First Semester AP Psychology (all units)
1/309
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
310 Terms
What is nature?
how they were born; enate to that person
What is nuture?
how they were raised; external or environmental
Evolutionary perspective
-BIOLOGICAL: genetic mutation—>survival; reproduction
-PSYCHOLOGICAL: thinking/feeling/preferences
Biological perspective
-Brain Structures (like tumors, etc.)
-Chemistry (Neurotransmitters and hormones)
-Genetics (traits, characteristics, and disorders)
Behavioral Learning Perspective
-blank slate—>our experiences/environment
-observation (watching and mimicking)
-associations (±)
-reinforcement (rewards/punishments)
Sociocultural perspectives
-social norms (expected behaviors; reflects values within a culture)
-sub groups within cultures (gender, race/ethnicity, religion, or socioeconomic status)
Psychoanalysis/Psycho dynamic perspectives
-Sigmund Freud (founded the idea of psychoanalysis)
-unconscious actions—> repression
-childhood influences
Humanistic perspectives
-Hierarchy of Needs
Self Actualization (best version of ourselves)
Esteem
Belonging
Safety
Biological
Cognitive perspective
-how we think (though process, memory,problem-solving…etc)
-schema—> efficiency
-computer
-memory
Developmental Psychology
-lifespan
-think (ways that we think change as we get older)
-childhood—>death
Therapist/Counselor
-adjustment/emotional problems
-coping mechanisms
Issues to see a counselor: grief, bullying,trauma, depression, and relationships.
Clinical Psychologist
-mental disorders
-in a clinical setting (psych-ward, eating disorder clinics, and rehabs)
-diagnose
-treatment plans
-research
Psychiatrist
-prescribe medication
-talk therapy
School Psychologist
-assess students w/ learning problems
-emotional problems
-learning disabilities
-creates accommodations (504s/IEPs)
Educational Psychologist
-how kids learn
-special population (special Ed, EL)
Human Factors Psychology
-how to get people to use products correctly
Consumer Psychology
how to get people to buy products
Sport Psychology
-confidence
-pressure
-motivation/burn out
Forensic Psychology
-profiling
-court system/ law “insane”
-police assessment
Industrial Organizational
-researching the psychology in the work place
-employee motivation
-employee satisfaction
-management
Ethics (Humans)
No Harm (physical/psychological) cannot be long term or long lasting
Informed Consent (need to tell what the research entails)
Withdrawal (right to withdraw)
Limit Deception (allowed to withhold information, depending on the research)
Debrief (explain the whole experiment)
Protect Identity (anonymity/confidential)
Privacy
What is naturalistic observation?
“assumed consent” in public settings
Ethics (Animals)
Humane treatment (treat them as humane as possible)
Practical Application (should create a benefit to animals or Humans)
Relevant Harm (should be relevant to the study)
Euthanize (if lasting harm occurs)
Correlational Methods: Interviews
-asking people (individually or in groups)
-reactions
-Lies! (social desirability)
Correlational Methods: Survey
-multiple choice, open ended, likert
-scale, True/False
-anonymity
-easy/fast
-less detailed/limited
-framing/wording effects
Correlational Methods: Observation
-naturalistic “assumed consent” (authentic behavior; lack of control)
-lab (unauthentic)
Correlational Methods: Case Study
-one person or group
-rare (or abnormalities)
-unethical
Correlational Methods: Meta-analysis
-compile pre-existing research (to create new conclusions)
Correlational Methods: Archival
-documental (that exists or can be accessed)
Experiment (Cause-Effect) Method: Manipulate Variable
-Independent Variable (IV): changing/manipulate
-Dependent Variable (DV): measuring
-Confounding Variables
Experiment (Cause-Effect) Method: Control-Condition vs Experimental Condition
-Control Condition: gets “neutral stimulus”
-Experimental Condition: gets “treatment”
*Random Assignment- confounding variables
Experiment (Cause-Effect) Method: Single-Blind Vs Double Blind
-single blind: researcher knows, participant doesn’t
-double blind: neither knows (limit bias)
*placebo effect*
Random Sampling
-equal chance of being selected
Opportunity/Convenience Sampling
-random assignment
Purposive Sampling
-sampling with a purpose
Snowball Sampling
-when one person tells another person about the sampling an so on
Stratified Sampling
-relevant subgroups (proportional) “Generalizable”
Bias in Research
-confirmation bias
-hindsight bias
-overconfidence
Bias in participants
-screw you effect
-social desirability
-hawthrone effect
What are the measures of central tendency and what are each?
