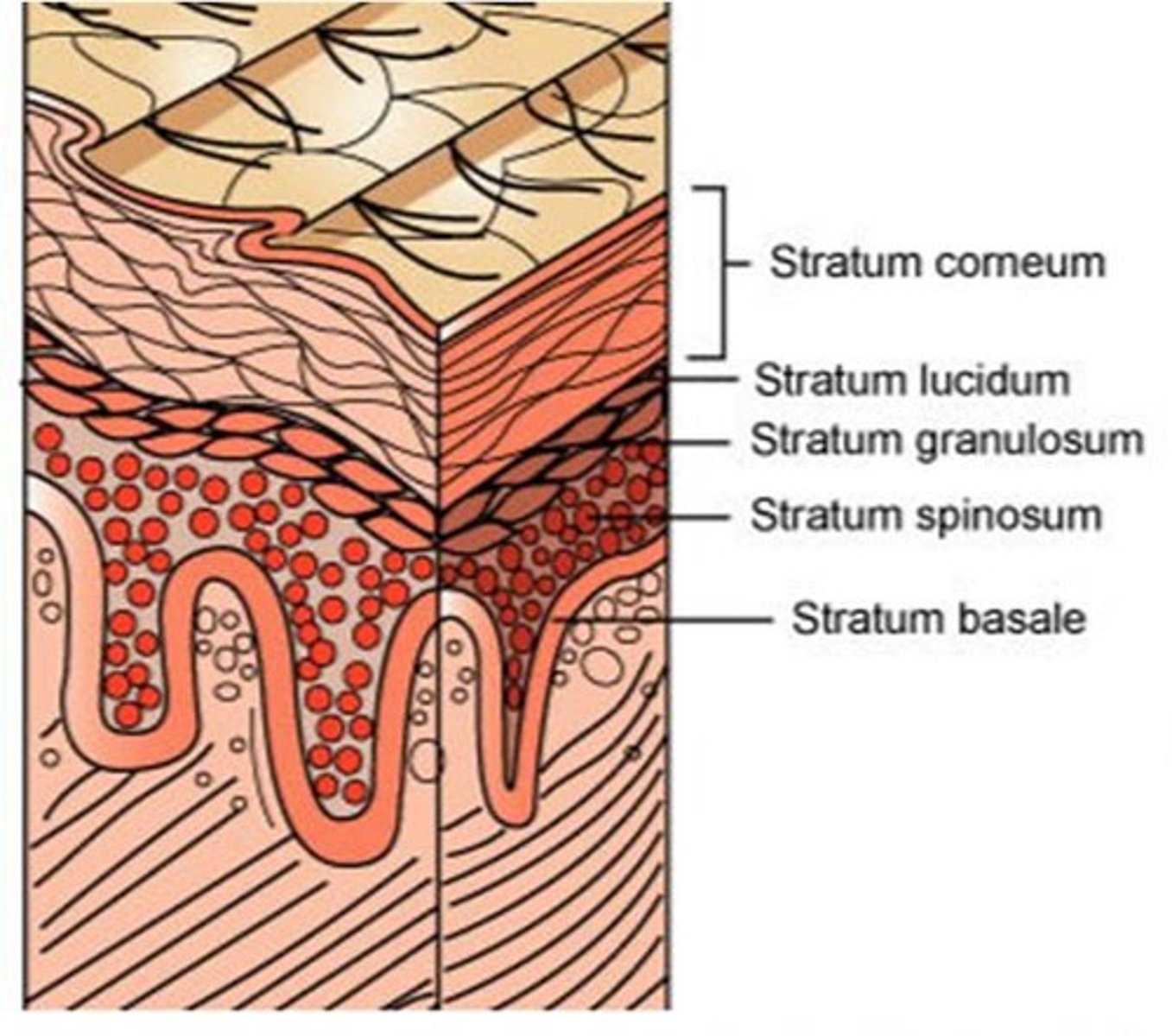
the keratinocytes in the stratum granulosum secrete ______ that form lipid-containing, hydrophobic membrane. This helps create the skin's ______
lamellar bodies; water barrier
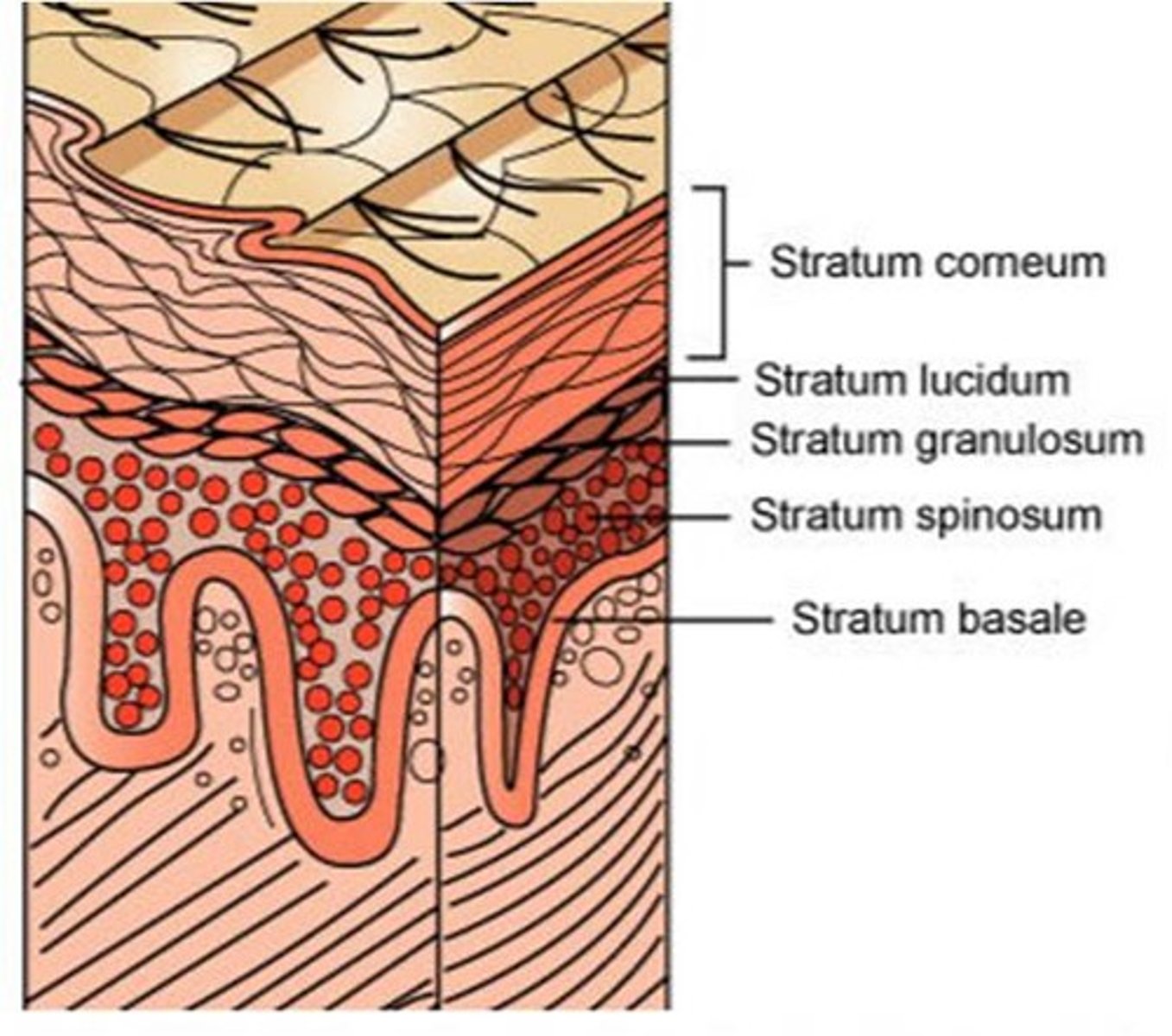
the stratum spinosum provides skin with strength and flexibility because of its high prevalence of _____ that hold keratinocytes together
desmosomes

the stratum spinosum contains the highest prevalence of _____ cells of all the epidermal layers
