human anatomy and physiology 1 Lab Exam 2
1/309
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
310 Terms
Hyaline Cartilage
provide support with flexibility and resilience
articular cartilage
cover the ends of most bones at movable joints
elastic
better for repeating bending (external
ear and epiglottis)
fibrocartilage
compressive with tensile strength (bundles of collagen)
• Menisci
• Intervertebral discs
bone functions
• Support
• Protection
• Anchorage
• Mineral and growth factor storage • Blood cell formation
• Fat storage
• Hormone production
2 regions the skeletal system is divided into
axial and appendicular
Axial skeleton
forms the central supporting axis of the body
• includes the skull, auditory ossicles, hyoid bone, vertebral column, and thoracic cage (ribs and sternum).
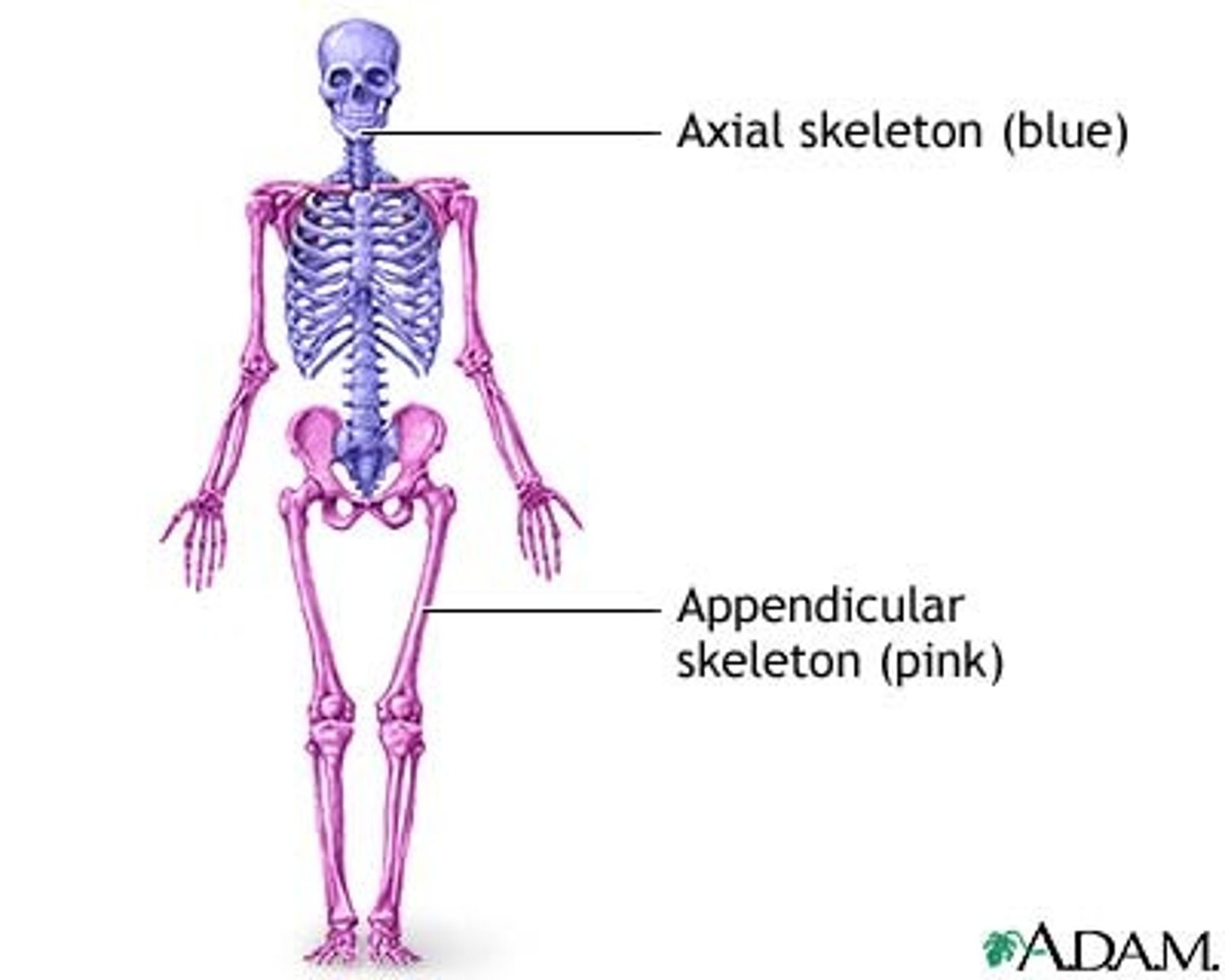
appendicular skeleton
includes the bones of the upper limb and pectoral girdle and the bones of the lower limb and pelvic girdle.