-Mean: “average”; (add all data terms, then divide by the # of data terms)
-Median: “middle value” (#s in order)
-Mode: “# that appears MOST frequently” (can be bimodal)
Having outliers does what to the data?
-skews it
High Outlier = positive skew
Low Outlier = negative skew
Range
(initial # - final #)
What is standard deviation?
how much the data deviates from the mean
What is a z-score?
a unit of standard deviation
What is inferential “Statistical Significance”?
-results that did not happen by chance
-sample size +different number of scores
What are correlations?
-relationship between two variables
-correlation does not equal causation
What is illusory correlation?
-appears to have correlation but does not
What is percentile?
when you do better than x% of people
What is a frequency histogram?
-a bar graph that touches each other
What is regression towards the mean?
replication; all new scores will go towards the mean
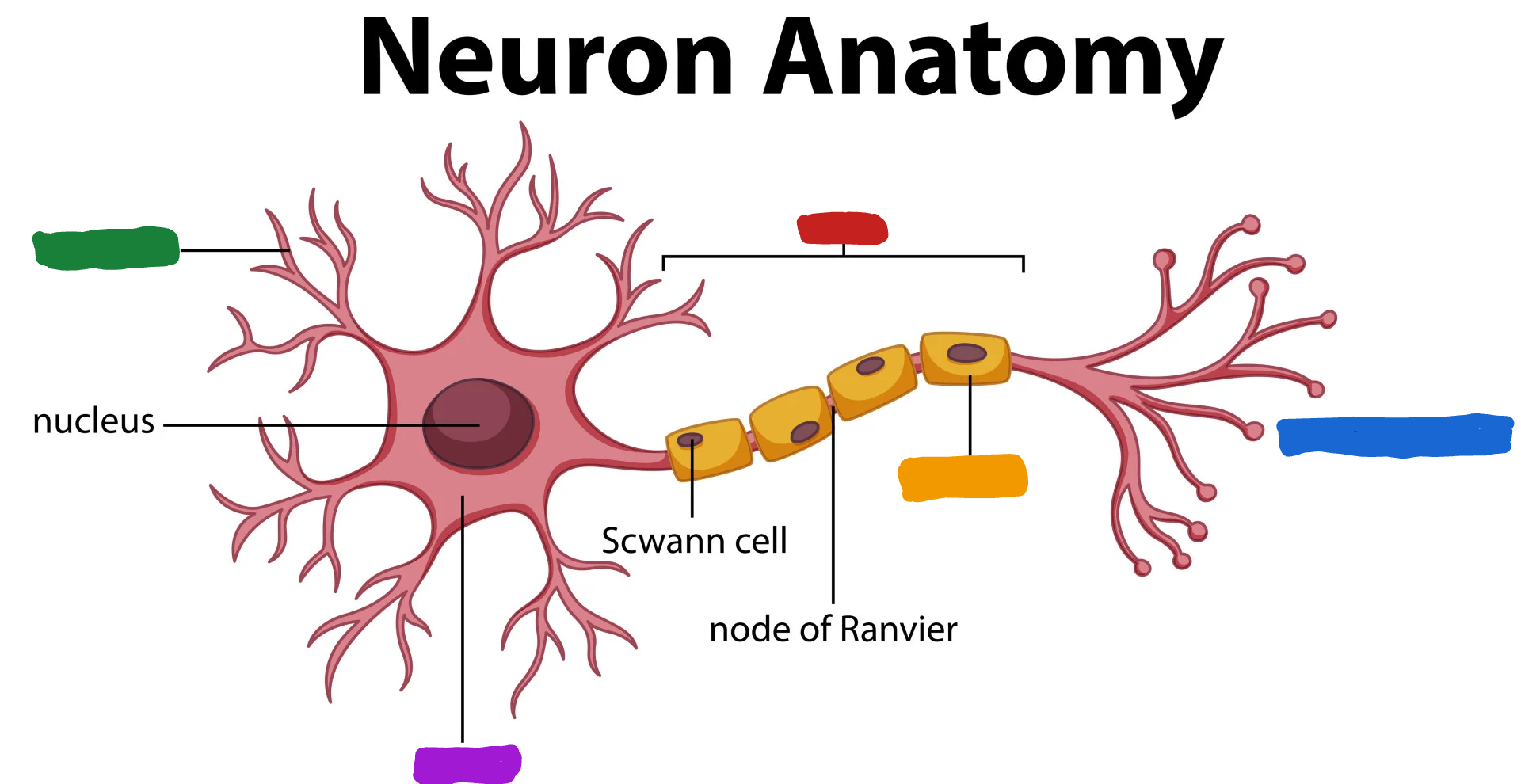
What part of the neuron is the one in red?