Langerhans
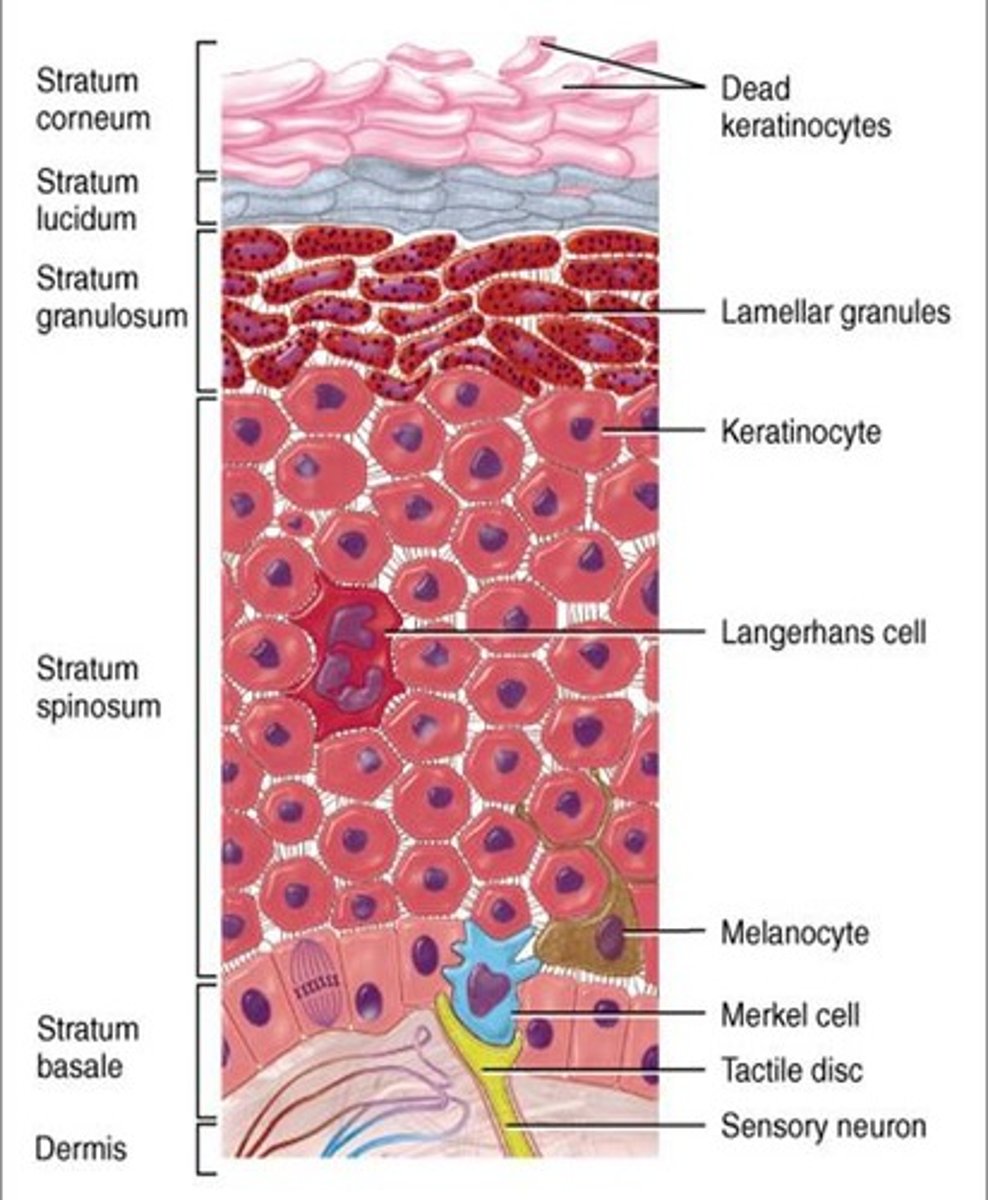
Langerhans cells, which are the ______ cells of the epidermis. This is because the are intregral to communication between the _____ and _____ immune systems
dendritic;
innate; adaptive
the stratum _____ provides continuous renewal of the epidermal ______, via keratinocyte stem cells
basale; keratinocytes
_____ are located in the stratum basale, and they generate the pigment melanin
melanocytes
