🔬 Biology chp 5 enzymes flashcards
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Enzymes
Proteins involved in all reactions, where they function as biological catalysts
Catalyst
A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction and is not changed during the reaction
Breakdown of starch
Amylase
Breakdown of proteins
Protease
Breakdown of carbohydrates
carbohydrase
Breakdown of lipids (fats and oils)
lipases
Breakdown of hydrogen peroxide to oxygen and water
Catalase
Amylase
A carbohydrase that breaks down starch
Maltase
A carbohydrase that breaks down maltose
Sucrase
A carbohydrase that breaks down sucrose
Fastest enzyme known
catalase
active site
part of an enzyme molecule to which the substrate temporarily binds
Substrate
The substance that an enzyme causes to react
[insert image]
The substrate has a complementary shape to the active site of the enzyme
![<img src="https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/98eff457-531e-4085-869d-03675eb20f8e.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center" alt=""><p>[insert image]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/98eff457-531e-4085-869d-03675eb20f8e.png)
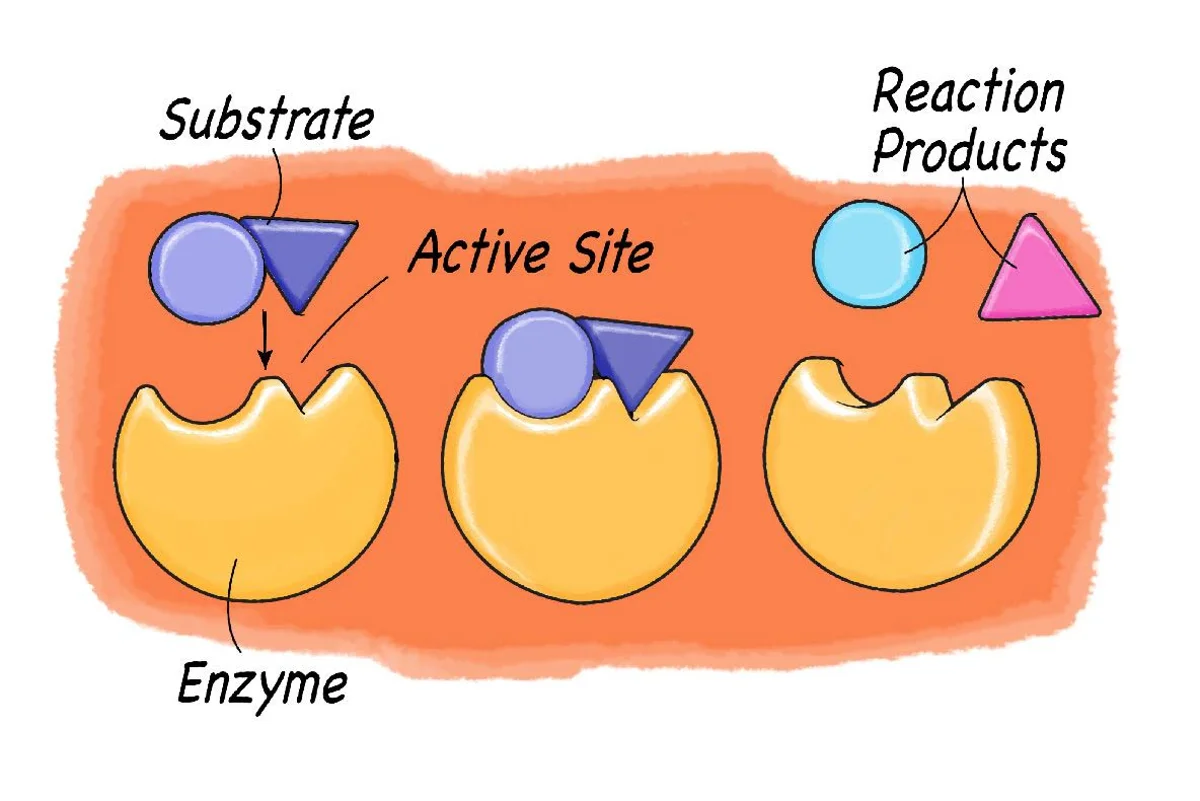
[insert image]
Enzyme changes the substrate to new molecules called “products”
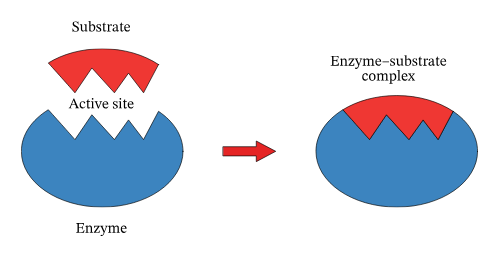

Enzyme-substrate complex
The short-lived structure formed as the substrate binds temporarily to the active site of an enzyme
Factors that affect the speed of the action of enzymes
optimum temperature and optimum pH
Average optimum temperature of human body
37 degrees Celsius
What happens when enzymes reach a temperature above 60 degrees Celsius?
They completely stop working
What does the term ‘denatured’ mean?
When enzymes reach a high temperature they stop working, because high temperature damages the enzyme, thus the enzyme is denatured and cannot catalyze its reaction anymore.
pH for most enzymes
7
what happens if an enzyme is placed in a liquid with a pH that is not its optimum pH?
The enzyme gets damaged, is denatured and cannot catalyze its reaction any further