long bone structure
Outer shell of dense compact bone
• Encloses the medullary cavity which contains bone
marrow
The central space is occupied by spongy bone
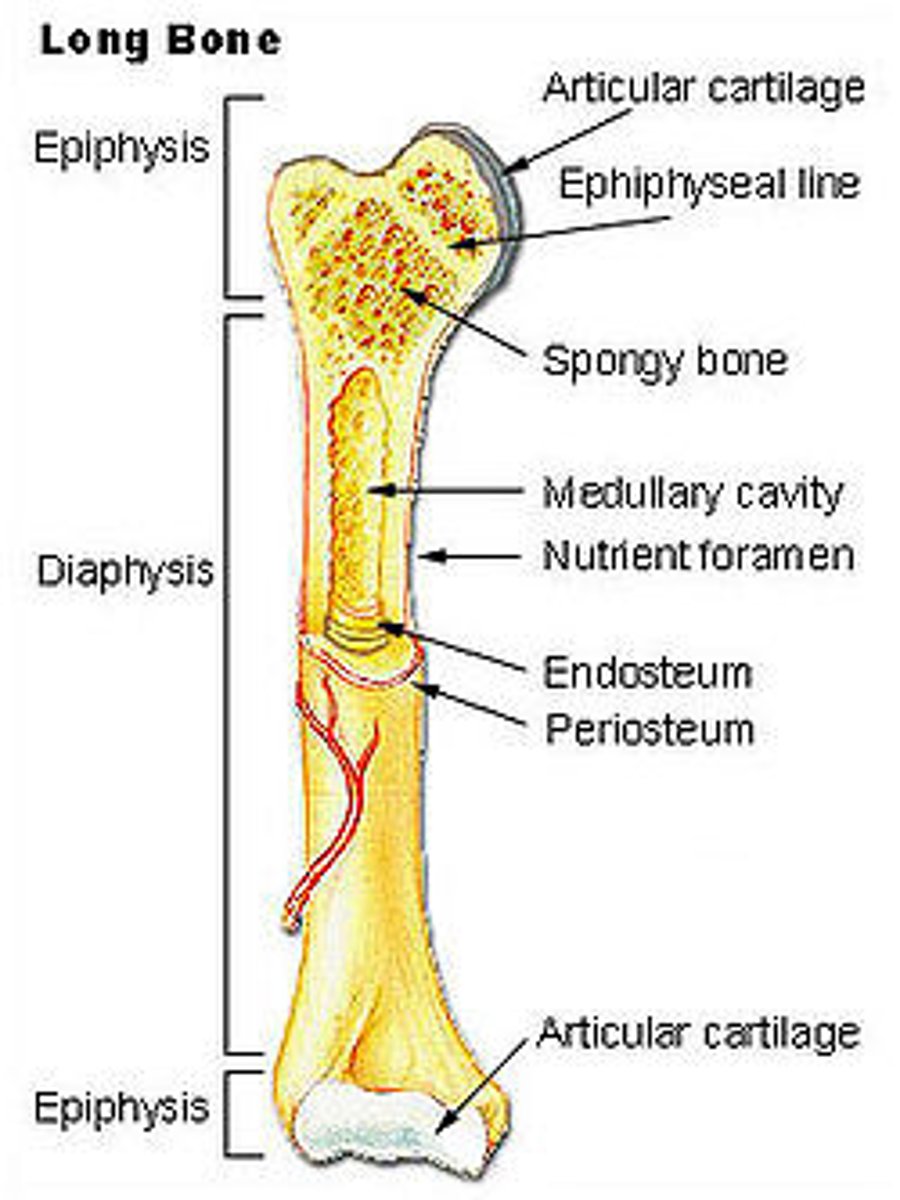
diaphysis
shaft (provides leverage)
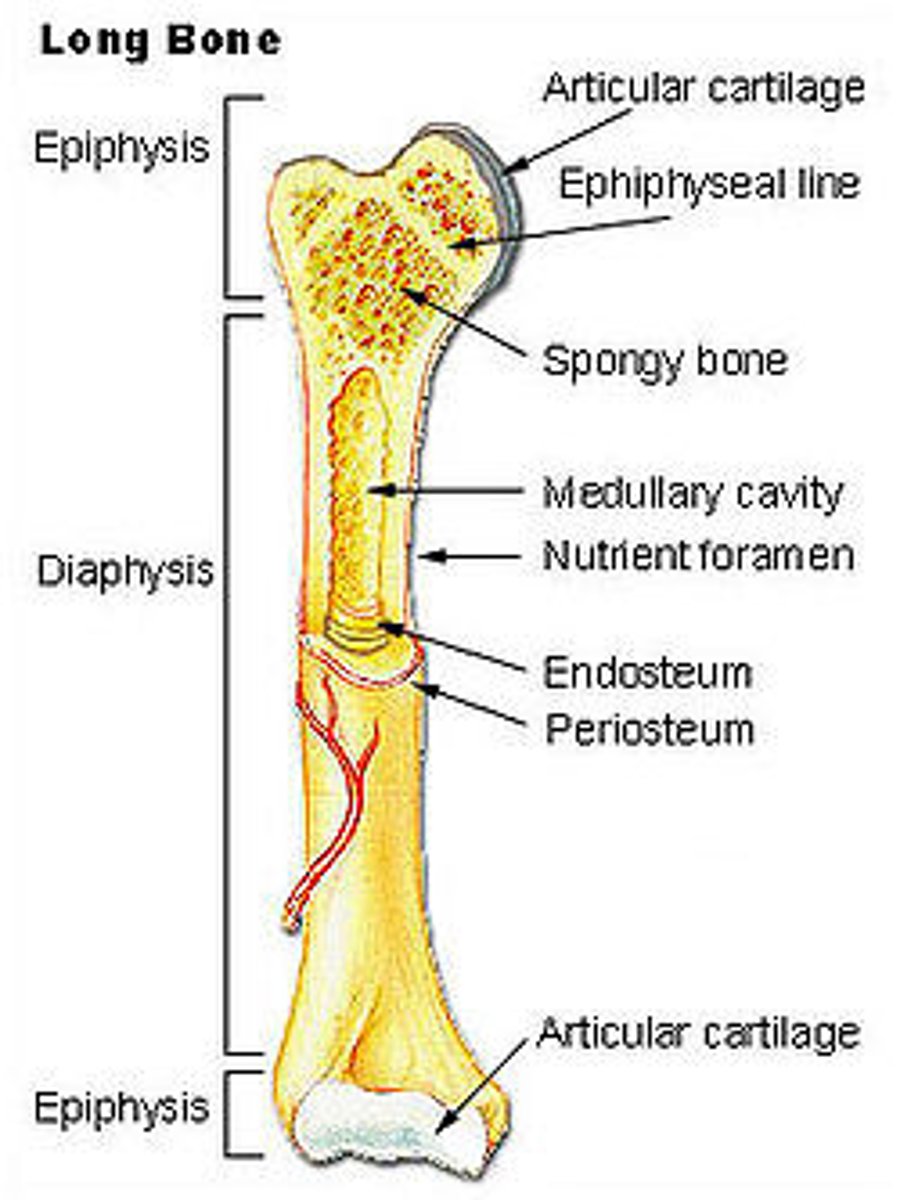
epiphysis
expanded head at each end (provides strength to the joint and attachment area)
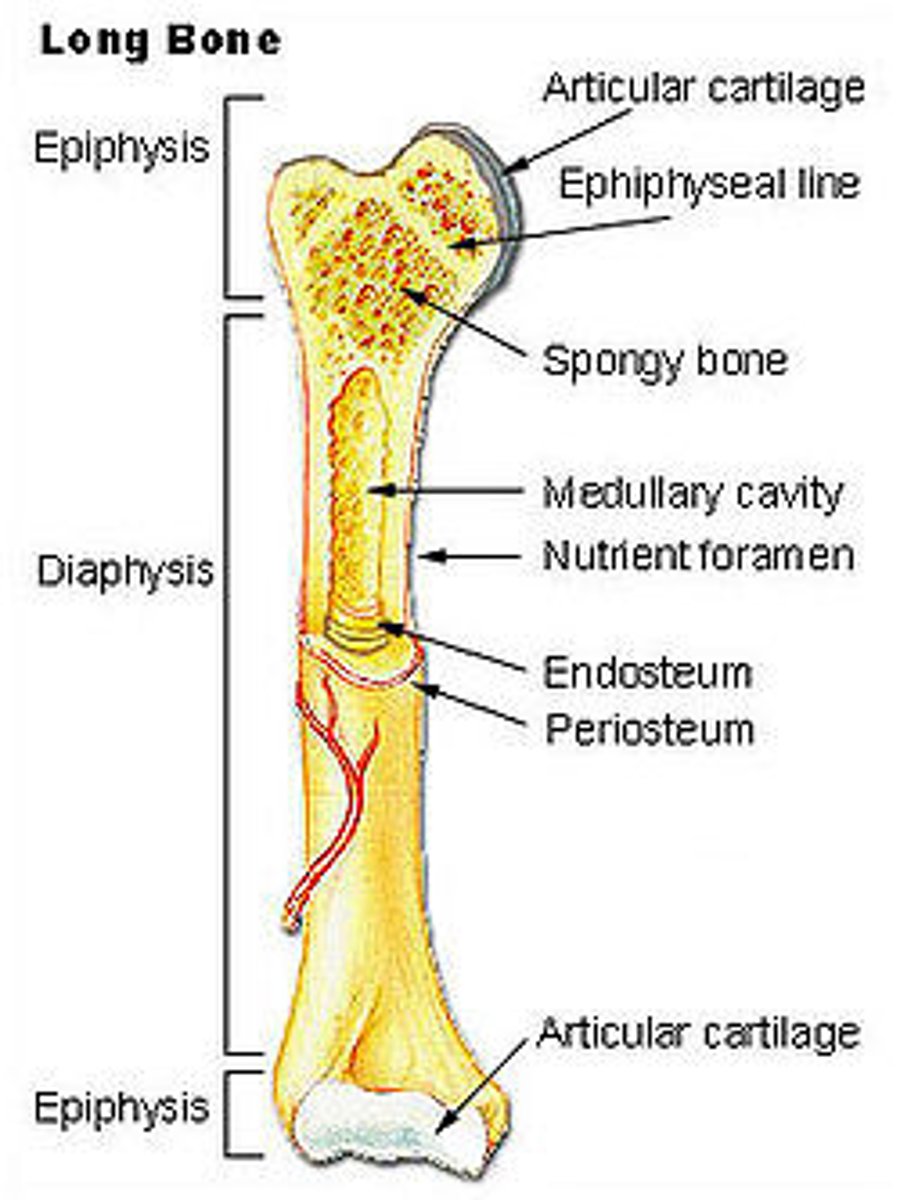
articular cartilage
hyaline cartilage at the joint surface (bone-to-bone cushion)
periosteum (collagen)
sheath covering the bone
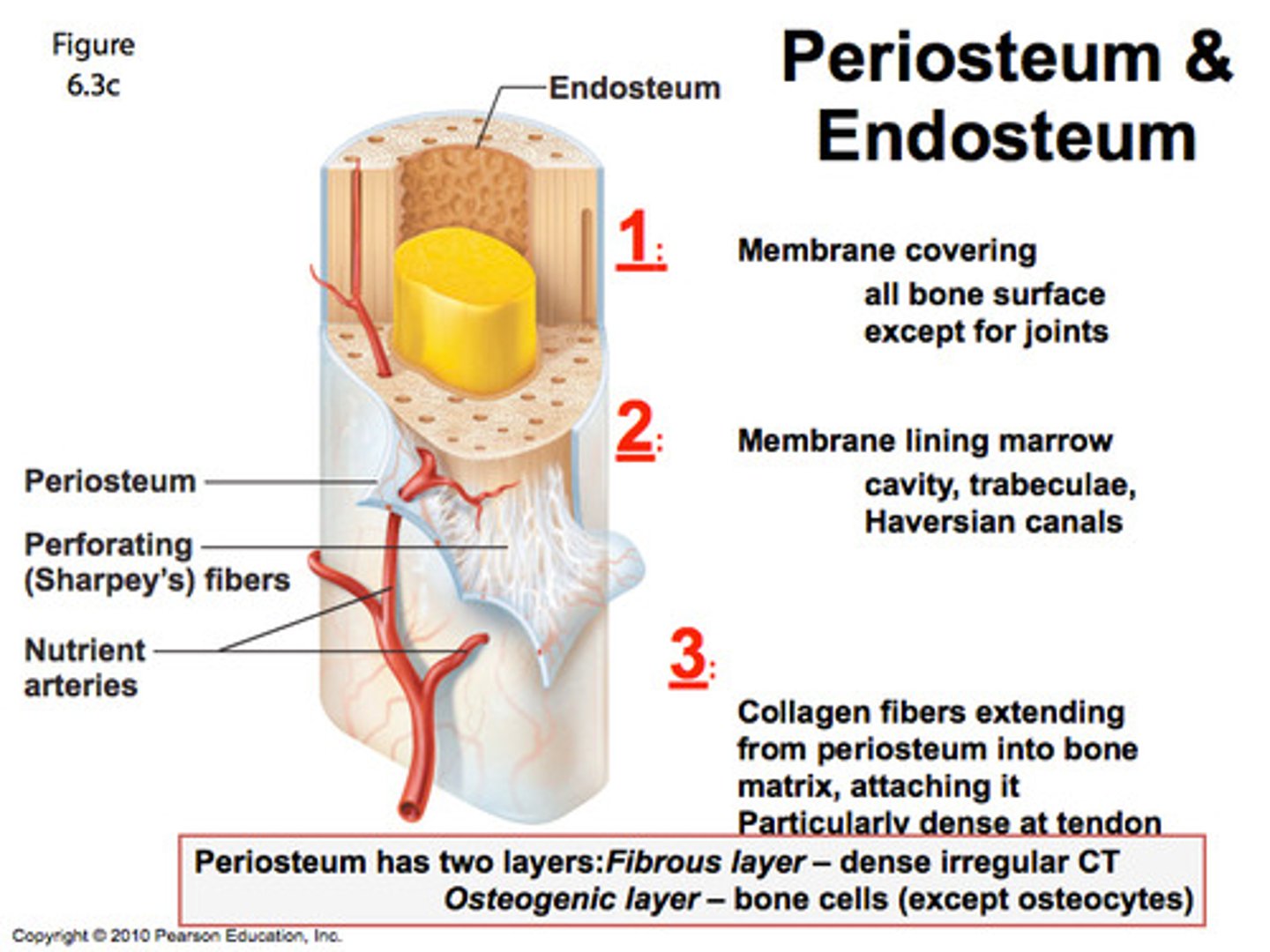
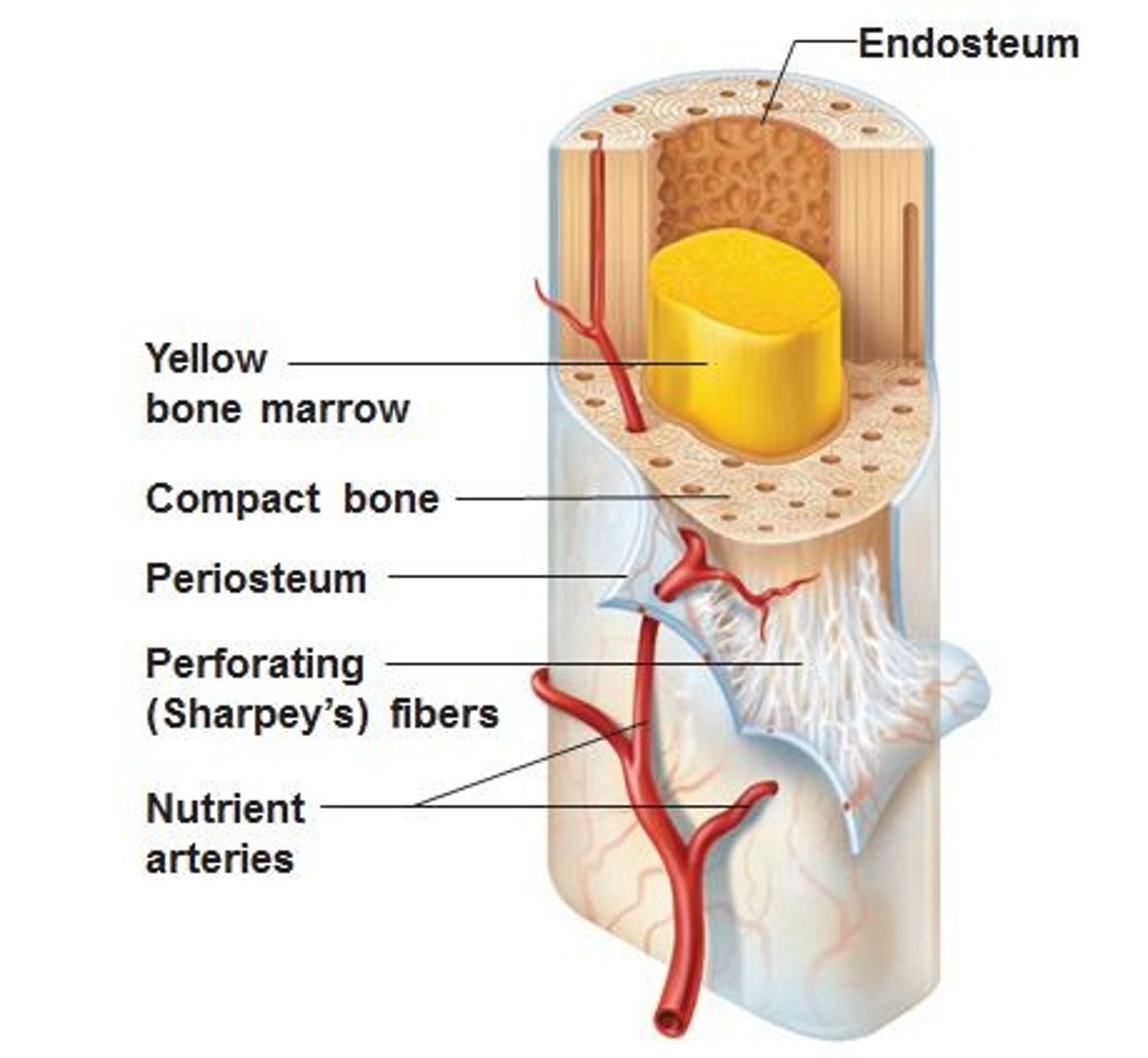
Endosteum
A thin layer of reticular connective tissue that lines the spongy bone
In children and adolescents, this separates the marrow spaces of the epiphysis and diaphysis; Is a zone where the bones grow in length
an epiphyseal plate of hyaline cartilage
In adults, the epiphyseal plate is depleted and the bones can grow no longer, but this marks where the plate used to be
epiphyseal line
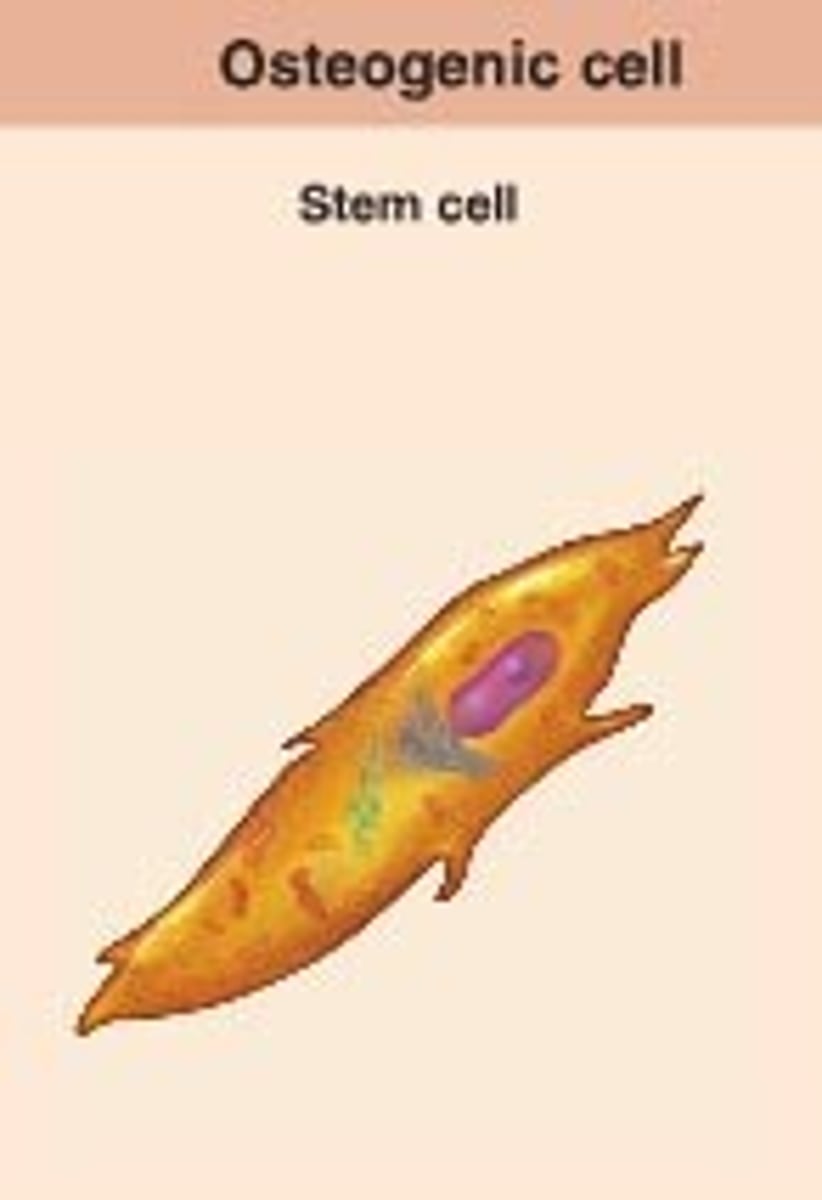
osteogenic cell
develops into an osteoblast
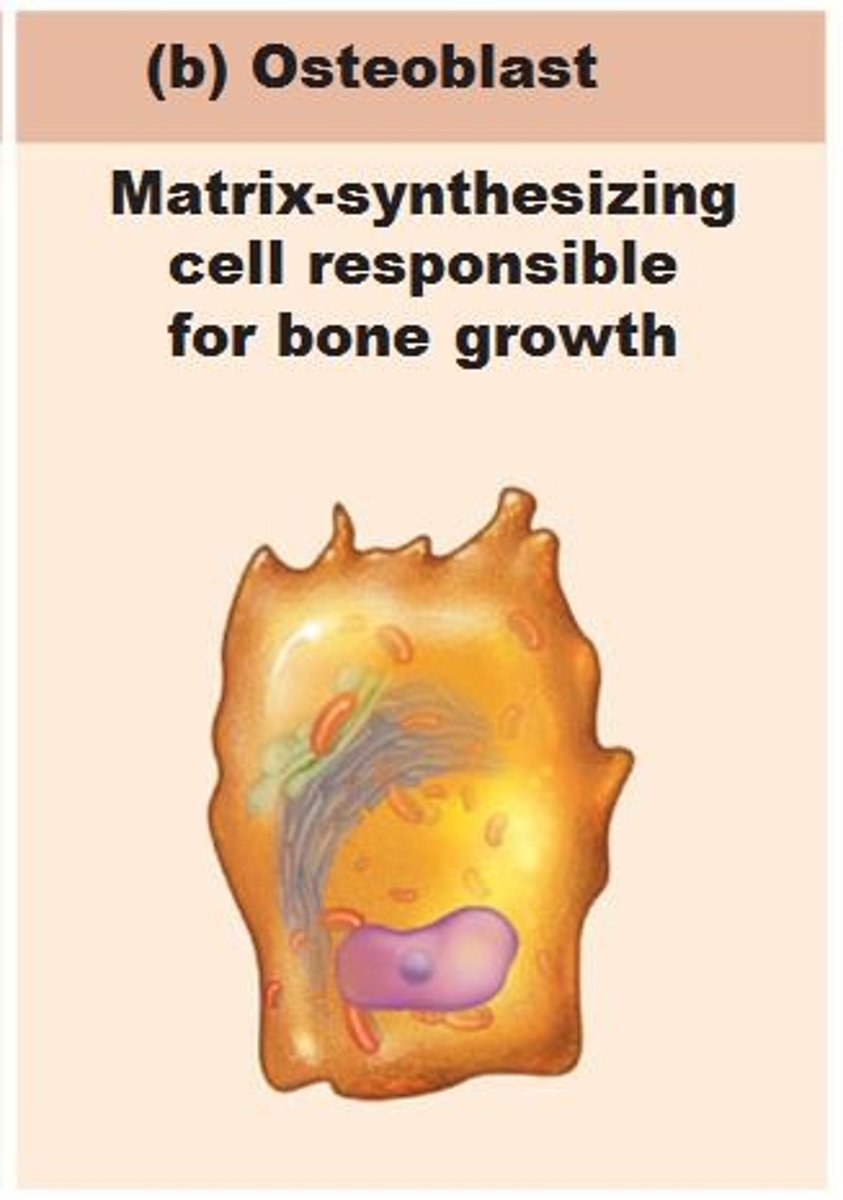
osteoblast