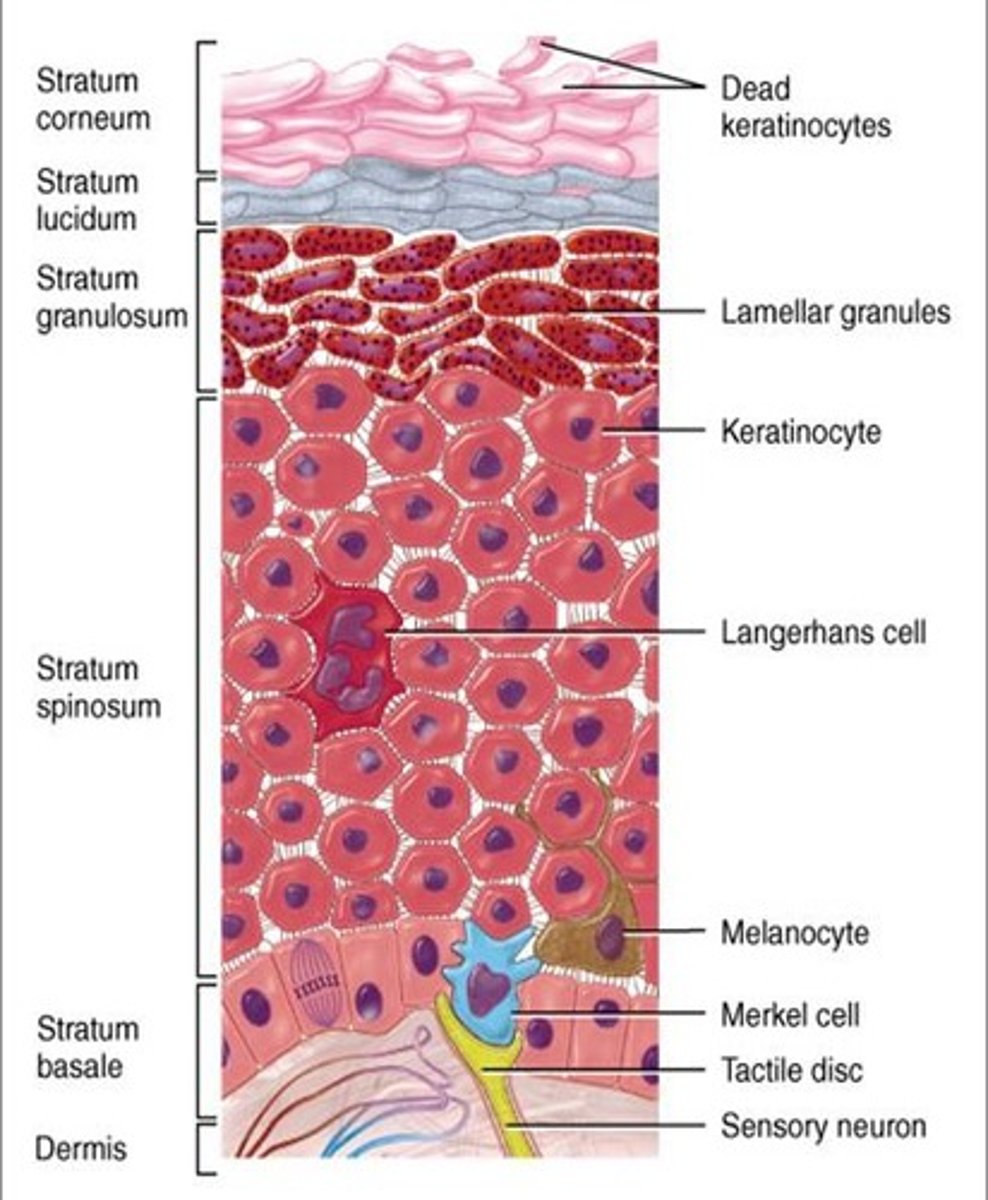
melanin is transported to ______, and it is responsible for the skin's ______ and protection from ______
keratinocytes; pigmentation; UV radiation (this is why individuals with greater levels of skin pigmentation generally have lower levels of skin cancer)
______ cells are located in the stratum basale, and they are specialized mechanoreceptor cells
Merkel
