BIOL 2252: Respiratory System & Immune System UNIT 3
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
What structure divides the nasal cavity into right and left parts?
nasal septum
What is the largest cartilage in the larynx?
thyroid cartilage
What function besides lubrication does pleural fluid serve?
holds the visceral and parietal pleural membranes together
Which region is lined with pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
nasopharynx
What is the correct airflow order from bronchi to alveoli?
terminal bronchiole → respiratory bronchiole → alveolar duct → alveolus
According to Boyle's law, as volume increases, pressure…
decreases
During expiration, alveolar pressure is…
greater than barometric pressure
What happens to airflow during an asthma attack?
decreases
What happens to lungs during pneumothorax?
collapse
What is the function of surfactant?
decreases surface tension of alveolar fluid
If lung compliance increases, lung expansion is…
easier
Which lung capacity is the largest?
vital capacity
Which volume represents air available for gas exchange each minute?
alveolar ventilation
Which respiratory volume remains in lungs after forced expiration?
residual volume
What is the name of the muscle primarily responsible for breathing?
diaphragm
What structure prevents food from entering the trachea?
epiglottis
What is the function of the nasal conchae?
create turbulence in inhaled air
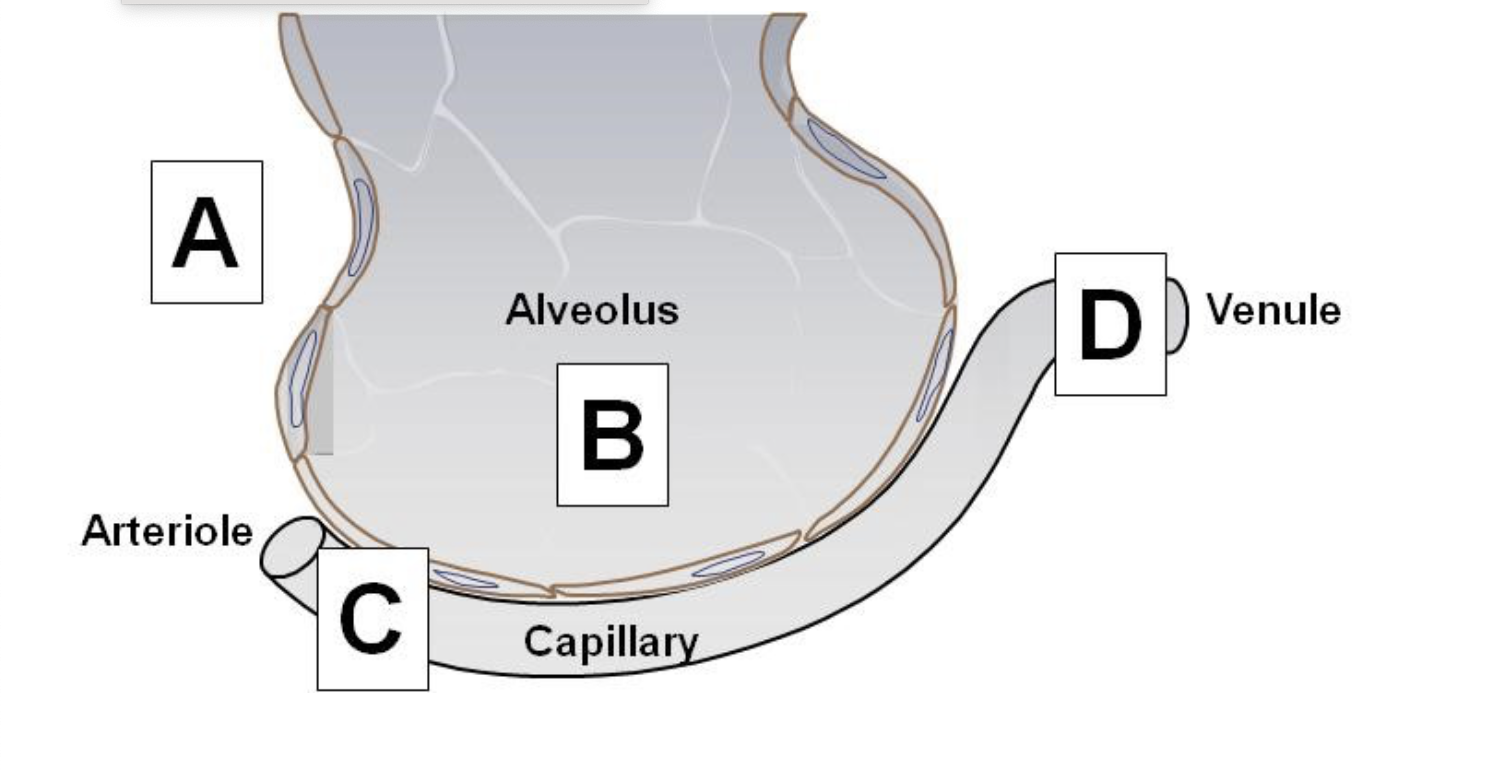
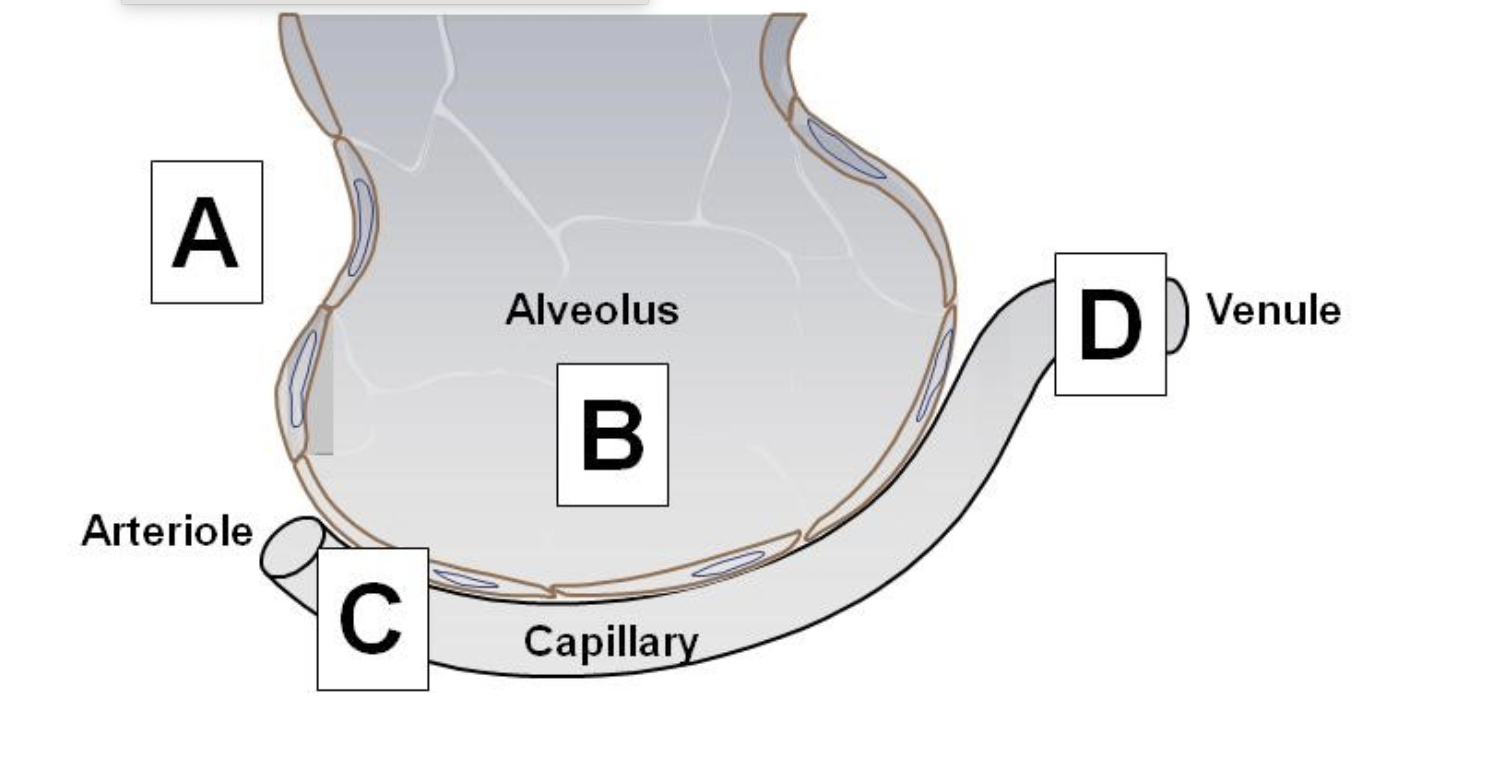
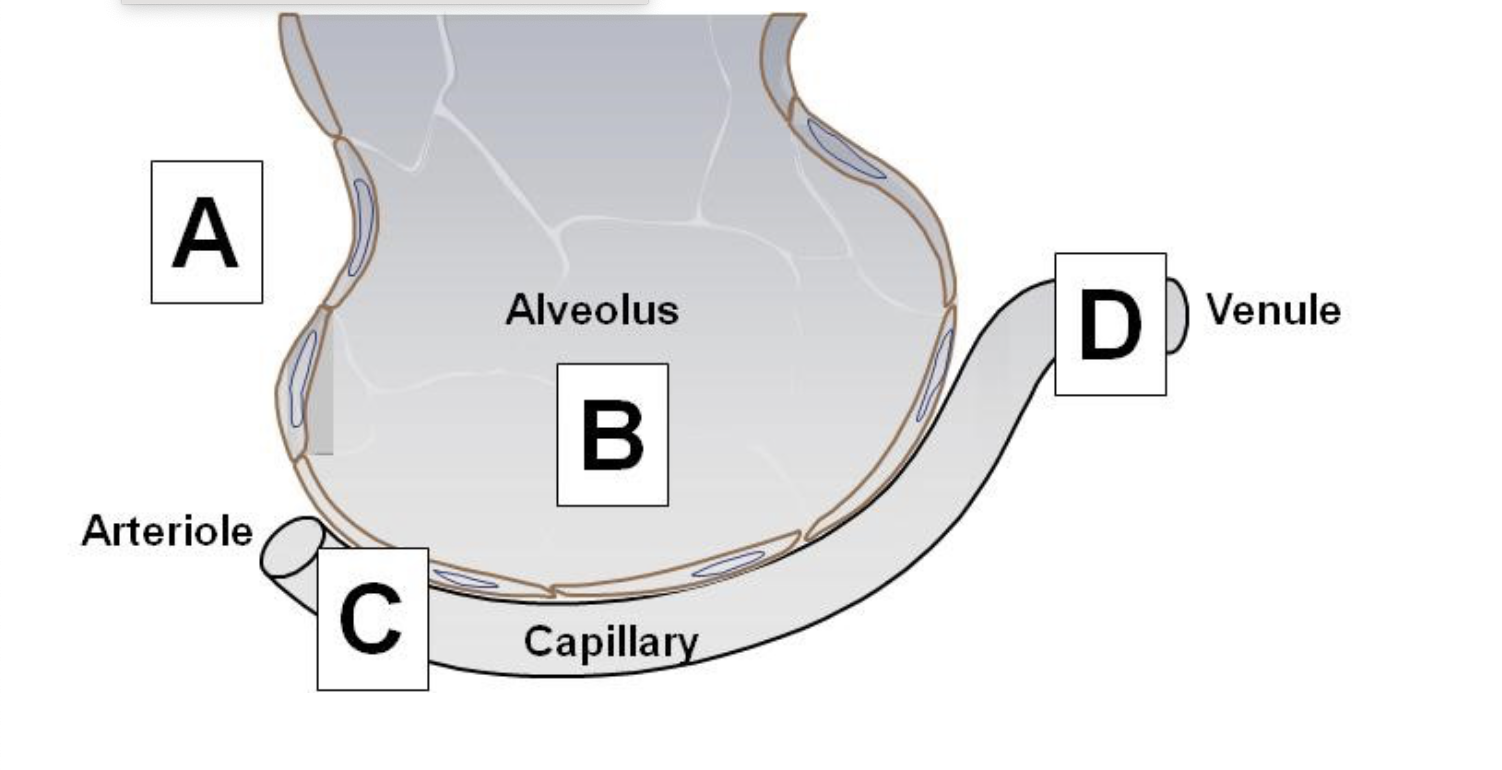
What tissue type lines alveoli for gas exchange?
simple squamous epithelium
What respiratory cells secrete surfactant?
type II alveolar cells (septal cells)
What is the function of alveolar macrophages?
remove debris and pathogens in alveoli
What part of the brain controls breathing rate?
medulla oblongata
Where is the respiratory control center located?
pons and medulla
What causes increased breathing rate during exercise?
increased CO₂ and hydrogen ion levels
What is the term for oxygen binding to hemoglobin?
oxygen loading
What enzyme facilitates CO₂ conversion in red blood cells?
carbonic anhydrase
Which direction does oxygen diffuse during gas exchange in lungs?
from alveoli to capillaries
Which immune system component is present at birth and nonspecific?
innate immunity
Which immune cell kills virus-infected and cancerous cells?