Axon
What do the Axon do?
the Axon fibers pass the message to other neurons or to muscle or glans (Axon speak)
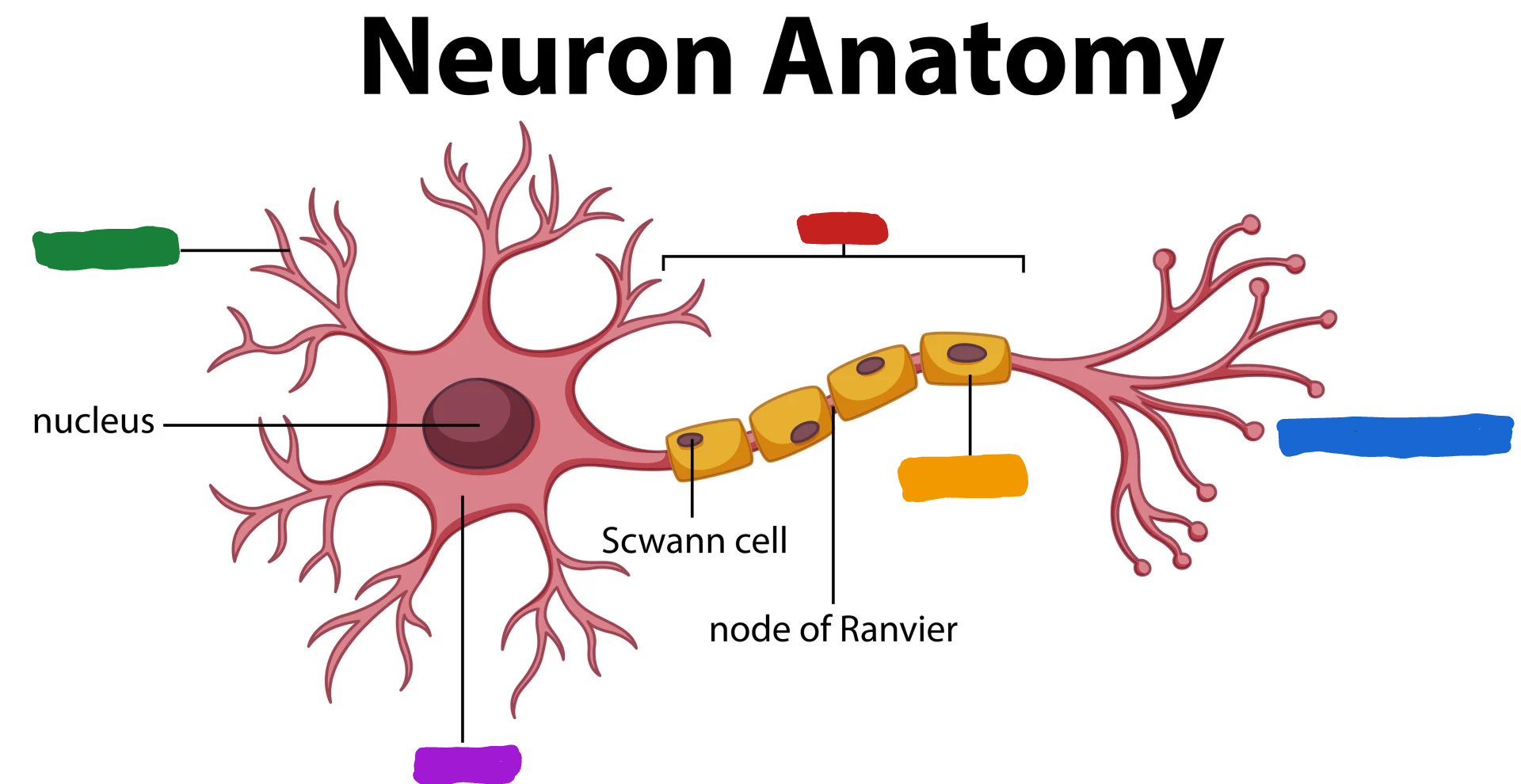
What part of the neuron is the one in green?
