A Level Pearson Edexcel Physics Topic 7 Fields
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
What is a force field
An area in which an object experiences a non-contact force
What can force fields be represented as
Vectors
These describe the direction of the force that would be exerted on the object
How can we use vectors
To represent the magnitude and direction of forces in a force field.
What does the distance between field lines represent
Represent the strength of the force exerted in that region
Define what is an electric field
A region in which a charged particle will experience a non-contact force. (electric-field)
Field lines diagram for a positive and negative charged particle.
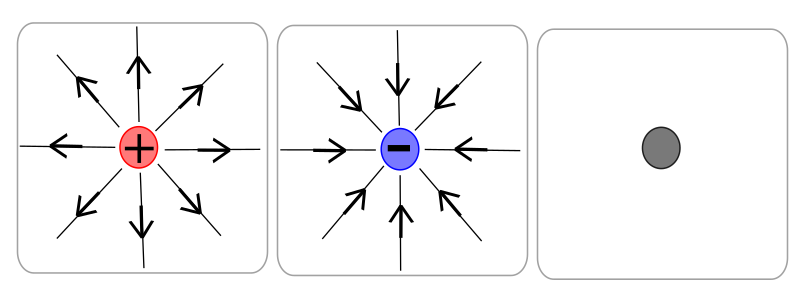
Filed lines diagram for a positive and negative charges attracting each other and a field lines diagram for two positive charges repelling each other.
Formula for electric field strength
E = F / Q
F is the force exerted, Q is the charge if the object.
What is the electric field strength
The force per unit charge experienced by an object in an electric field
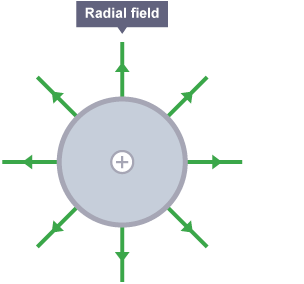
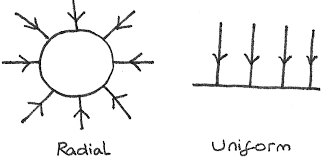
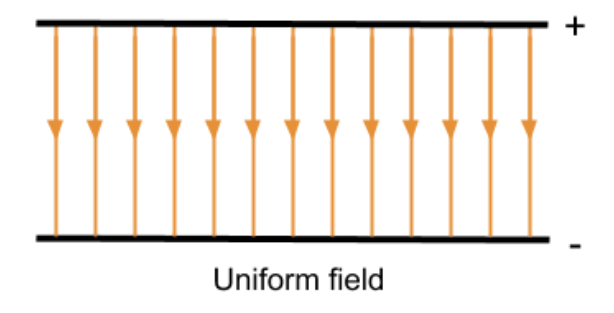
How does the value of an electric field strength vary in a uniform field and a radial field
In a uniform filed the value remains constant but in a radial filed the value varies
How does the electric field strength around a point charge change as you move further away from it
The point charge decreases as you move further away from it
What happens to the electric filed lines if the electric field strength gets weaker
