Lymphatic anatomy & edema pathophysiology
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
What is the lymphatic system?
What structures does it consist of?
1-way drainage system composed of tiny vessels which carry fluid from the interstitial tissues to the blood system
lymph vessels
lymph nodes
spleen, thymus, tonsils
What substances are in lymphatic loads?
protein
water
WBC
fat
salts
foreign debris
microorganisms
What are the functions of the lymphatic system?
immune surveillance: produces & distributes lymphocytes
transport system: returns excess water, fats, protein, & large molecules to venous system
prevent edemas
When do edemas form?
lymphatic load > lymphatic transport capacity
What are the consequences of edema?
impaired cellular nutrition (d/t increased interstitial diffusion distance for O2 & nutrients)
impaired tissue viability
increased risk for infection & wounds
pain
impaired mobility & function
What are the levels of organization of the lymphatic system?
lymphatic capillaries —> pre-collectors —> collectors —> nodes —> trunks —> ducts
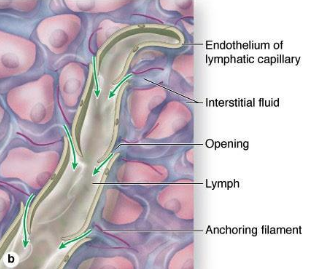
What is the function of the initial lymphatics/capillaries?
What is the structure of the initial lymphatics/capillaries?
absorb interstitial fluid from the interstitium
single layer of epithelial cells
no valves in the lumen
What is the function of the pre-collectors?
What is the structure of the pre-collectors?
connect the lymphatic capillaries to the lymphatic collectors; minimal absorption of fluid
valves prevent backflow
smooth mms for transport
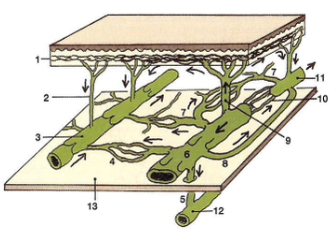
What is the function of the lymph collectors?
What is the structure of the lymph collectors?
transport lymph to the lymph nodes & trunks
valves prevent backflow
smooth mms for transport, similar to veins
lymphangion
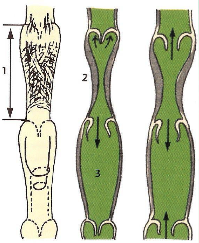
What is a lymphangion?
How does it function?
region b/w the valves; the functional unit of the lymph collectors (smooth mm rings)
influx of lymph —> stretch lymphangion —> smooth mms contract —> move fluid proximally
What is the lymphangiomotoricity?
frequency of lymphangion contraction
6-10x/min
increases by 10x w/ increased lymphatic load
What 4 things improve the transport abilities of lymph collectors?
respirations/diaphragmatic breathing
arterial/venous pulsations
skeletal mm movement
newly formed lymphatic fluid
What are the functions of lymph nodes?
immune reactions
allow macrophages to kill noxious substances (bacteria, viruses, toxins, dead cells)
produce lymphocytes —> systemic immunity
plays a role in spreading cancer
What will happen as a result of malignant tumors invading regional lymph nodes?
metastasis to other regions of the body
What will happen as a result of removal or irradiation of regional lymph nodes?
lymphedema
What regions drain into the axillary lymph nodes?
UE
skin of thorax above waist
most of mammary gland
What regions drain into the inguinal lymph nodes?
LE
abs
lumbar
gluteal
exterior genitalia
What are some of the lymphatic regions/territories?
L head/neck drains to L Cx region
R head/neck drains to R Cx region
L upper trunk drains to L axilla
R upper trunk drains to R axilla
L lower trunk drains to L inguinal
R lower trunk drains to R inguinal
Where do lymph fluid empty?
into the venous system at the venous angle (internal jugular & subclavian veins)
What are lymphatic trunks?
What happens at the lymphatic trunks?
largest lymphatic vessels that form the main parts of the transporting vessels
lymphatic fluid is mixed into the venous blood via lymphovenous anastomoses
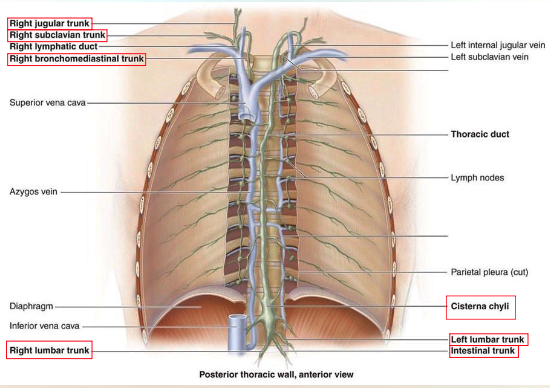
Which ANS innervates lymphatic trunks?
sympathetic
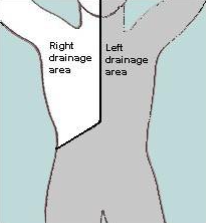
Which areas drain into the R lymphatic duct?