Dendrites
What are dendrites?
dendrites fibers receive information and conduct it toward the cell body (Dendrites listen)
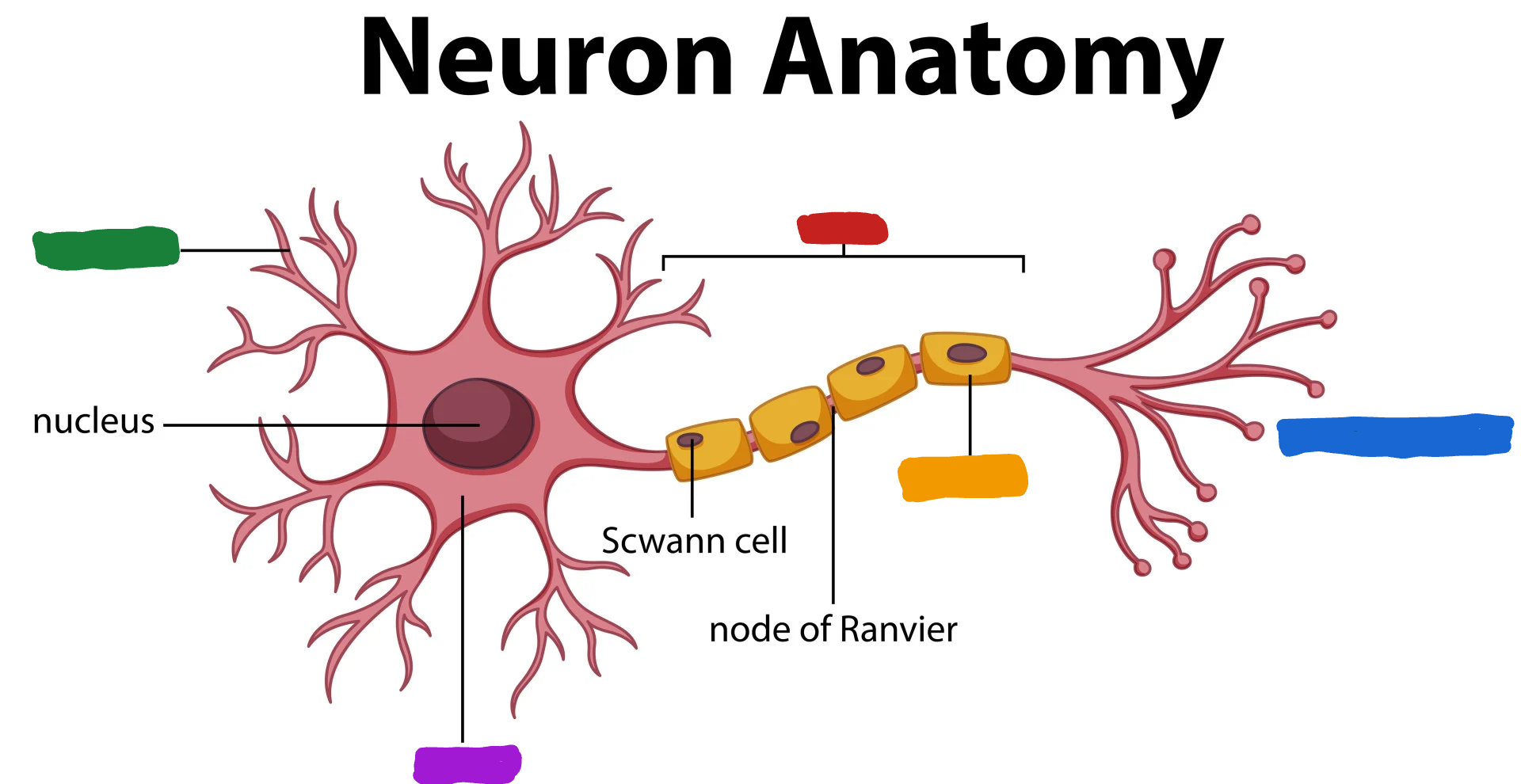
What is the part of the neuron in purple?