Merkel cells are specifically attuned to respond to _____ touch sensations, which is why they are extremely abundant in finger tips
light
each Merkel cell synapses with a ______ (hint: "body") afferent nerve fiber, which conveys the message to the central nervous system
somatosensory (somato = body)
a ______ is a cell that has the ability to respond to external stimuli
mechanoreceptor
the dermis is located just deep to the ______
epidermis
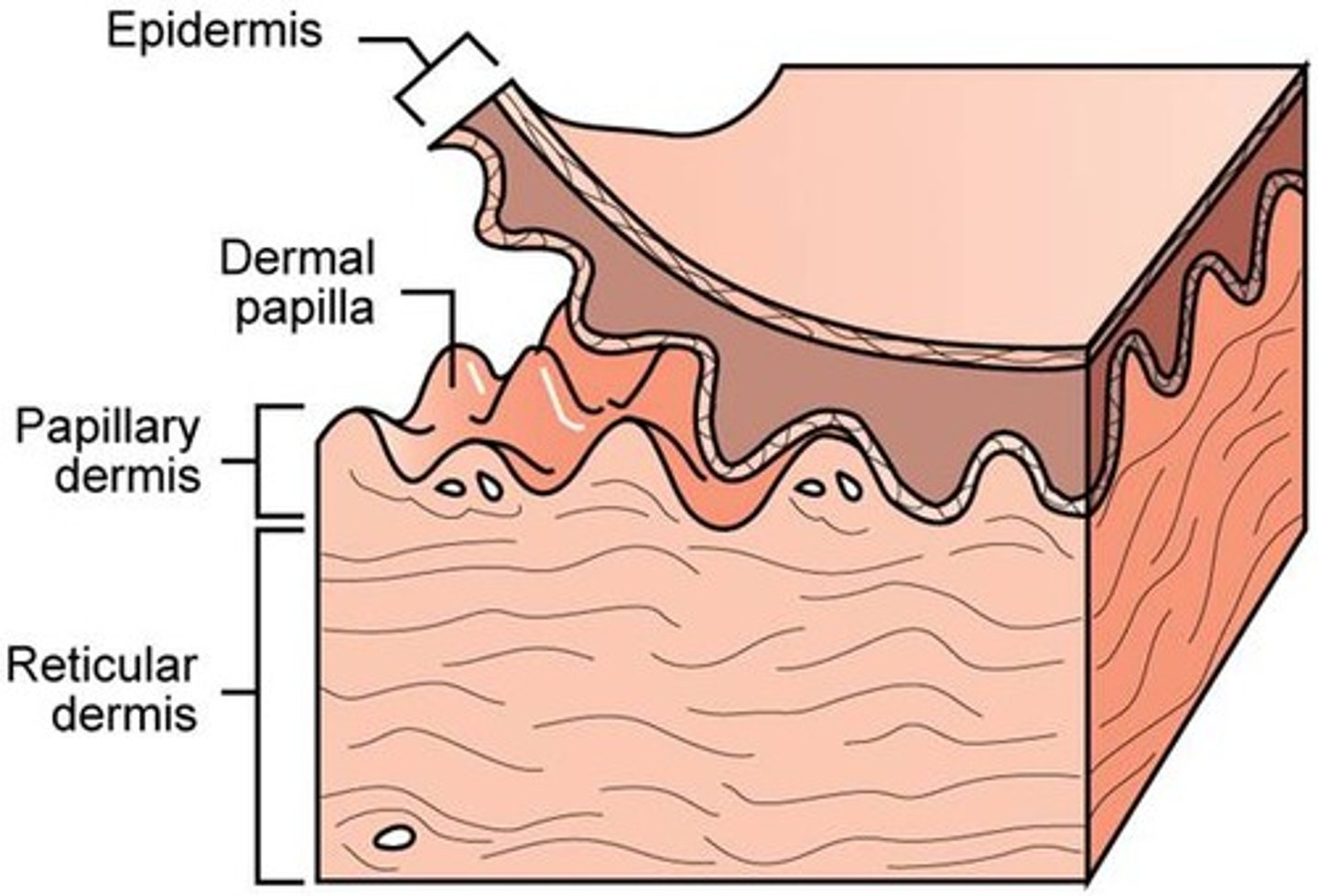