The electric filed lines will be less dense
What does Coulombs law state
That the magnitude of the force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of their charges, and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
Formula for Coulombs law
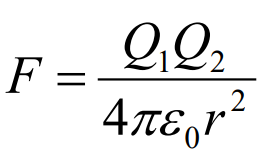
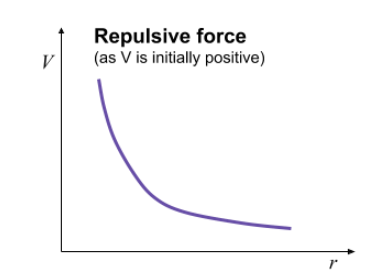
What if the charges have the same sign what will the force be
The force will be repulsive
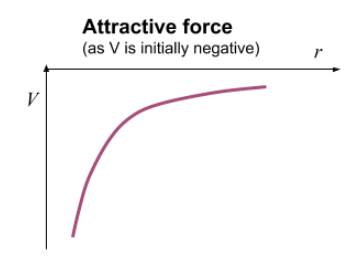
What if the charges have different signs what will the forces be
The force will be attractive
Electric filed strength formula for a radial field
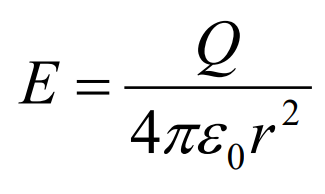
What is meant by radial field
A radial field in which the field lines are radii that radiate from a centre
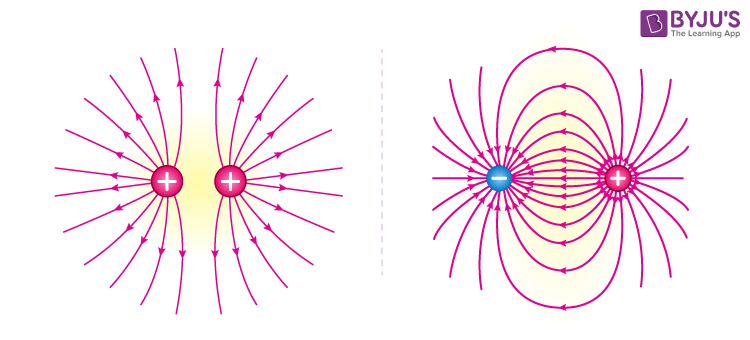
Radial and uniform field lines image
Define electric potential
Defined at a point. The work done moving a unit positive charge from an infinite distance away to that point
Graph for repulsive force
V on y-axis
R on x-axis
Graph for attractive force
V on y-axis
R on x-axis
What is the relation between electric fields and electric potential
The electric field is the negative gradient of electric potential. This means that the electric field points in the direction of decreasing electric potential.
Diagram for field lines and equipotential (equipotential lines) for radial and uniform fields
Dashed dots are equipotential lines, for radial fields they must be parallel to the field lines
(Dotted lines are the equipotential lines)
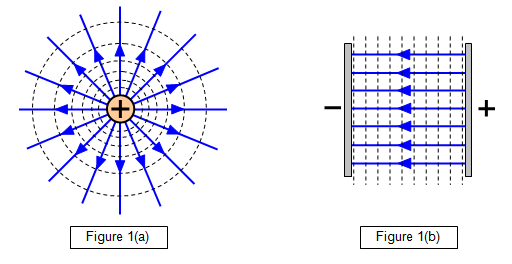
How is the magnitude of the electronic force affected in a radial field