Cell body/soma
What is the cell body/ soma?
it is the main structural component of a neuron; cell’s life support center
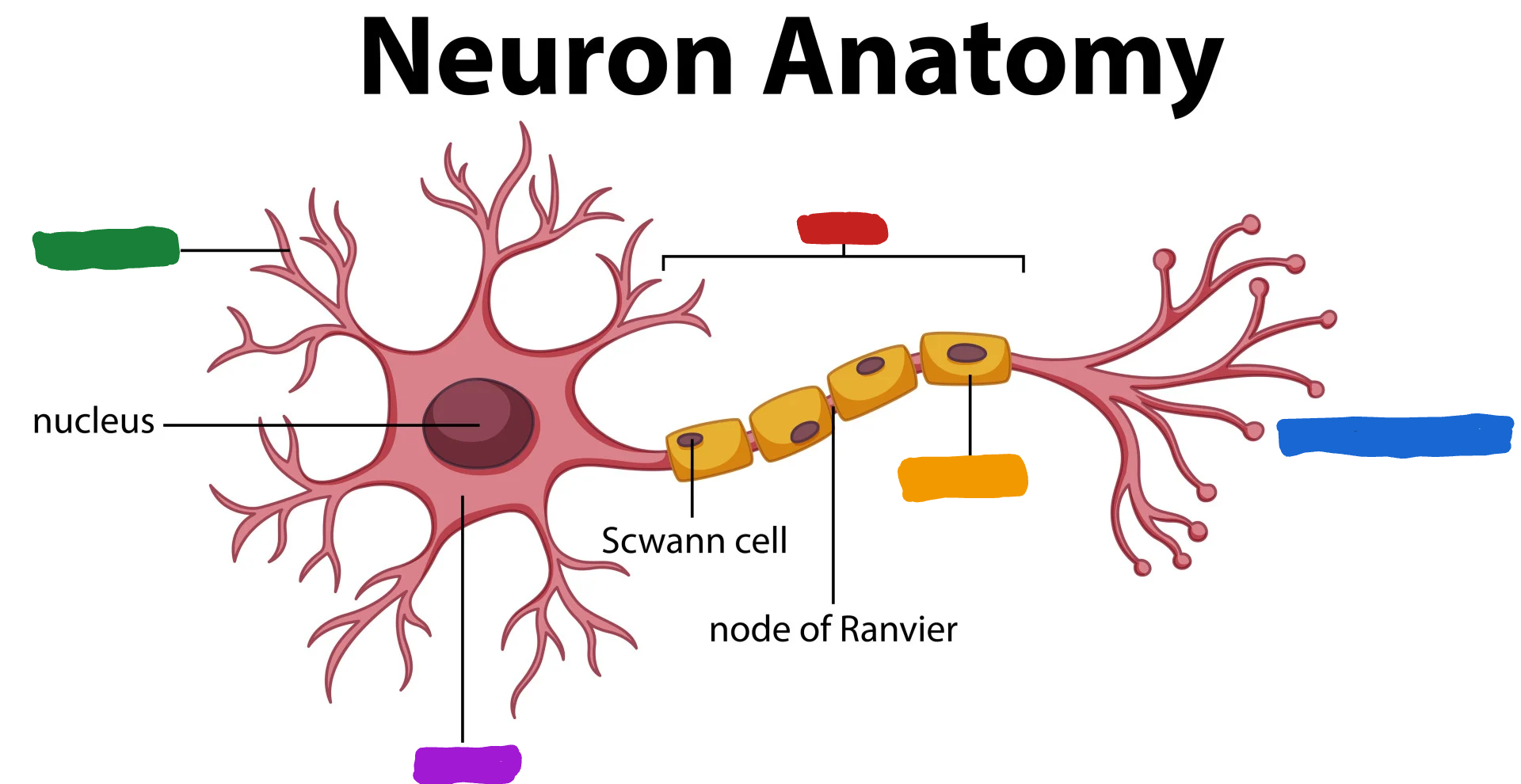
What is the part of the neuron in orange?