NK cells
What are the two main types of lymphocytes?
B cells and T cells
What protein messengers regulate immune activity?
cytokines
What is the function of interferons?
prevent viral replication in nearby cells
What organ is a primary lymphoid organ?
thymus
What is opsonization?
coating a pathogen to enhance phagocytosis
Which immune cell presents antigens to T cells?
dendritic cell
Which cell performs phagocytosis and is derived from monocytes?
macrophage
Which innate immune cells secrete histamine?
basophils and mast cells
Which line of defense involves skin and mucosal barriers?
first line of defense
Which line of defense involves fever and inflammation?
second line of defense
What is the term for programmed cell death initiated by NK cells?
apoptosis
What complement effect forms membrane pores in pathogens?
cytolysis
Which immune response is specific and slower to develop?
adaptive immunity
What is the role of helper T cells?
activate B cells and other immune cells
What do cytotoxic T cells do?
destroy infected or abnormal cells
What is the purpose of MHC molecules?
display antigens for recognition by T cells
What are antibodies produced by?
B cells (plasma cells)
Which antibody is the most abundant in blood?
IgG
Which antibody is found in secretions like saliva and tears?
IgA
What is the function of lymph nodes?
filter lymph and house immune cells
Which organ filters blood and recycles old red blood cells?
spleen
What is the function of the tonsils?
monitor pathogens entering through the mouth and nose
What is the effect of fever on pathogens?
inhibits growth and accelerates tissue repair
all of the above:
during hypercapnia
when CO2 concentration increases
if pyrogens are released
if blood becomes more acidic
ventral respiratory group of the medullary rhythmicity center
Alveolar cells that perform the function of phagocytosis are the
alveolar macrophages
As far as airflow is concerned, the rate of air flowing into the lungs is _______ related to the pressure gradient and _______ related to resistance.
directly; inversely
Why are the lungs able to stay inflated?
intrapleural pressure is exactly equal to intrapulmonary pressure.
As air travels through the respiratory tract, it travels from the pharynx to the _____ to the trachea?
Larnyx
Air that is inhaled has to go through a process called conditioning. Select the answer that is NOT part of the process that air goes through as it is inhaled.
The air is cooled.
The air is humidified.
The air is cleansed.
The air is moistened.
The air becomes turbulent.
The common name for the _______ is the voice box.
Larynx
What causes air to flow out of the body during expiration?
intrapulmonary pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure.
The pressure of a gas, according to Boyle's law, ______ if the volume of its container increases.
decreases
Oxygen can be carried bound to hemoglobin (in erythrocytes) or dissolved in plasma, approximately what percent of the oxygen in blood is transported by hemoglobin?
98%
The alveolar wall is made up of simple squamous cells referred to as
alveolar type I cell.
What keeps your trachea from collapsing?
The C-shaped cartilaginous rings
In regards to Gas volumes, the amount of air someone can forcibly inhale after a normal inspiration is
inspiratory reserve volume
Which one of the following region or regions of the respiratory tract is lined with pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
Nasopharynx
The conducting portion (zone) of the respiratory system consists of all of those
ЕХСЕРТ?
Alveoli
The respiratory membrane is where gas exchange occurs, which of the following IS NOT part of the respiratory membrane?
Plasma membrane of Type Il cell
Capillary endothelium
Plasma membrane of Type I cell
Fused basement membrane
In the lungs, pulmonary gas exchange of oxygen is best described by which of the following statements?
Oxygen diffuses from the alveolus to the blood because the alveolus has a higher partial pressure of oxygen
The left lung and right lung differ from each other, what is NOT TRUE about the LEFT LUNG?
It has an esophageal depression.
It has a cardiac notch.
It has 2 lobes and 1 fissure.
It has a cardiac impression.
It is slightly smaller than the right lung.
The normal rate of breathing at rest is about _____ times per minute
12
The serous fluid of the lungs serves to?
lubricate and reduce friction between pleural membranes around the lung