forms bone tissue
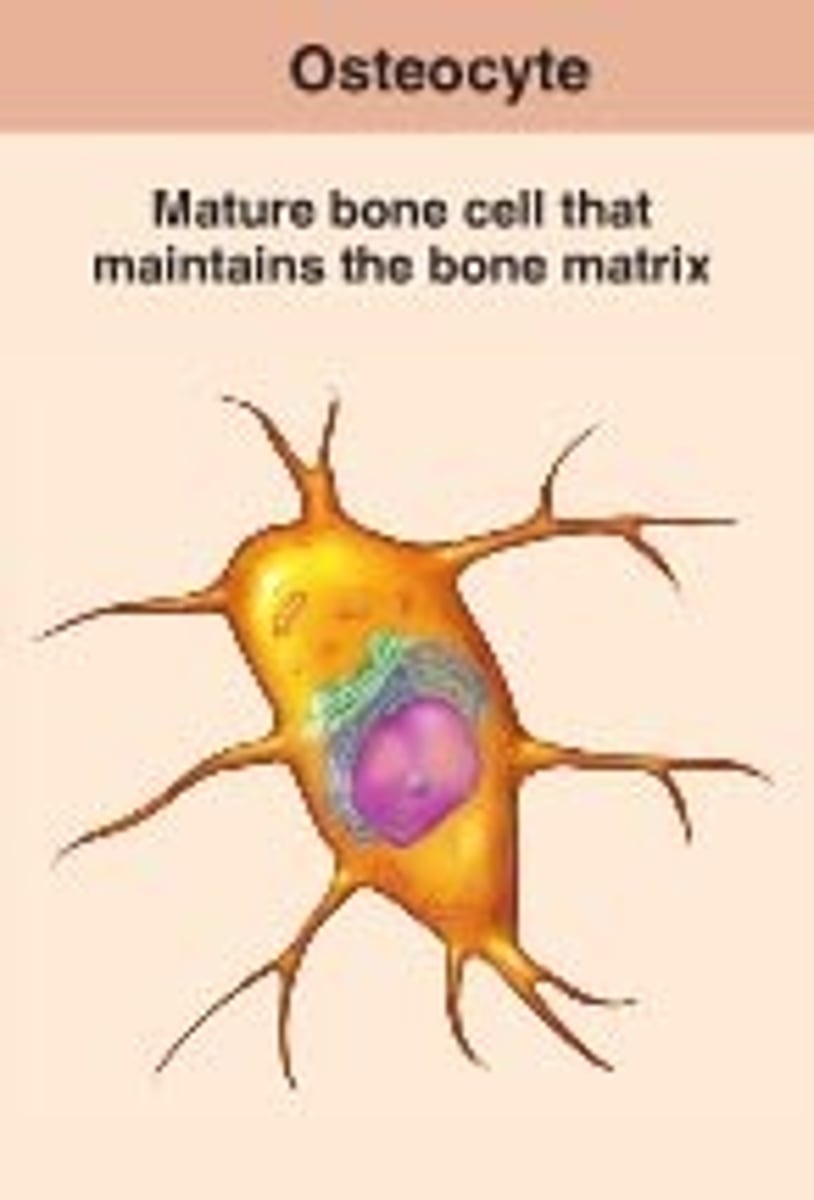
osteocyte
maintains bone tissue
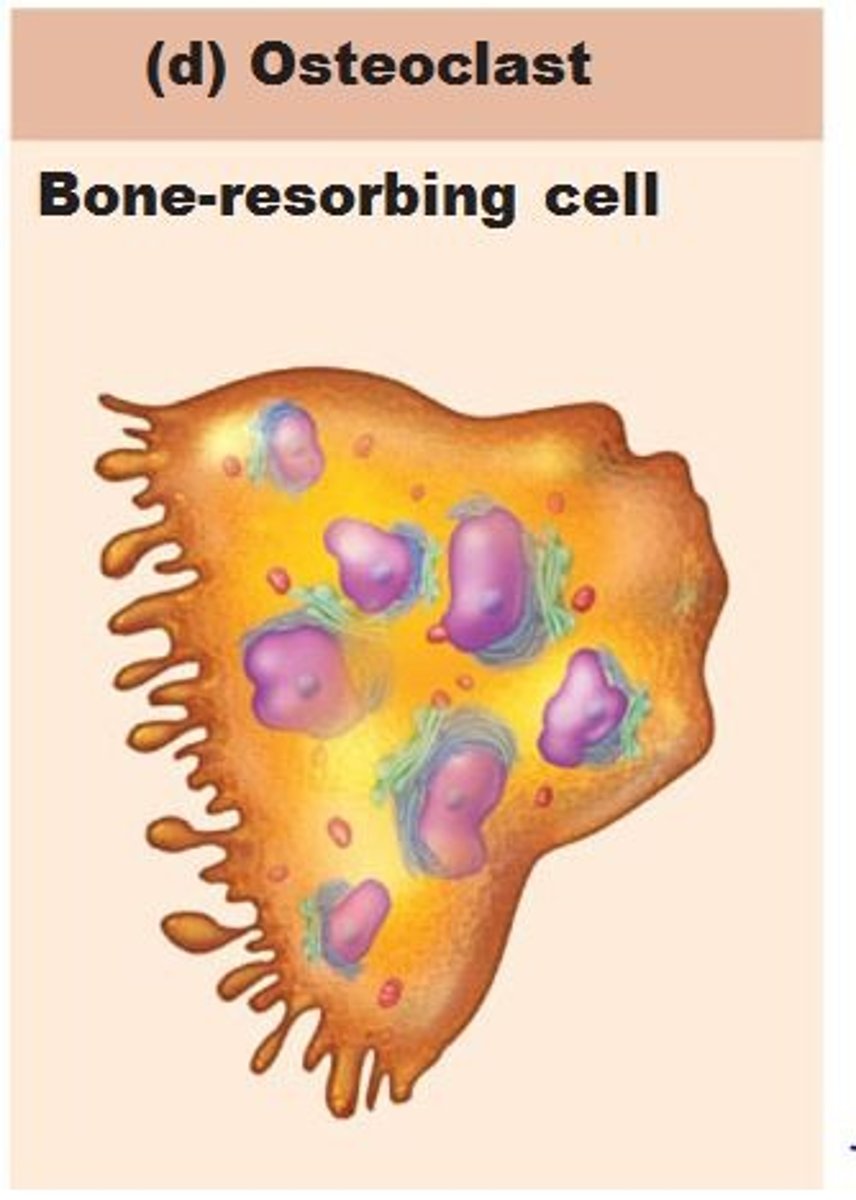
osteoclast
functions in resorption, destruction of bone matrix
tuberosity
large rounded projection, may be roughened
crest
narrow ridge of bone, usually prominent
trochanter
very large blunt irregularly shaped process (the only examples are the femur)
line
narrow ridge of bone, less prominent than crest
tubercle
small rounded projection or process
epicondyle
raised area on or above condyle
spine
sharp slender often pointed projection
process
any bone prominence
bone markings
projections that are sites of muscle and ligament attachments
head
boney expansion carried on narrow neck
facet
smooth, nearly flat articular surface
condyle
rounded articular projection
ramus
armlike bar of bone
meatus
canal-like passageway
sinus
cavity within a bone, filled with air and lined with a mucous membrane
fossa
shallow, basin-like depression in a bone, often serving as an articular surface
groove
furrow
fissure
narrow, slitlike opening
foramen
round or oval opening through a bone
calcitonin
"stores" Ca++ when we have too much