Myelin Sheath
What is the myelin sheath?
covers the Axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impluses
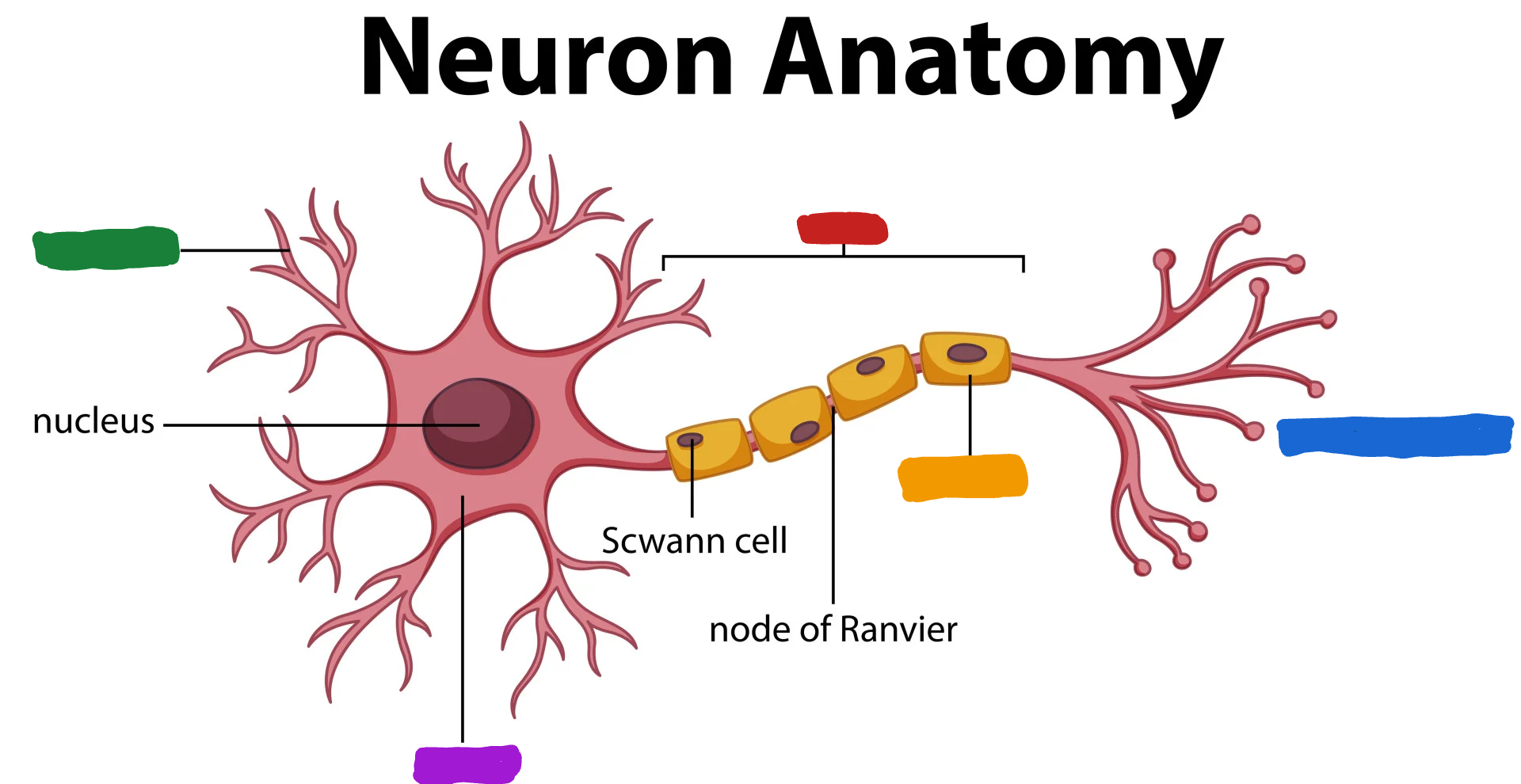
What is the part of the neuron in blue?
Axon terminal
What is the Axon terminal?