the _____ is a network of dense irregular connective tissue
dermis
the dermis functions to cushion the body from injury and provide a home for functional structures of the skin - what are some examples of those structures?
vessels, glands, nails, and hair
the dermis has ______ layers
2
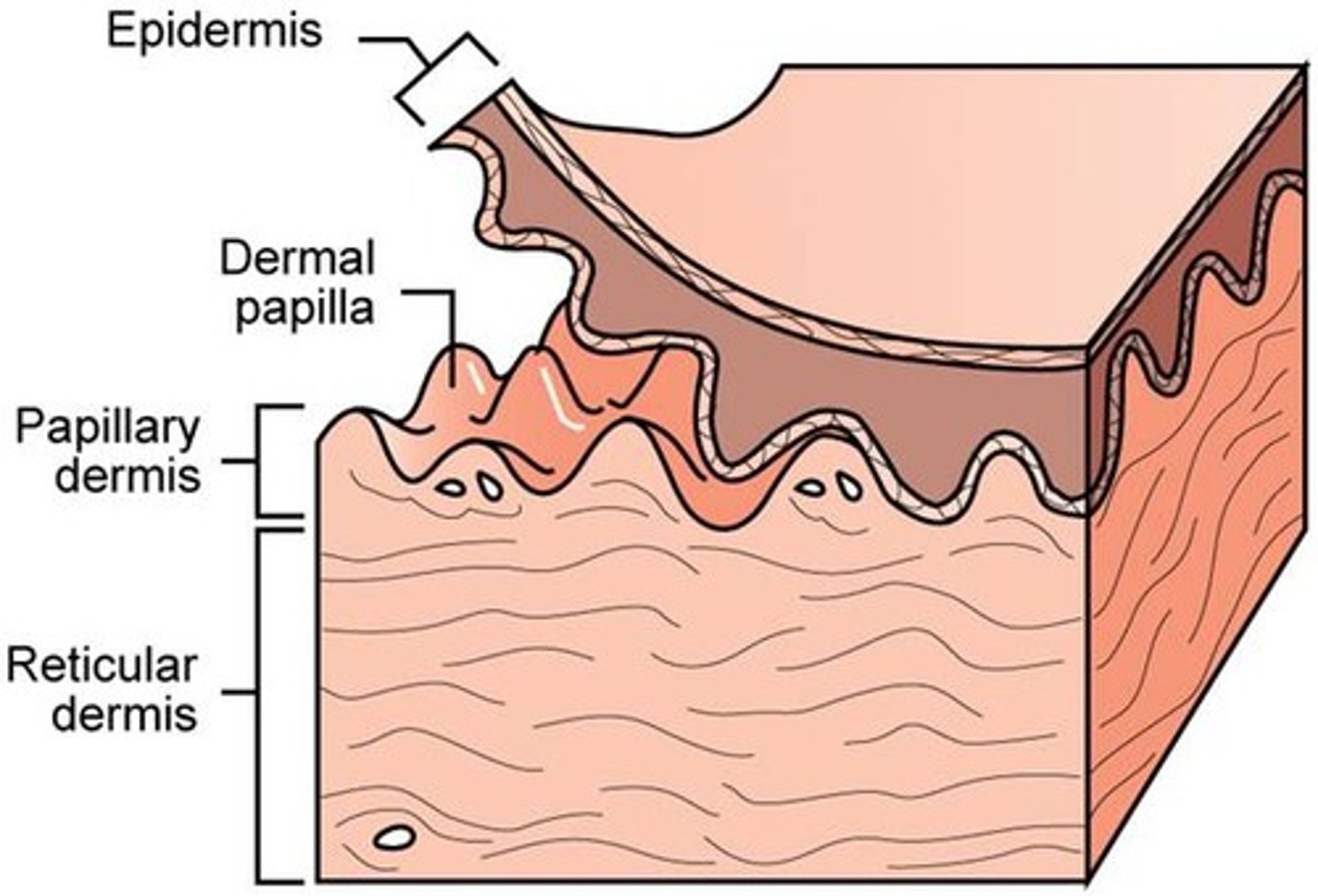
the papillary dermis is named for its _____, which are small nipple-like, upward projections of the dermis towards the epidermis
dermal papillae
