Chapter 21: Stacks and Queues
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
what are stacks and queues used for
temporary storage, but in different situations
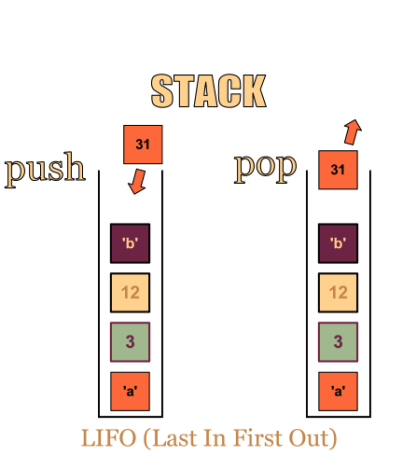
stacks are (acronym)
LIFO: last in first out
what are stacks specifically are used for
handling nested structures
- processing directories within directories
- evaluating expressions within expressions
- traversing a branching tree structure
- planning a move in a chess game
- tracking the sequence of method calls in a Java program (frame)
When is it better to use stacks?
when you want to process the most recent item
implementing iterative algorithms
parsing arithmetic expressions, checking balanced parentheses, evaluating expressions
What are stack functions
push, pop, peek, isEmpty
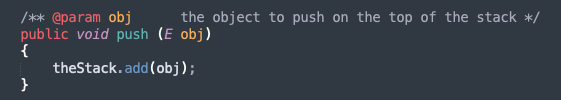
push
adding objects to the top of the stack
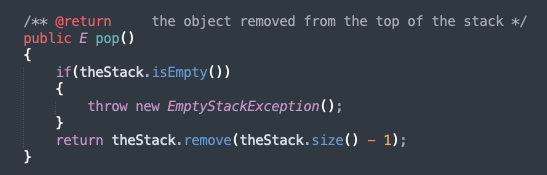
pop
removing object from the top of the stack
peek
look at the object on top of the stack

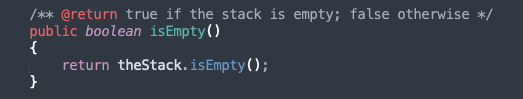
isEmpty
true if the stack contains no objects; false otherwise
Stack Pointer
Stack pointer is a register in the computer’s CPU that keeps track of the top of the stack in memory
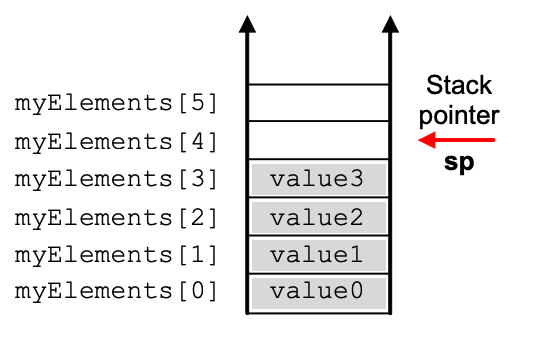
When is Stack Pointer used?
function calls (the function’s return address, local variables, and parameters are pushed onto the stack)
recursive handling (pushes a new stack frame); when recursion unwinds, the stack pointer moves back and removes previous stack frames
Hardware Stack Frame is created when
a java method call creates a stack frame
What is a hardware stack frame
a stack frame stores all the information of the method called (local variables, return types, parameters, etc). the stack frame is pushed to the top of the stack. this is how methods are called in order
What does the stack frame contain
all the necessary information to return (the “state”)
- the state means that each stack frame stores everything required to resume execution after a function call completes
What are the points
SP: Stack pointer in all stacks
BP: base pointer in stack frames
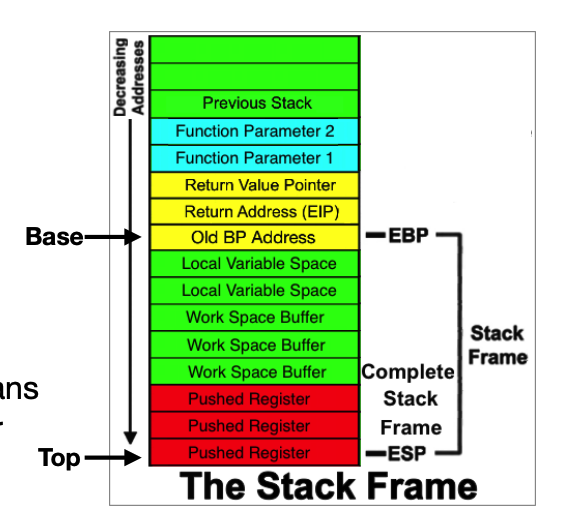
What does base pointer do
a fixed reference point within a function stack frame. it doesnt move while the function runs so you can access parameters and local variables
What does stack overflow mean
large (infinite) number of method calls
Properties of stack: in an efficient implementation push, pop, and peek methods run in an