Depends on the distance between two charges
What does distance between field lines represent
The magnitude (size) of the force
Where/When can you calculate electric field strength.
For an electric field between parallel plates (e.g. uniform field)
Formula for electric field strength
d is the distance between the plates and V is the potential difference across the plates
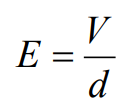
Define Electric potential difference
The energy needed to move a unit charge between two points
Define Capacitance
The amount of charge it can store per unit of potential difference
Formula for capacitance
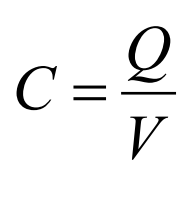
What is the formula for the electrical energy stored by a capacitor
Where:
Q is the charge stored
V is the potential difference across the capacitor
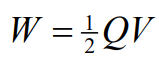
How can you derive variations of the energy stored formula

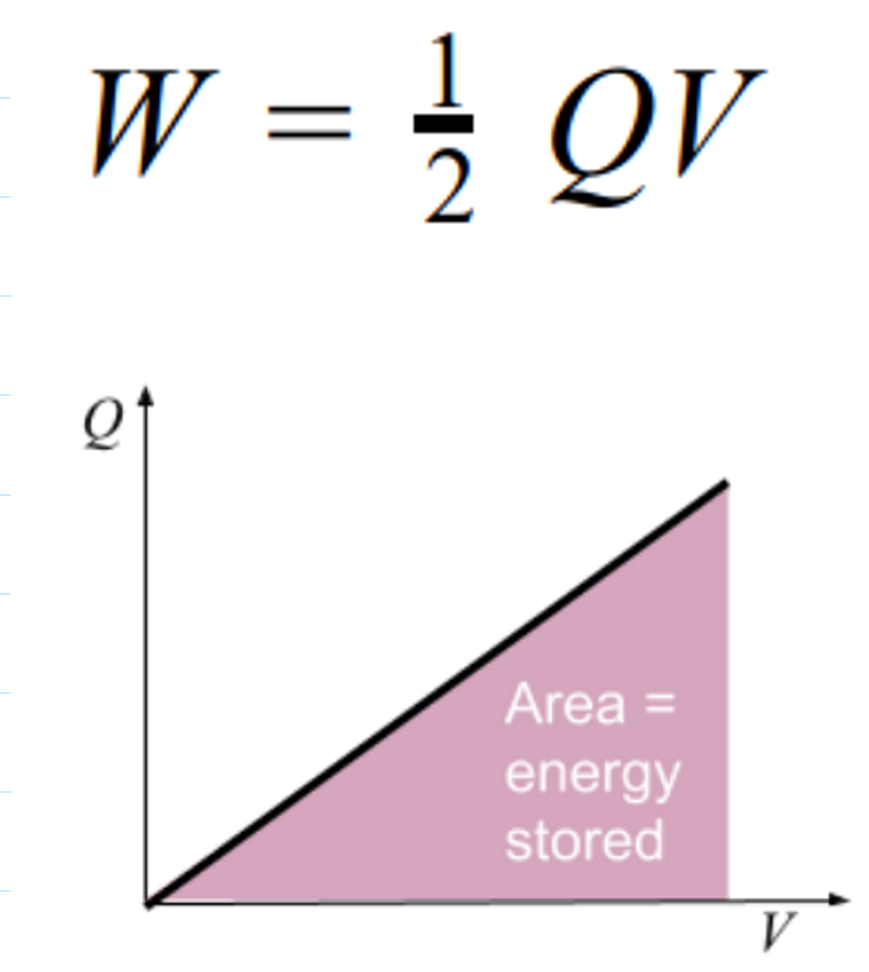
What is the graphical representation of energy stored in a capacitor
The graph of charge (Q) against potential difference (V) is a straight line through the origin. The area under this graph represents the energy stored.
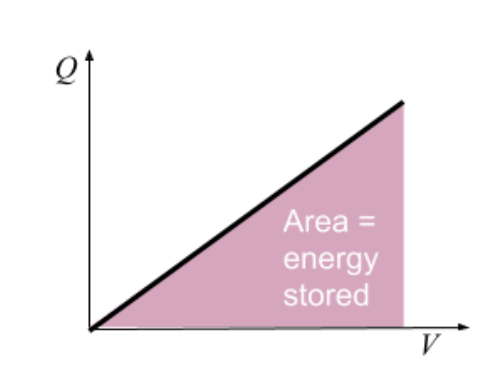
How can you calculate the energy stored from the graph
The area under the graph is a right-angled triangle. So, the energy stored can be calculated using the formula:
W = 1/2 * base * height
Capacitor circuit
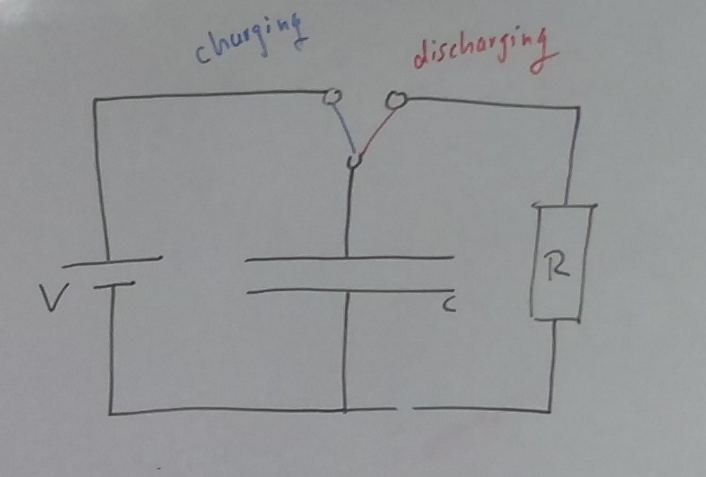
Inside the capacitor
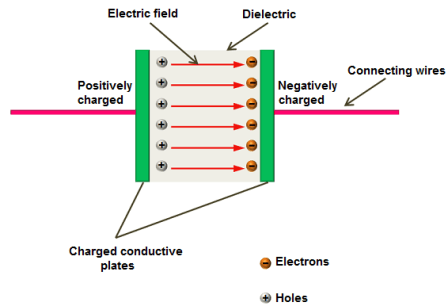
What is the process of capacitor charging
Connect a capacitor to a power supply and resistor.