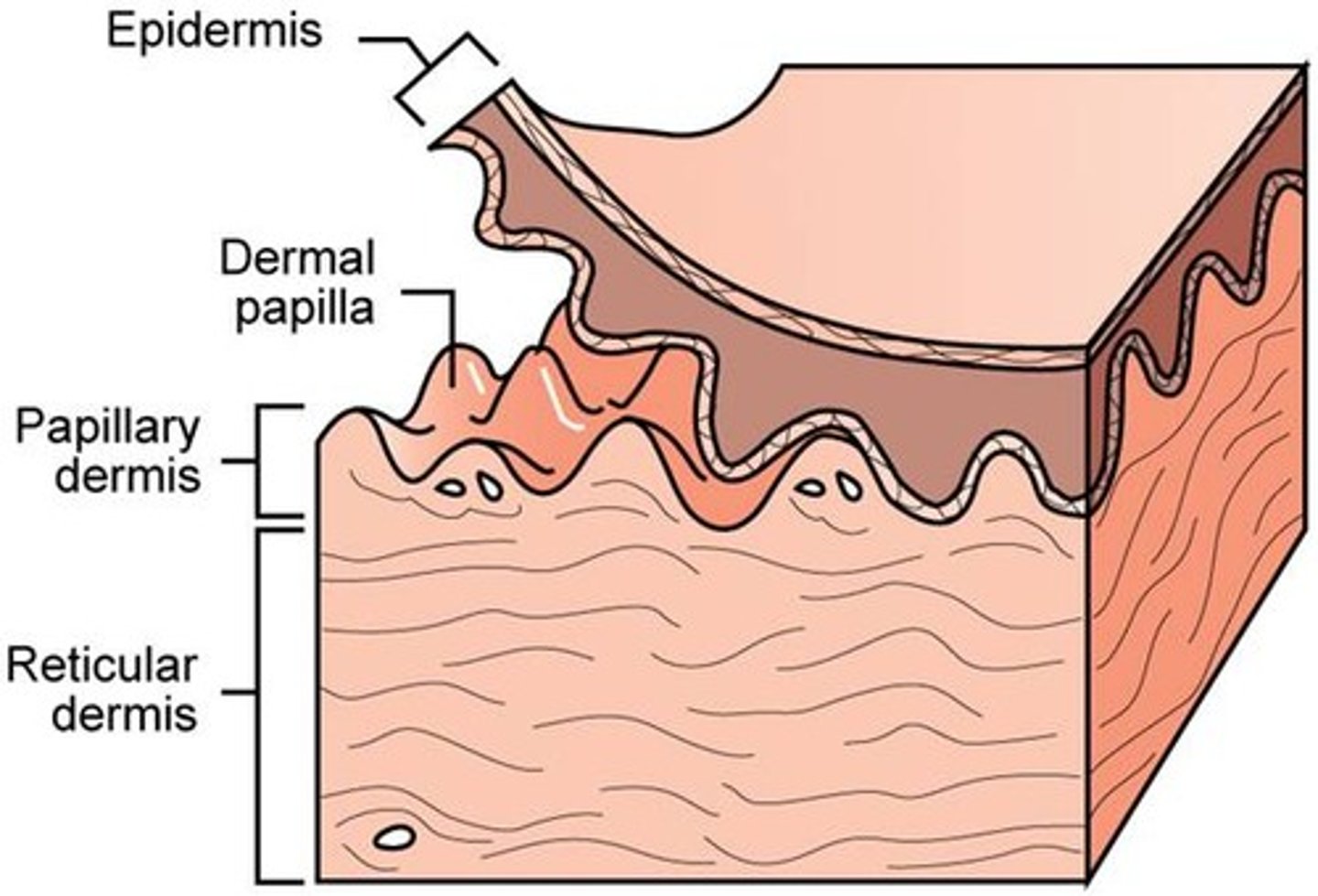
the more superficial, thinner layer is the ______ dermis, the deeper and thicker layer is the _______ dermis
papillary; reticular
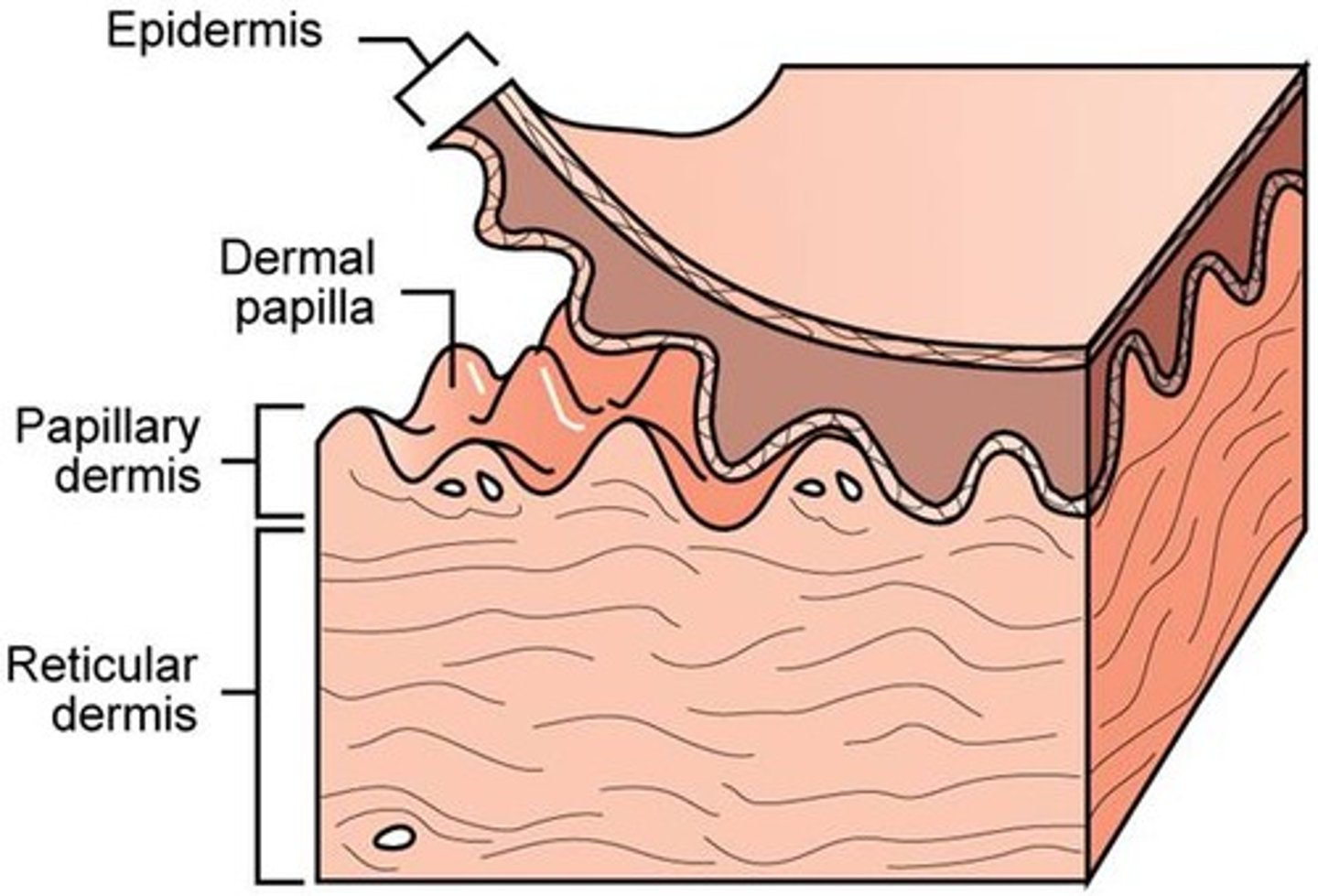
the ______ create our fingerprints and increase the surface area between the dermis and epidermis
dermal papillae
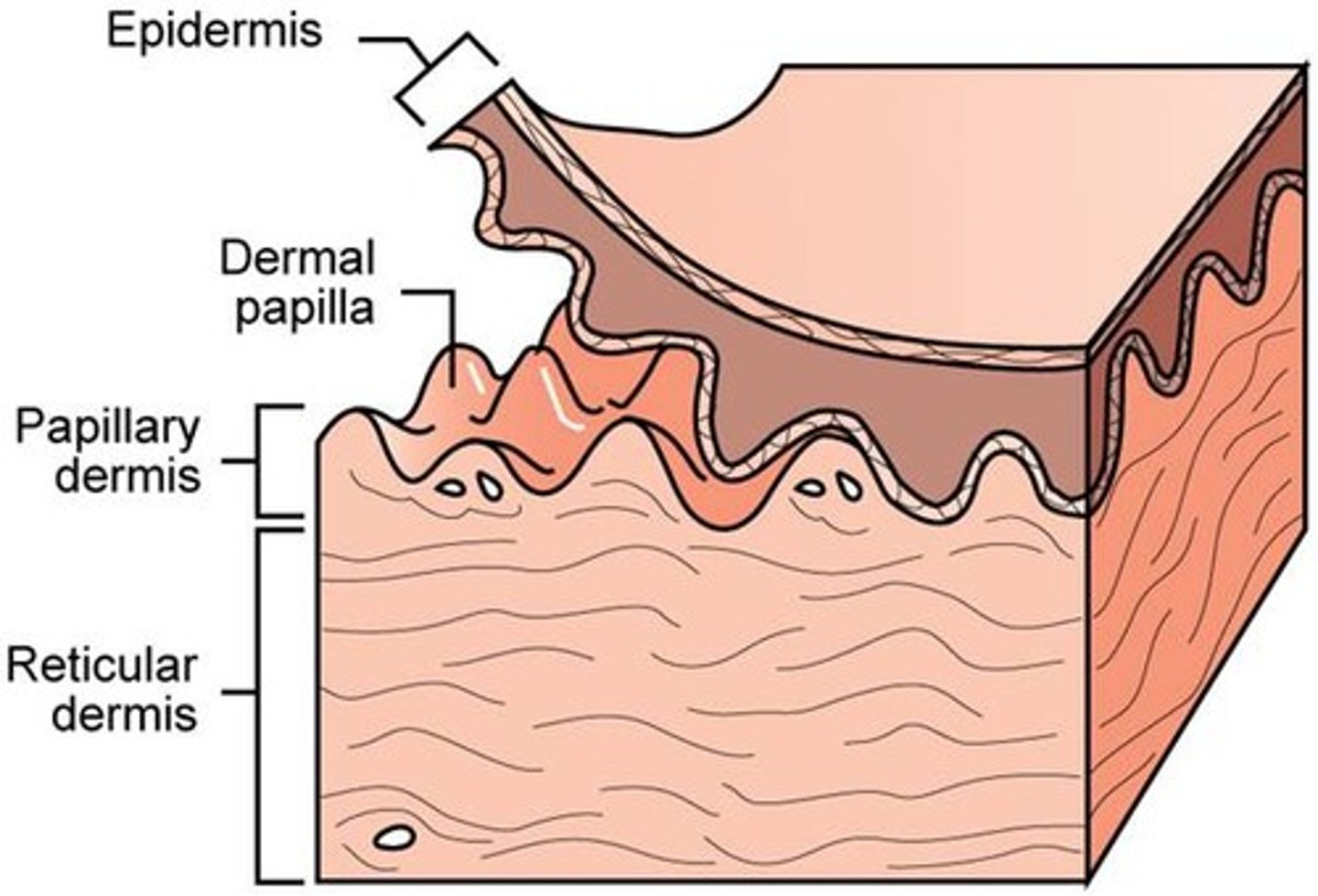
why is it good that the dermal papillae increase the surface area between the epidermis and dermis?