forms junctions of other cells
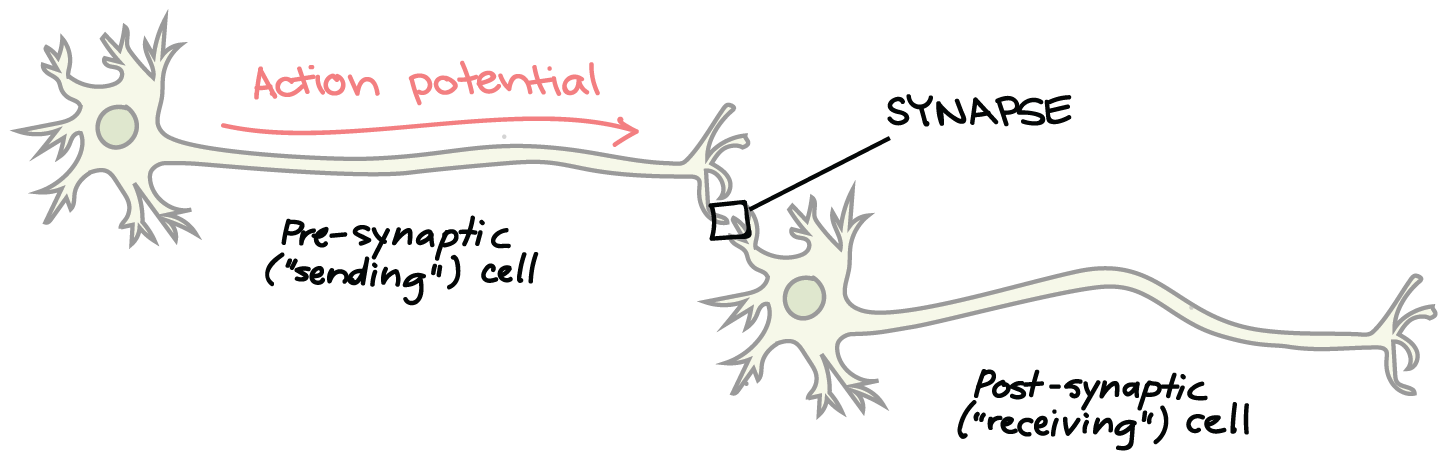
What is the synapse?
is the junction between the Axon of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell-body of the receiving neuron
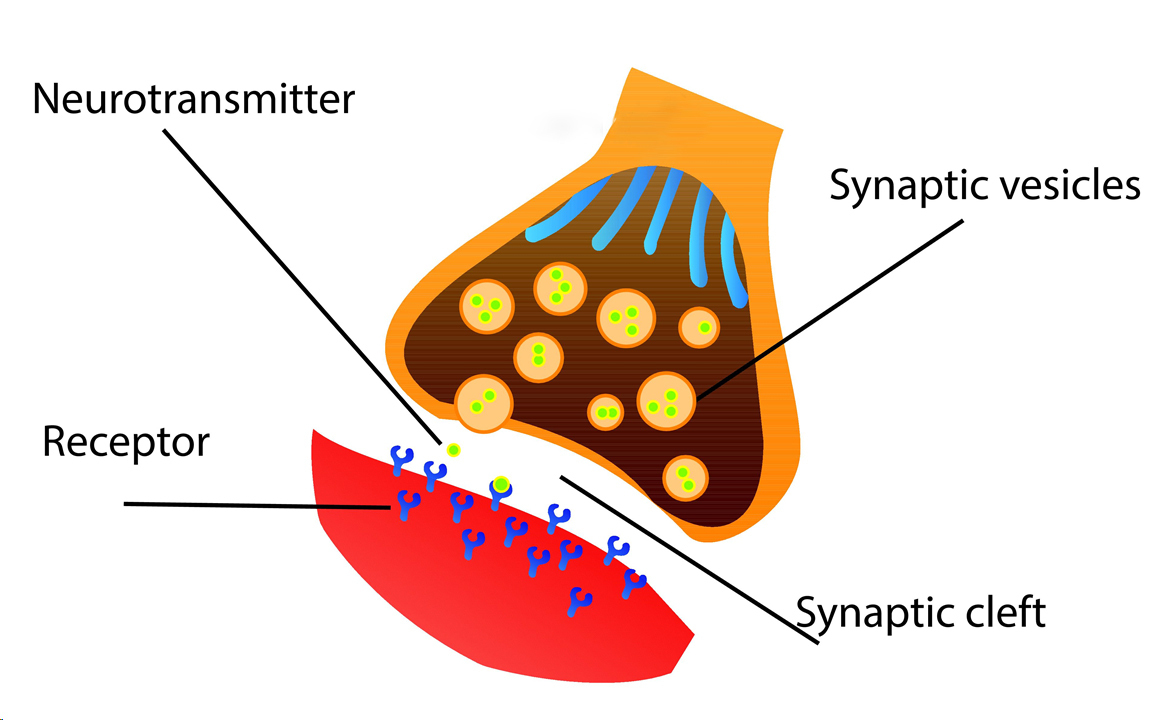
What is the neurotransmitters?
are chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gap of between neurons
What is neutral firing?
the process by which a neuron generates a brief electrical impulse, called an action potential, that travels down its axon to transmit information to other neurons or cells
What are the steps of neutral firing?