Current flows from the positive terminal of the power supply to the positive plate of the capacitor, building up positive charge.
The negative terminal of the power supply draws electrons from the negative plate of the capacitor, building up negative charge.
This creates an electrostatic potential difference across the capacitor plates.
What is the process of capacitor discharging
Disconnect the power supply and connect the capacitor to a resistor.
The capacitor discharges through the resistor, releasing stored energy.
The current flows in the opposite direction during discharging compared to charging.
Current-time graph for changing a capcacitor
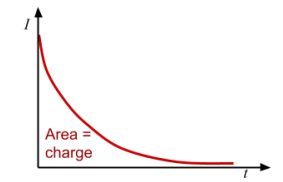
Voltage-time graph for charging a capacitor
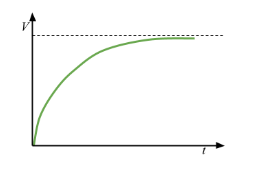
Charge-time graph for charging a capacitor
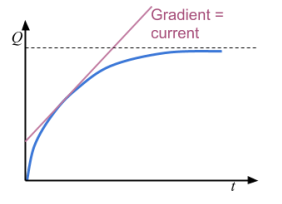
Current-time graph for discharging a capacitor
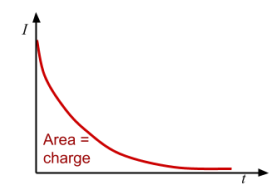
Voltage-time graph for discharging a capacitor
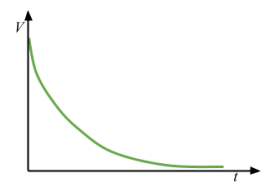
Charge-time graph for discharging a capacitor
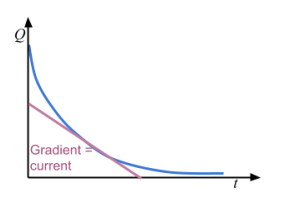
What is the time constant (RC)
It is the time taken for the capacitor to charge from zero to 63% of its full value or to discharge from full to 37% of its full value
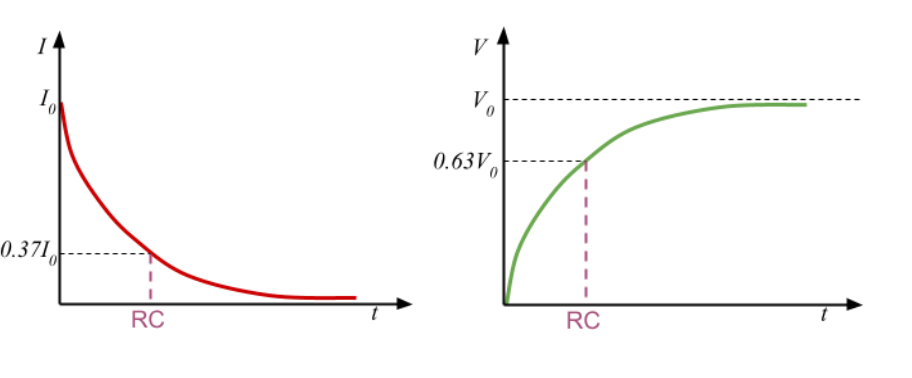
Formula for time constant
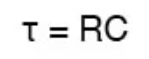
Why is the time constant (RC) significant
Time constant from discharge from full to what percentage
37%
Time constant to charge from zero to what precentage
63%
Equation for capacitor discharge (Charge decay)