it increases the capacity for delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the epidermis, which relies on the blood vessels of the papillary dermis for nourishment and waste removal;
increases the strength of the junction between the dermis and epidermis
_____ and _____ are present within the dense, irregular connective tissue of the reticular dermis
collagen; elastic fibers
reticular fibers make the reticular dermis _____ and _____
strong; elastic
the _____ dermis contains blood vessels, sensory receptors, hair follicles, nail beds, and glands
reticular
______ generate hair and keep it attached to the body surface
hair follicles
hair is a _____ filament that protects mammals from ______ and ______
keratin protein; UV radiation; hypothermia
_____ attach to hair follicles to erect the hair
erector pili muscles
*think of "goosebumps," in some mammals it plays a role in temperature regulation and scaring off predators
_____ glands are composed of specialized cells that create and secrete a product through a duct to an external surface, such as the skin or GI tract
exocrine
______ glands are exocrine sweat glands
sudoriferous
sudoriferous glands come in two types: ______ and ______, which differ in their location and product
eccrine; apocrine
______ glands are the main sweat glands of the body, and they are important for ______regulation
eccrine; thermo (thermoregulation is regulation of body temperature)
eccrine glands are located throughout the entire body surface, but they are most abundant in the ______ (armpit), palms of the hands, and the soles of the _____
axilla (armpit); feet
apocrine glands have more ______ and ______ sweat secretions than eccrine glands
oily; viscous
unlike eccrine glands, apocrine glands secrete their products into the _____ and are found in specific locations
hair follicle