O(1) time
pop and peek are expected to throw an
EmptyStackException if the stack is empty
If we implement the stack using an ArrayList, we need to explicitly
throw an EmptyStackException because ArrayLists do not throw this exception
a stack of objects holds
references to objects
if necessary, a stack can hold
multiple references to the same object
BE CAREFUL: changing a mutable object on a stack changes all of them
The best practice for pushing objects into a stack
is to push a copy of it to ensure all mutable objects in the stack retain their original value
the java.util.Stack class is part of
the Java Collections Framework (contains interfaces for data structures list, concrete implementations like arraylist<E>, algorithms)
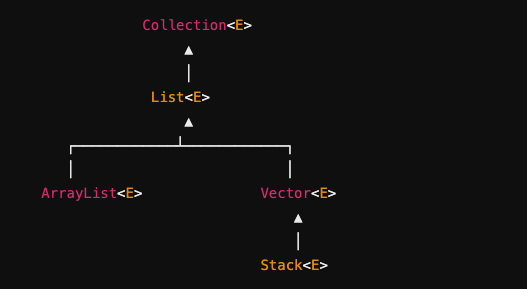
Stack is a _____ class
generic (can work with different data types while maintaining type safety ex. Stack<String>)
Based on the legacy ___ class
Vector class; similar to ArrayList
What is the vector class
legacy class that implements a dynamic array
queue methods:
push, pop, peek, isEmpty (has other methods but do not use them)
What are queues used for
Processing events or messages in order of their arrival
System tasks:
queueing print jobs
entering keystrokes
processing mouse clicks
what are the queue functions
add: adding object to the back of the queue
remove: removing object from the front of the queue
peek: look at the object at front of the queue
isEmpty: true if the queue contains no objects; false otherwise
queue are (acronym)
FIFO: first in first out
in an efficient implementation: add remove and run in
O(1) time
a queue of objects holds
references to objects
like a stack, a queue can hold multiple
references to the same object; but it is best to add a copy of the object
what is a ring buffer
an efficient implementation of a queue
instead of shifting elements to the front, just keep track of front (read) and back (write) pointers
What is a ring buffer cont.
hax a fixed capacity and cannot grow
two points: head (points the front or OLDEST element) and tail (points to next available slot NEWEST element)
wraps around: when tail reaches the end it wraps to the beginning
full when tail + 1 % size == head
empty when head == tail
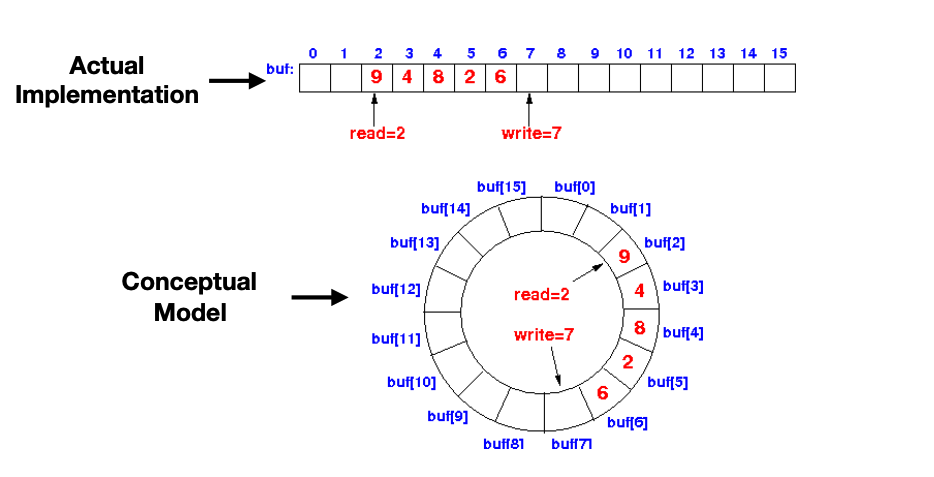
idk whats going on here
what is the java.util.Queue interface
a generic interface, part of the Java Collections Framework
java.util.Queue is implemented by other classes like
java.util.LinkedList and java.util.PriorityQueue