Q
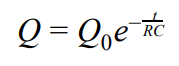
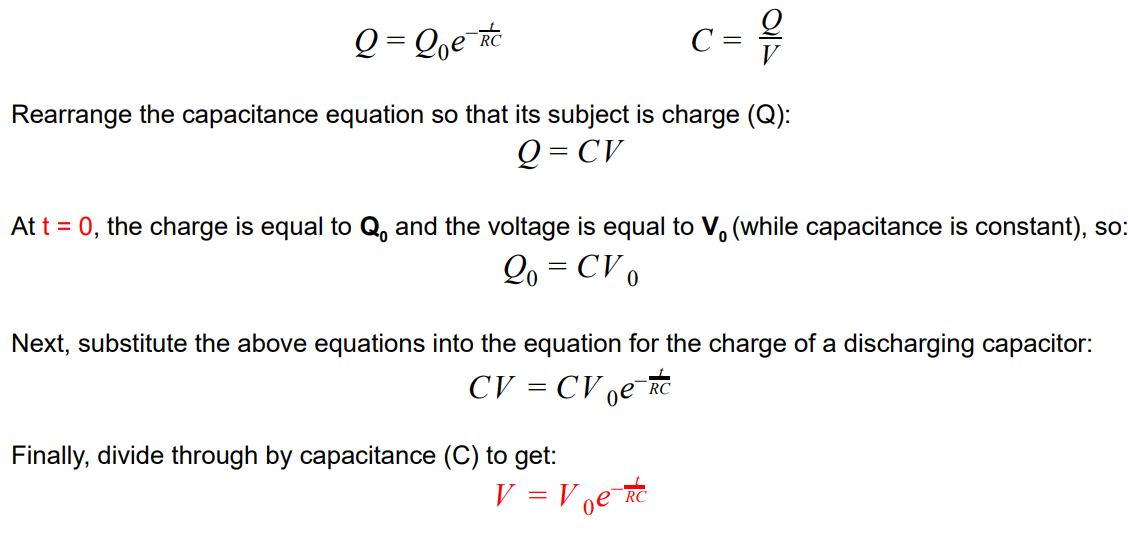
What two equations must be used to derive equations for calculating the potential difference of a discharging circuit

Derive the equation for the potential difference of a discharging circuit
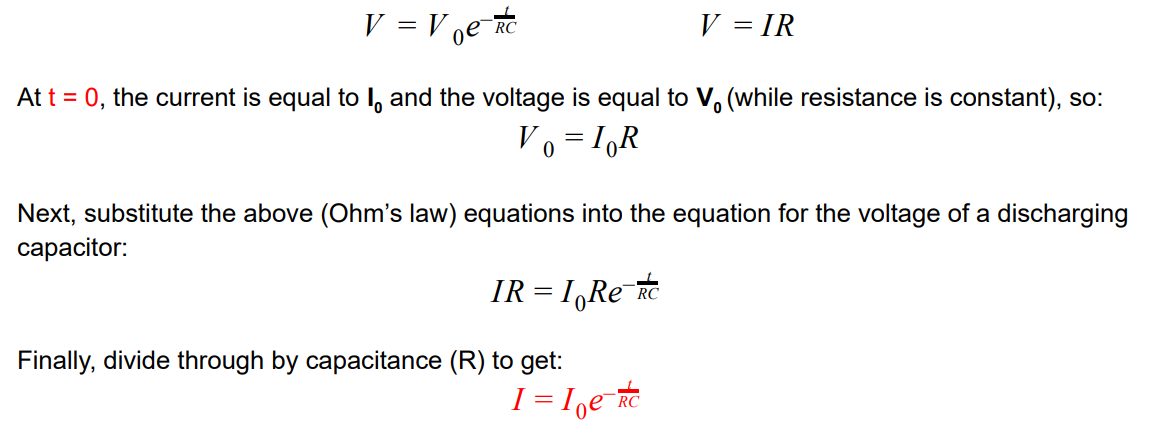
What two equations must be used to derive equations for calculating the current of a discharging circuit

Derive the equation for the current of a discharging circuit
Log equation for capacitor discharge (charge decay)
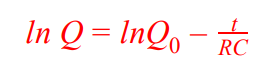
Log equation for capacitor discharge (current)
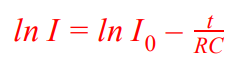
Log equation for capacitor discharge (potential difference)
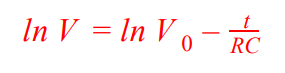
Define Magnetic Flux Density (B)
The strength of a magnetic field per unit area. (Unit: Tesla, T)
Define Magnetic Flux (ϕ)
The total magnetic field passing through a surface, given by ϕ = B × A × cos(θ). (Unit: Weber, Wb)
Define Flux Linkage (Nϕ)
The product of the number of turns in a coil (N) and the magnetic flux (ϕ) through the coil.
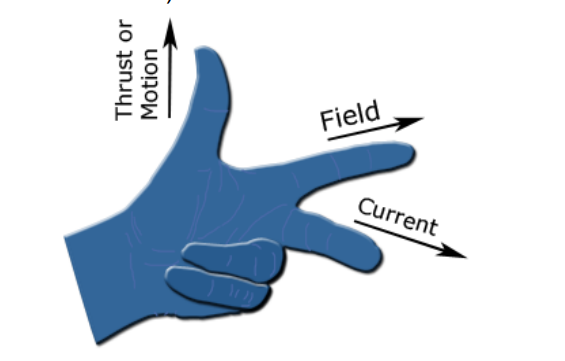
Fleming’s Left-hand rule
Remember: F B I
F = Force
B = Magnetic flux density
I = Current
(The finger are pointing in the direction of which way the force goes)
What is this equation used for : F=Bqvsinθ
Used to calculate the force on a moving charged particle in a magnetic field.
Follows Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule to determine direction.
What is F=BILsinθ used for
Used to calculate the force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field.