Regulating high blood calcium level
->thyroid-->calcitonin-->build up of bone by osteoblast-->blood Ca++level decreases-->normal blood calcium level
Regulating low blood calcium level
-->parathyroids-->parathyroid hormone-->breakdown of bone by osteoclasts-->blood Ca++level increases-->normal blood calcium level
parathyroid hormone
Gets Ca++ from bones when we need it
Skull
is composed of 22 bones and sometimes more
sutures
connects immovable joints of the skull which are visible as seams on the surface
foramina
holes that allow passage for nerves and blood vessels in the bones of the skull
cranial cavity
largest cavity in skull, encloses the brain, orbits(eye sockets), nasal cavity, oral (buccal) cavity, middle and inner ear cavity, and paranasal sinuses
paranasal sinuses
the frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, and maxillary sinuses
• They are connected with the nasal cavity, lined by mucous membranes, and filled with air.
foramen cecum
holds the obliterated thyroglossal duct
optic canal
holds the optic nerve and ophthalmic artery
foramen rotundum
holds the maxillary nerve
foramen spinosum
holds the meningeal artery
jugular foramen
holds the internal jugular vein
foramen magnum
holds the spinal cord
frontal bone
From the forehead back to a prominent coronal suture
coronal suture
crosses the crown of the head from right to left and joins the frontal bone to the parietal bones
supraorbital margin
a ridge that runs deep to the eyebrows
supraorbital foramen
passage for a nerve, artery, and veins; In some people, a supraorbital notch
glabella
The smooth just above the root of the nose
The right and left parietal bones
• Most of the cranial roof
• Part of its walls
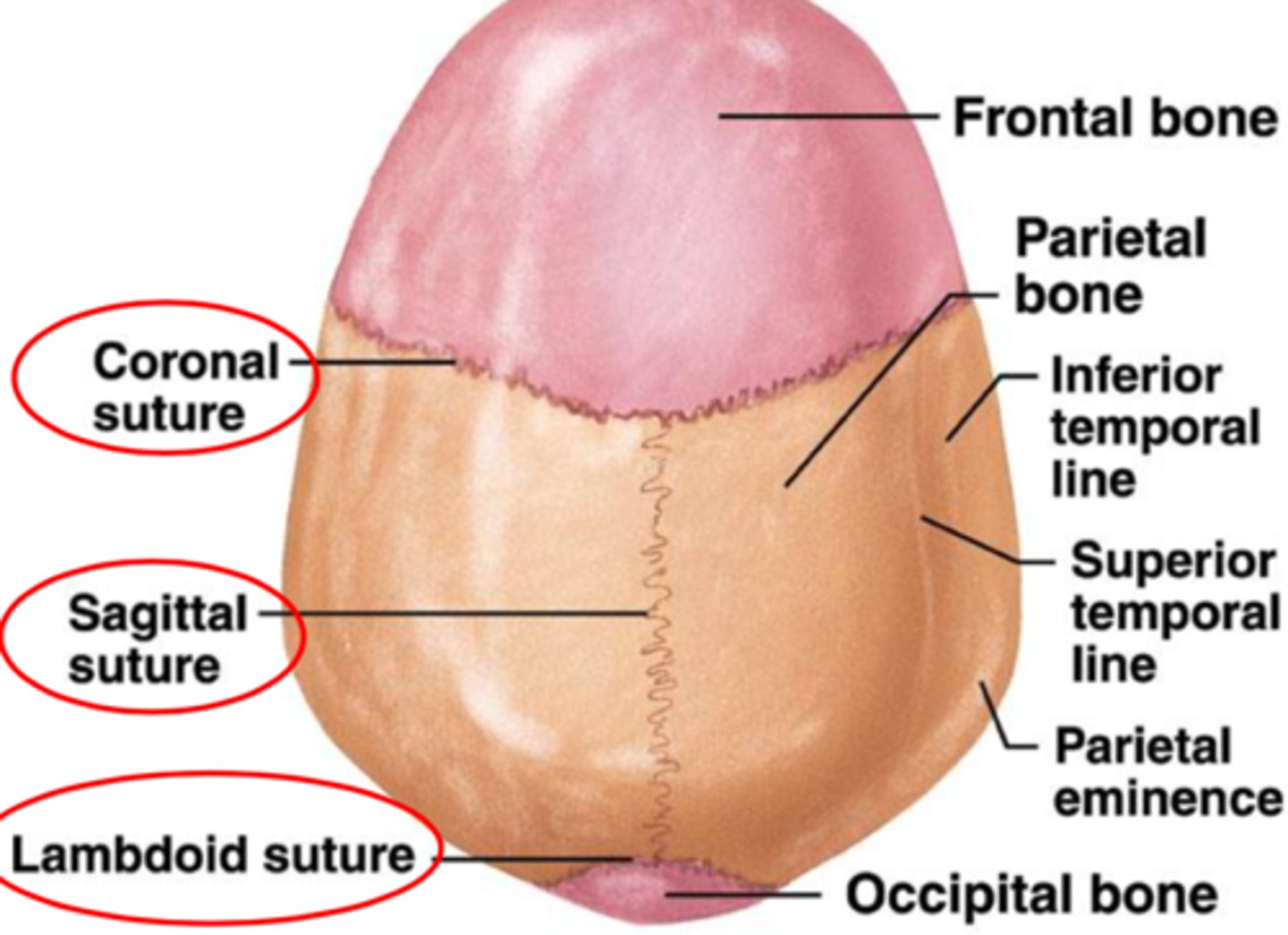
Each Parietal bone bordered by 4 sutures:
1. a sagittal suture between the parietal bones
2. the coronal suture at the anterior margin
3. the lambdoid suture at the posterior margin
4. the squamous suture laterally
4 sutures OF PARIETAL BONE IMAGE
parts of temporal bone
squamous part, tympanic part, mastoid part, and petrous part
squamous part
squamous suture
tympanic part
borders the external acoustic meatus, the opening into the ear canal
mastoid part
lies posterior to the tympanic part
mastoid process
is filled with small air sinuses that communicate with the middle-ear cavity