Which veins does the fluid enter?
R head/neck, trunk, arm
R internal jugular & subclavian veins (R venous angle)
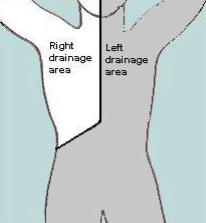
Which areas drain into the L lymphatic duct?
Which veins does the fluid enter?
lower body, L head/neck, trunk, arm
L internal jugular & subclavian veins (L venous angle)
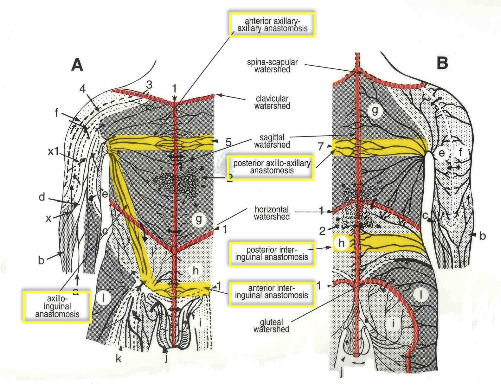
What are lympho-lymphatic anastomoses?
shared connections allowing drainage b/w 2 adjacent territories
inter-axillary/axillo-axillary
axillo-inguinal/inguino-axillary
inter-inguinal/inguino-inguinal
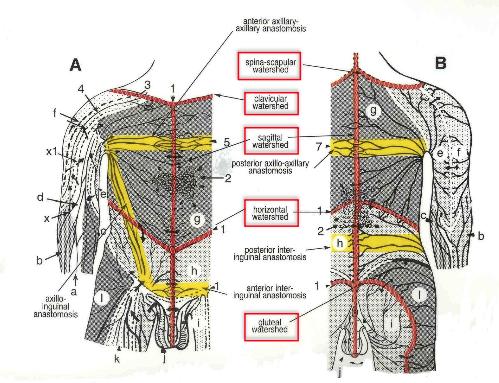
What are lymphatic watersheds?
theoretical boudnary b/w lymphatic territories d/t scarcity of lymphatic vessels; areas that are crossed by the lymphatic capillaries but not the deep collectors
median sagittal
transverse
clavicular
spine of scapula
chaps (gluteal)
What action promotes lymph flow through the thoracic duct?
deep breathing
What action promotes lymph flow through the lymphatic capillaries?
mm contraction
What is the MLD (manual lymphatic drainage) technique?
Usage of “pressure on” & “pressure off” stage to facilitate fluid entering the initial lymphatics and using the anastomoses to move fluid from congested areas to uninvolved areas
What is osmotic pressure?
What are the 2 osmotic pressure forces for normal circulation?
energy by which the more concentrated solution attracts water; low water concentration —> high osmotic pressure
plasma colloidal osmotic pressure (COPp)
interstitial colloidal osmotic pressure (COPi)
What is hydrostatic pressure?
What are the 2 hydrostatic pressure forces for normal circulation?
pressure exerted by fluid
blood capillary pressure (BCP)
interstitial pressure (IP)
What are colloids?
protein molecules
What is Starling’s Law?
rate & direction of fluid exchange b/w capillaries & interstitium determined by hydrostatic vs. osmotic pressures
balance b/w filtration & absorption
What is filtration?
fluid leaves the vessel d/t high hydrostatic pressure pushing water across membrane
typically at the arterial end
What is absorption?
fluid re-enters the vessel d/t osmosis
typically at the venous end
What are the 4 forces for a normal circulation?
blood capillary pressure (BCP)
interstitial pressure (IP)
plasma colloidal osmotic pressure (COPp)
interstitial colloidal osmotic pressure (COPi)
What is blood capillary pressure (BCP)?
fluid pressure in the capillary at both arterial & venous ends
major determinant of fluid movement in normal circulation
determined by arterial pressure, venous pressure, pre- & post-capillary resistance
favors filtration in the arteriole capillary
favors absorption in the venous capillary
What happens w/ an increase in venous capillary BCP w/ venous insufficiency?
decreased absorption —> edema
What is interstitial pressure (IP)?
fluid pressure in the interstitium
minimal effect on filtration or absorption
kn
What is plasma colloidal osmotic pressure (COPp)?
osmotic pressure d/t plasma protein concentration
favors absorption in the venous end
What is interstitial colloidal osmotic pressure (COPi)?