Follows Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule to determine direction.
Factors affecting induced e.m.f. (Electromotive Force)
Induced e.m.f. increases if the speed of motion between the coil and the magnet increases.
Greater magnetic field strength (B) leads to higher induced e.m.f.
More turns in the coil (N) increase induced e.m.f.
Factors affecting induced e.m.f. (Mutual Induction)
Induced e.m.f. in a coil can occur due to a changing current in another nearby coil.
Increasing the rate of current change in the first coil increases the induced e.m.f. in the second coil.
More turns in the secondary coil result in a larger induced voltage.
Lenz’s Law
The direction of the induced e.m.f. is always such that it opposes the change that caused it.
Relation to Energy Conservation: Ensures that energy is conserved by preventing perpetual motion.
Define Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction
The induced e.m.f. is proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux linkage.
Equation for Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction
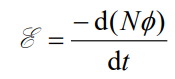
Terms in Alternating Current (AC)
Frequency (f): The number of cycles per second (Hz).
Period (T): The time for one complete cycle (T = 1/f).
Peak Value: The maximum amplitude of an AC signal.
Root Mean Square (RMS) Value: The equivalent DC value that produces the same power.
What is the application of root-mean-square value and use
Used to find the effective voltage and current in AC circuits.
RMS values allow comparison between AC and DC power outputs.