petrous part
separates the middle cranial fossa from the posterior fossa
internal acoustic meatus
allows passage of the vestibulocochlear nerve (hearing and balance)
from the inner ear to the brain
carotid canal
internal carotid artery
jugular foramen
internal jugular vein of the neck, glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves
occipital bone
the rear of the skull (occiput) and much of its base
foramen magnum
admits the spinal cord to the cranial cavity and provides a point of attachment for the dura mater.
• Has a smooth knob called the occipital condyle
occipital condyle
a smooth knob of which the skull rest on of the vertebral column
Hypoglossal canal
hypoglossal nerve (muscles of tongue)
superior nuchal line
a ride that defines the superior limit of the neck and provides attachment to the skull for several neck and back muscles
body of sphenoid bone contains:
a pair of sphenoid sinuses
• Sella turcica
The foramen rotundum and foramen ovale
sella turcica
Part of sphenoid bone that houses the pituitary
gland (hypophysis)
The foramen rotundum and foramen ovale
part of sphenoid bone that are passages for two branches of the trigeminal nerve
ethmoid bone
is an anterior cranial bone located between the eyes
3 major portions of the ethmoid bone
The vertical perpendicular plate; A horizontal cribriform plate and The labyrinth
crista galli
part of the horizontal cribriform plate of the Ethmoid bone that is an attachment point for the dura mater
cribriform(olfactory)foramina
part of the horizontal cribriform plate of the Ethmoid bone that contains olfactory nerves
labyrinth
major portion of ethmoid bone that contains a large mass on each side of the perpendicular plate
maxillae
They form the upper jaw and meet each other at a median inter maxillary suture where Alveolar processes grow into the spaces between the bases of the teeth
Infraorbital foramen
blood vessel to the face and a nerve that receives sensations from the nasal region and cheek
palate
forms the roof of the mouth and floor of the nasal cavityseparate the nasal cavity from the oral cavity (has Fleshy soft palate posteriorly
palatine processes
Bony hard palate anteriorly, extensions of the maxilla
zygomatic bones
form the angles of the cheeks at the inferolateral margins of the orbits and part of the lateral wall of each orbit; they extend about halfway to the ear
prominent zygomatic arch
that flares from each side of the skull is formed mainly by the union of the zygomatic bone, temporal bone, and maxilla
mandible
is the strongest bone of the skull and the only one that can move significantly
body
horizontal portion of mandible
ramus
the vertical to oblique posterior portion of mandible
condylar processes
bears the mandibular condyle
mandibular condyle
an oval knob that articulates with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bonethe temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
coronoid process
part of the mandible that is the point of insertion for the temporalis muscle
vertebral column contains
cervical (7), thoracic(12), lumbar(5), Sacrum(5, fused), coccyx(4, fused)
body of vertebral column
a mass of spongy bone and red bone marrow covered with a thin shell of compact bone
vertebral foramen
collectively form the vertebral canal, a passage for the spinal cord
vertebral arch
borders vertebral canal and is composed of two parts on each side: a pillar like pedicle and platelike lamina