Neurotransmitter—>Threshold Met—>Action Potential (“Firing”)—> Depolorization—>
Refractory Period—> Resting Potential (Repolorarized)
What is neural efficiency?
all or none
What are the parts of the Nervous System?
Central (CNS): Brain+Spinal Cord—> Peripheral (PNS)
What are the parts of peripheral (PNS)
Autonomic NS- sweating, breathing, digestion, pupil dilation, blinking, heartbeat (involuntary movement)
Somatic NS- voluntary movement sensory information
What are the parts of Autonomic NS?
Sympathetic NS (Fight or Flight) (UP)
Parasympathetic NS (Rest and Digest) (DOWN)
Neurotransmitters: What is serotonin?
mood states
too little serotonin=depression
Treament: SSRI’s: Selective Serotinin Reuptake Inhibtors—> Prevent Reuptake
Mnemonic for Serotonin
Sir (Serotonin) Sleeps (regulates Sleep) Eats (controls appetite), & Feels Fine (stabilizes mood and happiness)
Neurotransmitters: What is Dopamine?
pleasure
too much pleasure can lead to addiction
also relates to movement; if you have too little it can lead to Parkinson’s
also relates to attention; if you have too much it can lead to Schizophernia
Mnemonic for Dopamine
DOPAMINE: Drive, Openness, Pleasure, Attention, Motivation, Integration, Nurturing, Energy
Neurotransmitters: What are endorphins?
-painkillers in the body that makes you feel physically good
Mnemonic for Endorphins
Endorphins= End Pain (natural painkillers) + Feel Fine (reduce stress)
Neuraltransmitters: What is epinephrine/neuropinphrine?
-adrenaline
-it causes heart rate to go up, pupilsto dilate, breathing to increase, blood flow increases, and neural firing increases
Mnemonic for Epinephrine
Epinephrine= Emergency Energy!
Neuraltransmitters: What is acetylcholine? (ACh)
-movement
-also relates to memory; if it decreases it can cause alzheimer’s
Mnemonic for Acetylcholine (ACh)
ACh= Attention, Contraction, and Harmony
Neuraltransmitters: What is GABA?
an inhibitor (the ability to suppress or restrain thoughts, emotions, or behaviors)
Mnemonic for GABA
GABA= Gone And Be At-ease
Neuraltransmitters: What is Glutamate?
-an excitatory (increase the likelihood that a neuron will "fire" or generate an action potential, leading to increased activity in the brain)
Mnemonic for Glutamate
Glutamate= Go!, like glucose gives u energy
What are afferent/sensory neurons?
neurons that carry incoming information from the body’s tissue and sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
What are efferent/motor neurons?
neurons that carry out going information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
What are inter neurons?
neurons within the brain and spinal cord; they communicate internally and process information between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
What is action potential?
a neural impulses; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
What is the resting potential?
the stable electrical charge across a neuron’s membrane when its not sending signals
What is Reuptake?
a neurotransmitter’s re absorption by the sending neuron
What is the threshold?
the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
What is the nervous system?
the body’s speedy,electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerves cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems
What is the central nervous system?
the brain and the spinal cord
What is the peripheral nervous system?
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS)t the rest of the body
What is the somatic nervous system?
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body’s skeletal muscles
What is the autonomic nervous system?
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy
What is the parasymphatic nervous system?
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
What are spinal reflexes?
composed of a single sensory neuron and single motor neuron; a simple autonomic response to a sensory stimulus
What are neurotransmitters? (more specific)
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons; they travel across the synapse and bind to a receptor sites on the receiving neuron
What is the endocrine system?
the body’s “slow” chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
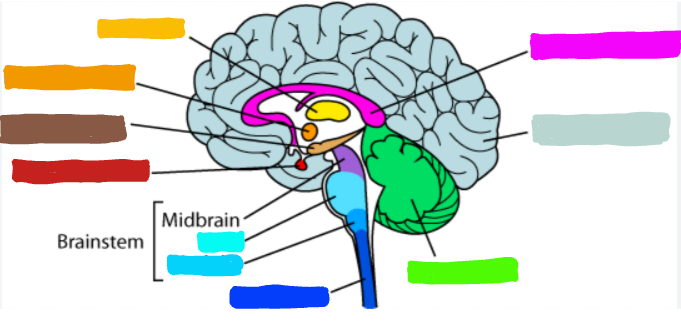
What is the part of the brain in yellow?
Thalamus