what are some of the specific locations where apocrine glands are found?
armpit, nipple, ear canal, eyelid, nostril, and parts of the pubic area
______ glands are specialized apocrine glands that product ear wax
ceruminous glands
ceruminous glands produce _____, which is secreted into the external auditory canal
earwax (cerumen)
______ glands are specialized apocrine glands that produce milk
mammary
mammary glands are located below the ______
nipple (areola)
_____ glands secrete oily and waxy products (sebum) into the hair follicle
sebaceous
sebum ______ and ______ the hair and surrounding skin
lubricates; waterproofs
sebaceous glands are located throughout the entire body surface with the exception of the _______ and the ______
palms of the hands; soles of the feet
the ______ is located beneath the dermis, and it is not considered to be a part of the skin
hypodermis (hypo = below)
(part of the integumentary system)
the hypodermis is also called the ______ tissue
subcutaneous
the _____ contains larger nerves, blood vessels than those in the dermis
hypodermis
the main components of the hypodermis are ______ tissue and ______ tissue
loose connective; adipose (fat)
the main function of the hypodermis is _____
fat storage
it helps to conserve body heat, and it helps prevent injury by acting as a shock absorber
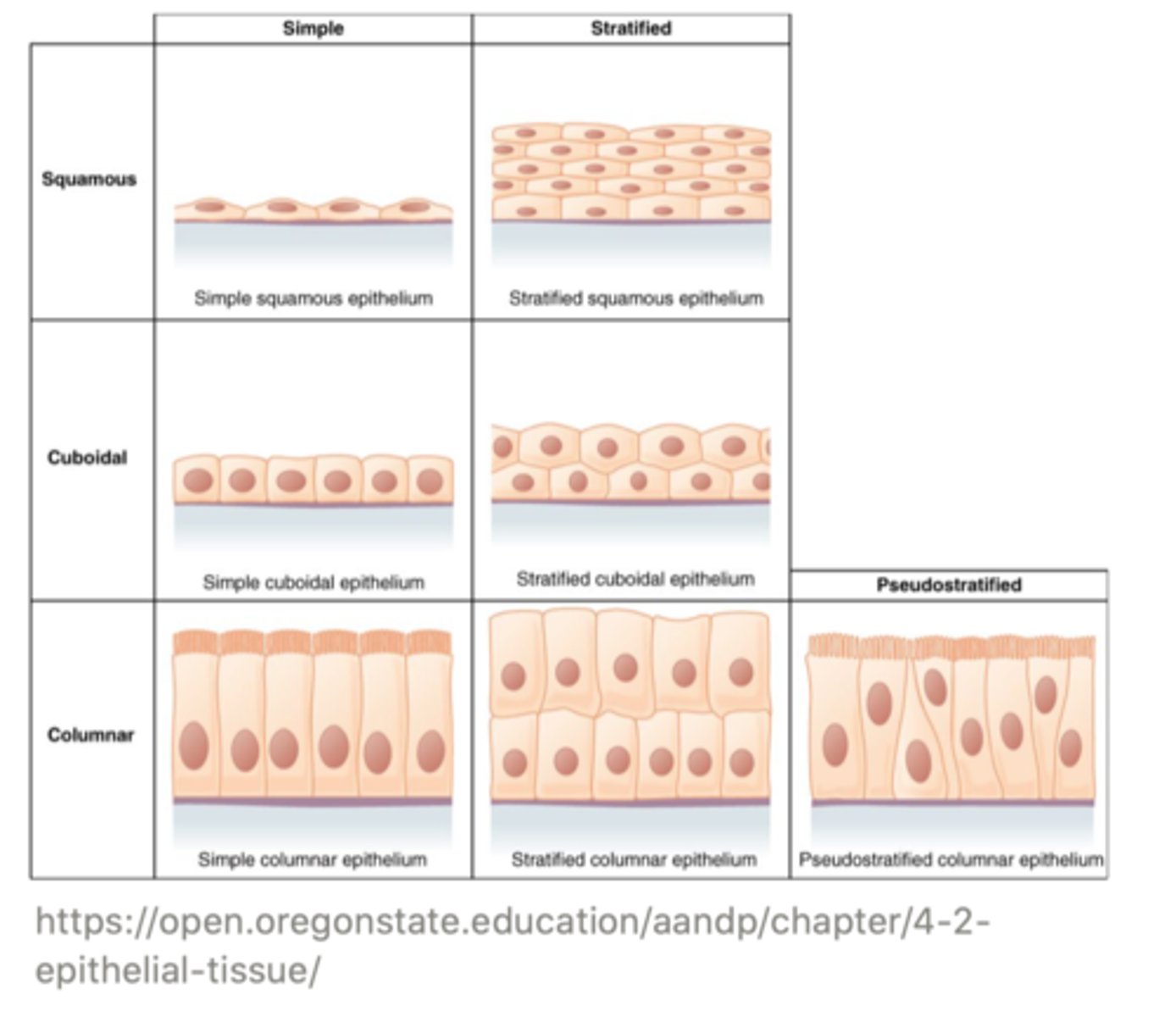
There are three types of epithelial cells, which are based on their ______
shape
the three types of epithelial cells are ______ (flattened); ______ (as wide as they are tall); and _______ (taller than they are wide)
squamous; cuboidal; columnar
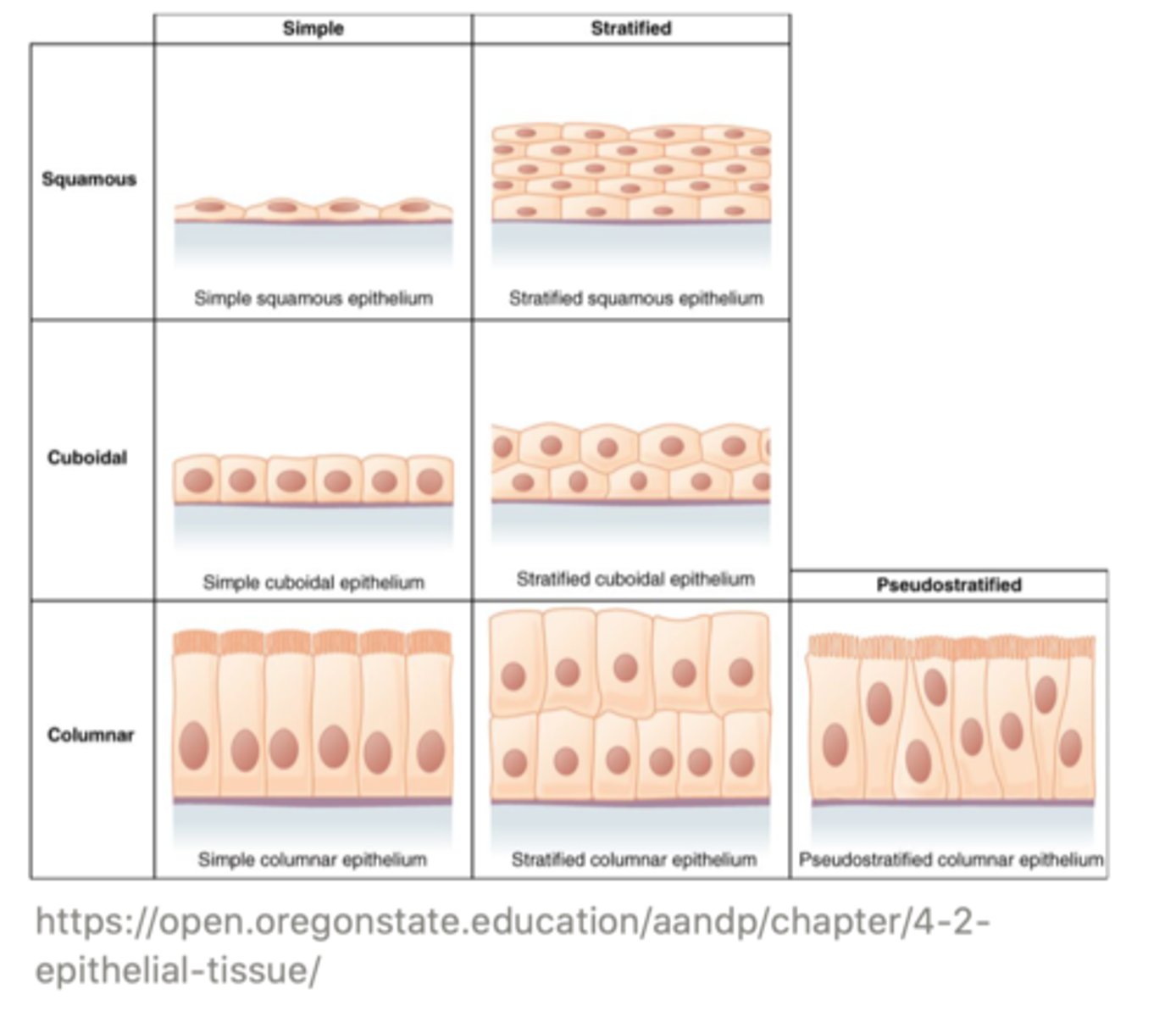
if the epithelial cells are arranged as a single layer, it is referred to as ______; however, if they are arranged in multiple layers, they are considered ______
simple; stratified