What happens to COPi w/ lymphedema?
osmotic pressure d/t interstitial fluid protein concentration
increases d/t reduced uptake of proteins of lymphatic system —> proteins stay in interstitium —> reduced absorption
Normal circulation results in..?
net filtration
90% of fluid & cells are absorbed by venous system
10% absorbed by lymphatics (ultrafiltrate)
What is ultrafiltrate?
What substances are included in ultrafiltrate?
lymph obligatory load
large proteins & fats that cannot be reabsorbed through the venous system
What factors influence the lymphatic system?
lymphatic load (LL)
transport capacity (TC)
functional reserve (FR)
What is lymphatic load (LL)?
amt. of substances that have to be removed from the interstitium by the lymphatic system (water, proteins, fat, cells)
What is transport capacity (TC)?
max amt. of lymph volume that can be transported by the lymphatics at a time
What is functional reserve (FR)?
TC - LL
What is lymphatic sufficiency in terms of TC & LL?
TC > LL
What is dynamic insufficiency in terms of TC & LL??
What does it lead to?
TC < LL d/t increased LL —> low protein edema (still healthy lymphatic system)
What is mechanical insufficiency in terms of TC & LL?
What does it lead to?
TC < LL d/t decreased TC —> high protein edema (diseased lymphatic system; lymphedema)
What are the normal lymphatic compensations?
increased TC
collateral circulation
lympho-lymphatic anastomoses
lympho-venous anastomoses
plasma protein reduction by macrophages (???)
How does long-standing edema change and how?
pitting to fibrosis d/t accumulation of unabsorbed proteins in interstitial space
What is edema?
excess fluid in the interstitial space d/t increased filtration &/or reduced absorption
can be localized or generalized
What conditions can cause generalized edema?
CHF
renal failure
cirrhosis of liver (salt & water retention)
nephrotic syndrome (low COPp)
How does CHF cause generalized edema?
inefficient heart pump —> increase hydrostatic pressure of venule end of capillaries —> reduced absorption
L ventricular failure —> pulmonary capillaries involved 1st
R ventricular failure —> systemic capillaries involved 1st
What does renal failure cause generalized edema?
reduced ability of kidneys to filter fluid —> more fluid reaches venous system
COPp reduced —> reduced absorption
How does venous stasis cause localized edema?
How can you treat this?
increased hydrostatic pressure at venous capillary; can lead to lymphedema if long-standing
treat w/ compression
How does inflammation cause localized edema?
How can you treat this?
vasodilation of capillaries —> increased blood flow
increased membrane permeability to fluid & proteins
treat w/ MLD & compression
How does lymphedema cause localized edema?
What can happen as a result of lymphedema?
How can you treat this?
lymphatic system unable to absorb lymph obligatory load d/t protein accumulation in the interstitium —> increased COPi
causes chronic inflammation & reactive fibrosis of the affected tissues
treat w/ Complete Decongestive Therapy
What is primary lymphedema?
lymphedema caused by congenital malformation of lymphatic system
What is secondary lymphedema?
lymphedema caused by known pathological condition:
dissection or radiation of lymph nodes
trauma
chronic inflammation of lymph vessels/nodes
cancer
filariasis
infection
chronic venous insufficiency
How can you treat filariasis?
hygiene
exercise, compression, elevation
What are the characteristics of lymphedema?
gradual onset
pitting early
distal to proximal
squaring of toes, (+) Stemmer’s sign
dorsum of foot “Buffalo hump”
loss of ankle contour
asymmetric if BIL
cellulitis common
rarely painful
heaviness, achiness
hyperkeratosis, papillomas, Peau d’Orange
ulcerations unusual
What are the stages of lymphedema?
stage 0: swelling not visible, but lymphatic transport impaired; Sx’s & subtle tissue changes may be noted
stage 1: early onset of visible swelling, subsides w/ elevation, pitting
stage 2: consistent volume change, elevation rarely reduces swelling, pitting
stage 3: skin thickening, hyerpigmentation, papillomas, increased skin folds, fibrosis, no pitting, maybe fungal infections
What is lipedema?
What are the characteristics of lipedema?
BIL accumulation of fat deposition in the LE & buttocks
gradual swelling of LE, sparing of the feet
nonpitting
varicose veins
painful
How can you treat lipedema?
weight control
CDT
liposuction
What are some functional outcome measures when examining pts w/ edema?
Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy - Breast (FACT-B +4)
Disability of Arm, Shoulder, & Hand Questionnaire (DASH)